Abstract
Alkaline phosphatase prepared from mammalian cell cultures was found to have alkaline inorganic pyrophosphatase activity. Both of these activities appear to be associated with a single protein, as demonstrated by: (1) concomitant purification of alkaline phosphatase and alkaline inorganic pyrophosphatase; (2) proportional precipitation of alkaline phosphatase and inorganic pyrophosphatase activities by titrating constant amounts of an enzyme preparation with increasing concentration of antibody; (3) immune electrophoresis, which showed that precipitin bands that have alkaline phosphatase activity also have pyrophosphatase activity; (4) inhibition of pyrophosphatase activity by cysteine, an inhibitor of alkaline phosphatase activity; (5) similar subcellular localization of the two enzyme activities as demonstrated by histochemical methods; (6) hormonal and substrate induction of alkaline phosphatase activity in mammalian cell cultures, which produced a nearly parallel rise in inorganic pyrophosphatase activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agus S. G., Cox R. P., Griffin M. J. Inhibition of alkaline phosphatase by cysteine and its analogues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 5;118(2):363–370. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN W. H., GREEN S., INGLIS N. I. Organ-specific behavior exhibited by rat intestine and liver alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 13;62:363–375. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90266-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRABAR P., WILLIAMS C. A. Méthode permettant l'étude conjuguée des proprietés électrophorétiques et immunochimiques d'un mélange de protéines; application au sérum sanguin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Jan;10(1):193–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh N. K., Fishman W. H. On the mechanism of inhibition of intestinal alkaline phosphatase by L-phenylalanine. I. Kinetic studies. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jun 10;241(11):2516–2522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M. J., Cox R. P. Studies on the mechanism of hormonal induction of alkaline phosphatase in human cell cultures. I. Effects of puromycin and actinomycin D. J Cell Biol. 1966 Apr;29(1):1–9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.29.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M. J., Cox R. P. Studies on the mechanism of hormone induction of alkaline phosphatase in human cell cultures, II. Rate of enzyme synthesis and properties of base level and induced enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):946–953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLOW L. S. A histochemical procedure for localizing and evaluating leukocyte alkaline phosphatase activity in smears of blood and marrow. Blood. 