Abstract
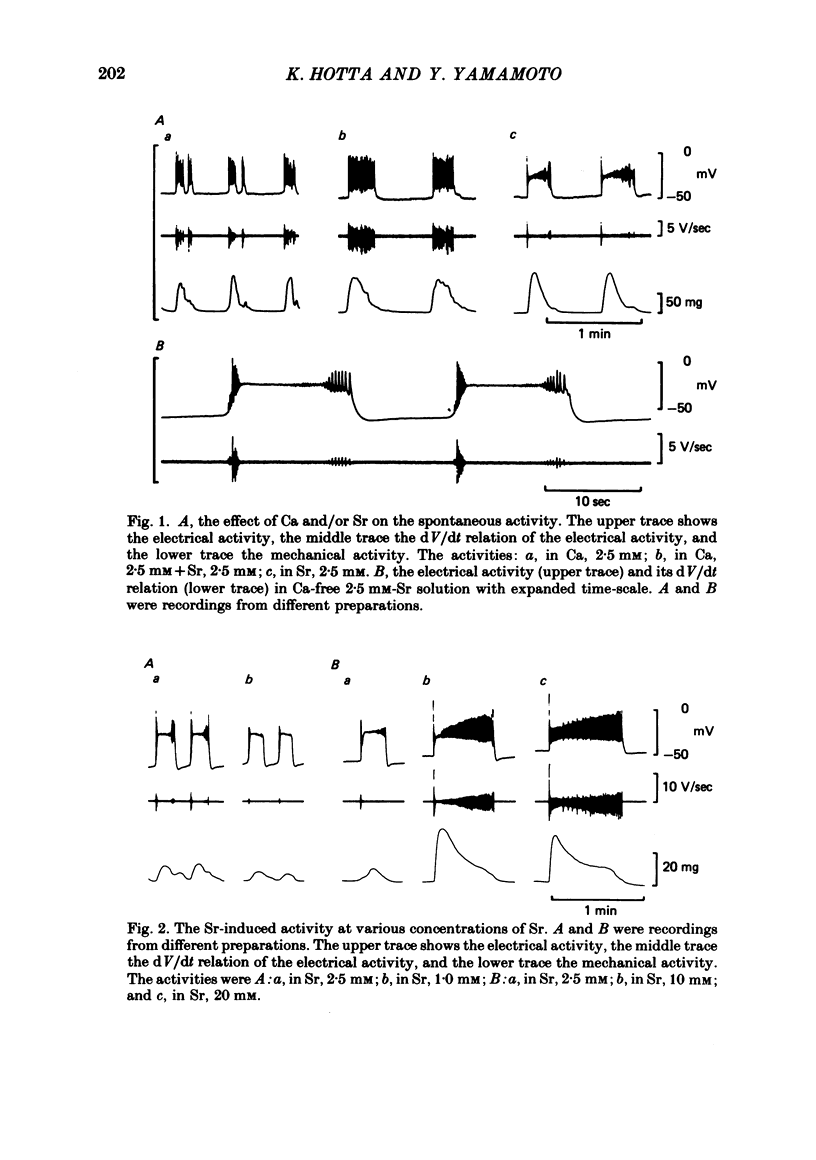
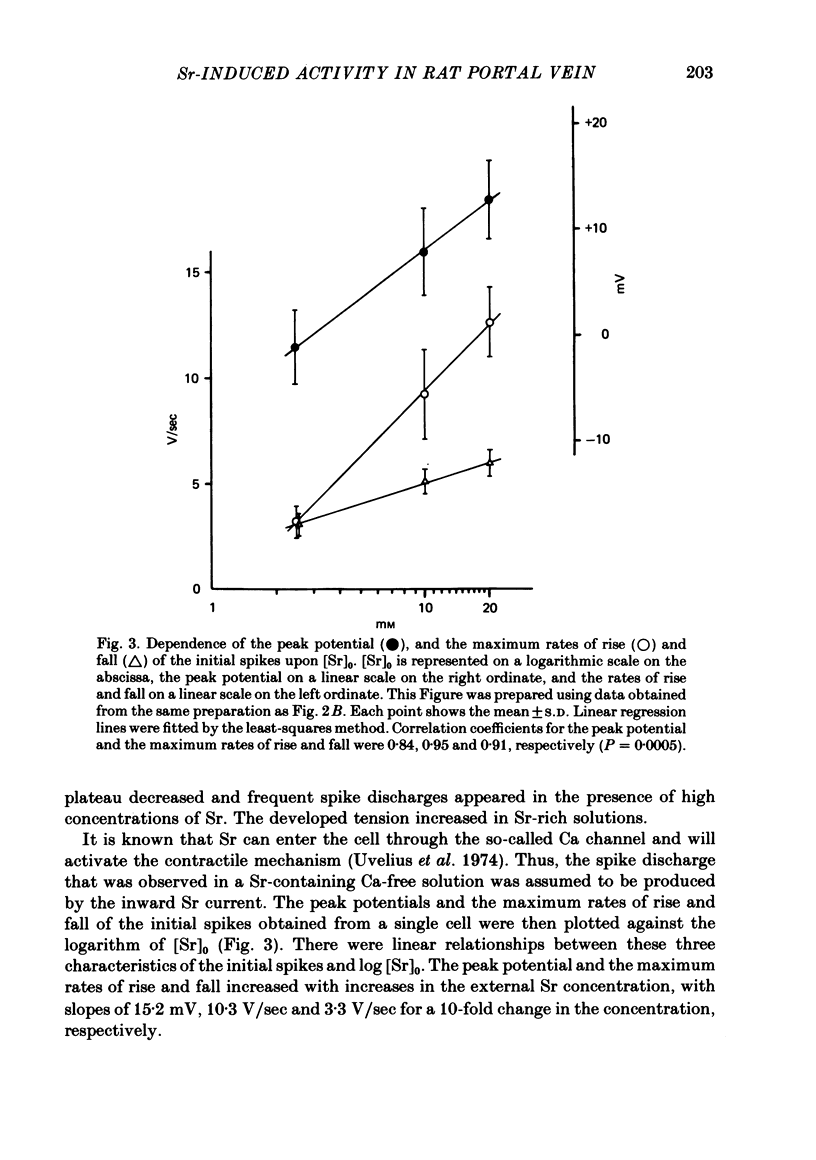
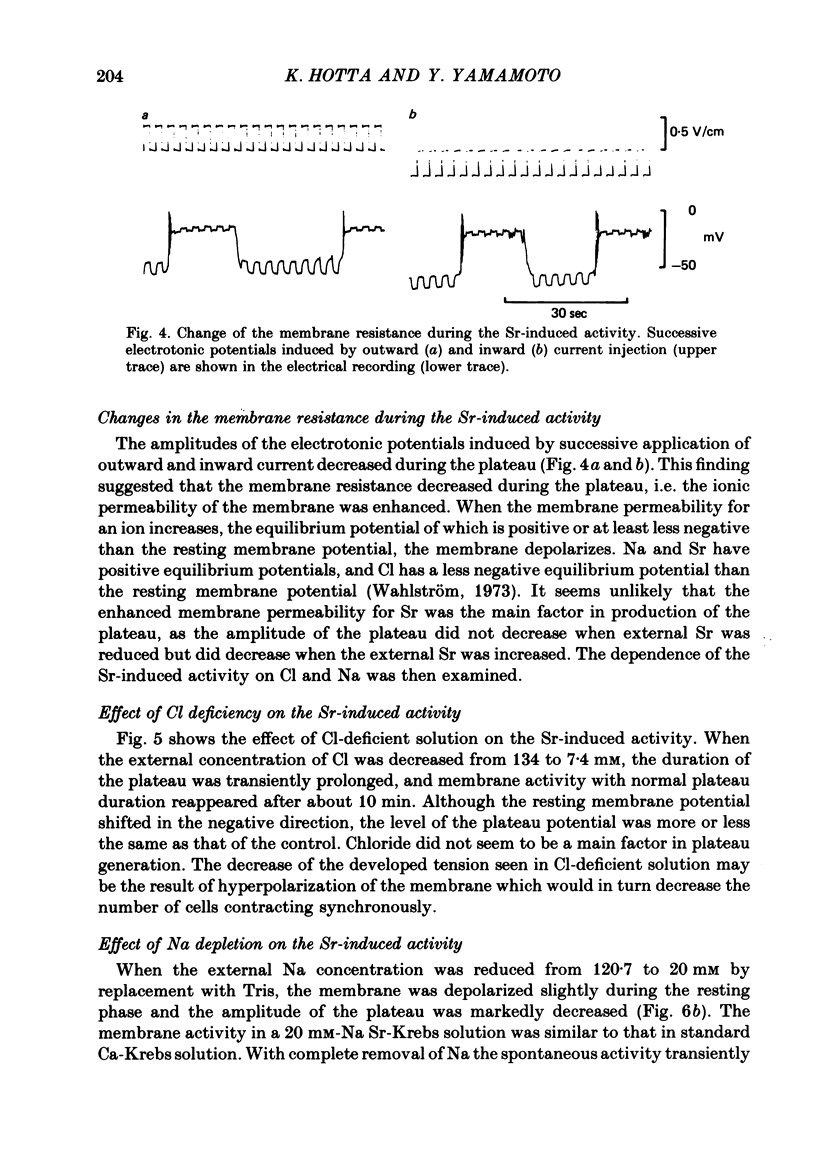
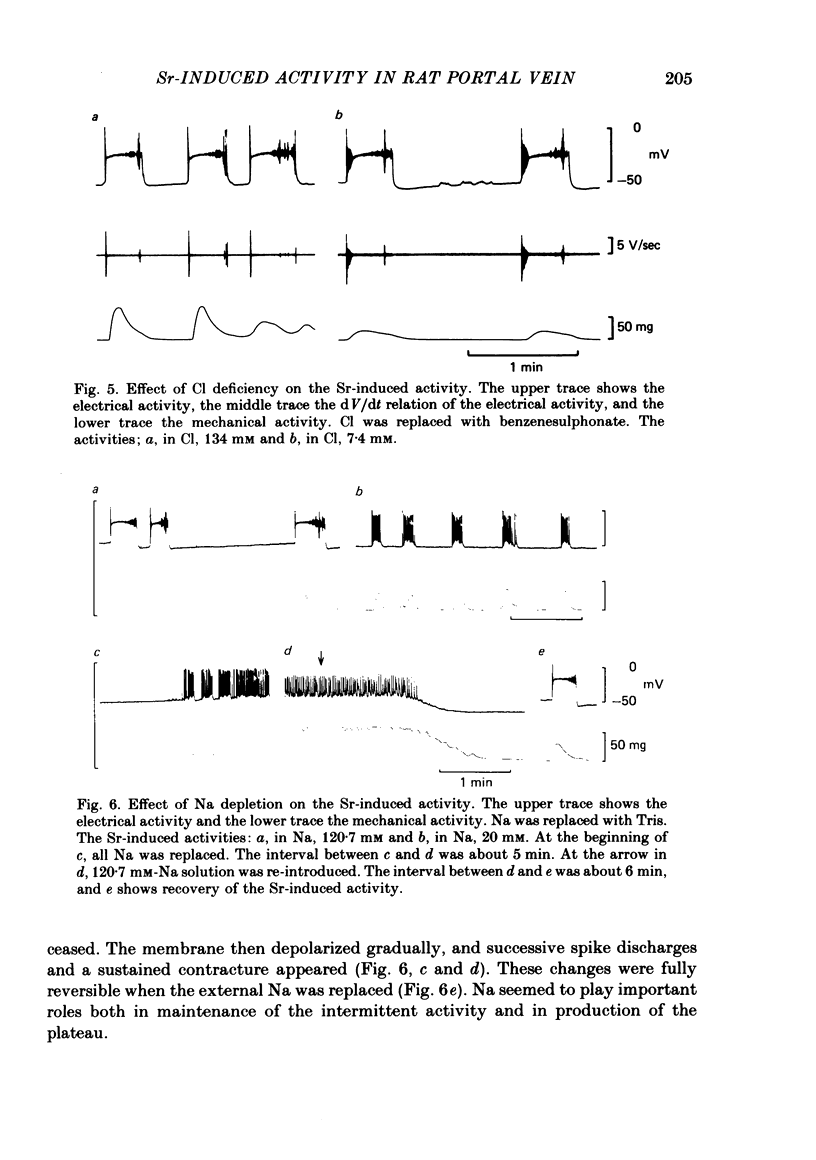
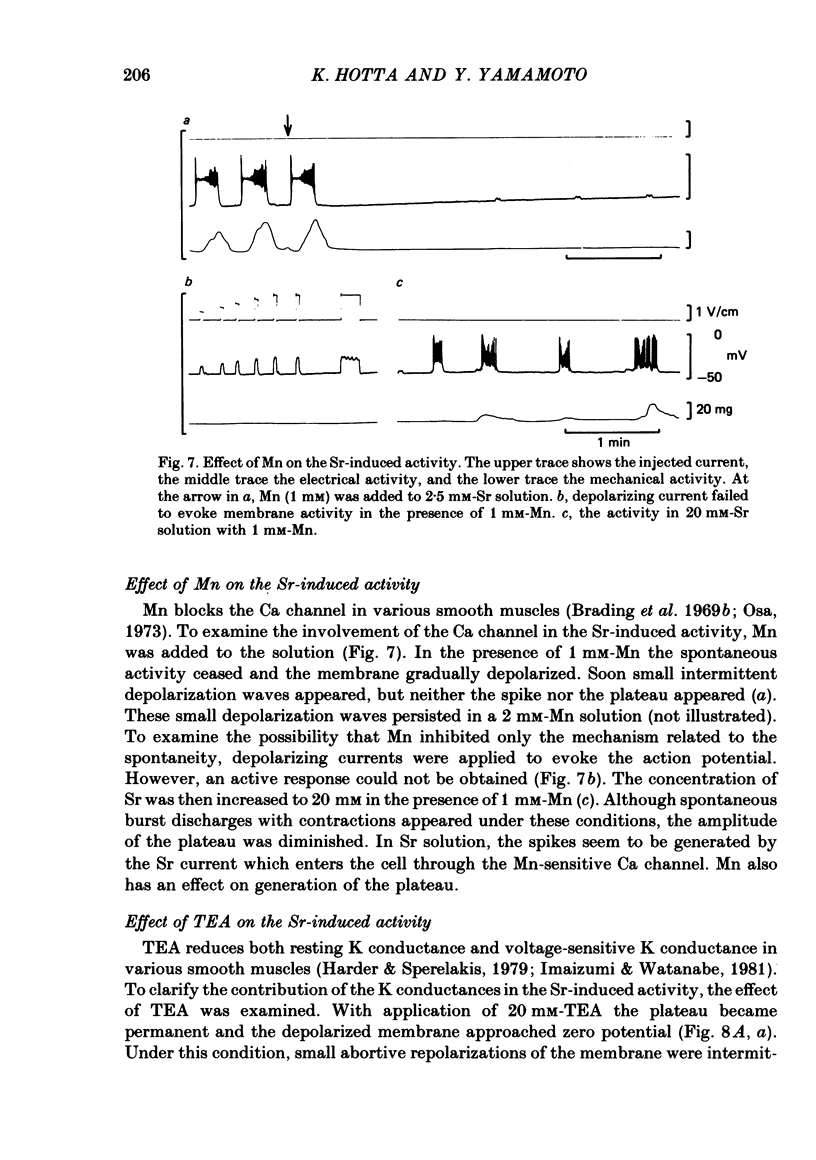
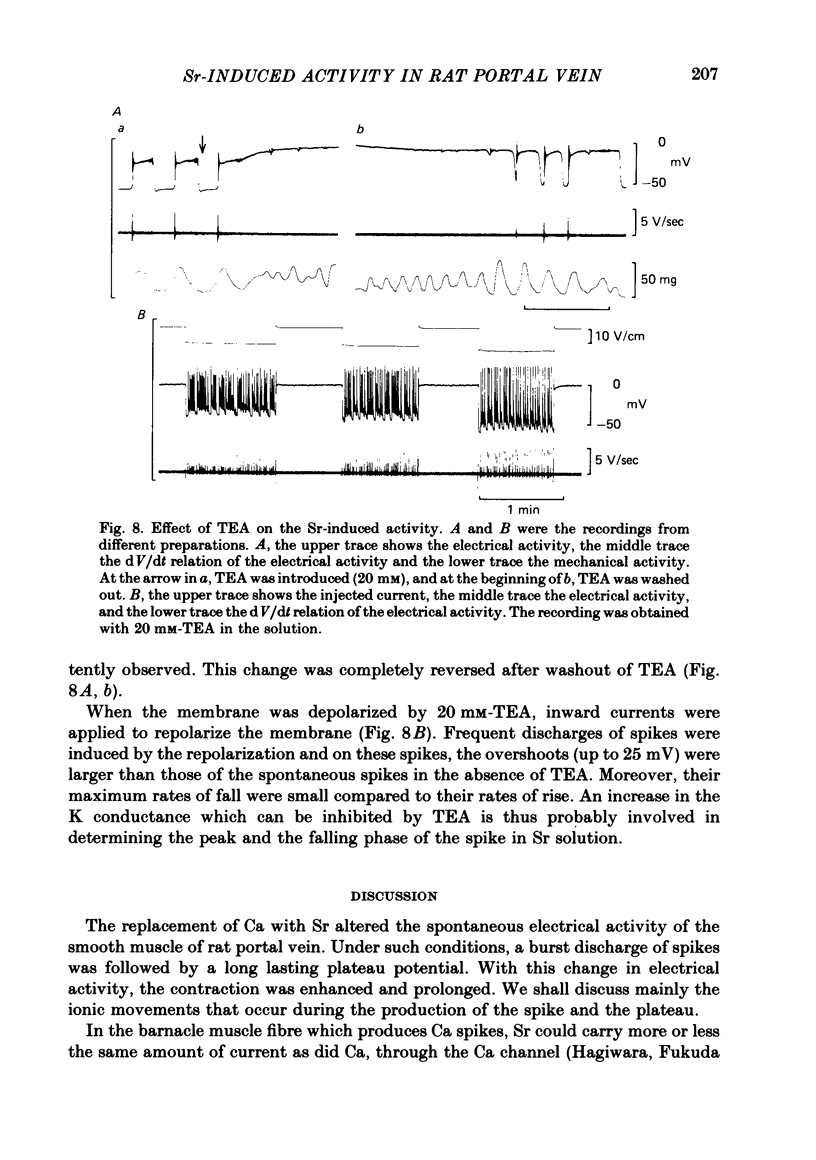
The action of Sr on the smooth muscle of rat portal vein was studied electrophysiologically using micro-electrodes. By replacing Ca with Sr (2.5 mM), the spontaneous membrane activity was altered and spikes were followed by a long lasting plateau potential. The mechanisms which generated the spike and the plateau in the Sr-induced activity were elucidated. As the concentration of Sr was increased, the peak potential and the maximum rates of rise and fall of the initial spike in each discharge increased. The peak potential varied by 15.2 mV with a 10-fold change in [Sr]o. As there was a decrease in the membrane resistance during the plateau, an increase in the permeability of the membrane for Sr, Cl or Na could be responsible for generation of the plateau. The amplitude of the plateau decreased with increase in the concentration of Sr, remained unchanged in a low-Cl solution, but was diminished in a low-Na solution. Mn (1-2 mM) inhibited not only the spike but also the