Abstract
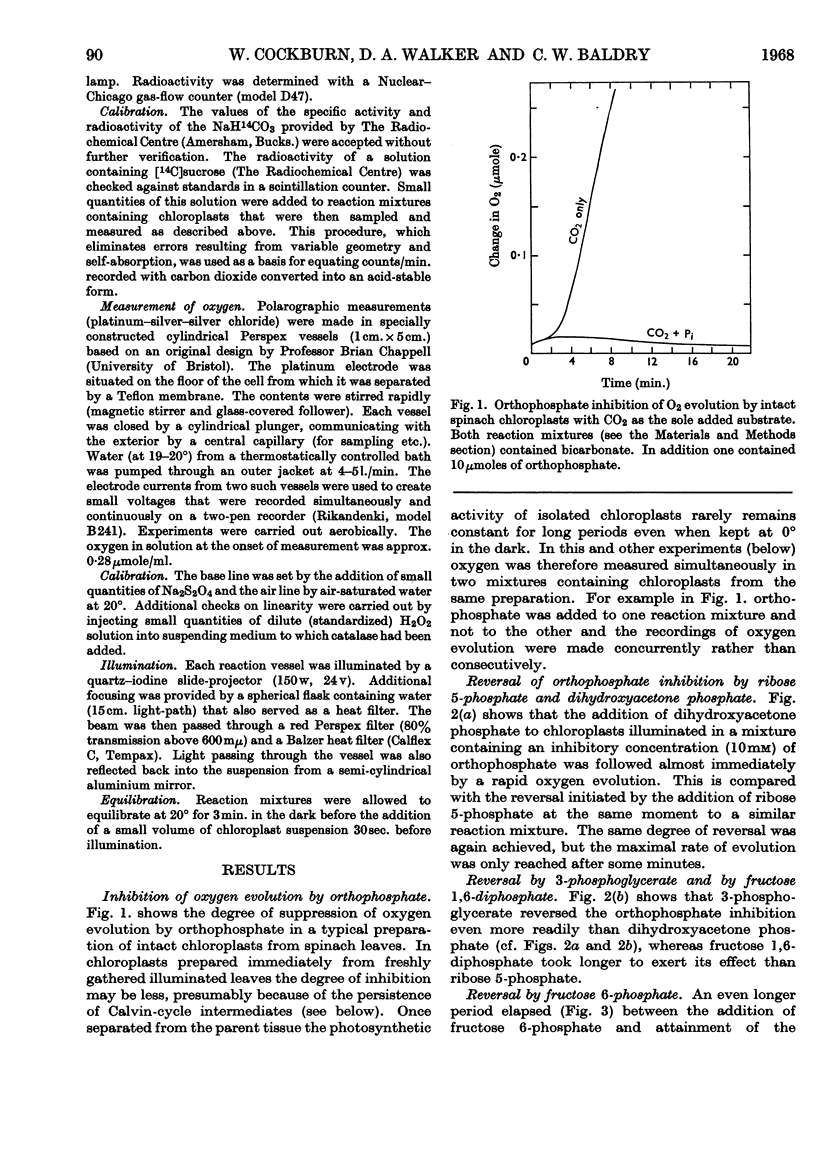
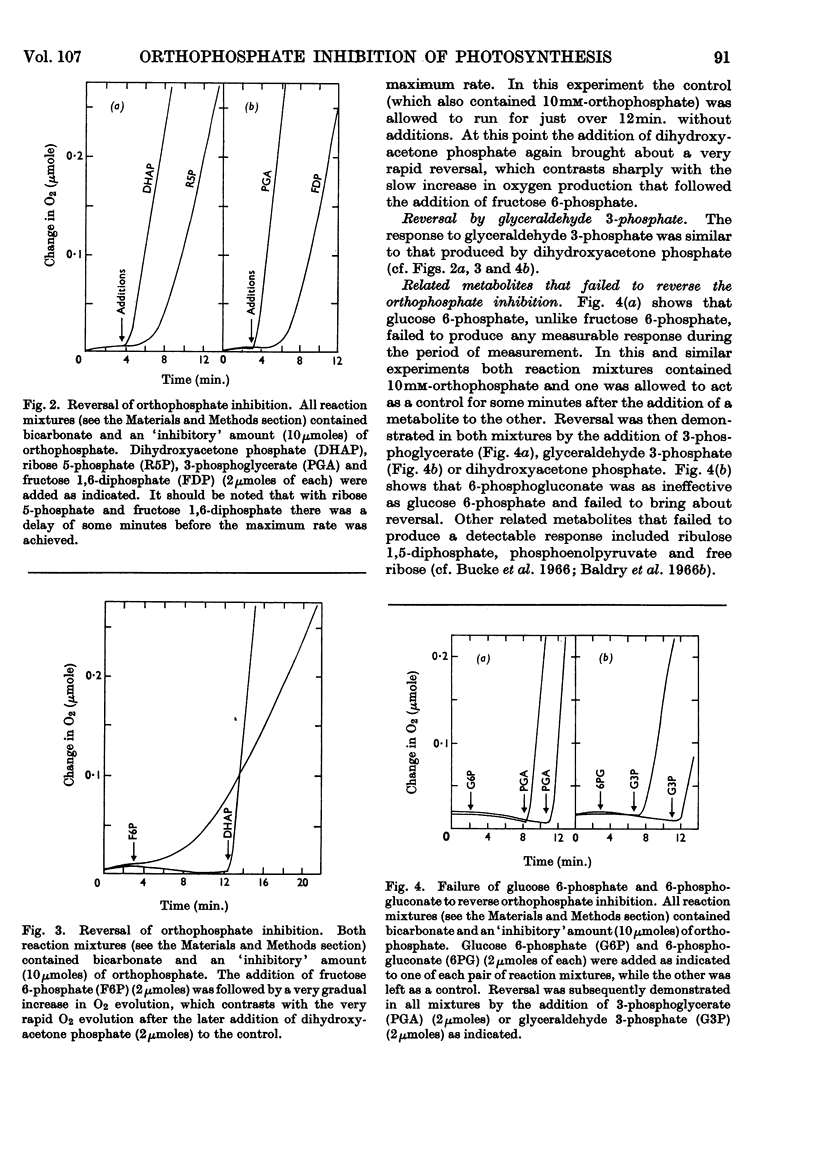
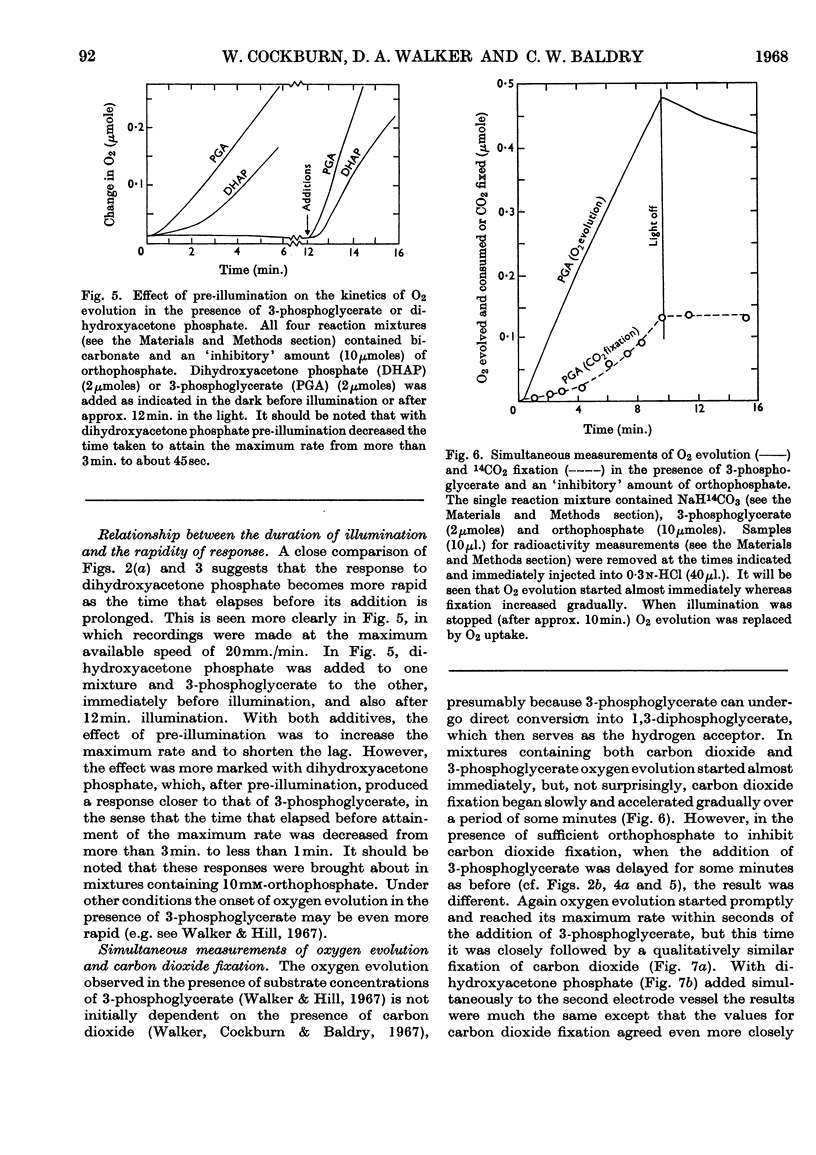
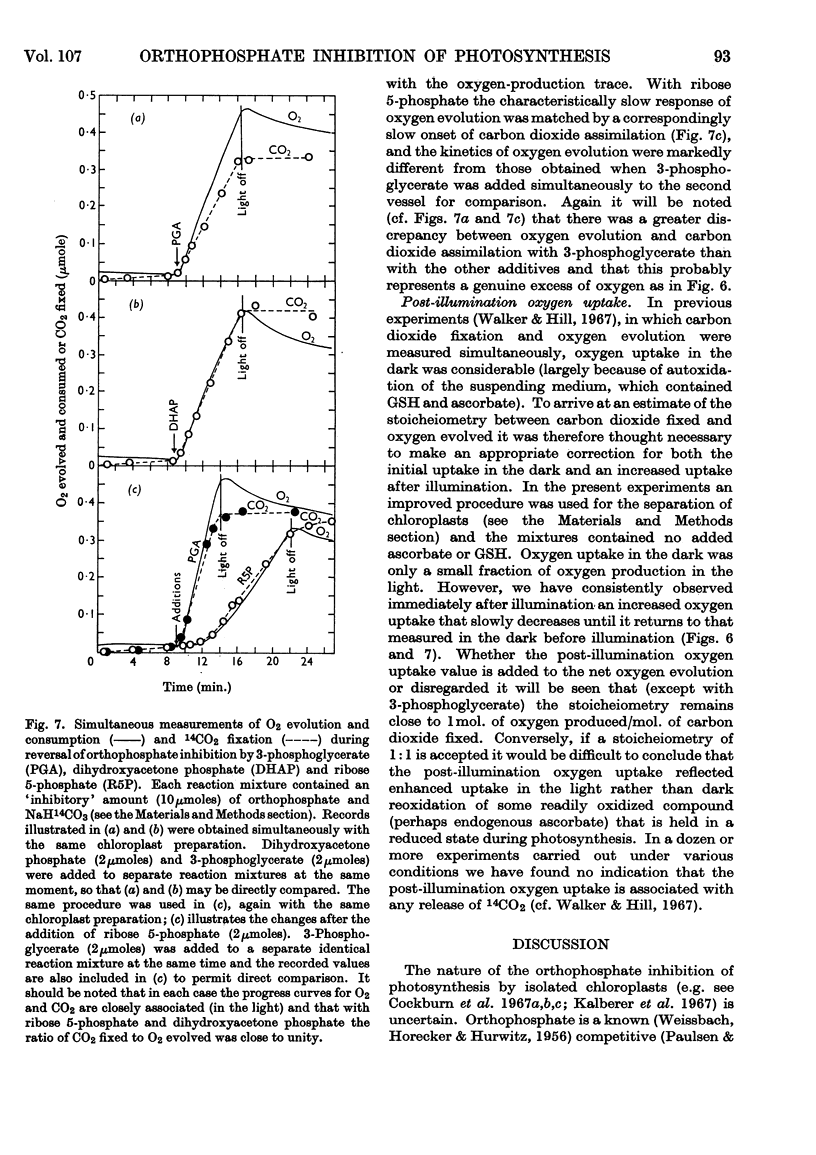
1. The orthophosphate inhibition of photosynthesis by isolated spinach chloroplasts can be reversed by 3-phosphoglycerate, dihydroxyacetone phosphate, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, fructose 6-phosphate and fructose 1,6-diphosphate. 2. Metabolically related compounds such as ribulose 1,5-diphosphate, glucose 6-phosphate, 6-phosphogluconate and phosphoenolpyruvate are ineffective. 3. The kinetics of reversal are characteristic of the intermediate used, but, in each instance, the onset of oxygen evolution is accompanied by a carbon dioxide fixation and except with 3-phosphoglycerate the stoicheiometry is close to unity. 4. The nature of orthophosphate inhibition and its reversal is discussed in relation to metabolic control of photosynthesis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldry C. W., Bucke C., Walker D. A. Temperature and photosynthesis. I. Some effects of temperature on carbon dioxide fixation by isolated chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 10;126(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldry C. W., Walker D. A., Bucke C. Calvin-cycle intermediates in relation to induction phenomena in photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation by isolated chloroplasts. Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):642–646. doi: 10.1042/bj1010642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucke C., Walker D. A., Baldry C. W. Some effects of sugars and sugar phosphates on carbon dioxide fixation by isolated chloroplasts. Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):636–641. doi: 10.1042/bj1010636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn W., Baldry C. W., Walker D. A. Oxygen evolution by isolated chloroplasts with carbon dioxide as the hydrogen acceptor. A requirement for orthophosphate or pyrophosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 9;131(3):594–596. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn W., Baldry C. W., Walker D. A. Photosynthetic induction phenomena in spinach chloroplasts in relation to the nature of the isolating medium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;143(3):606–613. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn W., Baldry C. W., Walker D. A. Some effects of inorganic phosphate on O2 evolution by isolated chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;143(3):614–624. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good N. E., Winget G. D., Winter W., Connolly T. N., Izawa S., Singh R. M. Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):467–477. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. G., Bassham J. A. Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1095–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalberer P. P., Buchanan B. B., Arnon D. I. Rates of photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1542–1549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen J. M., Lane M. D. Spinach ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2350–2357. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. A. Correlation between Photosynthetic Activity and Membrane Integrity in Isolated Pea Chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1965 Nov;40(6):1157–1161. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.6.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. A., Hill R. The relation of oxygen evolution to carbon assimilation with isolated chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Mar 8;131(2):330–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


