Abstract
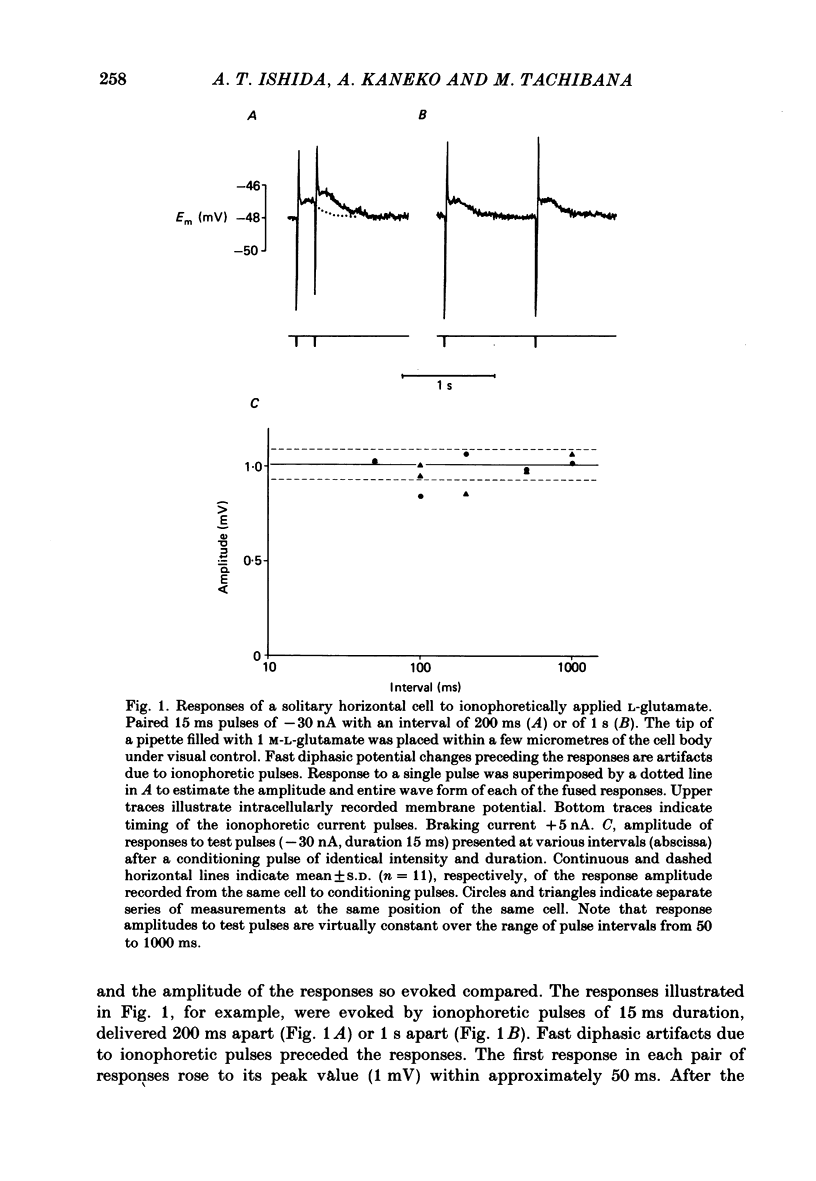
