Abstract
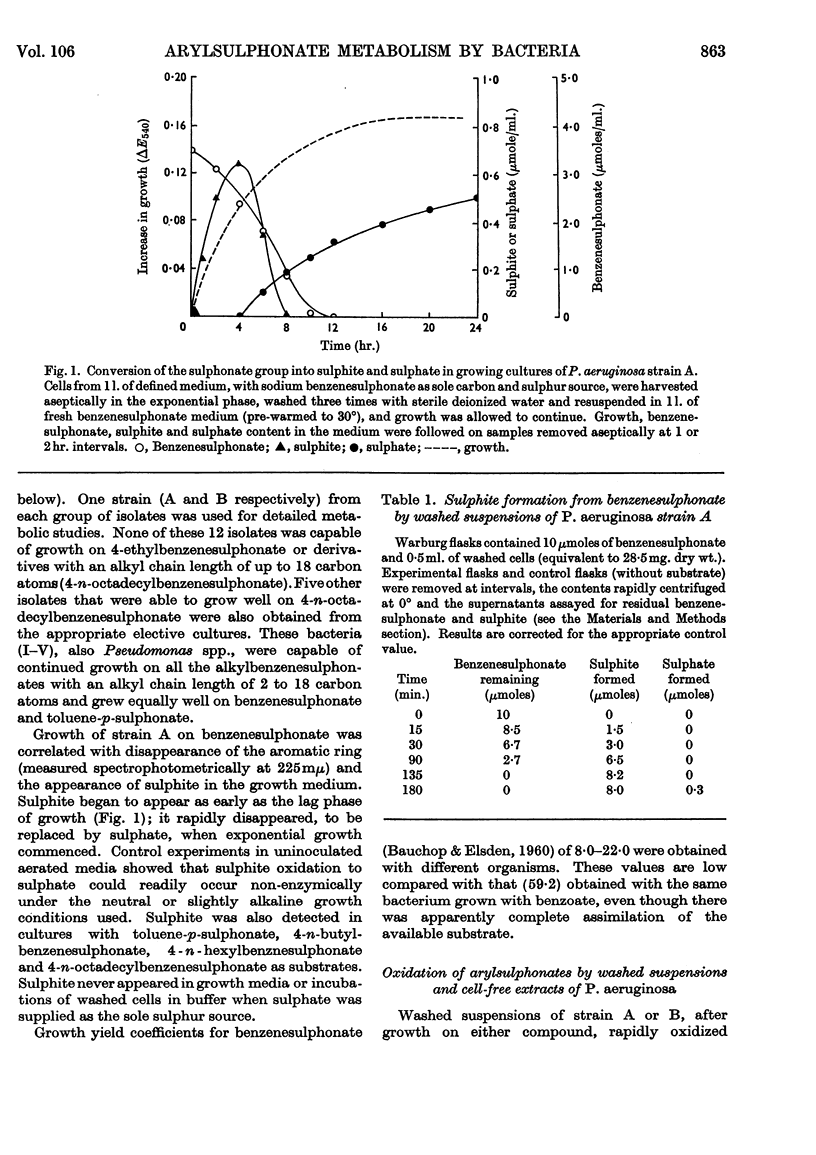
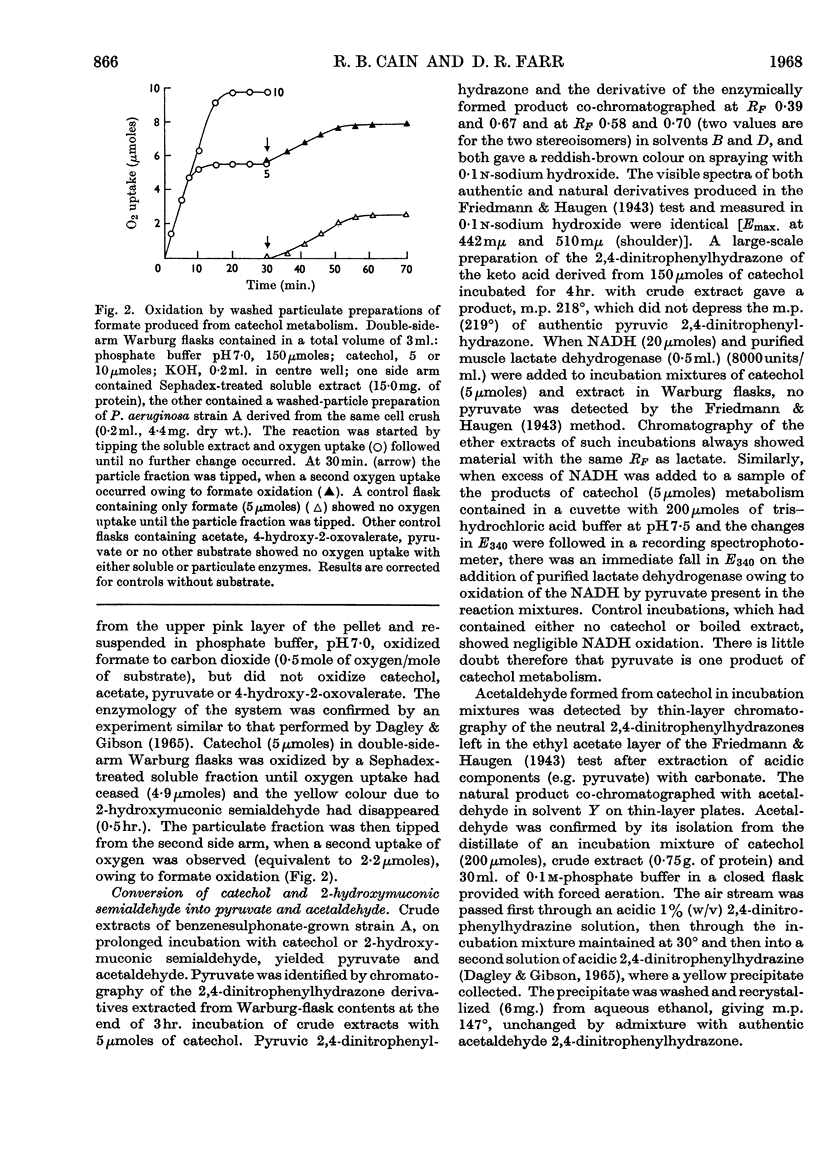
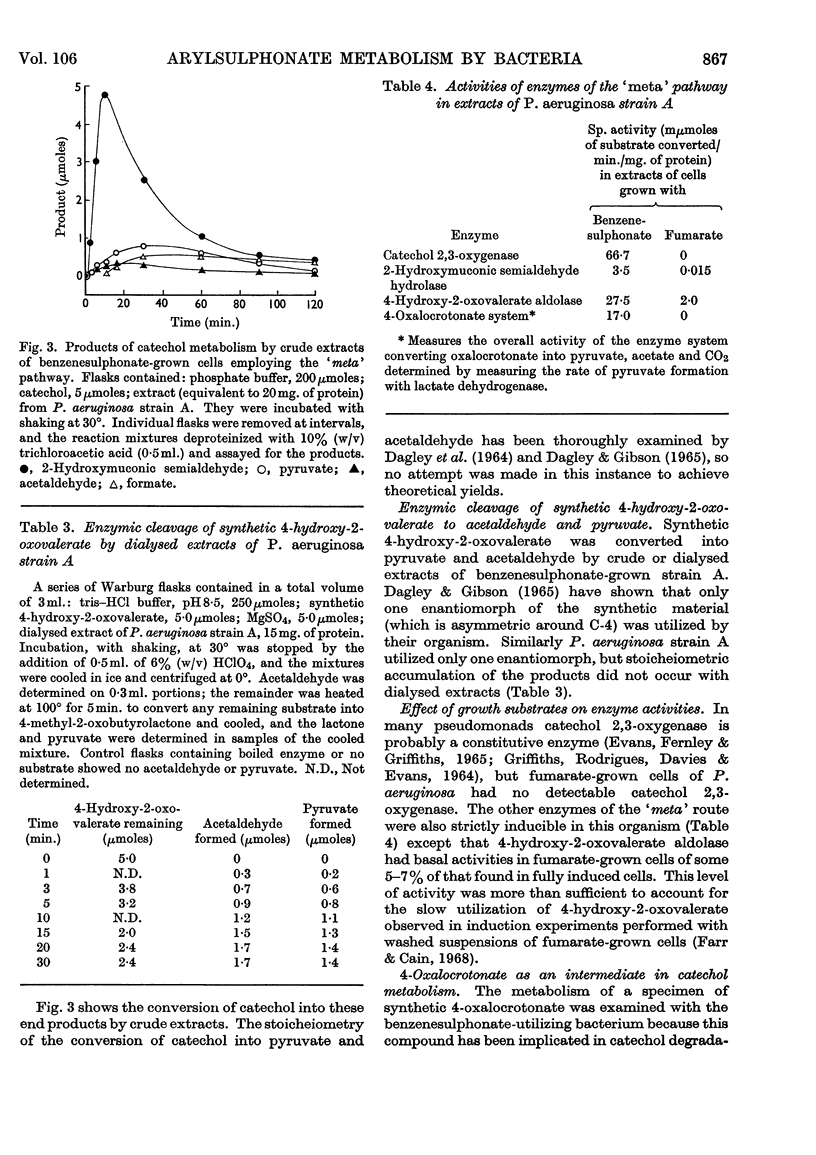
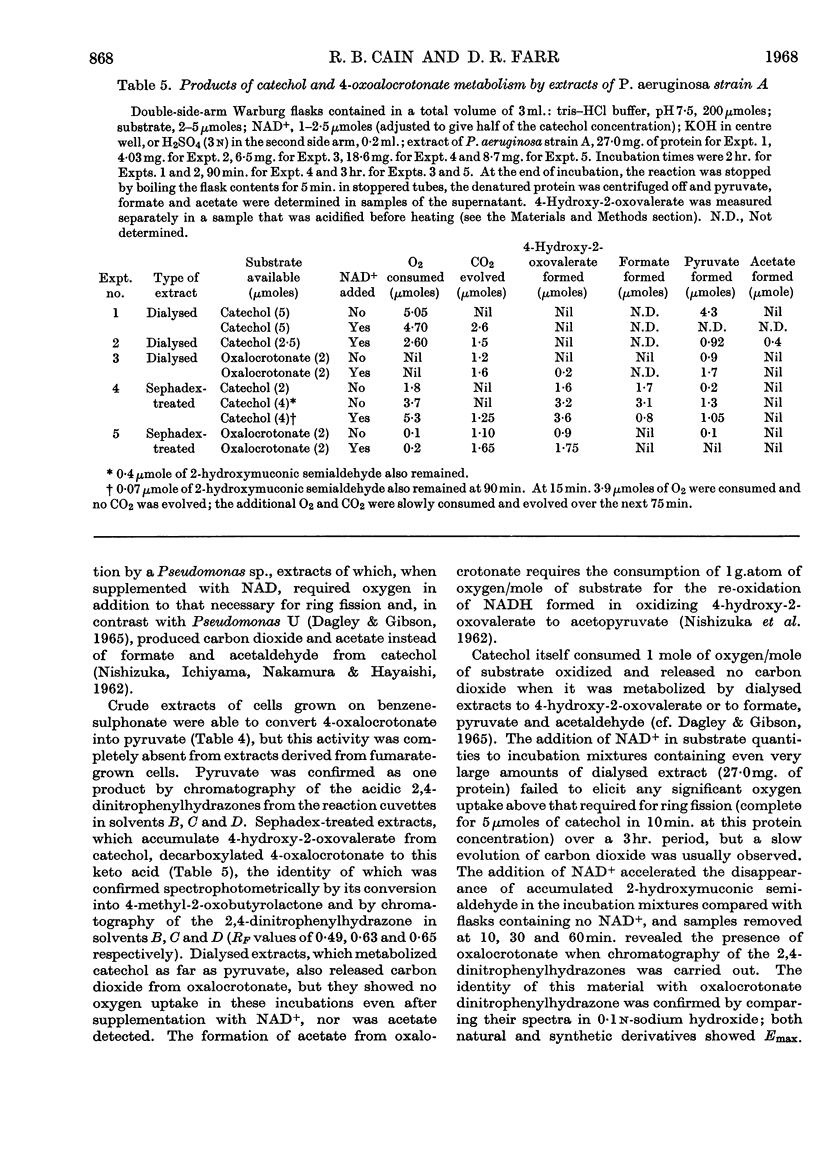
1. Species of Pseudomonas capable of degrading arylsulphonates and detergents of the alkylbenzenesulphonate type were isolated from sewage and river water. 2. Benzenesulphinate, benzenesulphonate and toluene-p-sulphonate were rapidly degraded by these organisms with the release of the sulphonate group as sulphite; detergent homologues with a chain length up to 16 carbon atoms (4-n-hexadecyl-benzenesulphonate) also released sulphite. Sulphite oxidation to sulphate in the medium can occur non-enzymically. 3. Growth on benzenesulphonate and toluene-p-sulphonate elicited a catechol 2,3-oxygenase, which effected a `meta' cleavage of the ring. The metabolic route for benzenesulphonate was determined as: benzenesulphonate→catechol→2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde→formate and 4-hydroxy-2-oxovalerate→acetaldehyde and pyruvate; the enzymes catalysing these steps were all inducible. 