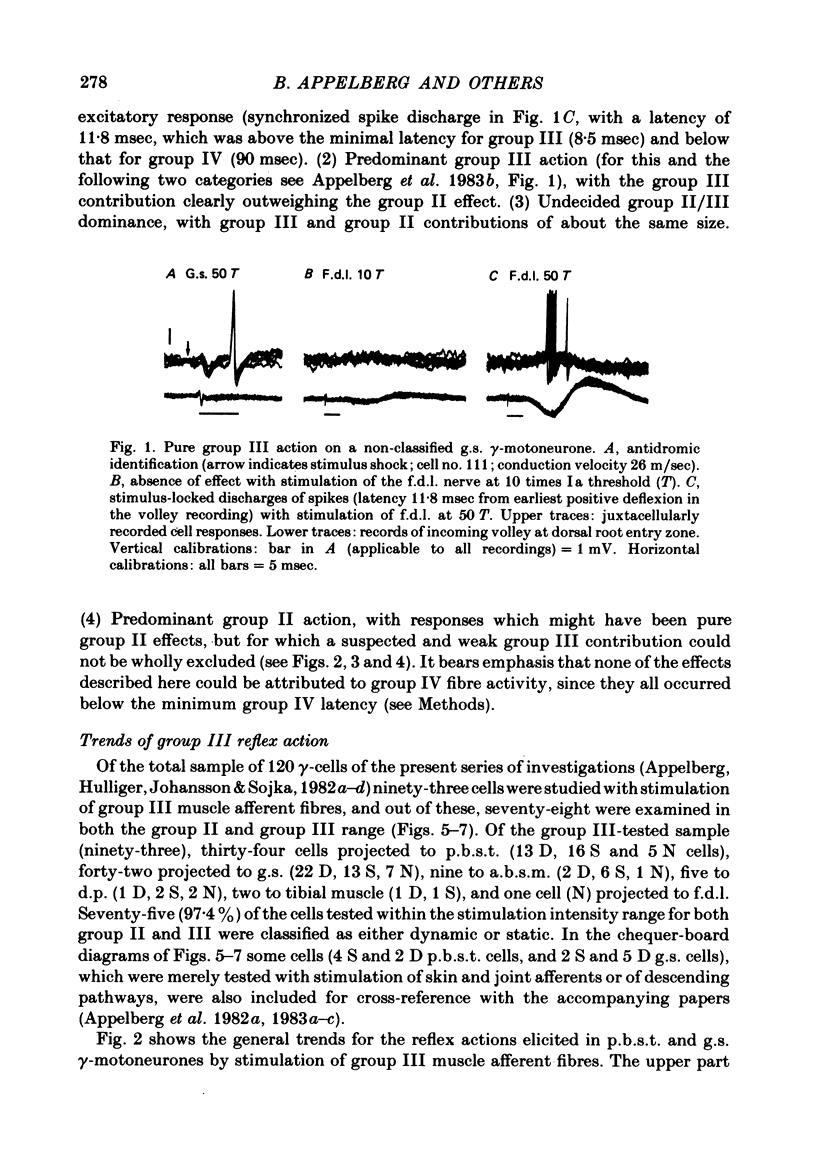
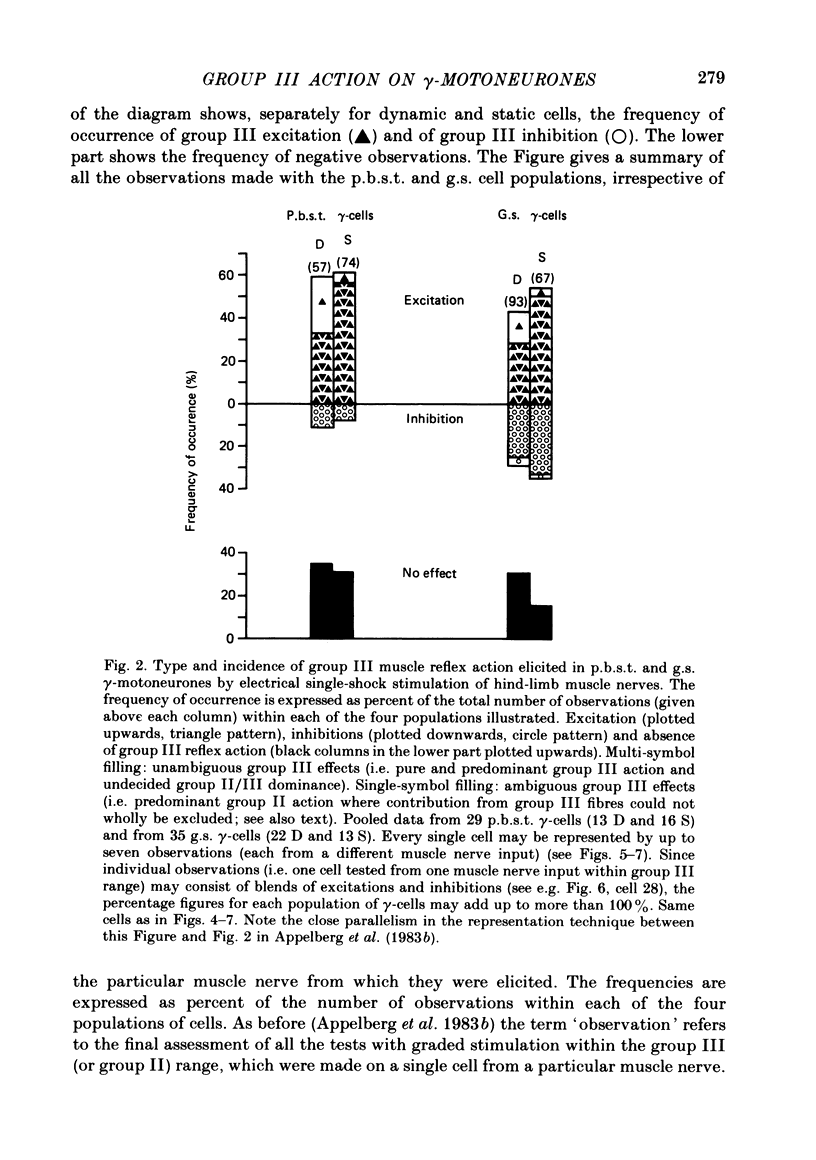
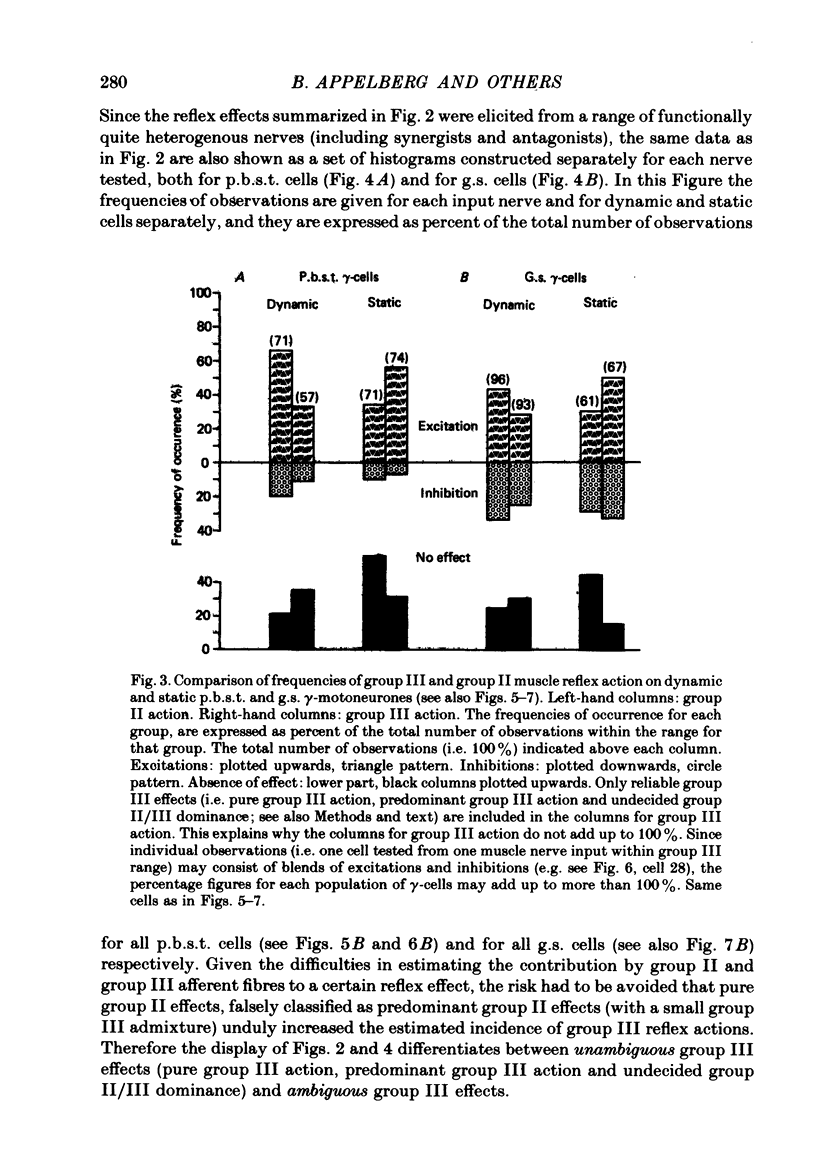
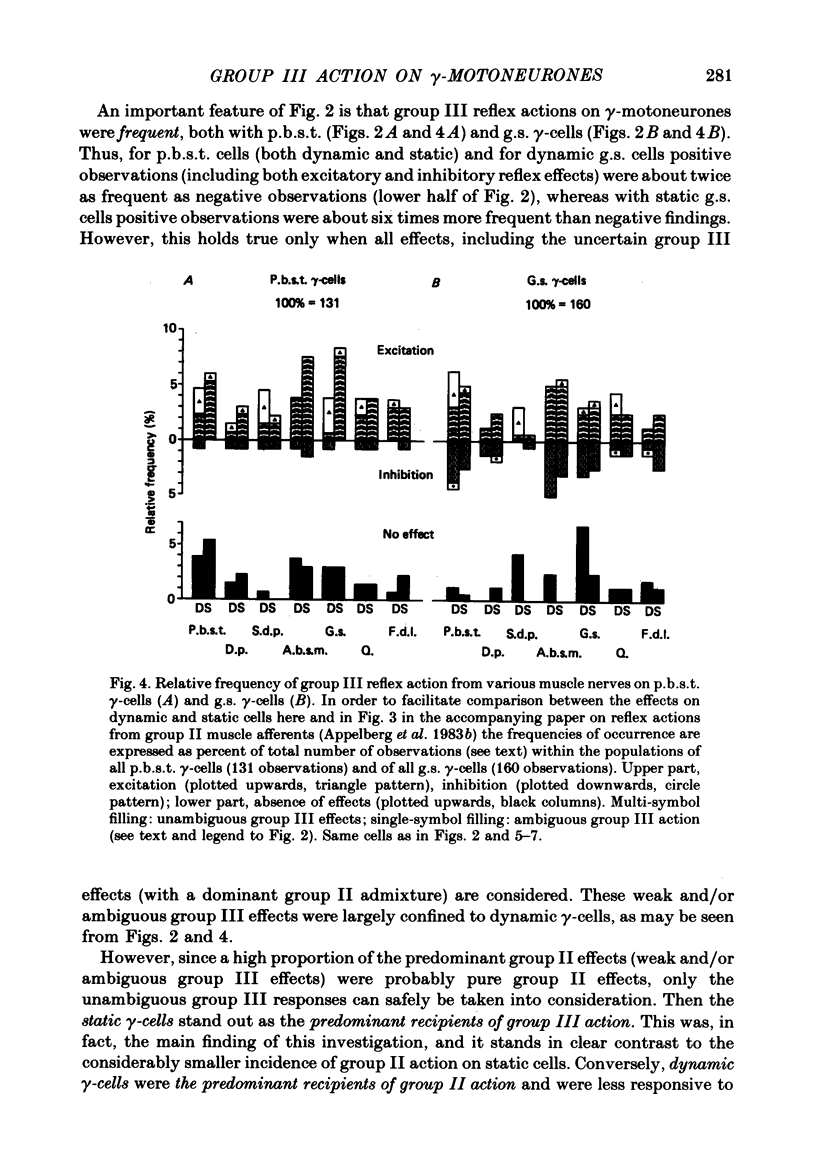
Abstract
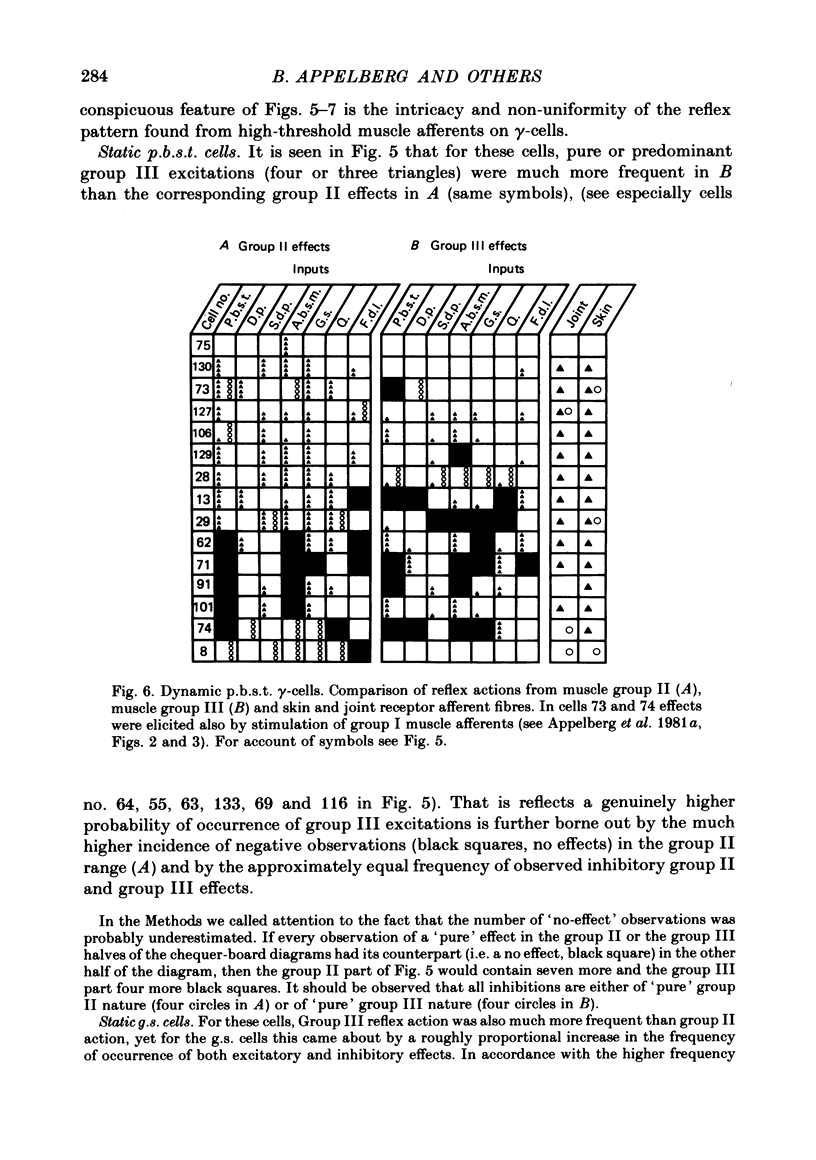
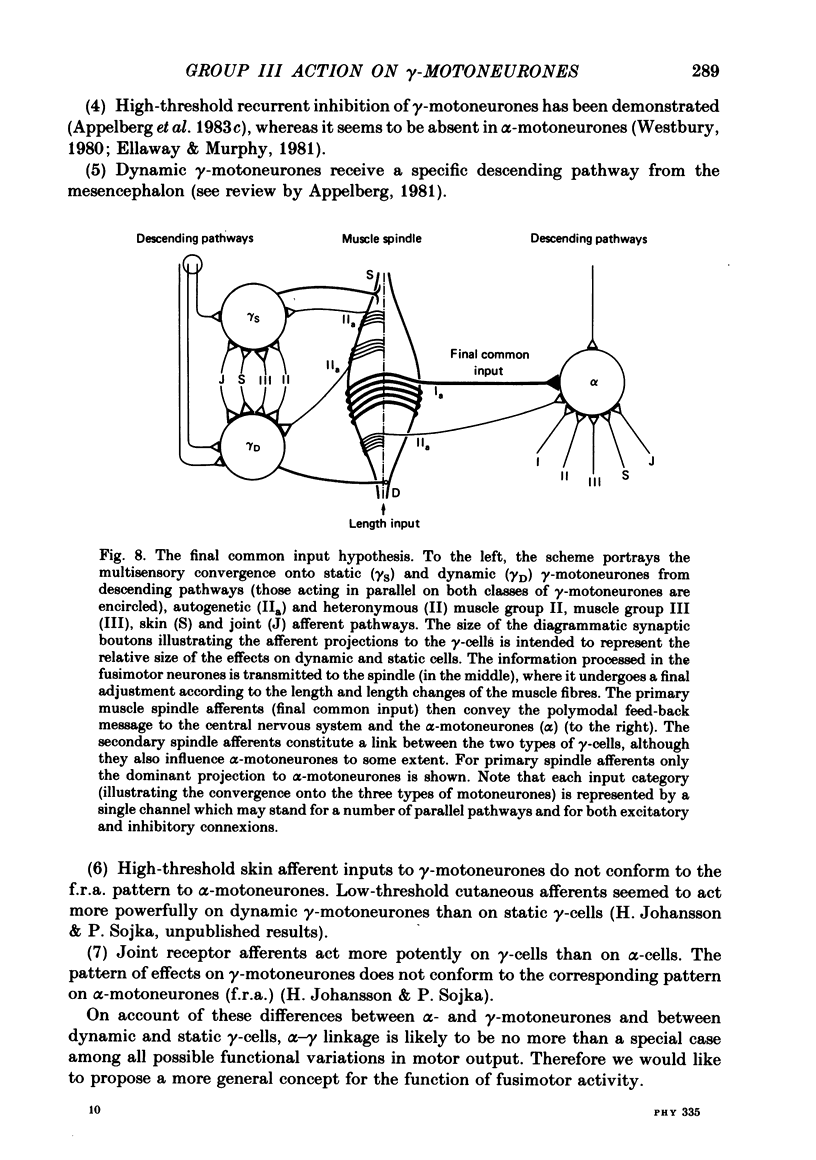
The reflex actions evoked by electrical stimulation of group III muscle afferent fibres were investigated with micro-electrode recordings from ninety-three gamma-motoneurones projecting to hind-limb muscles of cats anaesthetized with chloralose. For seventy-eight of the ninety-three gamma-cells the frequency of occurrence and types of effects mediated via group II and group III muscle fibres were compared. Seventy-seven of the cells tested at intensities which excited group III and seventy-five of the cells tested at intensities which excited both group II and group III afferent fibres were classified as either static or dynamic, using the method of mesencephalic stimulation (Appelberg, 1981). The responsiveness of the whole sample of gamma-motoneurones to inputs from group III muscle fibres was high and comparable to that found with group II fibres. It was found that group III muscle fibres acted preferentially on static