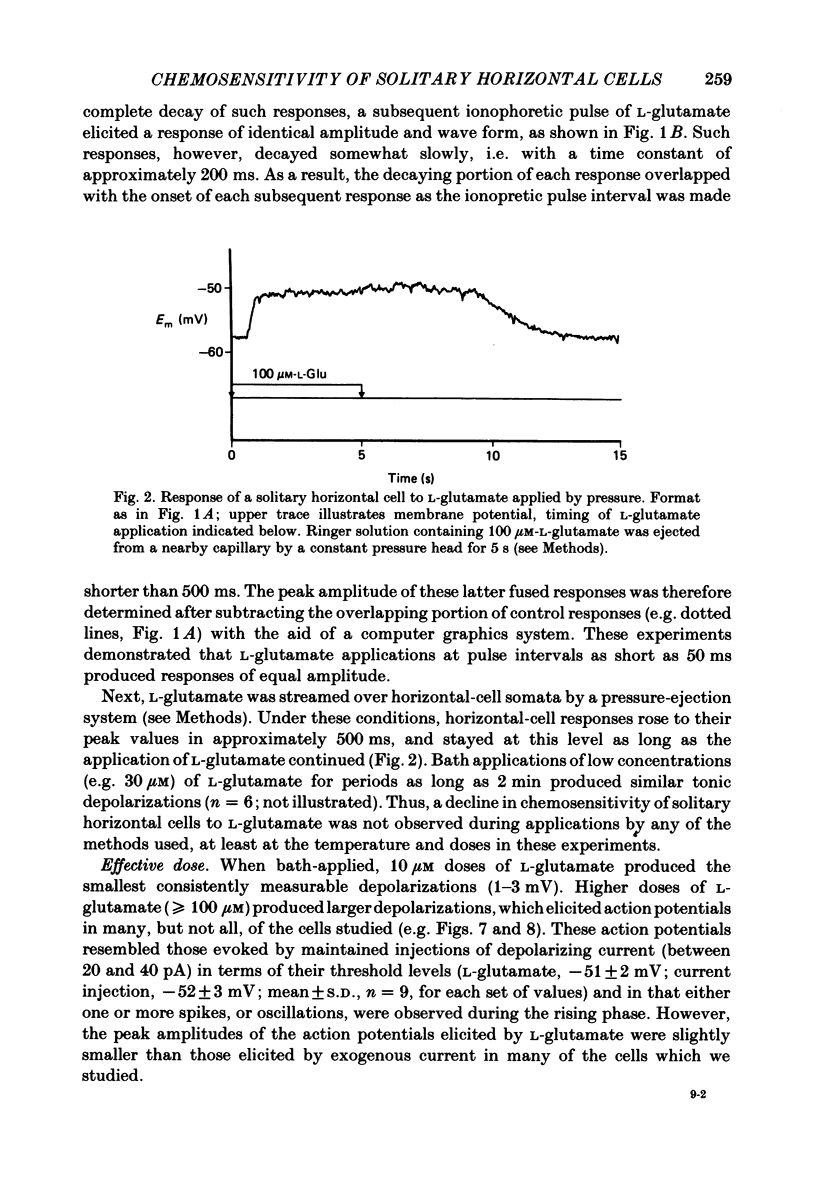
