Abstract
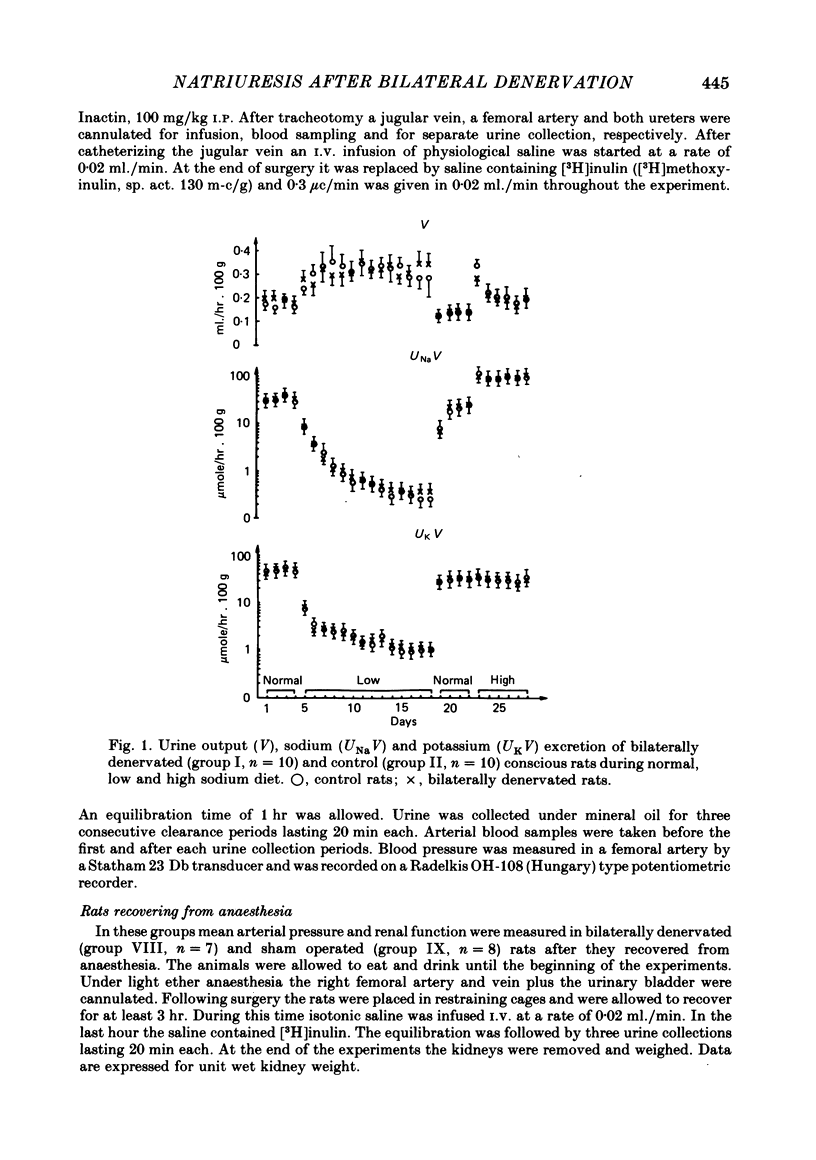
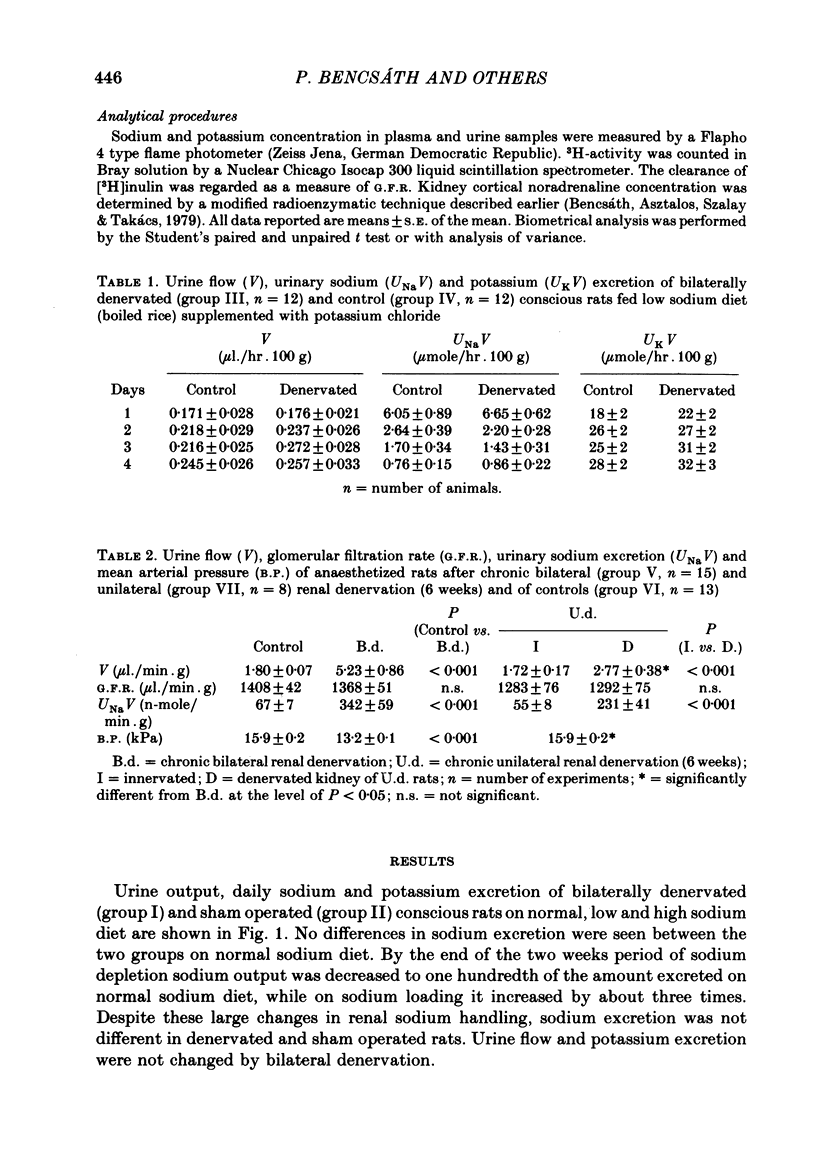
1. The effect of bilateral renal denervation on sodium excretion was studied in conscious rats on normal, low and high sodium diet, and in rats recovering from anaesthesia, as well as in anaesthetized rats fed a normal sodium diet. 2. Sodium excretion of bilaterally denervated conscious rats on normal sodium intake and during either 2 weeks of sodium depletion or 6 days of sodium loading was not different from that of controls, despite changes in sodium supply of more than two orders of magnitude. Cortical noradrenaline concentration of control kidneys was 138 +/- 12 ng/g, but was only 7 +/- 3 ng/g (P less than 0 . 001) 6 weeks after denervation. 3. In rats recovering from anaesthesia urine flow, sodium excretion and glomerular filtration rate (G.F.R.) were not affected by denervation. 4. In anaesthetized non-diuretic rats on normal sodium diet chronic bilateral renal denervation increased urine flow and sodium excretion four and five times, respectively, with no changes in G.F.R. 5. Mean arterial blood pressure in bilaterally denervated anaesthetized rats and in those recovering from anaesthesia was decreased by 2 . 7 kPa, P less than 0 . 001 and 1 . 2 kPa, P less than 0 . 05, respectively. 6. The participation of renal nerves in the regulation of sodium excretion in conscious rats seems improbable. The denervation natriuresis in anaesthetized rats can be related to higher pre-denervation renal sympathetic nervous activity due to narcosis and surgical stress.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bello-Reuss E., Colindres R. E., Pastoriza-Muñoz E., Mueller R. A., Gottschalk C. W. Effects of acute unilateral renal denervation in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul;56(1):208–217. doi: 10.1172/JCI108069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bello-Reuss E., Pastoriza-Muńoz E., Colindres R. E. Acute unilateral renal denervation in rats with extracellular volume expansion. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jan;232(1):F26–F32. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.1.F26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bencsáth P., Asztalos B., Szalay L., Takács L. Renal handling of sodium after chronic renal sympathectomy in the anesthetized rat. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):F513–F518. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.6.F513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubacher E. S., Vander A. J. Sodium deprivation and renin secretion in unanesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jan;214(1):15–21. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colindres R. E., Spielman W. S., Moss N. G., Harrington W. W., Gottschalk C. W. Functional evidence for renorenal reflexes in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1980 Sep;239(3):F265–F270. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.239.3.F265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F., Rios L. L. Renal nerves in compensatory renal response to contralateral renal denervation. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jan;238(1):F26–F30. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.1.F26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D., Peart W. S., Wilcox C. S. Requirement of the adrenergic nervous system for conservation of sodium by the rabbit kidney [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:24P–24P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotshall R. W., Davis J. O., Shade R. E., Spielman W., Johnson J. A., Braverman B. Effects of renal denervation on renin release in sodium-depleted dogs. Am J Physiol. 1973 Aug;225(2):344–349. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.2.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk C. W. Renal nerves and sodium excretion. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:229–240. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMM D. E., LEVINSKY N. G. THE MECHANISM OF DENERVATION NATRIURESIS. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jan;44:93–102. doi: 10.1172/JCI105131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline R. L., Stuart P. J., Mercer P. F. Effect of renal denervation on arterial pressure and renal norepinephrine concentration in Wistar-Kyoto and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;58(11):1384–1388. doi: 10.1139/y80-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kállay K., Bencsáth P. Idiopathic orthostatic hypotension. Pathophysiological observations with special reference to the renal handling of sodium. Cardiology. 1976;61 Suppl 1:168–178. doi: 10.1159/000169830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgunov N., Baines A. D. Renal nerves and catecholamine excretion. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):F75–F81. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.1.F75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski J., Kurkus J., Gellert R. Denervated and intact kidney responses to saline load in awake and anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1979 Oct;237(4):F262–F267. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.237.4.F262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. S., Aminoff M. J., Slater J. D. Sodium homeostasis in patients with autonomic failure. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1977 Oct;53(4):321–328. doi: 10.1042/cs0530321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