plateau. TEA (20 mM) shifted the plateau potential in a positive direction and the plateau became permanent. When inward currents were applied in the presence of TEA, spikes with large overshoots and small rates of fall were induced. These results indicate that Sr and K conductances of the membrane generate the spike and that slow-inactivating voltage-dependent Na conductance produces the plateau.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe Y., Tomita T. Cable properties of smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):87–100. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brading A., Bülbring E., Tomita T. The effect of sodium and calcium on the action potential of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(3):637–654. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brading A., Bülbring E., Tomita T. The effect of temperature on the membrane conductance of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(3):621–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Effects of Ca removal on the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(1):217–232. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. The effects of Ba2+ and Mn2+ on the smooth muscle of guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(2):137P–139P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. The membrane properties of the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit main pulmonary artery. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):41–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Hermann A. Internal effects of divalent cations on potassium permeability in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:393–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Fukuda J., Eaton D. C. Membrane currents carried by Ca, Sr, and Ba in barnacle muscle fiber during voltage clamp. J Gen Physiol. 1974 May;63(5):564–578. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.5.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder D. R., Sperelakis N. Action potentials induced in guinea pig arterial smooth muscle by tetraethylammonium. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jul;237(1):C75–C80. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.237.1.C75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta Y., Tsukui R. Effect on the guinea-pig taenia coli of the substitution of strontium or barium ions for calcium ions. Nature. 