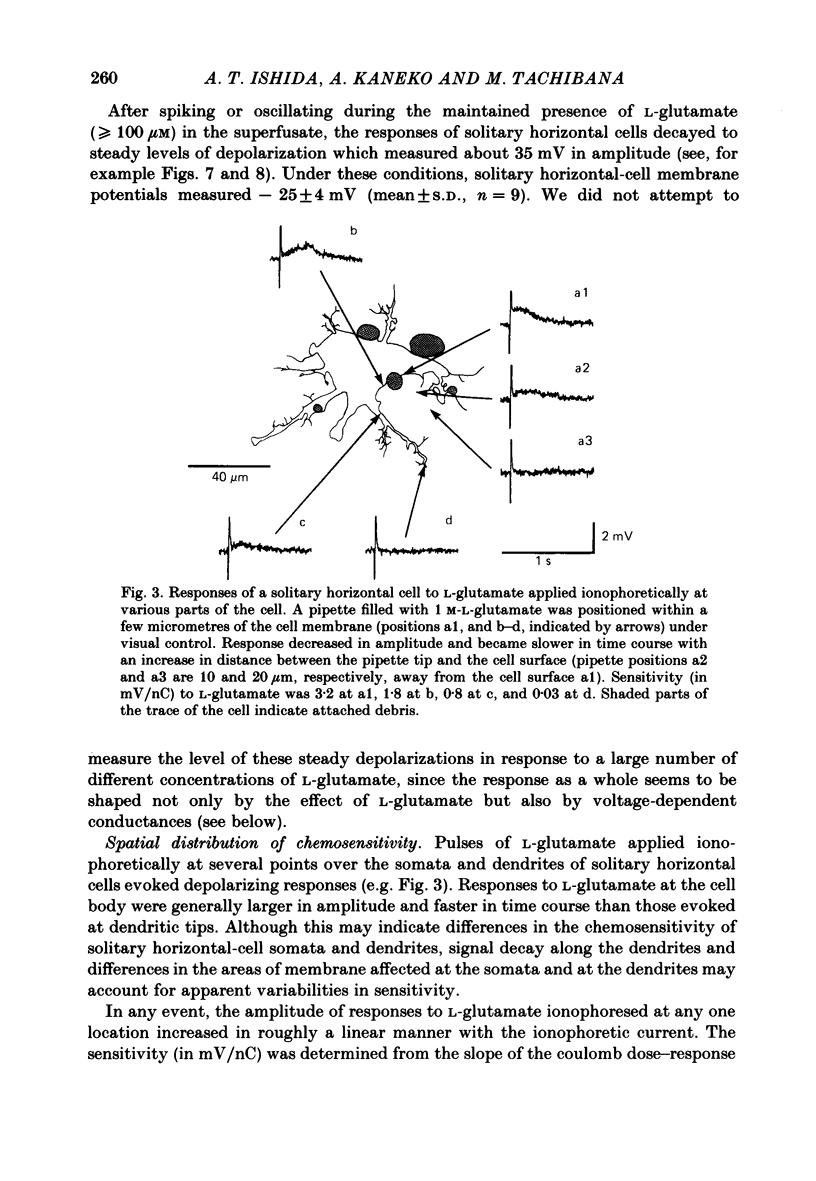
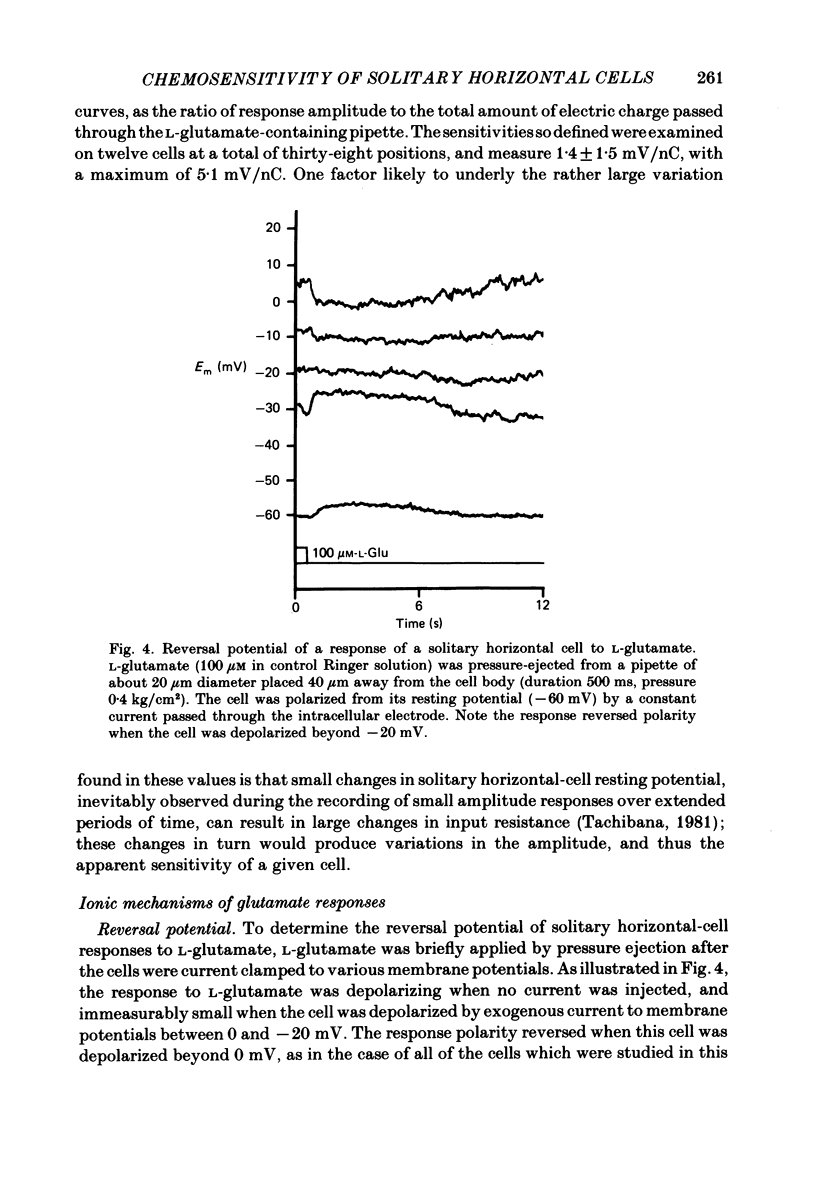
