Abstract
1. The muscarinic inhibitory post-synaptic potential (i.p.s.p.) in sympathetic C neurones has been characterized in an isolated preparation of bullfrog paravertebral chain ganglia. Interactions between the i.p.s.p. and two other synaptic potentials have also been examined. 2. A single presynaptic stimulus to a C cell produces a nicotinic excitatory post-synaptic potential (e.p.s.p.) followed by a muscarine i.p.s.p. The latency of the i.p.s.p. is 50 msec or longer and the response lasts for seconds. C cells receive multiple cholinergic innervation but the thresholds for activation of the e.p.s.p. and i.p.s.p. are inseparable. Trains of 50 or more presynaptic stimuli produce a non-cholinergic e.p.s.p. which follows the nicotinic e.p.s.p. and i.p.s.p. and which lasts for tens of seconds. 3. The i.p.s.p. produced by a single presynaptic stimulus can be 30 mV in amplitude. However, in most cells, a short train of stimuli applied at an optimal frequency of 10 Hz is required to produce a large i.p.s.p. 4. The i.p.s.p. is blocked by atropine but is not affected by catecholamine antagonists. 5. Ionophoretically applied acetylcholine (ACh) mimics the i.p.s.p. in its latency, time course and amplitude. In addition, the i.p.s.p. and the muscarinic response to ACh reverse polarity at the same membrane potential: -102 mV in normal Ringer solution. The i.p.s.p. reversal potential shifts by 55 mV/decade change in extracellular K+ concentration and is insensitive to the Cl- gradient. 300 microM-Ba2+ totally blocks the muscarinically activated conductance in a reversible manner. 6. Action potentials, when initiated by a supramaximal nicotinic e.p.s.p. or by an antidromic impulse, are not blocked by the i.p.s.p. 7. Near resting potential (-50 to -60 mV), C cells can fire repetitively. The non-cholinergic slow e.p.s.p. is often accompanied by oscillations in membrane potential and firing of action potentials. This repetitive firing of C cells, which appears to be enhanced by the non-cholinergic e.p.s.p., is strongly inhibited by the i.p.s.p. The inhibition can be mimicked by injection of very small hyperpolarizing currents (e.g. 25 pA). Interactions between the i.p.s.p. and the non-cholinergic e.p.s.p. can generate phasic bursting patterns in C cells. 8. The mechanism underlying the i.p.s.p. and the consequences of these findings for ganglionic integration are discussed.
