Abstract
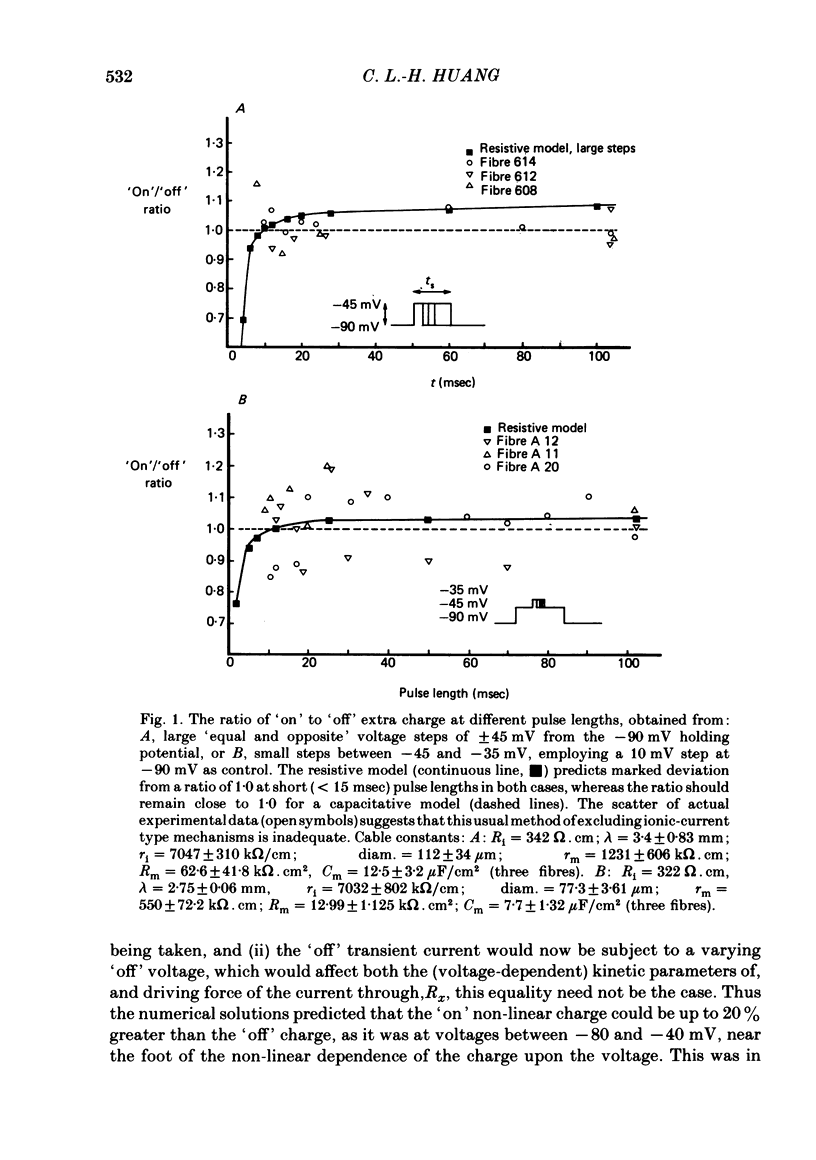
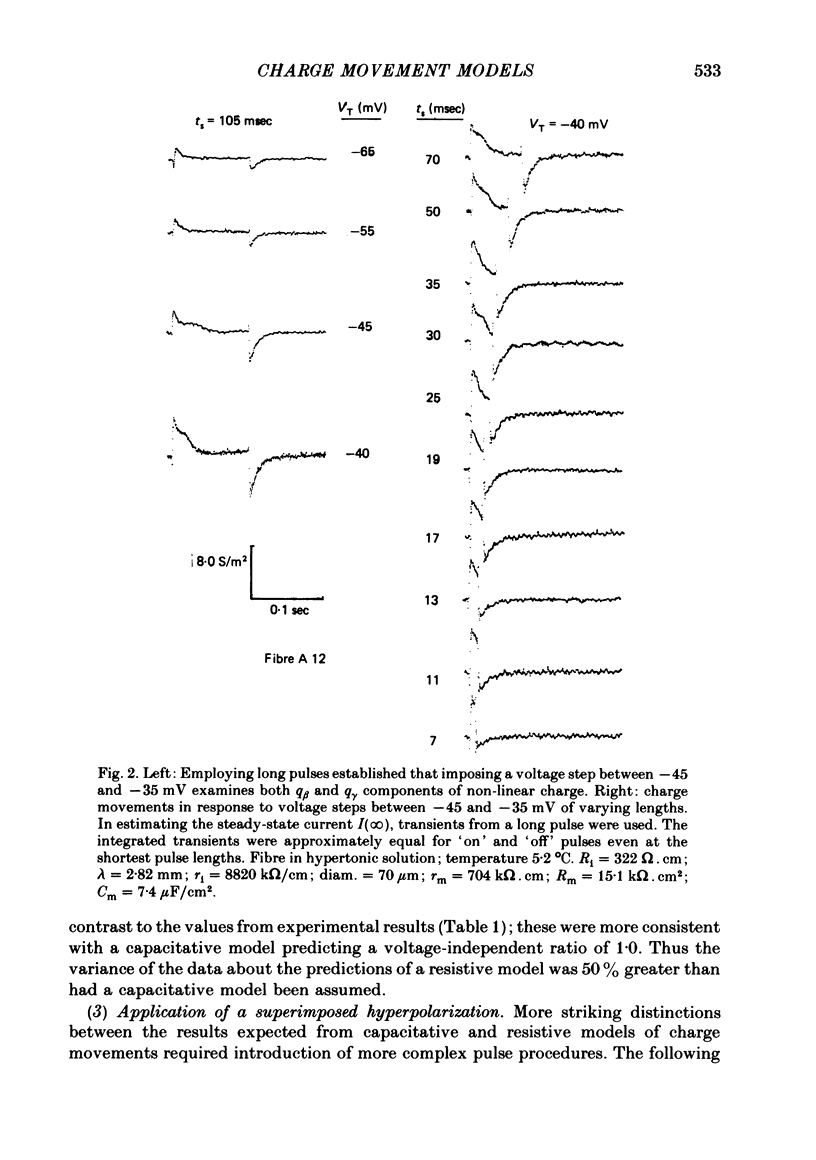
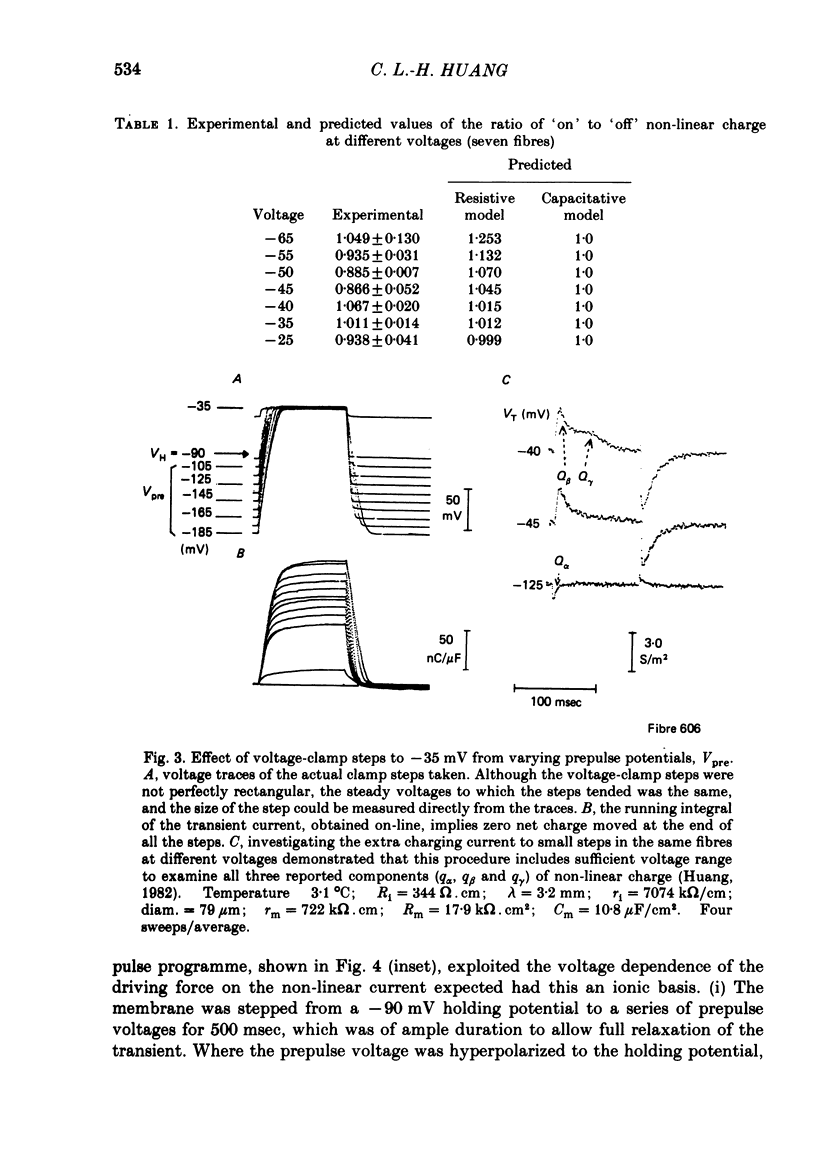
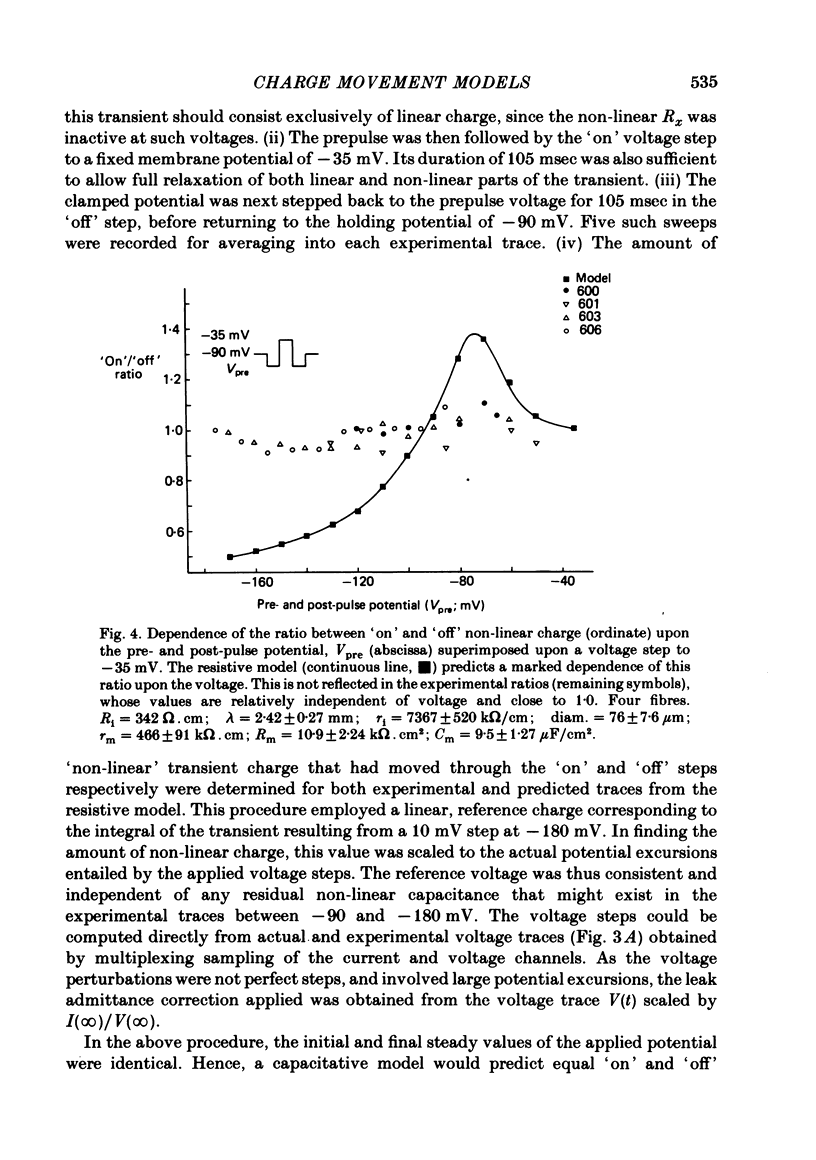
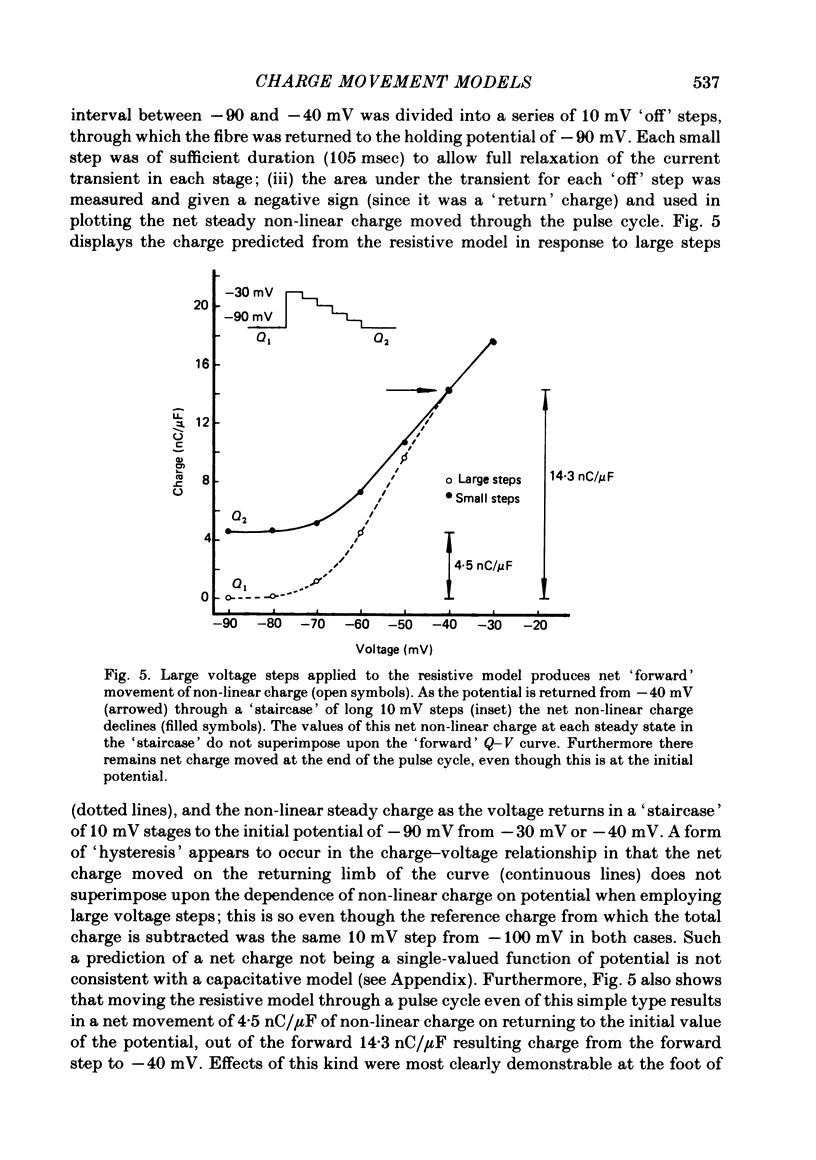
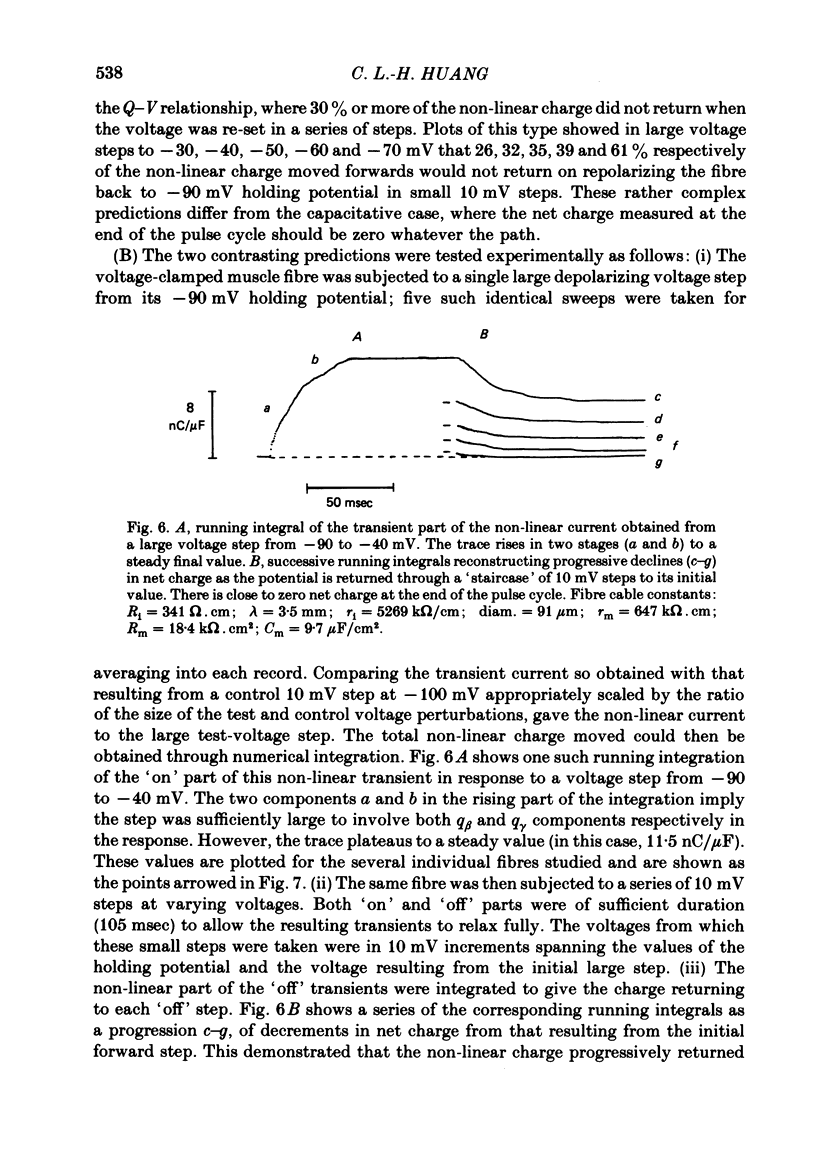
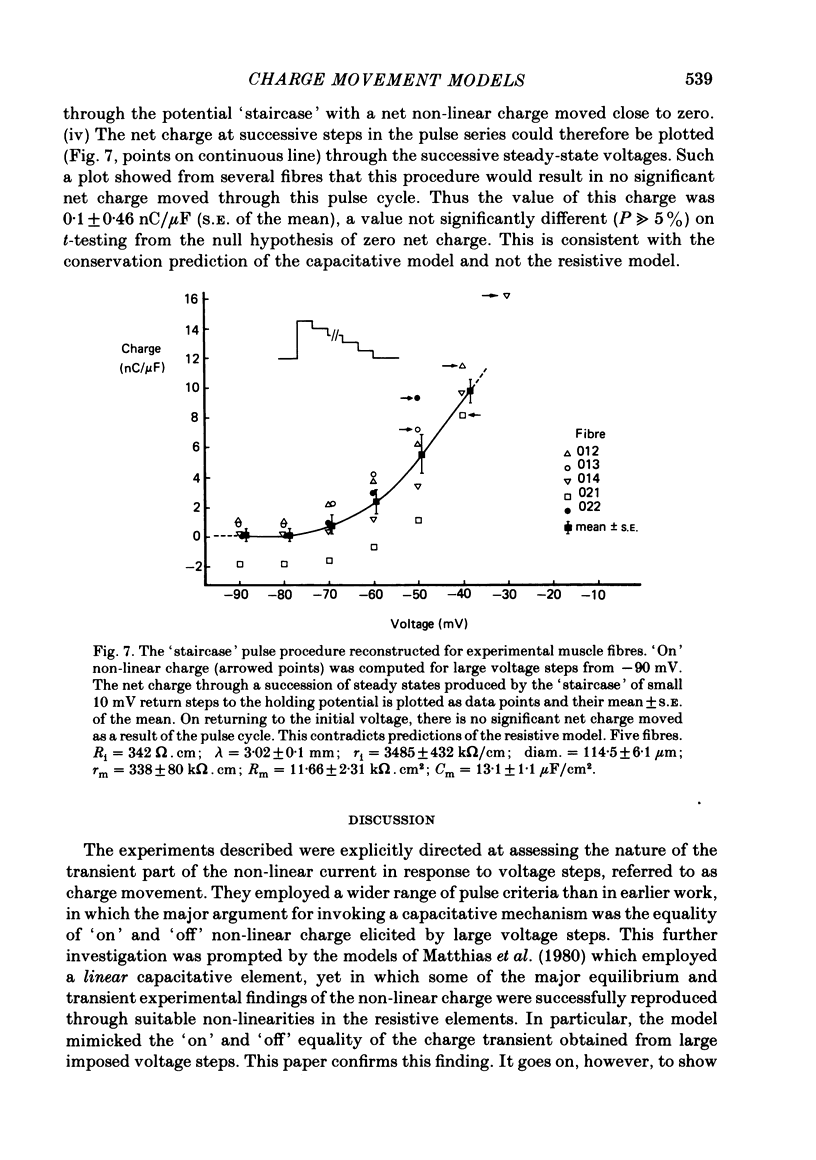
A series of pulse procedures was used to distinguish experimentally between a 'capacitative' (Schneider & Chandler, 1973) and a 'resistive' (Matthias, Levis & Eisenberg, 1980) model of 'charge movements' in skeletal muscle. A general condition describing the conservation of charge in a non-linear capacitor that was used as the basis for the