Abstract
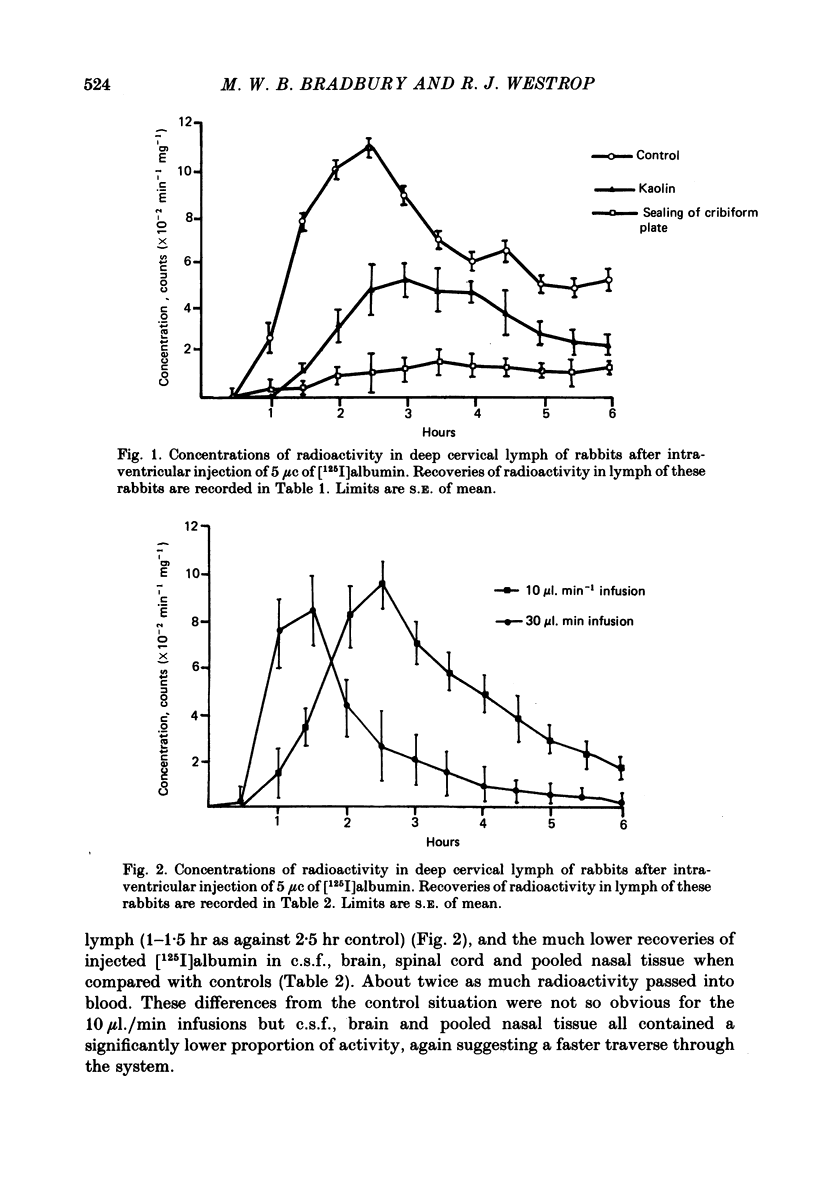
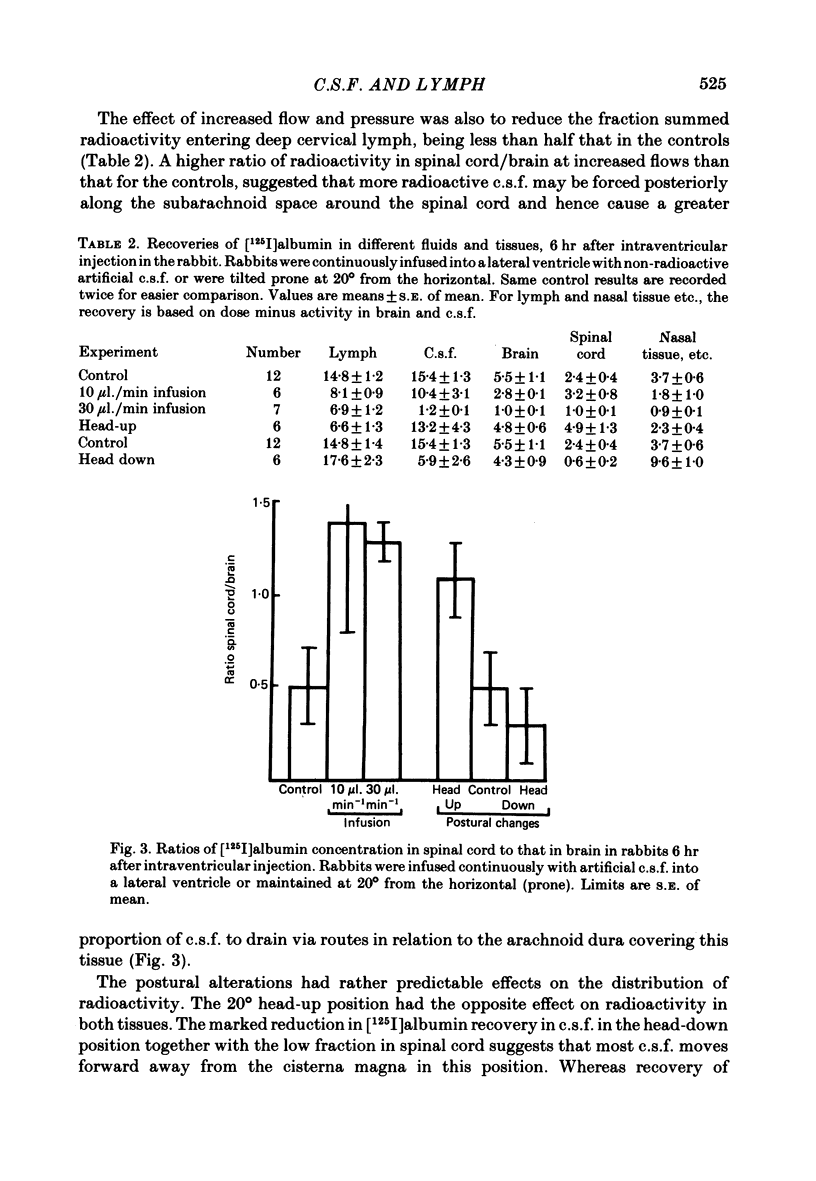
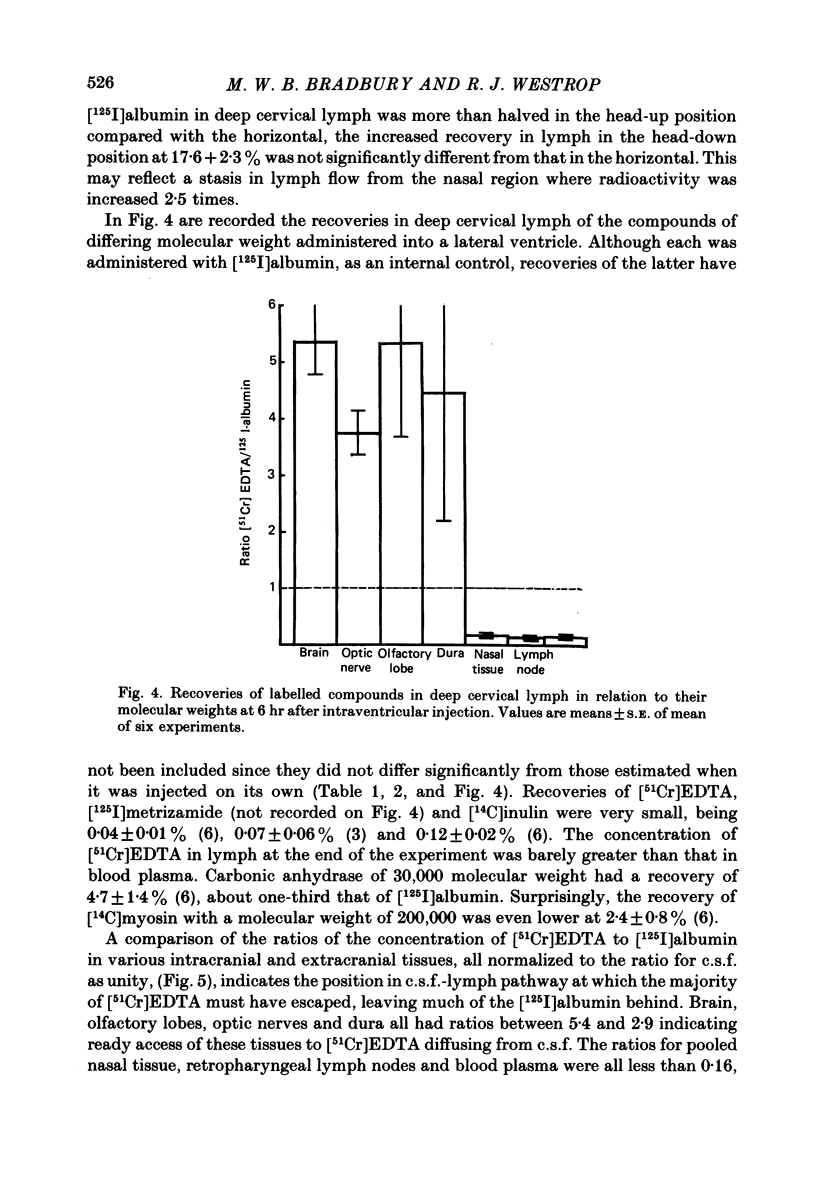
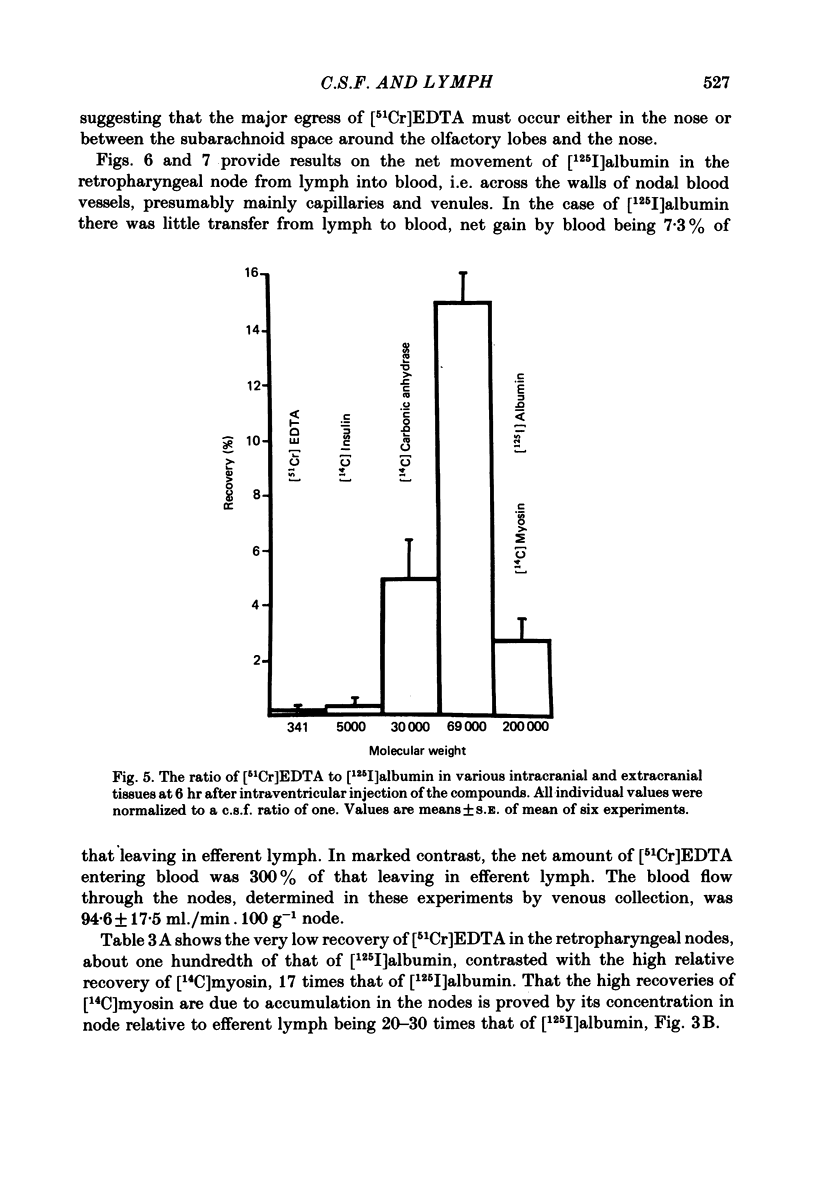
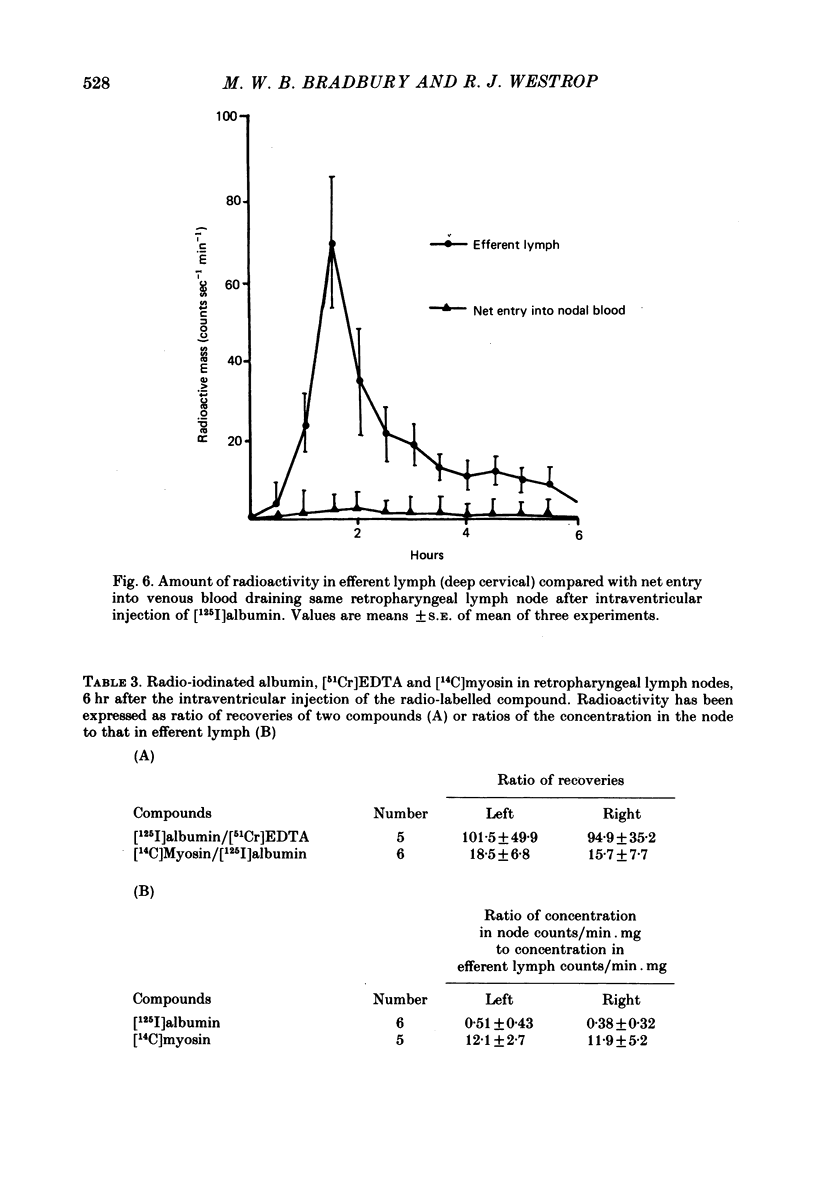
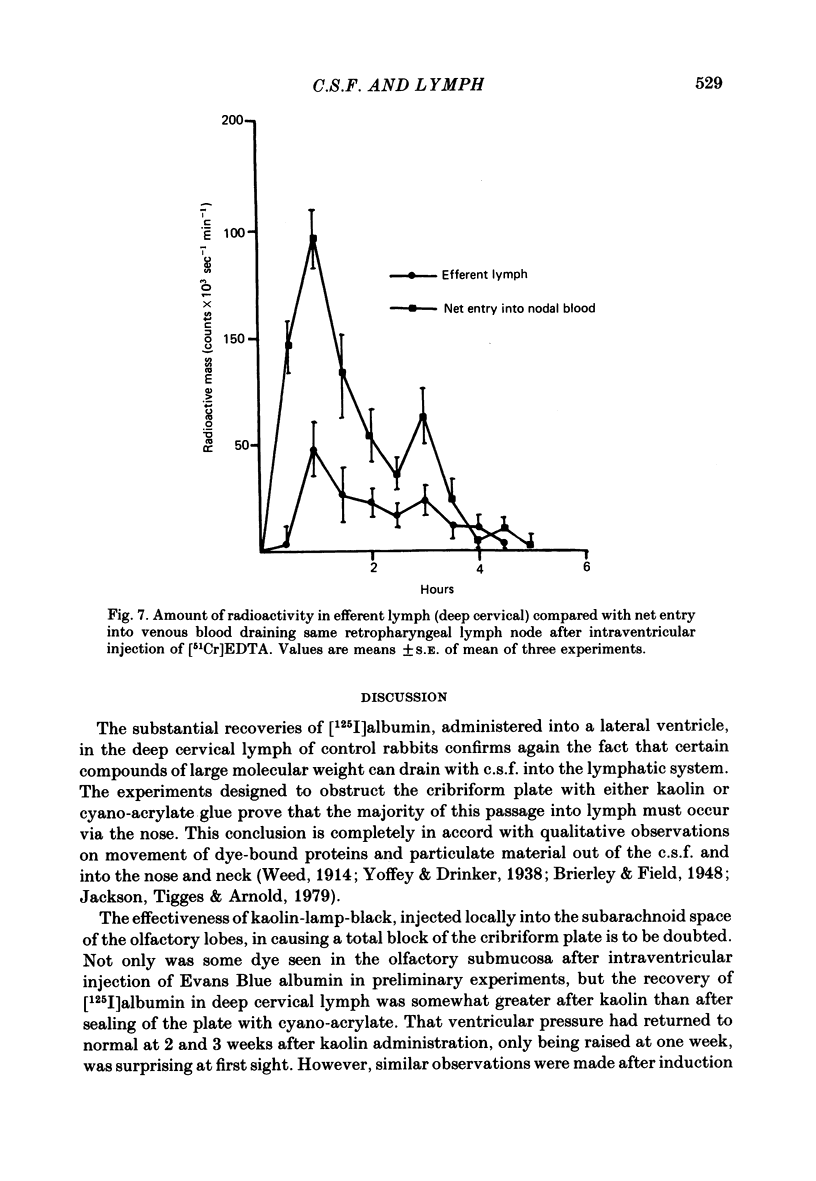
Experiments have been made to determine the main route by which radio-iodinated albumin reaches deep cervical lymph from cerebrospinal fluid (c.s.f.) in the anaesthetized rabbit. Other factors, influencing drainage through this pathway, have been investigated. After single injection of [125I]albumin into a lateral ventricle of control rabbits, a mean of 14.8% of the radioactivity lost from brain-c.s.f. was recovered during 6 hr in the lymph of the cannulated jugular trunk of one side. Injection of kaolin into the olfactory fossa or sealing of the cribriform plate with cyanoacrylate glue reduced the recovery of [125I]albumin to 3.3% and 1.9% respectively at 2-3 weeks after the procedure designed to block the cribriform plate. This confirms the traditional view that the major connexions between c.s.f. and deep cervical lymph is via prolongations of subarachnoid space around the olfactory nerves, leading into the interstitial