Abstract
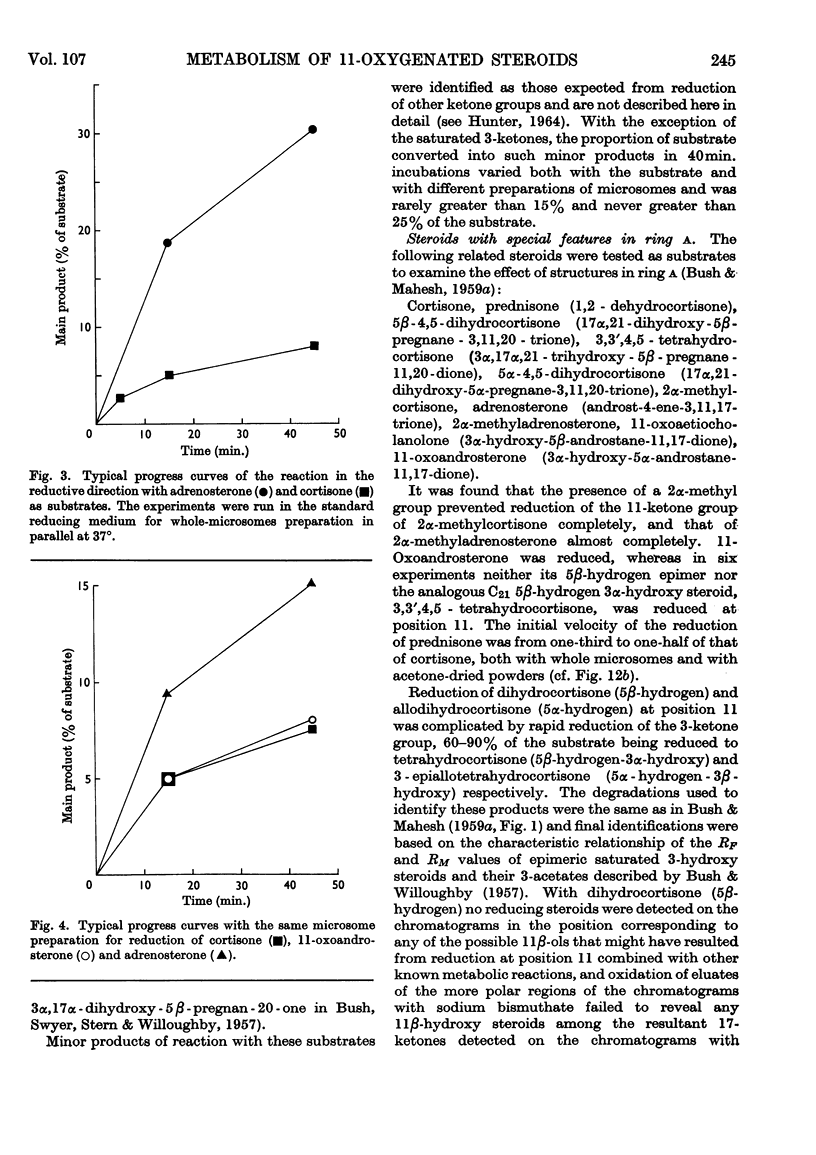
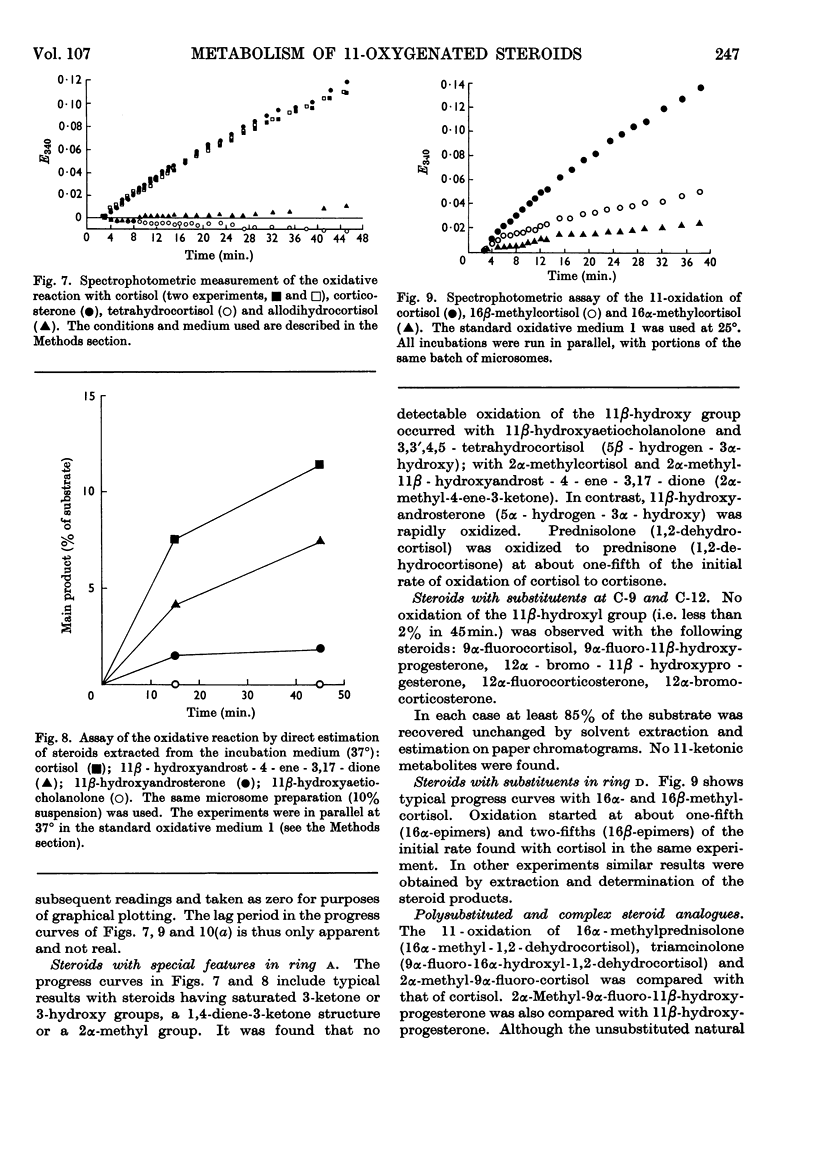
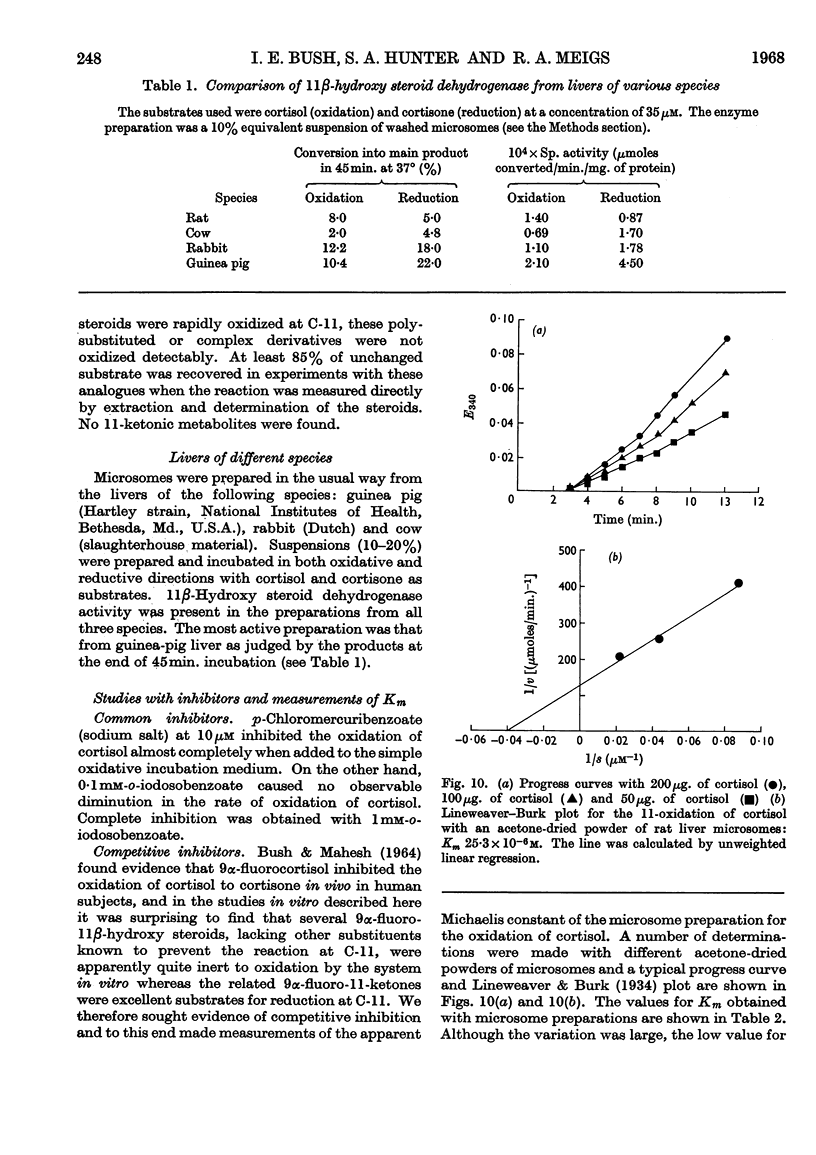
1. The isolation and partial purification of 11β-hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase from rat and guinea-pig liver microsomes has been achieved by conventional methods. 2. The efficiency of different 11-oxygenated steroids as substrates has been examined. The relative efficiencies confirm in the main the stereochemical theory of the enzyme–coenzyme–substrate complex that was proposed earlier on the basis of studies in vivo. Δ4-3-Ketones and 5α-hydrogen steroids are readily metabolized by the enzyme. 5β-Hydrogen steroids and Δ4-3-ketones with certain large α-substituents are metabolized to a limited extent or not at all. Halogen substitution in the 9α-position enhances the rate of reduction of 11-ketones but blocks the oxidation of the related 11β-ols. 3. 9α-Fluorocortisol is a competitive inhibitor of the oxidation of cortisol, but 9α-fluorocortisone is reduced at five to ten times the initial velocity of cortisone. 4. 11β-Hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase activity has been found in liver microsomes of rat, guinea pig, rabbit and calf. 5. Relative substrate efficiencies and Km values are similar in whole (debris-free) homogenates, washed microsomes and acetone-dried powders of washed microsomes. 6. A variety of conditions have been examined for the observation of 11β-hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase activity. NADP(H) is an efficient and NAD(H) a very poor coenzyme for the reaction.
Full text
PDF
















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN-GRANT K., FORCHIELLI E., DORFMAN R. I. The delta4-hydrogenases of guinea pig adrenal gland. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1317–1320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON R. B., KEUTMANN E. H., WATERHOUSE C., SCHULER E. A. The conversion of cortisone acetate to other alphaketolic steroids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1953 Jan;13(1):48–63. doi: 10.1210/jcem-13-1-48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSH I. E. Chemical and biological factors in the activity of adrenocortical steroids. Pharmacol Rev. 1962 Sep;14:317–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSH I. E., MAHESH V. B. Metabolism of 11-oxygenated steroids. 