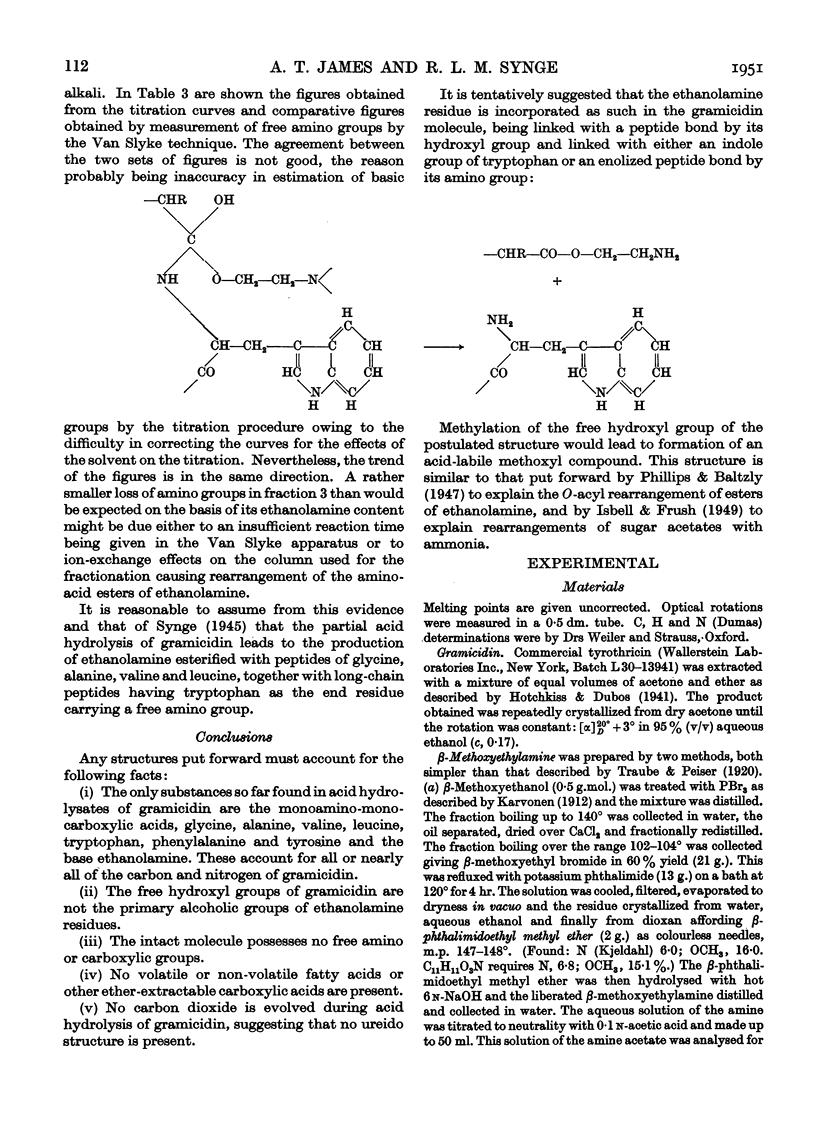
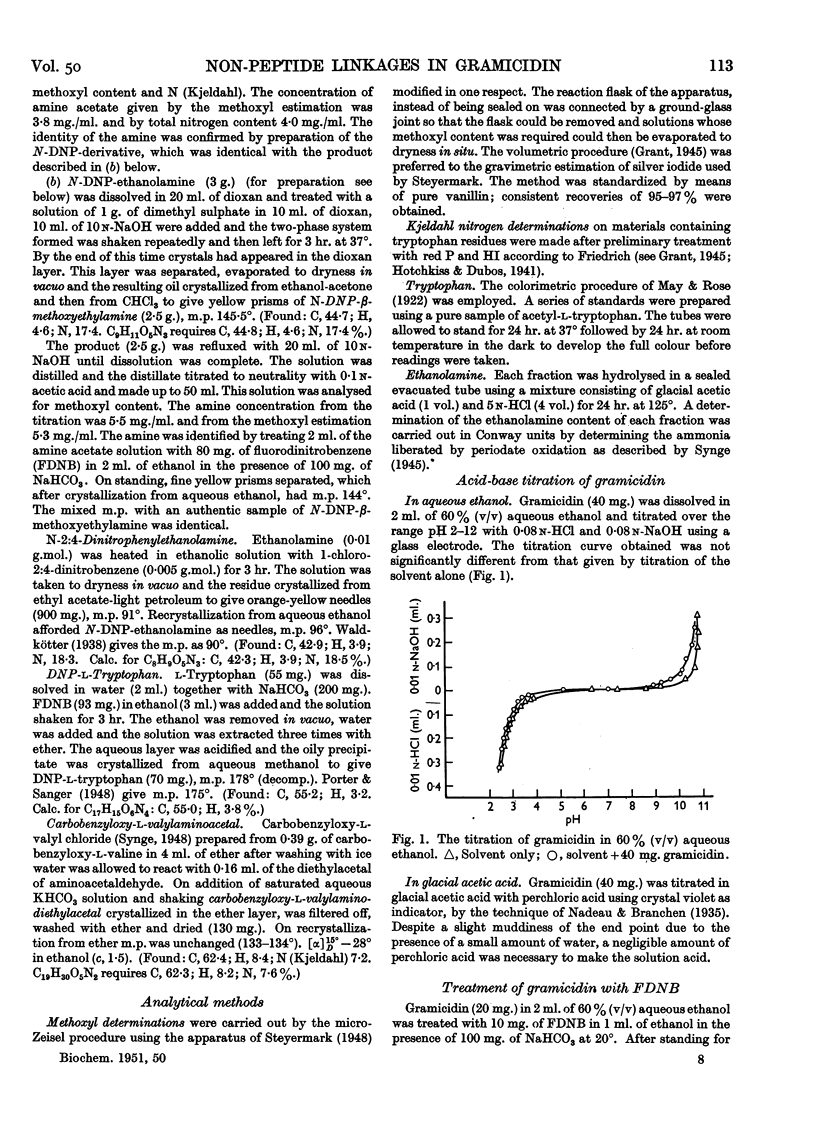
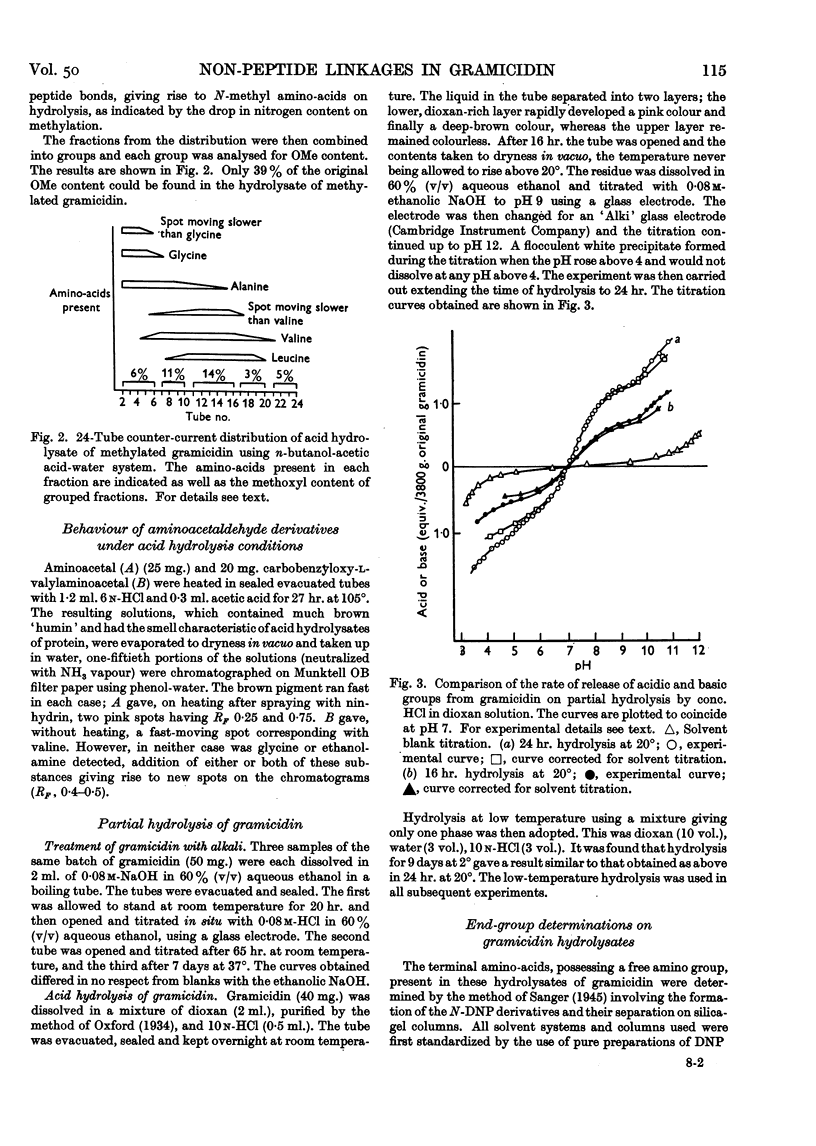
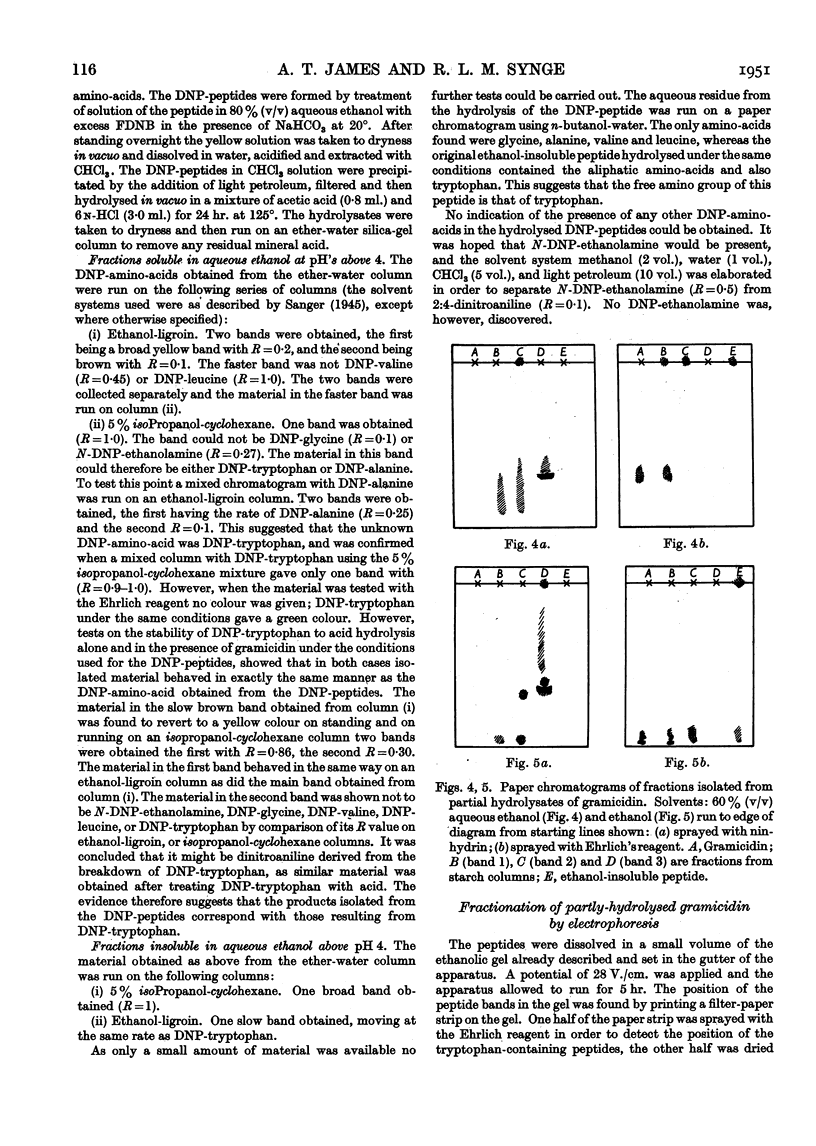
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CRAIG L. C., GREGORY J. D., BARRY G. T. Studies on polypeptides and amino acids by countercurrent distribution. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1950;14:24–31. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1950.014.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consden R., Gordon A. H., Martin A. J. Ionophoresis in silica jelly: A method for the separation of animo-acids and peptides. Biochem J. 1946;40(1):33–41. doi: 10.1042/bj0400033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. H., Martin A. J., Synge R. L. The etherification of hydroxyamino-acid residues in silk fibroin by dimethyl sulphate. Biochem J. 1943;37(5):538–543. doi: 10.1042/bj0370538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN D. C. X-ray analysis and protein structure. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1950;14:65–78. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1950.014.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford A. E. Note on the use of dioxan as solvent in the determination of molecular weights by the cryoscopic method. Biochem J. 1934;28(4):1325–1329. doi: 10.1042/bj0281325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R., Sanger F. The free amino groups of haemoglobins. Biochem J. 1948;42(2):287–294. doi: 10.1042/bj0420287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYNGE R. L. M. Physical and chemical studies of gramicidin and some implications for the study of proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1950;14:191–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1950.014.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. The free amino groups of insulin. Biochem J. 1945;39(5):507–515. doi: 10.1042/bj0390507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Synge R. L. The hydroxyamino component of gramicidin hydrolysates. Biochem J. 1945;39(4):355–362. doi: 10.1042/bj0390355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Synge R. L. The synthesis of some dipeptides related to gramicidin S. Biochem J. 1948;42(1):99–104. doi: 10.1042/bj0420099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