4. Toluene-p-sulphonate was degraded via 2-hydroxy-5-methylmuconic semialdehyde to formate and 4-hydroxy-2-oxohexanoate and the latter was cleaved to propionaldehyde and pyruvate. Propionaldehyde and propionate were oxidized rapidly by toluene-p-sulphonate-grown cells but slowly by fumarate-grown organisms. 5. The specificity of the catechol 2,3-oxygenase induced by the arylsulphonates, towards catechol and the methylcatechols, varied during the purification and suggested that 3-methylcatechol was probably oxidized by a separate enzyme. Detergents of the alkylbenzenesulphonate type also induced a catechol 2,3-oxygenase in these bacteria. 6. A few isolates, after growth on benzenesulphonate, opened the ring of catechol by an `ortho' route to form cis–cis-muconate. The enzymes to degrade this intermediate to β-oxoadipate were also present in induced cells.
Full text
PDF






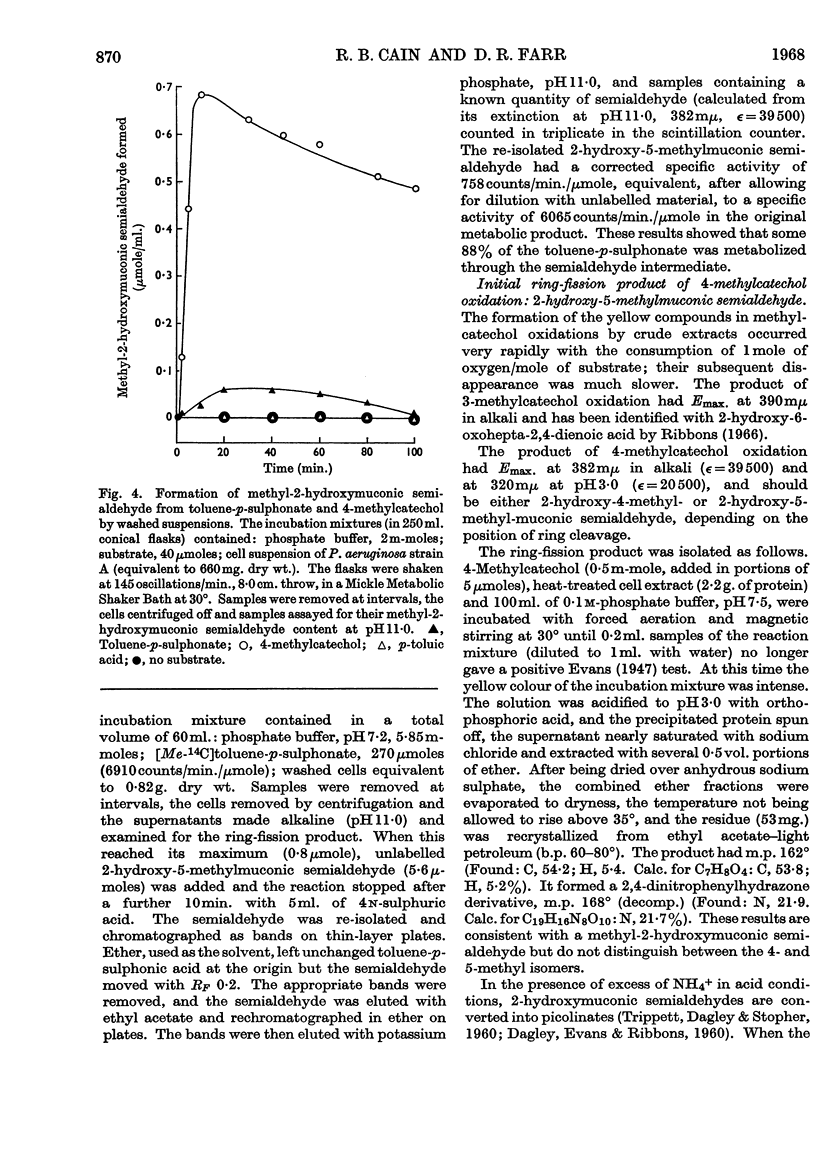
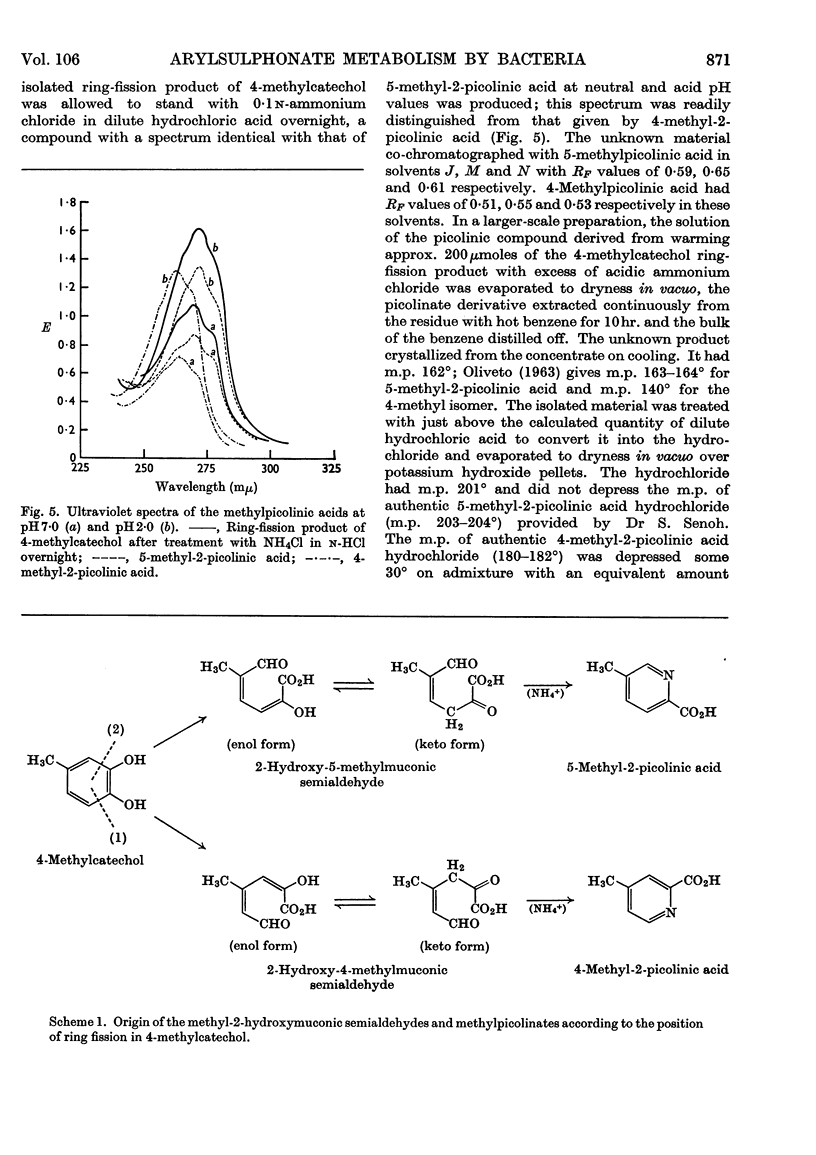
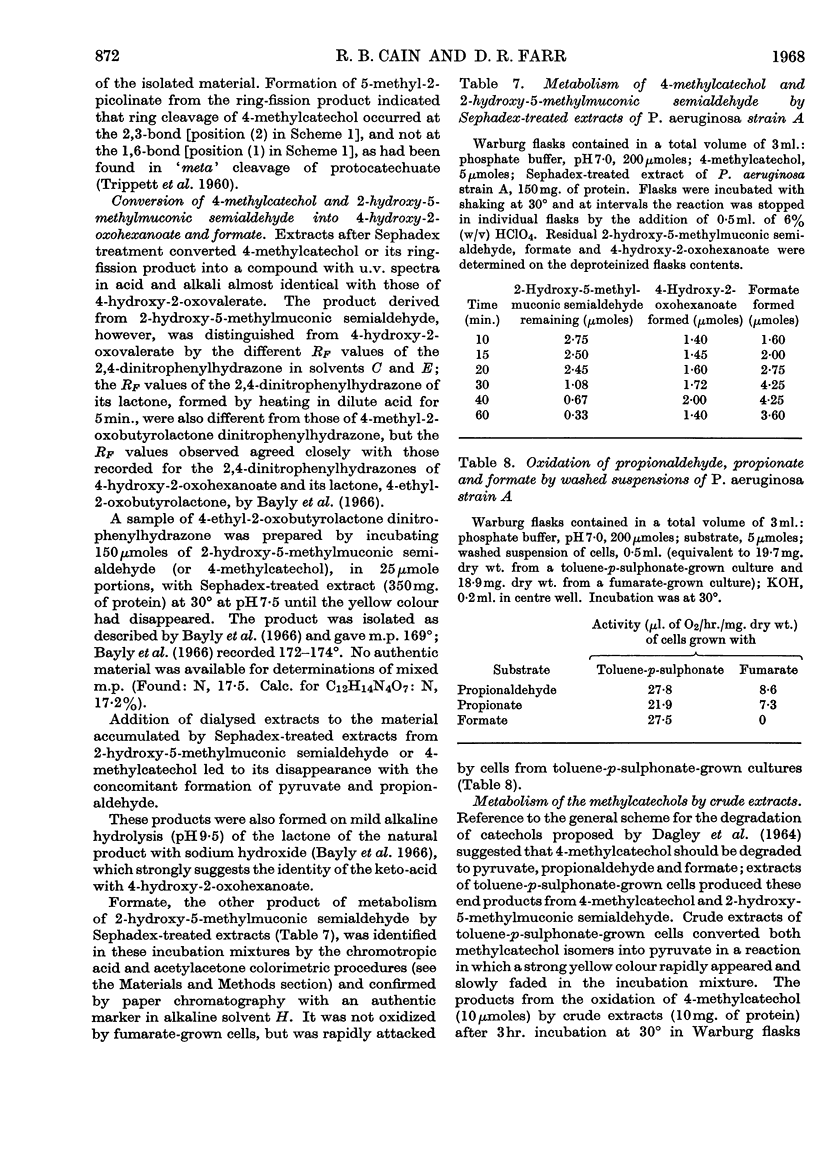
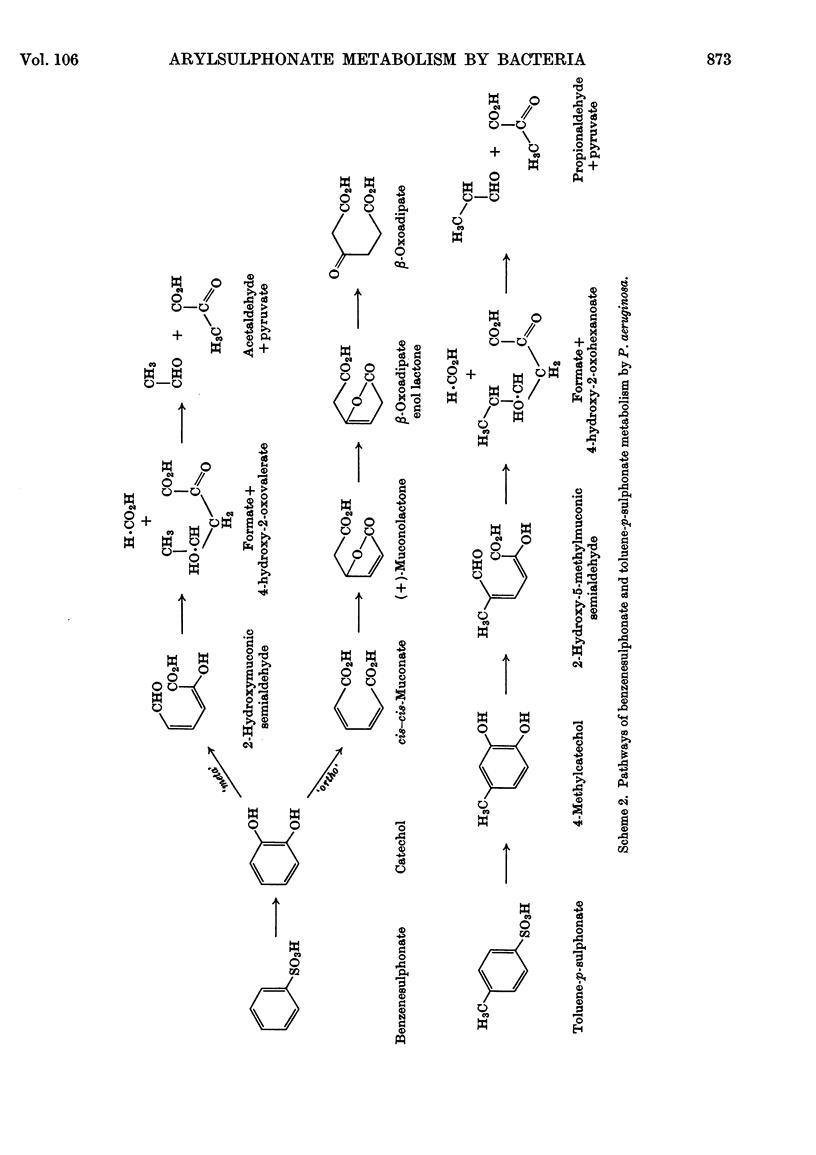



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAUCHOP T., ELSDEN S. R. The growth of micro-organisms in relation to their energy supply. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:457–469. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S., Gibson D. T. The metabolism of cresols by species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):293–301. doi: 10.1042/bj1010293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAIN R. B. New aromatic ring-splitting enzyme, protocatechuic acid-4:5-oxygenase. Nature. 1962 Mar 3;193:842–844. doi: 10.1038/193842a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAIN R. B. The metabolism of protocatechuic acid by a vibrio. Biochem J. 1961 May;79:298–312. doi: 10.1042/bj0790298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain R. B. Utilization of anthranilic and nitrobenzoic acids by Nocardia opaca and a flavobacterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Feb;42(2):219–235. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-2-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., CHAPMAN P. J., GIBSON D. T., WOOD J. M. DEGRADATION OF THE BENZENE NUCLEUS BY BACTERIA. Nature. 1964 May 23;202:775–778. doi: 10.1038/202775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., EVANS W. C., RIBBONS D. W. New pathways in the oxidative metabolism of aromatic compounds by microorganisms. Nature. 1960 Nov 12;188:560–566. doi: 10.1038/188560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., GIBSON D. T. THE BACTERIAL DEGRADATION OF CATECHOL. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:466–474. doi: 10.1042/bj0950466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWKINS M. J., JUDAH J. D., REES K. R. The mechanism of action of chlorpromazine. Reduced diphosphopyridine nucleotidecytochrome c reductase and coupled phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:16–23. doi: 10.1042/bj0730016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS W. C., FERNLEY H. N., GRIFFITHS E. OXIDATIVE METABOLISM OF PHENANTHRENE AND ANTHRACENE BY SOIL PSEUDOMONADS. THE RING-FISSION MECHANISM. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:819–831. doi: 10.1042/bj0950819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C. Oxidation of phenol and benzoic acid by some soil bacteria. Biochem J. 1947;41(3):373–382. doi: 10.1042/bj0410373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr D. R., Cain R. B. Catechol oxygenase induction in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(4):879–885. doi: 10.1042/bj1060879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES D. E. A press for disrupting bacteria and other micro-organisms. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Apr;32(2):97–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULLIN R. P., NOBLE R. L. The determination of lacic acid in microgram quantities. Biochem J. 1953 Sep;55(2):289–291. doi: 10.1042/bj0550289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway by Pseudomonas putida. I. Synthesis of enzymes by the wild type. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1140–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1140-1154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOJIMA Y., ITADA N., HAYAISHI O. Metapyrocatachase: a new catechol-cleaving enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1961 Aug;236:2223–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDONOUGH S. Paper chromatography for the separation of neutral 17-ketosteroids in urine. Nature. 1954 Apr 3;173(4405):645–646. doi: 10.1038/173645b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NASH T. The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzsch reaction. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):416–421. doi: 10.1042/bj0550416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHIZUKA Y., ICHIYAMA A., NAKAMURA S., HAYAISHI O. A new metabolic pathway of catechol. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:PC268–PC270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOZAKI M., KAGAMIYAMA H., HAYAISHI O. METAPYROCATECHASE. I. PURIFICATION, CRYSTALLIZATION AND SOME PROPERTIES. Biochem Z. 1963;338:582–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. IV. Regulation. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3800–3810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIBBONS D. W., EVANS W. C. Oxidative metabolism of protocatechuic acid by certain soil pseudomonads: a new ring-fission mechanism. Biochem J. 1962 Jun;83:482–492. doi: 10.1042/bj0830482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON H. C. THE REDUCTION OF INORGANIC SULPHATE TO INORGANIC SULPHITE IN THE SMALL INTESTINE OF THE RAT. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:687–691. doi: 10.1042/bj0940687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of omicron-cresol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain T1. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Aug;44(2):221–231. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLEEPER B. P. The bacterial oxidation of aromatic compounds. V. Metabolism of benzoic acids labeled with C14. J Bacteriol. 1951 Nov;62(5):657–662. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.5.657-662.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scales B. A new scintillator for liquid scintillation counting. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1967 Jan;18(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(67)90165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANIUCHI H., KOJIMA Y., KANETSUNA F., OCHIAI H., HAYAISHI O. The mechanism of the autoxidation of oxygenases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Jun 19;8:97–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