Full text
PDF


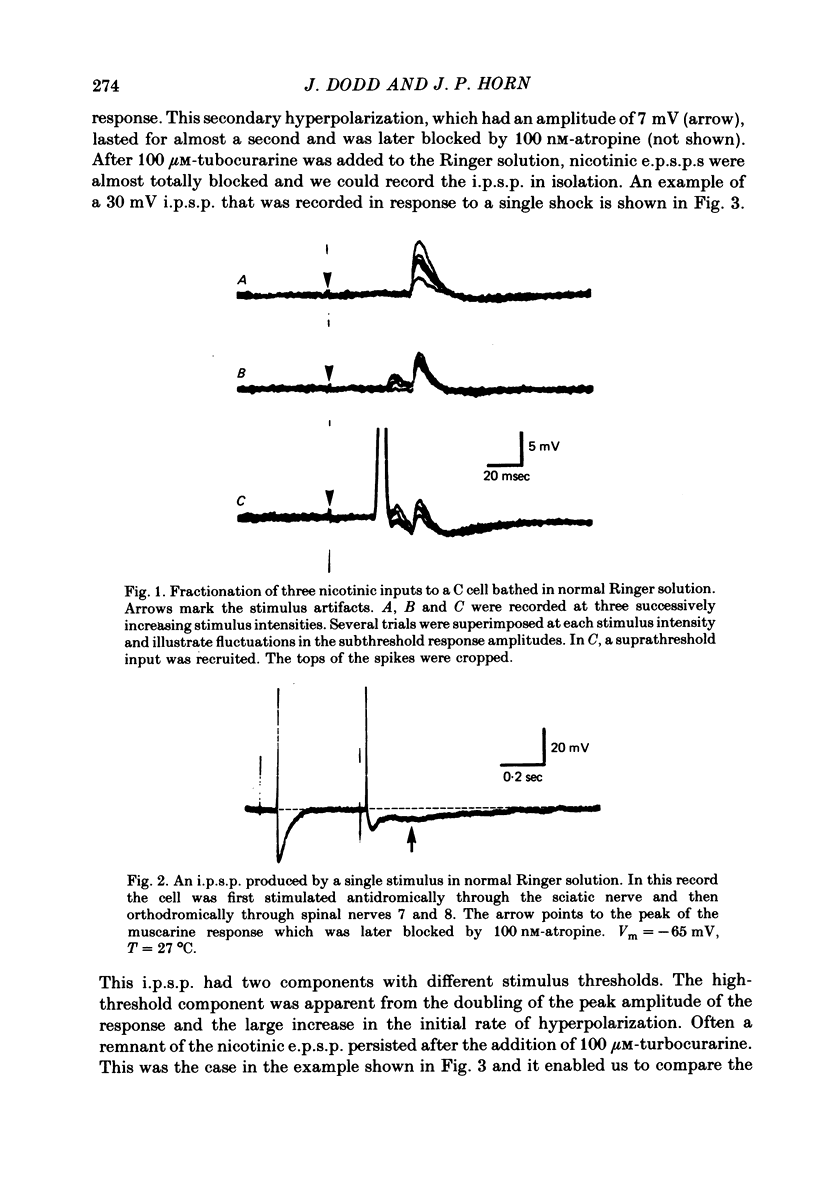




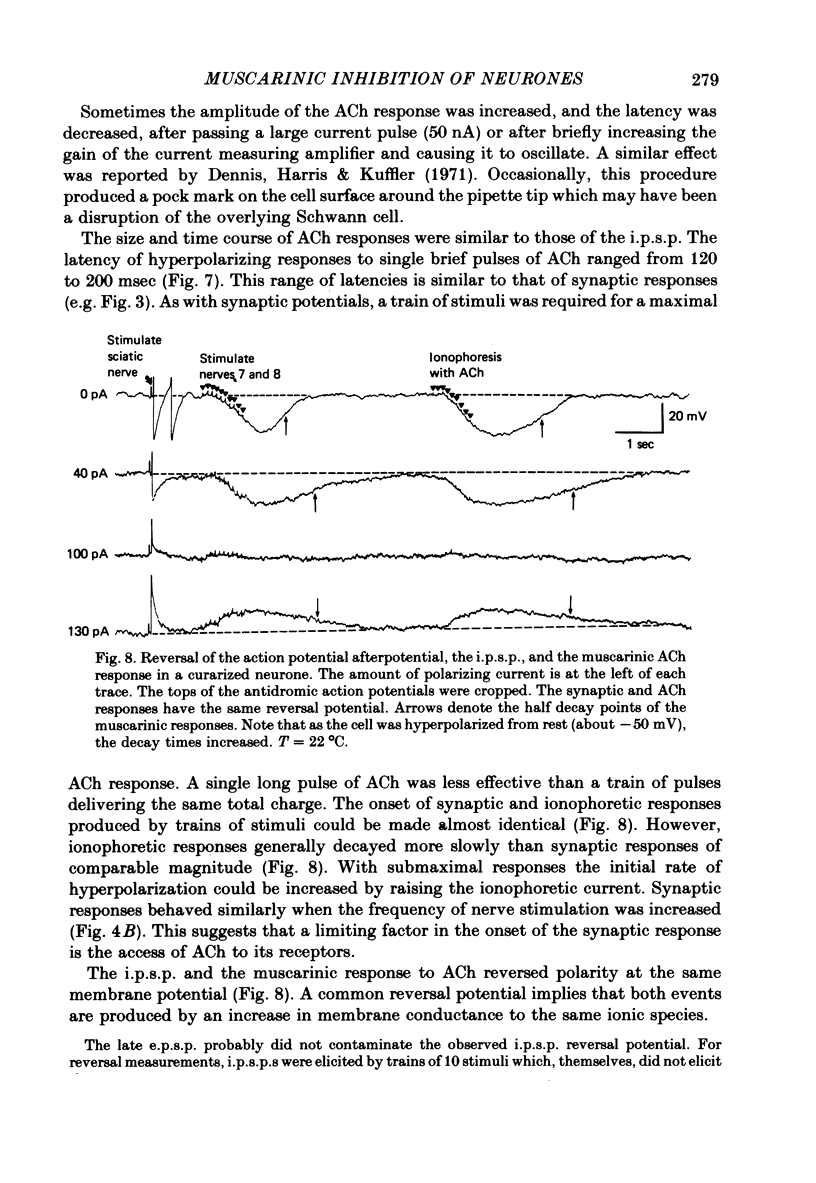

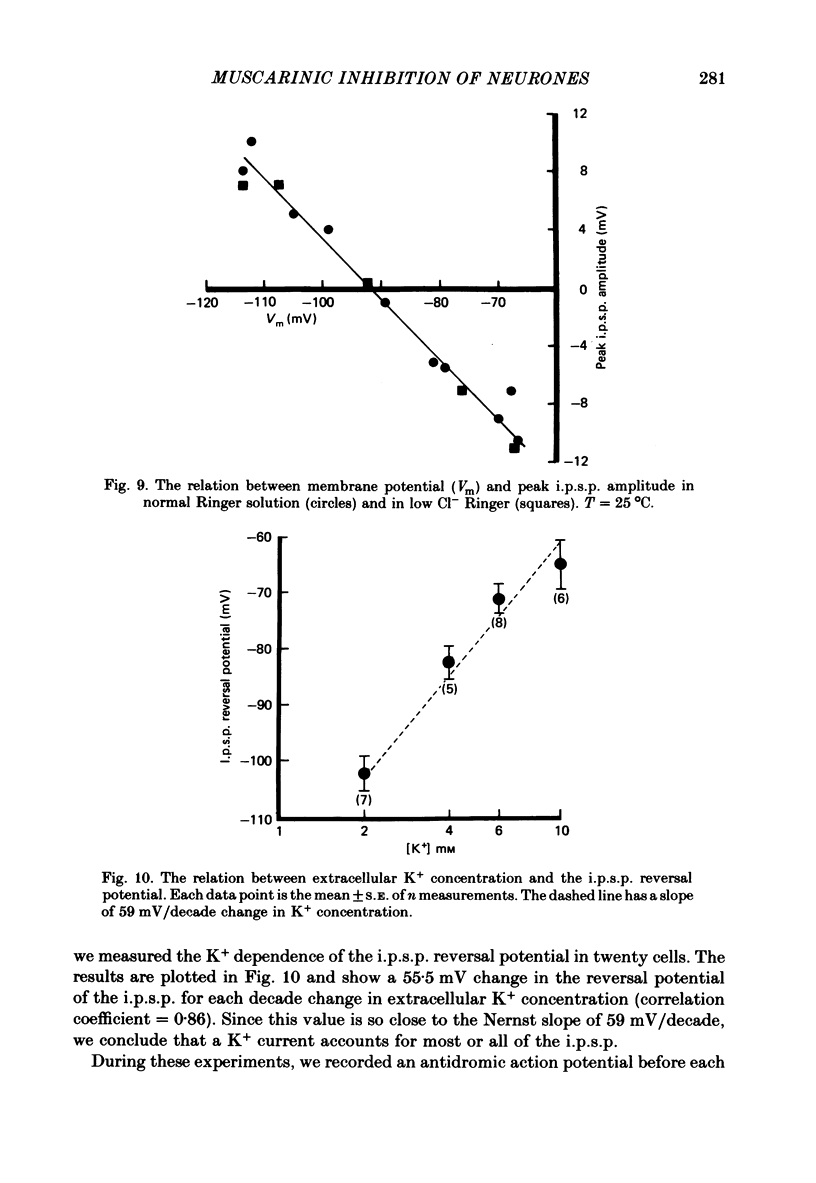



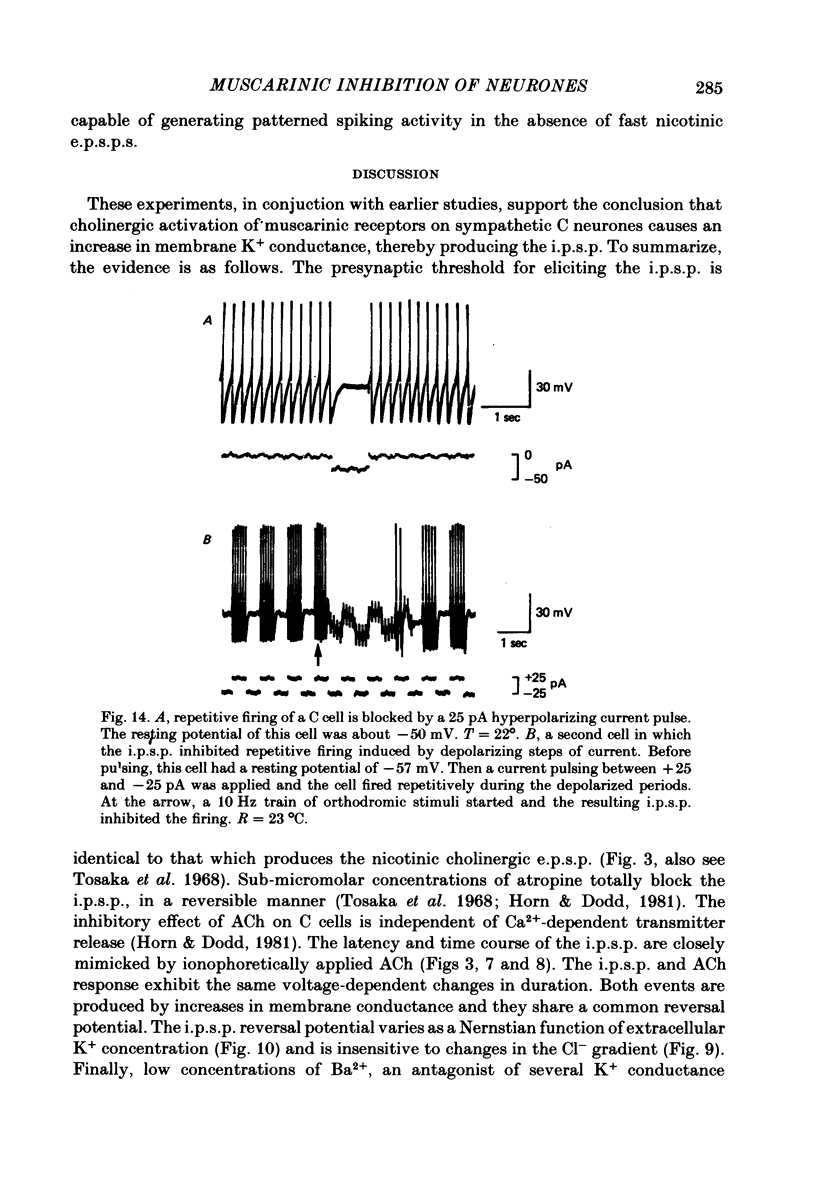





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Luteinizing hormone-releasing factor and muscarinic agonists act on the same voltage-sensitive K+-current in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;68(3):353–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb14547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACKMAN J. G., GINSBORG B. L., RAY C. Spontaneous synaptic activity in sympathetic ganglion cells of the frog. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167:389–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACKMAN J. G., GINSBORG B. L., RAY C. Synaptic transmission in the sympathetic ganglion of the frog. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167:355–373. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beddoe F., Nicholls P. J., Smith H. J. Inhibition of the muscarinic receptor by dibenamine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Dec;20(12):3367–3376. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90441-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Adams P. R. Muscarinic suppression of a novel voltage-sensitive K+ current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):673–676. doi: 10.1038/283673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Caulfield M. P., Kirby P. J. Relation between catecholamine-induced cyclic AMP changes and hyperpolarization in isolated rat sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):441–451. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Constanti A. Intracellular observations on the effects of muscarinic agonists on rat sympathetic neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Dec;70(4):593–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb09778.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. E., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Alpha-adrenoceptor and dopamine receptor antagonists do not block the slow inhibitory postsynaptic potential in sympathetic ganglia. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 7;187(1):226–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. E., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Comparison of the receptors mediating the catecholamine hyperpolarization and slow inhibitory postsynaptic potential in sympathetic ganglia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 May;217(2):440–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Who do barium ions imitate acetylcholine? Brain Res. 1981 Feb 9;206(1):244–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Harris A. J., Kuffler S. W. Synaptic transmission and its duplication by focally applied acetylcholine in parasympathetic neurons in the heart of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Apr 27;177(1049):509–539. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd J., Horn J. P. A reclassification of B and C neurones in the ninth and tenth paravertebral sympathetic ganglia of the bullfrog. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:255–269. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunant Y., Dolivo M. Relations entre les potentiels synaptiques lents et l'excitabilité du ganglion. J Physiol (Paris) 1967 Jul-Aug;59(4):281–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LIBET B. Origin and blockade of the synaptic responses of curarized sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1961 Aug;157:484–503. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. C., Brodwick M. S. Effects of barium on the potassium conductance of squid axon. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Jun;75(6):727–750. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.6.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Hermann A. Internal effects of divalent cations on potassium permeability in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:393–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith W. H., 3rd, Gallagher J. P., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Sucrose-gap recordings of nerve-evoked potentials in mammalian parasympathetic ganglia. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 30;209(2):446–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90168-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Moody W., Patlak J. Blocking effects of barium and hydrogen ions on the potassium current during anomalous rectification in the starfish egg. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:167–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Stickgold R., Yoshikami D. Synaptic excitation and inhibition resulting from direct action of acetylcholine on two types of chemoreceptors on individual amphibian parasympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(3):817–846. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Gorman A. L. Blockade of voltage-dependent and Ca2+-dependent K+ current components by internal Ba2+ in molluscan pacemaker neurons. Experientia. 1979 Feb 15;35(2):229–231. doi: 10.1007/BF01920633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn J. P., Dodd J. Monosynaptic muscarinic activation of K+ conductance underlies the slow inhibitory postsynaptic potential in sympathetic ganglia. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):625–627. doi: 10.1038/292625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn J. P., McAfee D. A. Alpha-drenergic inhibition of calcium-dependent potentials in rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:191–204. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Brownfield M. S. Peptidergic transmitters in synaptic boutons of sympathetic ganglia. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):380–382. doi: 10.1038/288380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y., Kuffler S. W. A peptide as a possible transmitter in sympathetic ganglia of the frog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1501–1505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y., Kuffler S. W. Further evidence for peptidergic transmission in sympathetic ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):5008–5012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.5008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Petzold G. L., Greengard P. Dopamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in caudate nucleus of rat brain, and its similarity to the "dopamine receptor". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2145–2149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koketsu K., Nishi S. Characteristics of the slow inhibitory postsynaptic potential of bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Life Sci. 1967 Sep 1;6(17):1827–1836. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90211-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Nishi S. Characteristics of fast excitatory postsynaptic current in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Effects of membrane potential, temperature and Ca ions. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Jan 31;378(3):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00592737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libet B., Chichibu S., Tosaka T. Slow synaptic responses and excitability in sympathetic ganglia of the bullfrog. J Neurophysiol. 1968 May;31(3):383–395. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libet B., Kobayashi H. Adrenergic mediation of slow inhibitory postsynaptic potential in sympathetic ganglia of the frog. J Neurophysiol. 1974 Jul;37(4):805–814. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.4.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Connor E. A., Dionne V. E., Parsons R. L. Voltage clamp study of fast excitatory synaptic currents in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Jan;75(1):39–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHI S., KOKETSU K. Electrical properties and activities of single sympathetic neurons in frogs. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1960 Feb;55:15–30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030550104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. The characteristics of synaptic currents and responses to acetylcholine of rat submandibular ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:23–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selyanko A. A., Derkach V. A., Skok V. I. Fast excitatory postsynaptic currents in voltage-clamped mammalian sympathetic ganglion neurones. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1979 Dec;1(2):127–137. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(79)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosaka T., Chichibu S., Libet B. Intracellular analysis of slow inhibitors and excitatory postsynaptic potentials in sympathetic ganglia of the frog. J Neurophysiol. 1968 May;31(3):396–409. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