1955 Oct;10(10):1023–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURATA Y., MAEDA S. Histochemical demonstration of pyrophosphatase. Stain Technol. 1956 Jan;31(1):13–16. doi: 10.3109/10520295609113763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinsmith L. J., Allfrey V. G., Mirsky A. E. Phosphorylation of nuclear protein early in the course of gene activation in lymphocytes. Science. 1966 Nov 11;154(3750):780–781. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3750.780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON R. K. The purification of aklaline phosphatases of animal tissues. Biochem J. 1954 Aug;57(4):595–603. doi: 10.1042/bj0570595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
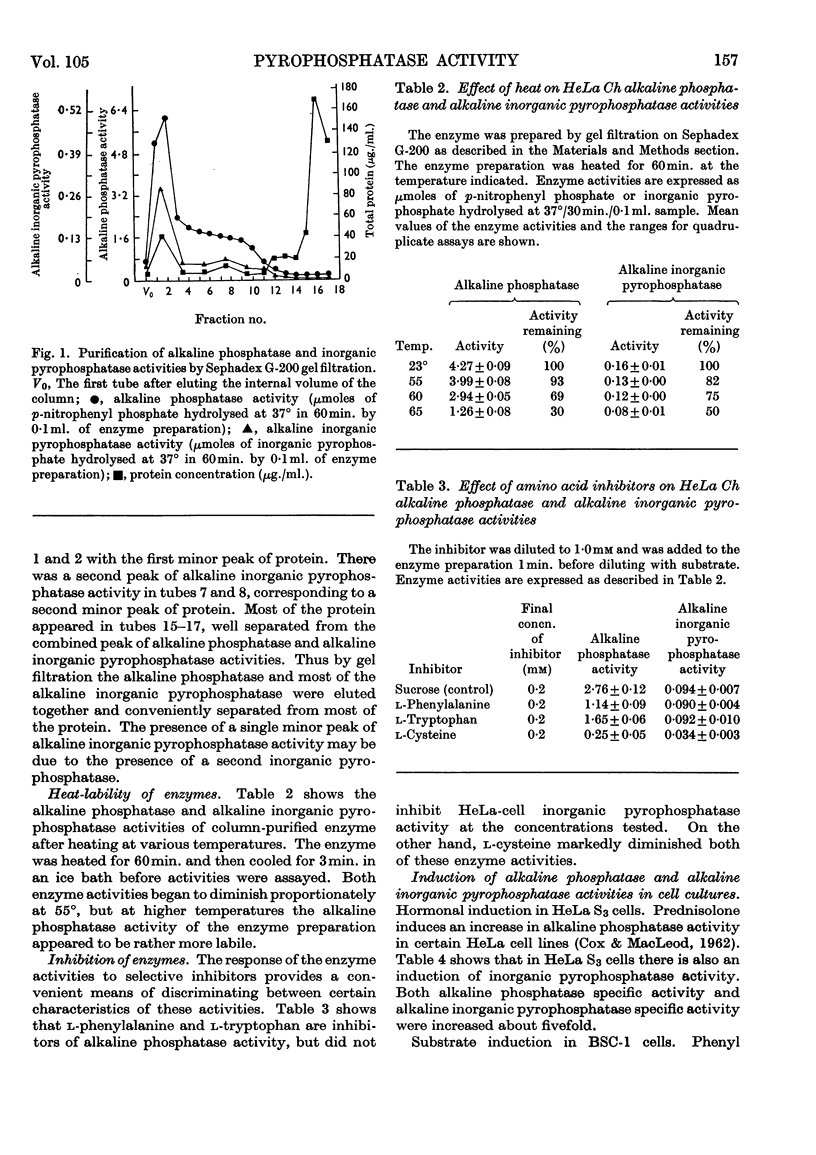
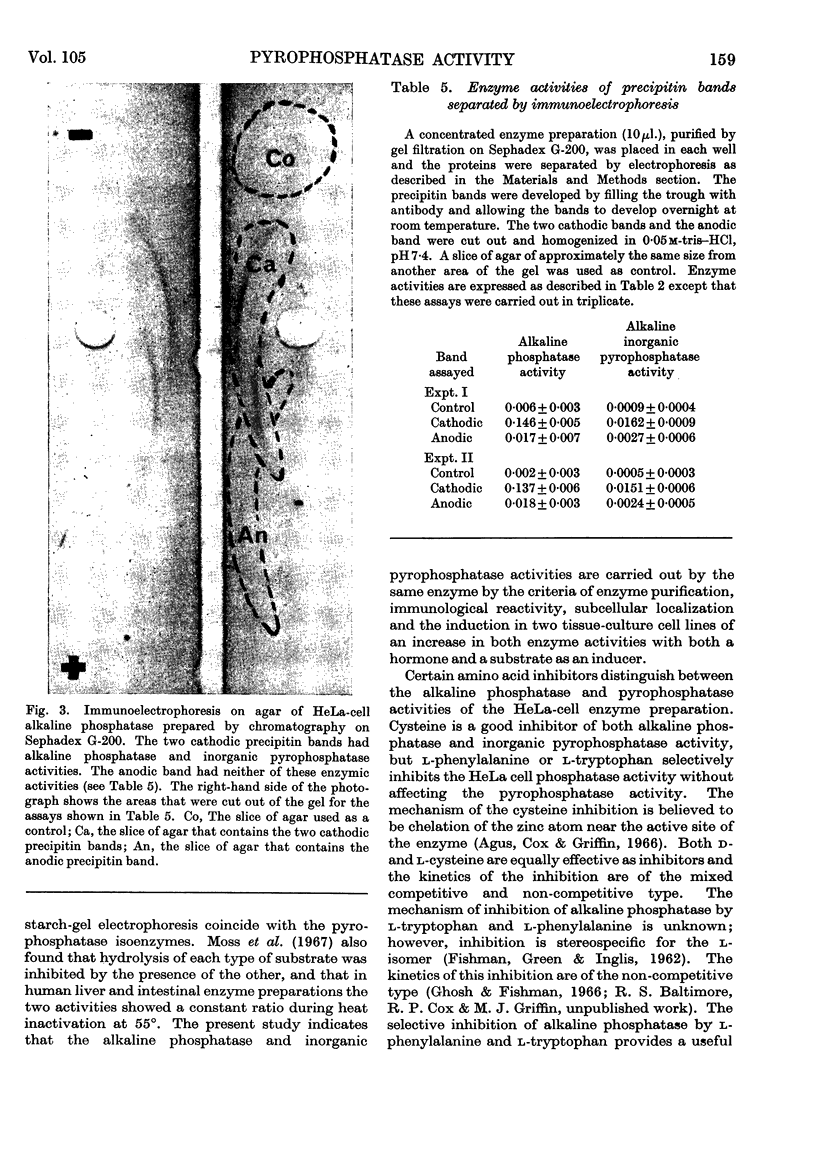
- Moss D. W., Eaton R. H., Smith J. K., Whitby L. G. Association of inorganic-pyrophosphatase activity with human alkaline-phosphatase preparations. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):53–57. doi: 10.1042/bj1020053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORDLIE R. C., GEHRING A. W. INORGANIC PYROPHOSPHATE HYDROLYSIS BY RAT-LIVER MICROSOMES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 3;77:100–107. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90472-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORDLIE R. C., LARDY H. A. Sub-cellular distribution of ratliver inorganic pyrophosphatase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jun 10;50:189–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)91083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PYNES G. D., YOUNATHAN E. S. THE SUBCELLULAR DISTRIBUTION OF INORGANIC PYROPHOSPHATASE IN PIGEON PANCREAS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 23;92:150–151. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90279-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STETTEN D., Jr Biosynthesis and pyrophosphate. Am J Med. 1960 Jun;28:867–870. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90195-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWANSON M. A. Phosphatases of the liver. III. "Neutral" pyrophosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):685–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAYMOUTH C. Rapid proliferation of sublines of NCTC clone 929 (strain L) mouse cells in a simple chemically defined medium (MB 752/1). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959 May;22(5):1003–1017. doi: 10.1093/jnci/22.5.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]