spaces of the nasal submucosa. The dense lymphatic plexus in this tissue is known to drain into the retropharyngeal (deep cervical) lymph nodes. Constant infusion of artificial c.s.f. into a lateral ventricle at 10 microliters/min or 30 microliters/min, in order to approximately double or quadruple flow through the system respectively, decreased the recovery of intraventricular [125I]albumin to 8.1% and 6.9% respectively. It also appeared that the increased c.s.f. pressures induced forced relatively more radioactivity from inside the skull into the c.s.f. spaces of the spinal cord. Maintaining the rabbit prone but at 20 degrees from the horizontal caused recoveries of [125I]albumin in lymph of 17.6% (head-up position and 6.6% (head-down). The amounts of radioactivity in nose and spinal cord markedly increased and decreased respectively in the head-down position. They changed in the opposite directions in the head-up position. The amounts of [51Cr]EDTA, [125I]metrizamide and [14C]inulin in deep cervical lymph were negligible after intraventricular injection. Estimations of the ratio of [51Cr]EDTA/[125I]albumin in various tissues on the pathway into lymph, together with measurements of arterio-venous fluxes across the retropharyngeal nodes, indicate that [51Cr]EDTA passed from c.s.f./lymph into blood within both the nose and the lymph nodes.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradbury M. W., Cole D. F. The role of the lymphatic system in drainage of cerebrospinal fluid and aqueous humour. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:353–365. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W., Stulcová B. Efflux mechanism contributing to the stability of the potassium concentration in cerebrospinal fluid. J Physiol. 1970 Jun;208(2):415–430. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley J. B., Field E. J. The connexions of the spinal sub-arachnoid space with the lymphatic system. J Anat. 1948 Jul;82(Pt 3):153–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauna N., Hinderer K. H. Fine structure of blood vessels of the human nasal respiratory mucosa. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1969 Aug;78(4):865–879. doi: 10.1177/000348946907800418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davson H., Hollingsworth G., Segal M. B. The mechanism of drainage of the cerebrospinal fluid. Brain. 