Abstract
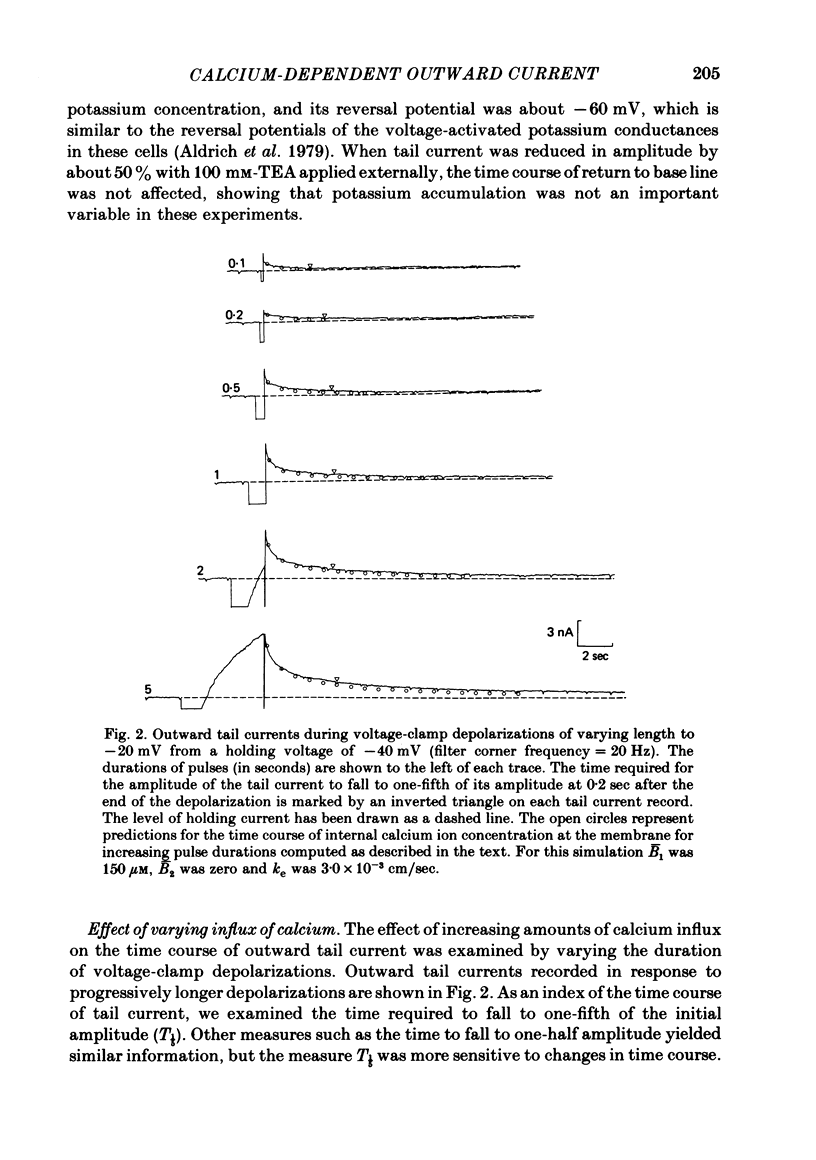
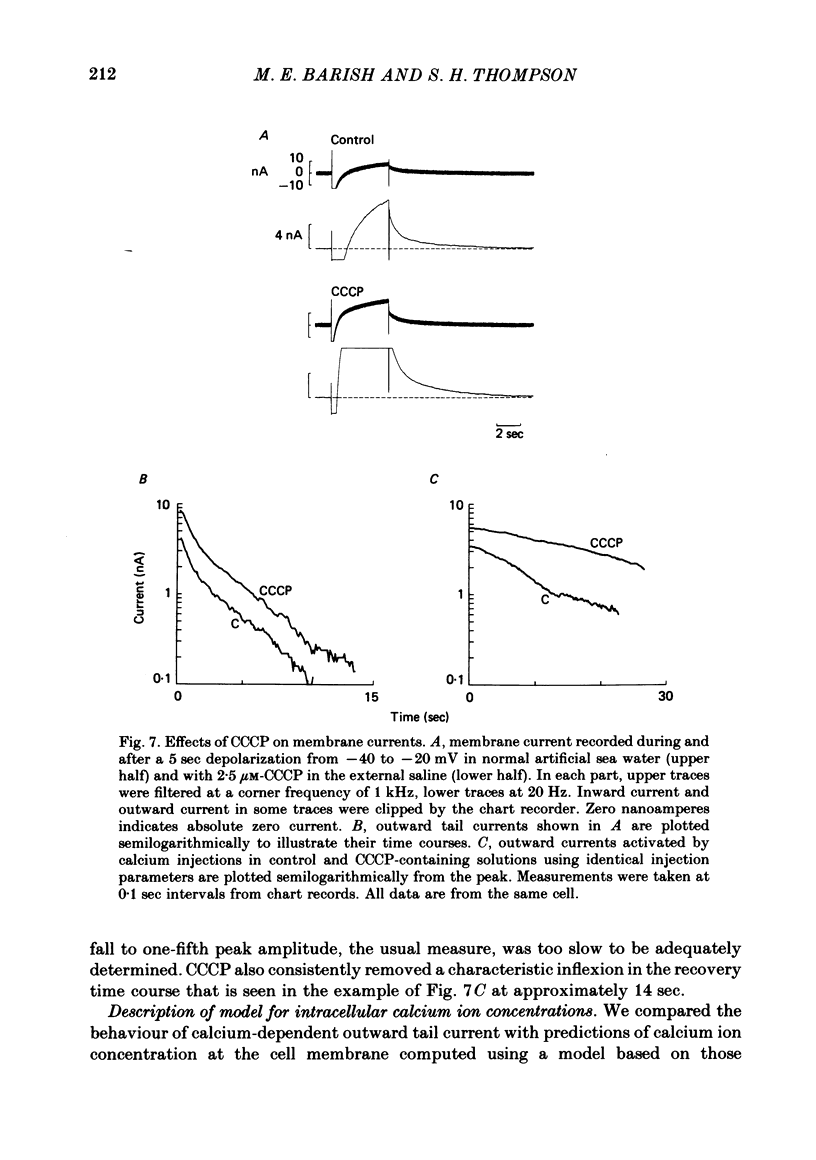
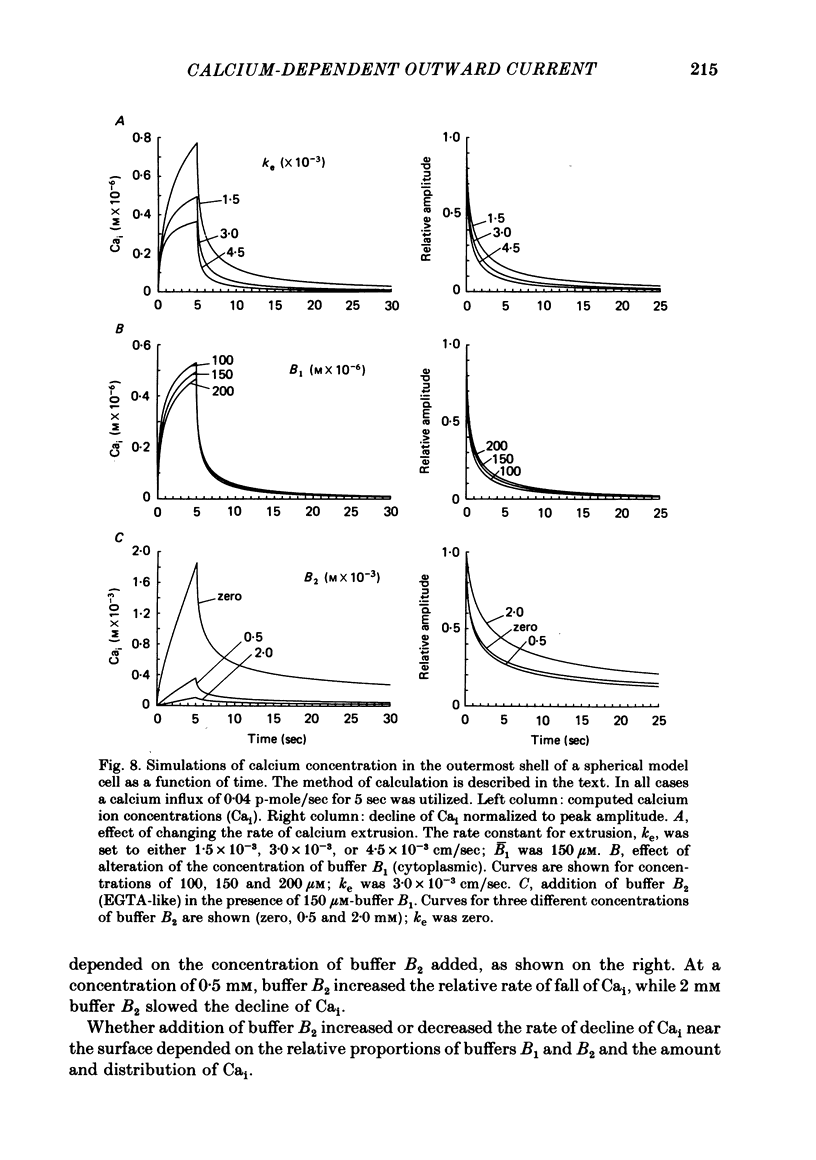
Calcium entry into molluscan neurones during depolarizing voltage-clamp steps activates an outward current which on repolarization decays over periods of more than 30 sec. This slowly decaying tail current was used to study the relation between calcium buffering in cytoplasm and the decline of a calcium-activated membrane process. Calcium-dependent outward current was also studied after injection of calcium into the cytoplasm. The time course of the fall of outward tail current was much less sensitive than tail current amplitude to the amount of calcium entry. Increasing bath temperature from 5 to 15 degrees C decreased the rate of fall of outward tail current activated by calcium entry. In contrast, outward current activated by calcium injection declined more rapidly at higher temperatures. Injection of sufficient EGTA to give maximum depression of outward current during depolarizations reduced the amplitude of outward tail current by at most 50%. After EGTA injection outward tail current declined more rapidly immediately following repolarization, but returned to base line at about the same time as the control. After injection of EGTA, outward current activated by calcium injection was reduced or completely blocked, and returned to base line more rapidly. Application of the mitochondrial uncoupler carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone (CCCP) did not alter the decay time course of outward tail current, but markedly prolonged the decline of outward current activated by calcium injection. The slow kinetics of outward tail current were compared to predictions of the concentration of calcium ions at the outermost surface of a spherical model cell following calcium influx. We conclude that after depolarization and calcium entry, the diffusion and binding of free calcium to cytoplasmic buffers plays a key role in determining the rate of fall of outward tail current. Further, different mechanisms influence the decline of calcium-dependent outward current following injection of calcium into the cytosol.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Smith S. J., Thompson S. H. Ionic currents in molluscan soma. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1980;3:141–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.03.030180.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Constanti A., Brown D. A., Clark R. B. Intracellular Ca2+ activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):746–749. doi: 10.1038/296746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed Z., Connor J. A. Intracellular pH changes induced by calcium influx during electrical activity in molluscan neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Apr;75(4):403–426. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.4.