gamma-motoneurones. In contrast, group II fibres acted preferentially on dynamic gamma-motoneurones. Both excitatory and inhibitory effects were provoked by stimulation of group III fibres. Generally excitation was more frequent than inhibition. A strong dominance of excitation over inhibition was found in flexor muscles, and a weaker prevalence of excitation was also encountered in extensor muscles. This prevalence of excitation in extensor gamma-motoneurones is in contrast to the striking predominance of group III-evoked inhibition of extensor alpha-motoneurones as described by the flexion reflex afferents concept. A comparative survey is also given of the patterns of responses elicited in individual posterior biceps-semitendinosus and gastrocnemius-soleus gamma-cells by stimulation of group II and group III fibres. These data further corroborate the view that reflexes from high-threshold muscle afferent fibres to gamma-motoneurones are organized differently from those to alpha-motoneurones. The functional implications of these findings are discussed. It is proposed that the pools of gamma-motoneurones should be considered as integrative systems intercalated between descending and reflex pathways on the one hand and the skeletomotor neurones on the other. The descending messages and the multisensory peripheral information, integrated in the fusimotor neurones, undergo final adjustment in the muscle spindle. The link to the skeletomotor neurones is formed by the primary spindle afferents. These constitute a final common input, conveying integrated detailed polymodal feed-back, to the central nervous system. This new concept is referred to as the 'final common input' hypothesis.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelberg B., Hulliger M., Johansson H., Sojka P. Actions on gamma-motoneurones elicited by electrical stimulation of group I muscle afferent fibres in the hind limb of the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:237–253. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Hulliger M., Johansson H., Sojka P. Actions on gamma-motoneurones elicited by electrical stimulation of group II muscle afferent fibres in the hind limb of the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:255–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Hulliger M., Johansson H., Sojka P. Excitation of dynamic fusimotor neurones of the cat triceps