1970;93(4):665–678. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.4.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon W. E., Halliburton W. D. The cerebro-spinal fluid: IV. Circulation. J Physiol. 1916 Feb 29;50(3):198–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1916.sp001749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entrup R., Paiewonsky D., Hughes M., Jue J., Bittar D., Wégria R. Effect of posture on formation and evacuation of lymph. Am J Physiol. 1966 May;210(5):943–949. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.5.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDY H. F. Circulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the spinal region of the cat. J Physiol. 1962 Oct;163:457–465. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochwald G. M., Lux W. E., Jr, Sahar A., Ransohoff J. Experimental hydrocephalus. Changes in cerebrospinal fluid dynamics as a function of time. Arch Neurol. 1972 Feb;26(2):120–129. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490080038003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. T., Tigges J., Arnold W. Subarachnoid space of the CNS, nasal mucosa, and lymphatic system. Arch Otolaryngol. 1979 Apr;105(4):180–184. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1979.00790160014003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYERSON H. S., PATTERSON R. M., McKEE A., LEBRIE S. J., MAYERSON P. Permeability of lymphatic vessels. Am J Physiol. 1962 Jul;203:98–106. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.1.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J. D., Butler A. B., Rosenthal J. E., Maffeo C. J., Johnson R. N., Bass N. H. Regulation of intracranial pressure in rat, dog, and man. Ann Neurol. 1978 Feb;3(2):156–165. doi: 10.1002/ana.410030212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Duma R. J., Nelson E. C., Moretta F. L. Experimental naegleria meningoencephalitis in mice. Penetration of the olfactory mucosal epithelium by Naegleria and pathologic changes produced: a light and electron microscope study. Lab Invest. 1973 Aug;29(2):121–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComb J. G., Davson H., Hyman S., Weiss M. H. Cerebrospinal fluid drainage as influenced by ventricular pressure in the rabbit. J Neurosurg. 1982 Jun;56(6):790–797. doi: 10.3171/jns.1982.56.6.0790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quin J. W., Shannon A. D. The influence of the lymph node on the protein concentration of efferent lymph leaving the node. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(2):307–321. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMMONDS W. J. The absorption of blood from the cerebrospinal fluid in animals. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1952 Jun;30(3):261–270. doi: 10.1038/icb.1952.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELCH K., POLLAY M. The spinal arachnoid villi of the monkeys Cercopithecus aethiops sabaeus and Macaca irus. Anat Rec. 1963 Jan;145:43–48. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091450107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoffey J. M., Drinker C. K. Some observations on the lymphatics of the nasal mucous membrane in the cat and monkey. J Anat. 1939 Oct;74(Pt 1):45–52.3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B., Röpke C., Westergaard E. Ultrastructure and permeability of lymph node microvasculature in the mouse. Cell Tissue Res. 1976 May 26;168(4):507–525. doi: 10.1007/BF00216000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