experiments is derived in the Appendix. It was shown that earlier criteria concerning equality of 'on' and 'off' charge in response to large steps are insufficient to exclude resistive models. However, the capacitative, but not the resistive model successfully explained results bearing on charge conservation assessed through pulse procedures involving: (i) small, 10 mV voltage steps from a series of prepulse voltages, (ii) voltage steps to a fixed potential from a series of hyperpolarized voltages, (iii) pulse sequences incorporating a 'staircase' of voltage steps. It is concluded that the earlier use of 'on' and 'off' equality in response to large voltage steps is insufficient to exclude a resistive basis for the non-linear transient. However pulse procedures explicitly designed to distinguish the two models give results consistent with a capacitative model for the non-linear charge and at variance with a resistive one.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Charge movement in the membrane of striated muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):339–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Peres A. Charge movement and membrane capacity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:83–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Rakowski R. F. Reactivation of membrane charge movement and delayed potassium conductance in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:533–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Currents related to movement of the gating particles of the sodium channels. Nature. 1973 Apr 13;242(5398):459–461. doi: 10.1038/242459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. A non-linear voltage dependent charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):245–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duane S., Huang C. L. A quantitative description of the voltage-dependent capacitance in frog skeletal muscle in terms of equilibrium statistical mechanics. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Apr 22;215(1198):75–94. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. The effect of diameter on the electrical constants of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):105–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowicz P., Schneider M. F. Membrane charge moved at contraction thresholds in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:595–633. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Dielectric components of charge movements in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1981;313:187–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Membrane capacitance in hyperpolarized muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981;313:207–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Pharmacological separation of charge movement components in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:375–387. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T., Levis R. A., Eisenberg R. S. Electrical models of excitation-contraction coupling and charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Jul;76(1):1–31. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