surae by contralateral joint afferents. Brain Res. 1979 Jan 19;160(3):529–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)91081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Hulliger M., Johansson H., Sojka P. Fusimotor reflexes in triceps surae elicited by natural stimulation of muscle afferents from the cat ipsilateral hind limb. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:211–229. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Hulliger M., Johansson H., Sojka P. Recurrent actions on gamma-motoneurones mediated via large and small ventral root fibres in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:293–305. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELDRED E., GRANIT R., MERTON P. A. Supraspinal control of the muscle spindles and its significance. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):498–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Murphy P. R. A comparison of the recurrent inhibition of alpha- and gamma-motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:43–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner S., Hongo T., Lund S. Descending monosynaptic and reflex control of gamma-motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Apr;75(4):592–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulliger M. The responses of primary spindle afferents to fusimotor stimulation at constant and abruptly changing rates. J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:461–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Characteristics of the excitatory pathway from group II muscle afferents to alpha motoneurones. Brain Res. 1975 May 9;88(3):538–542. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90667-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Comments on reflex actions evoked by electrical stimulation of group II muscle afferents. Brain Res. 1977 Feb 25;122(3):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90466-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A. Multisensory control of spinal reflex pathways. Prog Brain Res. 1979;50:11–28. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60803-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westbury D. R. Lack of a contribution from gamma motoneurone axons to Renshaw inhibition in the cap spinal cord. Brain Res. 1980 Mar 17;186(1):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


