Abstract
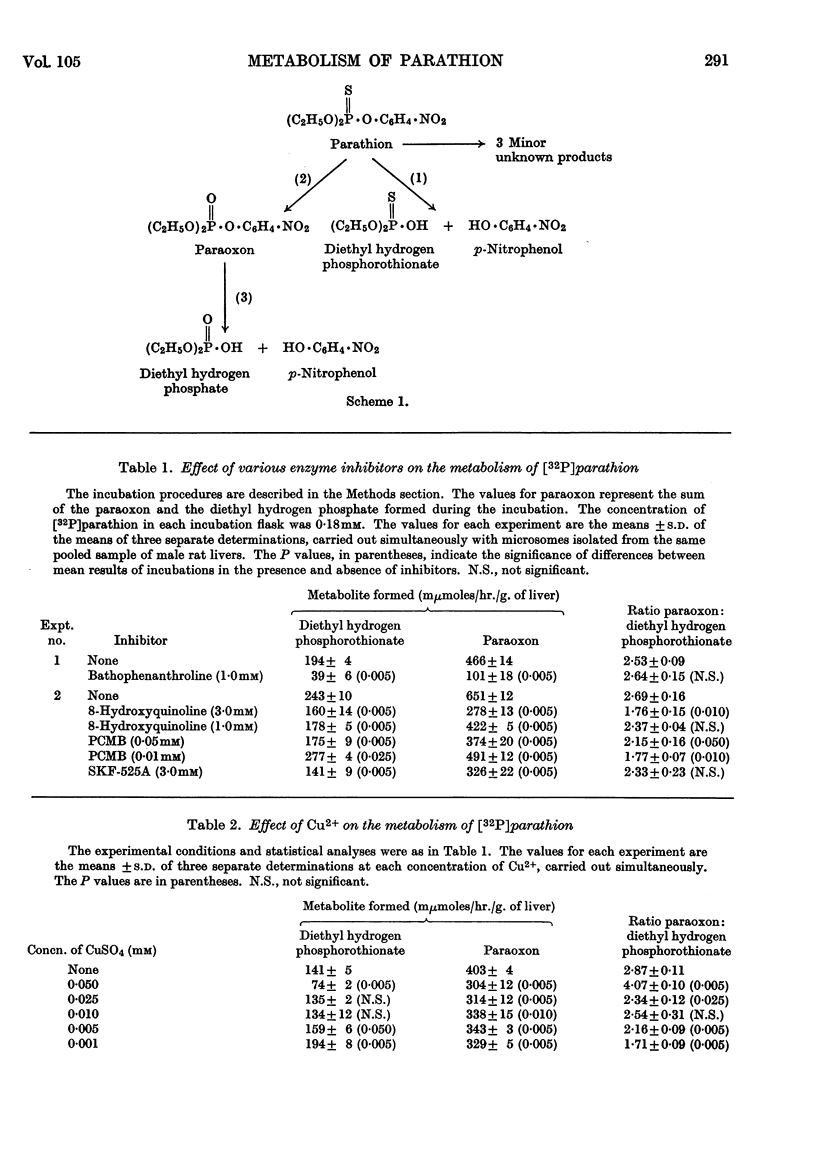
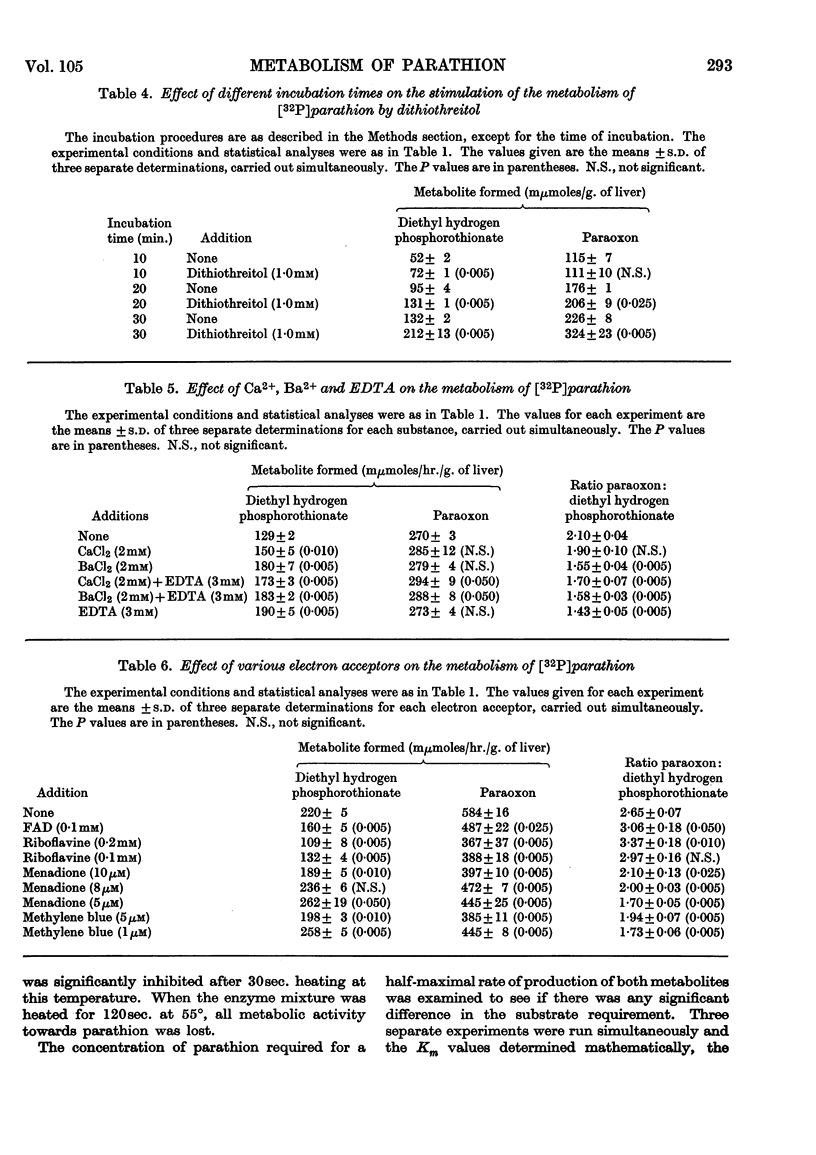
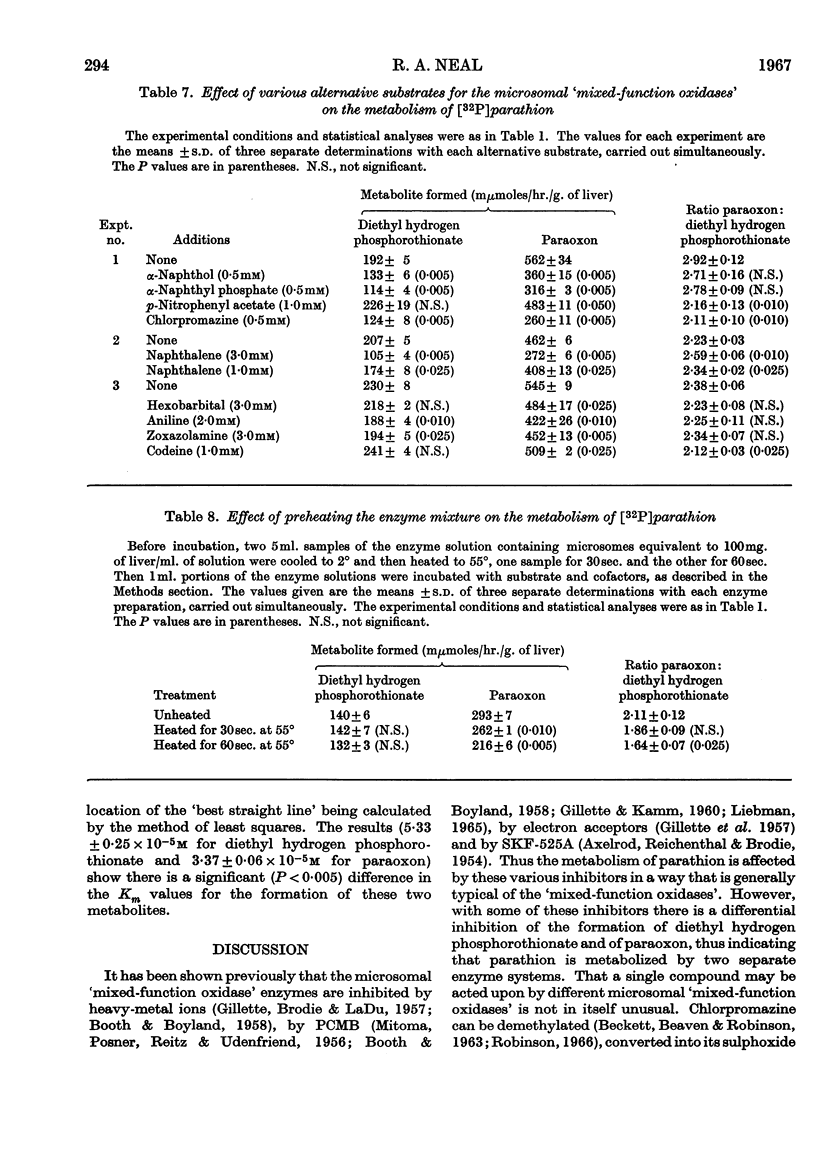
1. The metabolism of parathion by rat liver microsomes is affected by various enzyme inhibitors in a manner quite typical of the `mixed-function oxidase' enzyme systems. 2. With many of these inhibitors (p-chloromercuribenzoate, Cu2+, 8-hydroxyquinoline) the conversion of parathion into diethyl hydrogen phosphorothionate is less inhibited than conversion into diethyl 4-nitrophenyl phosphate (paraoxon). 3. Compounds containing reduced sulphur stimulate the overall metabolism of parathion. However, the conversion of parathion into diethyl hydrogen phosphorothionate is stimulated more than its conversion into paraoxon. 4. The metabolism of parathion to diethyl hydrogen phosphorothionate is also stimulated by EDTA, Ca2+ and Ba2+, but these stimulatory effects are not additive. 5. The electron acceptors FAD, riboflavine, menadione and methylene blue exhibit a concentration-dependent differential inhibition of the metabolism of parathion to diethyl hydrogen phosphorothionate and to paraoxon. 6. The concentration of parathion required for the half-maximal rate of production of diethyl hydrogen phosphorothionate is significantly different from the concentration required for half-maximal rate of production of paraoxon. 7. The results are discussed in terms of either two separate enzyme systems metabolizing parathion to diethyl hydrogen phosphorothionate and to paraoxon or two different binding sites for parathion, which share a common electron-transport pathway.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Serum esterases. II. An enzyme hydrolysing diethyl p-nitrophenyl phosphate (E600) and its identity with the A-esterase of mammalian sera. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):117–124. doi: 10.1042/bj0530117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AXELROD J., REICHENTHAL J., BRODIE B. B. Mechanism of the potentiating action of beta-diethylaminoethyl diphenylpropylacetate. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 Sep;112(1):49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKETT A. H., BEAVEN M. A., ROBINSON A. E. METABOLISM OF CHLORPROMAZINE IN HUMANS. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Aug;12:779–794. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOOTH J., BOYLAND E. Metabolism of polycyclic compounds. 13. Enzymic hydroxylation of naphthalene by rat-liver microsomes. Biochem J. 1958 Dec;70(4):681–688. doi: 10.1042/bj0700681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNEY A. H., GILLETTE J. R., INSCOE J. K., TRAMS E. R., POSNER H. S. Induced synthesis of liver microsomal enzymes which metabolize foreign compounds. Science. 1959 Nov 27;130(3387):1478–1479. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3387.1478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creaven P. J., Parke D. V., Williams R. T. A fluorimetric study of the hydroxylation of biphenyl in vitro by liver preparations of various species. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):879–885. doi: 10.1042/bj0960879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAUDETTE L. E., BRODIE B. B. Relationship between the lipid solubility of drugs and their oxidation by liver microsomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1959 Aug;2:89–96. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(59)90075-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLETTE J. R., BRODIE B. B., LA DU B. N. The oxidation of drugs by liver microsomes: on the role of TPNH and oxygen. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957 Apr;119(4):532–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLETTE J. R., KAMM J. J. The enzymatic formation of sulfoxides: the oxidation of chlorpromazine and 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl sulfide by guinea pig liver microsomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1960 Nov;130:262–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram T. E., Fouts J. R. Time course differences in the metabolism of drugs by hepatic microsomes from rats, rabbits and mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Jun;152(3):363–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamin H., Masters B. S., Gibson Q. H., Williams C. H., Jr Microsomal TPNH-cytochrome c reductase. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1164–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntzman R., Lawrence D., Conney A. H. Michaelis constants for the hydroxylation of steroid hormones and drugs by rat liver microsomes. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Sep;1(2):163–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibman K. C. Metabolism of trichloroethylene in liver microsomes. I. Characteristics of the reaction. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Nov;1(3):239–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITOMA C., POSNER H. S., REITZ H. C., UDENFRIEND S. Enzymatic hydroxylation of aromatic compounds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Apr;61(2):431–441. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason H. S., North J. C., Vanneste M. Microsomal mixed-function oxidations: the metabolism of xenobiotics. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1172–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEAL R. A., DUBOIS K. P. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF DETOXIFICATION OF CHOLINERGIC PHOSPHOROTHIOATES. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 May;148:185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal R. A. Studies on the metabolism of diethyl 4-nitrophenyl phosphorothionate (parathion) in vitro. Biochem J. 1967 Apr;103(1):183–191. doi: 10.1042/bj1030183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibayashi H., Omura T., Sato R. Stimulation by vitamin K3 of NADPH oxidation in liver microsomes. J Biochem. 1966 Aug;60(2):172–183. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura T., Sato R., Cooper D. Y., Rosenthal O., Estabrook R. W. Function of cytochrome P-450 of microsomes. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1181–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS A. H., LANGDON R. G. Hepatic triphosphopyridine nucleotide-cytochrome c reductase: isolation, characterization, and kinetic studies. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2652–2660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardanis A. Activation of some organophosphorus insecticides by liver microsomes from phenobarbital-treated mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Jun;15(6):749–752. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