1968 Mar 2;217(5131):867–869. doi: 10.1038/217867b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi Y., Watanabe M. The effect of tetraethylammonium chloride on potassium permeability in the smooth muscle cell membrane of canine trachea. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:33–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inomata H., Kao C. Y. Ionic mechanisms of repolarization in the guinea-pig taenia coli as revealed by the actions of strontium. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):443–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Tomita T. The action potential in the smooth muscle of the guinea pig taenia coli and ureter studied by the double sucrose-gap method. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Feb;55(2):147–162. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.2.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mironneau J., Savineau J. P. Effects of calcium ions on outward membrane currents in rat uterine smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1980 May;302:411–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osa T. The effects of sodium, calcium and manganese on the electrical and mechanical activities of the myometrial smooth muscle of pregnant mice. Jpn J Physiol. 1973 Apr;23(2):113–133. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.23.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser C. L., Kreulen D. L., Weigel R. J., Yau W. Prolonged potentials in gastrointestinal muscles induced by calcium chelation. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jul;233(1):C19–C24. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.233.1.C19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Divalent cations as charge carriers in excitable membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1973;26:1–43. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(73)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuba M. F. The effect of sodium-free and potassium-free solutions, ionic current inhibitors and ouabain on electrophysiological properties of smooth muscle of guinea-pig ureter. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(3):837–851. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uvelius B., Sigurdsson S. B., Johansson B. Strontium and barium as Substitutes for calcium on electrical and mechanical activity in rat portal vein. Blood Vessels. 1974;11(5-6):245–259. doi: 10.1159/000158019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