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed Z., Connor J. A. Measurement of calcium influx under voltage clamp in molluscan neurones using the metallochromic dye arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:61–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Lee K. S., Brown A. M. The calcium current of Helix neuron. J Gen Physiol. 1978 May;71(5):509–531. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.5.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich R. W., Jr, Getting P. A., Thompson S. H. Inactivation of delayed outward current in molluscan neurone somata. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:507–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Leefmans F. J., Rink T. J., Tsien R. Y. Free calcium ions in neurones of Helix aspersa measured with ion-selective micro-electrodes. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:531–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Potassium permeability activated by intracellular calcium ion concentration in the pancreatic beta-cell. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:575–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Schlaepfer W. W. Uptake and binding of calcium by axoplasm isolated from giant axons of Loligo and Myxicola. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:103–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Schlaepfer W. Proceedings: Calcium uptake by axoplasm extruded from giant axons of Loligo. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(1):37P–38P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:177–223. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Levitan H. Mitochondrial uncoupling agents. Effects on membrane permeability of molluscan neurons. J Membr Biol. 1975;25(3-4):361–380. doi: 10.1007/BF01868584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshaw S. E. Dye injection and electrophysiological mapping of giant neurons in the brain of Archidoris. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Mar 16;192(1109):393–419. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Ratzlaff R. W., Schweitzer E. S. Control of intracellular calcium in presynaptic nerve terminals. Fed Proc. 1980 Aug;39(10):2790–2795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Eckert R., Tillotson D. Calcium-mediated inactivation of calcium current in Paramecium. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:193–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr Calcium buffering in squid axons. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:363–392. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Hagiwara S. Calcium currents in internally perfused nerve cell bodies of Limnea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:503–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A. Calcium current in molluscan neurones: measurement under conditions which maximize its visibility. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:41–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A. Time course separation of two inward currents in molluscan neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 7;119(2):487–492. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90330-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipolo R., Requena J., Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J., Scarpa A., Tiffert T. Ionized calcium concentrations in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Apr;67(4):433–467. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Tillotson D. Potassium activation associated with intraneuronal free calcium. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):437–439. doi: 10.1126/science.644308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engasser J. M., Horvath C. Buffer-facilitated proton transport. pH profile of bound enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 17;358(1):178–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gola M. Neurones à ondes-salves des mollusques. Variations cycliques lentes des conductances ioniques. Pflugers Arch. 1974;352(1):17–36. doi: 10.1007/BF01061947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Hermann A. Internal effects of divalent cations on potassium permeability in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:393–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Changes in the intracellular concentration of free calcium ions in a pace-maker neurone, measured with the metallochromic indicator dye arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:357–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Intracellular calcium accumulation during depolarization in a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:259–285. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Potassium conductance and internal calcium accumulation in a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:287–313. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Effects of the intracellular Ca ion concentration upon the excitability of the muscle fiber membrane of a barnacle. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):807–818. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harafuji H., Ogawa Y. Re-examination of the apparent binding constant of ethylene glycol bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid with calcium around neutral pH. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1305–1312. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart M. Identification and function of intracellular calcium stores in axons and cell bodies of neurons. Fed Proc. 1980 Aug;39(10):2783–2789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmeier G., Lux H. D. The time courses of intracellular free calcium and related electrical effects after injection of CaCl2 into neurons of the snail, Helix pomatia. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Sep;391(3):242–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00596178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D. Voltage, temperature and ionic dependence of the slow outward current in Aplysia burst-firing neurones. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:145–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A. Effects of calcium and calcium-chelating agents on the inward and outward current in the membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):569–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Neher E., Marty A. Single channel activity associated with the calcium dependent outward current in Helix pomatia. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Mar;389(3):293–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00584792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Membrane potential oscillations in molluscan "burster" neurones. J Exp Biol. 1979 Aug;81:93–112. doi: 10.1242/jeb.81.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Thomas R. C. Effect of measured calcium chloride injections on the membrane potential and internal pH of snail neurones. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:111–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirolli M., Talbott S. R. The geometrical factors determining the electrotonic properties of a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(1):19–34. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J., Requena J. Calcium measurement in the periphery of an axon. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Sep;74(3):393–413. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallotta B. S., Magleby K. L., Barrett J. N. Single channel recordings of Ca2+-activated K+ currents in rat muscle cell culture. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):471–474. doi: 10.1038/293471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. F., Posey V. A. Calcium and adenosine triphosphate binding to renal membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jan;55(1):89–103. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Tsien R. W. Calcium-activated transient outward current in calf cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:485–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Zucker R. S. Aequorin response facilitation and intracellular calcium accumulation in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:167–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B. Ca channel inactivation by intracellular Ca injection into Helix neurones. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):158–159. doi: 10.1038/293158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D., Gorman A. L. Non-uniform Ca2+ buffer distribution in a nerve cell body. Nature. 1980 Aug 21;286(5775):816–817. doi: 10.1038/286816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D. Inactivation of Ca conductance dependent on entry of Ca ions in molluscan neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1497–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASINGTON F. D., MURPHY J. V. Ca ion uptake by rat kidney mitochondria and its dependence on respiration and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2670–2677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolum J. C., Gorman A. L. Time dependence of the calcium-activated potassium current. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):297–302. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84729-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