1. Influence of the A/B ring junction on the reduction of 11-oxo groups. Biochem J. 1959 Apr;71(4):705–717. doi: 10.1042/bj0710705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSH I. E., MAHESH V. B. Metabolism of 11-oxygenated steroids. 2. 2-Methyl steroids. Biochem J. 1959 Apr;71(4):718–742. doi: 10.1042/bj0710718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSH I. E. The 11-oxygen function in steroid metabolism. Experientia. 1956 Sep 15;12(9):325–331. doi: 10.1007/BF02165330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSH I. E., WILLOUGHBY M. The excretion of allo tetrahydrocortisol in human urine. Biochem J. 1957 Dec;67(4):689–700. doi: 10.1042/bj0670689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush I. E. Applications of the R-M treatment in chromatographic analysis. Methods Biochem Anal. 1965;13:357–438. doi: 10.1002/9780470110317.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush I. E., Mahesh V. B. Metabolism of 11-oxygenated steroids. 3. Some 1-dehydro and 9 alpha-fluoro steroids. Biochem J. 1964 Nov;93(2):236–255. doi: 10.1042/bj0930236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASPI E. Y., LEVY H., HECHTER O. M. Cortisone metabolism in liver. II. Isolation of certain cortisone metabolites. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Jul;45(1):169–182. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGHERTY T. F., BERLINER M. L., BERLINER D. L. Hormonal influence on lymphocyte differentiation from RES cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jun 21;88:78–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWD J. E., RIGGS D. S. A COMPARISON OF ESTIMATES OF MICHAELIS-MENTEN KINETIC CONSTANTS FROM VARIOUS LINEAR TRANSFORMATIONS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:863–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISH C. A., HAYANO M., PINCUS G. Conversion of cortisone to 17-hydrocorticosterone by liver homogenates. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Feb;42(2):480–481. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90380-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIED J., KESSLER W. B., BORMAN A. Some biological activities of certain progestogens. II. 9-And 12-halo-11-oxygenated progesterones. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Jul 30;71(5):494–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb46780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOAGLAND M. B., KELLER E. B., ZAMECNIK P. C. Enzymatic carboxyl activation of amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):345–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFSTEE B. H. Non-inverted versus inverted plots in enzyme kinetics. Nature. 1959 Oct 24;184:1296–1298. doi: 10.1038/1841296b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBENER H. J., FUKUSHIMA D. K., GALLAGHER T. F. Substrate specificity of enzymes reducing the 11- and 20-keto groups of steroids. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jun;220(2):499–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAR N. C., CHATTERJEE I. B., GHOSH N. C., GUHA B. C. Further observations on the intracellular location and mechanism of action of liver enzymes catalysing the synthesis of L-ascorbic acid. Biochem J. 1962 Jul;84:16–25. doi: 10.1042/bj0840016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOERNER D. R., HELLMAN L. EFFECT OF THYROXINE ADMINISTRATION ON THE 11-BETA-HYDROXYSTEROID DEHYDROGENASES IN RAT LIVER AND KIDNEY. Endocrinology. 1964 Oct;75:592–601. doi: 10.1210/endo-75-4-592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner D. R. 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase of lung and testis. Endocrinology. 1966 Nov;79(5):935–938. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-5-935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN S., KATZENELLENBOGEN E. R., SCHNEIDER R., STUDER P. E., DOBRINER K. Isolation of urinary steroids after cortisone and adrenocorticotropic hormone. J Biol Chem. 1953 Nov;205(1):87–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHESH V. B., ULRICH F. Metabolism of cortisol and cortisone by various tissues and subcellular particles. J Biol Chem. 1960 Feb;235:356–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEIGS R. A., ENGEL L. L. The metabolism of adrenocortical steroids by human tissues. Endocrinology. 1961 Jul;69:152–162. doi: 10.1210/endo-69-1-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OFNER P., RYAN K. J., SMITH O. W., FRIED J., MUNSON P. L. Androstane derivatives of interest in therapy of breast cancer: classification of androgens according to convertibility to estrogens in vitro. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1962 Feb;16:285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSINSKI P. A. Steroid 11beta-ol dehydrogenase in human placenta. Nature. 1960 Aug 27;187:777–777. doi: 10.1038/187777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold H. J., Graves J. M., Clark A., Bellas T. Experimental strategy for delineation of the enzyme region involved in substrate recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):255–261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAHL T. J., TAPLEY D. F. TRANSPORT OF ADRENAL CORTICAL STEROIDS BY RAT INTESTINE IN VITRO. Endocrinology. 1963 Aug;73:271–272. doi: 10.1210/endo-73-2-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWEAT M. L., BRYSON M. J. The role of phosphopyridinenucleotides in the metabolism of cortisol by peripheral tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Nov 4;44:217–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91556-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALALAY P. Enzymatic mechanisms in steroid metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1957 Jul;37(3):362–389. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1957.37.3.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMKINS G. M. Enzymatic metabolism of corticosteroids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Oct 14;82:836–845. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb44965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