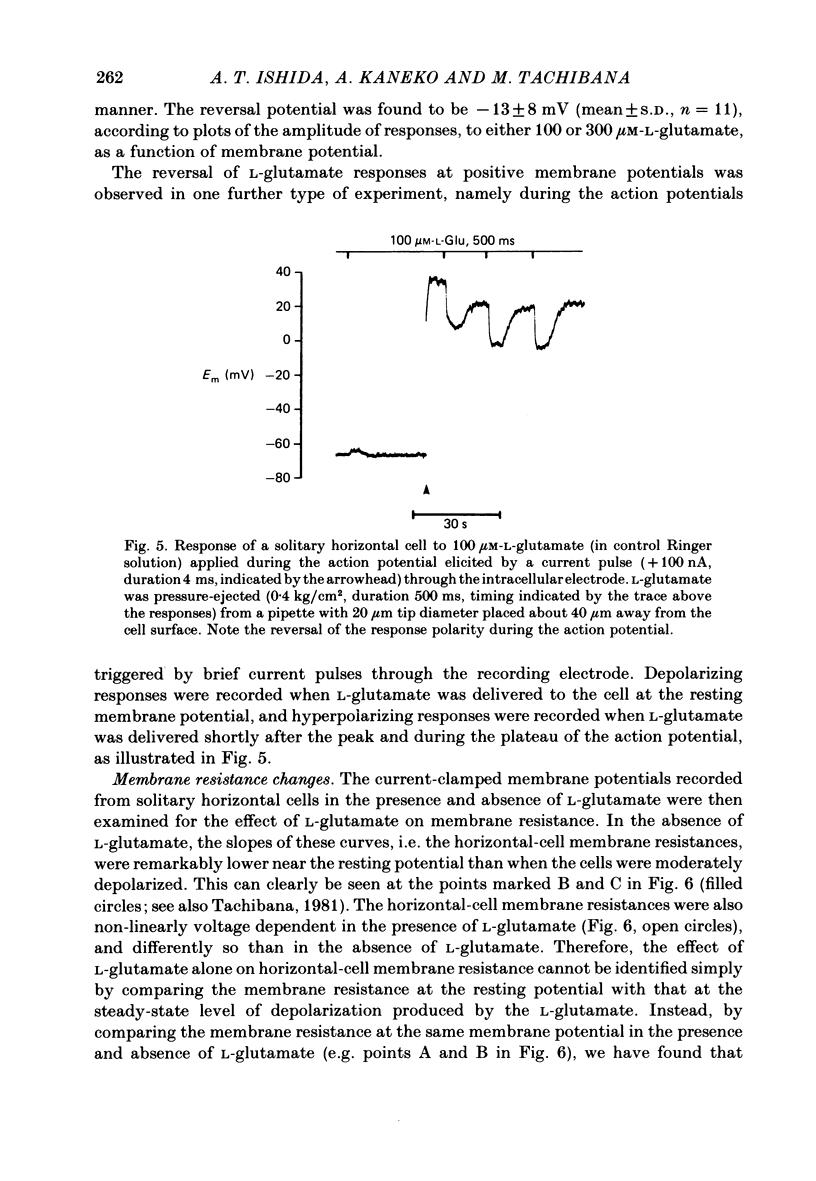
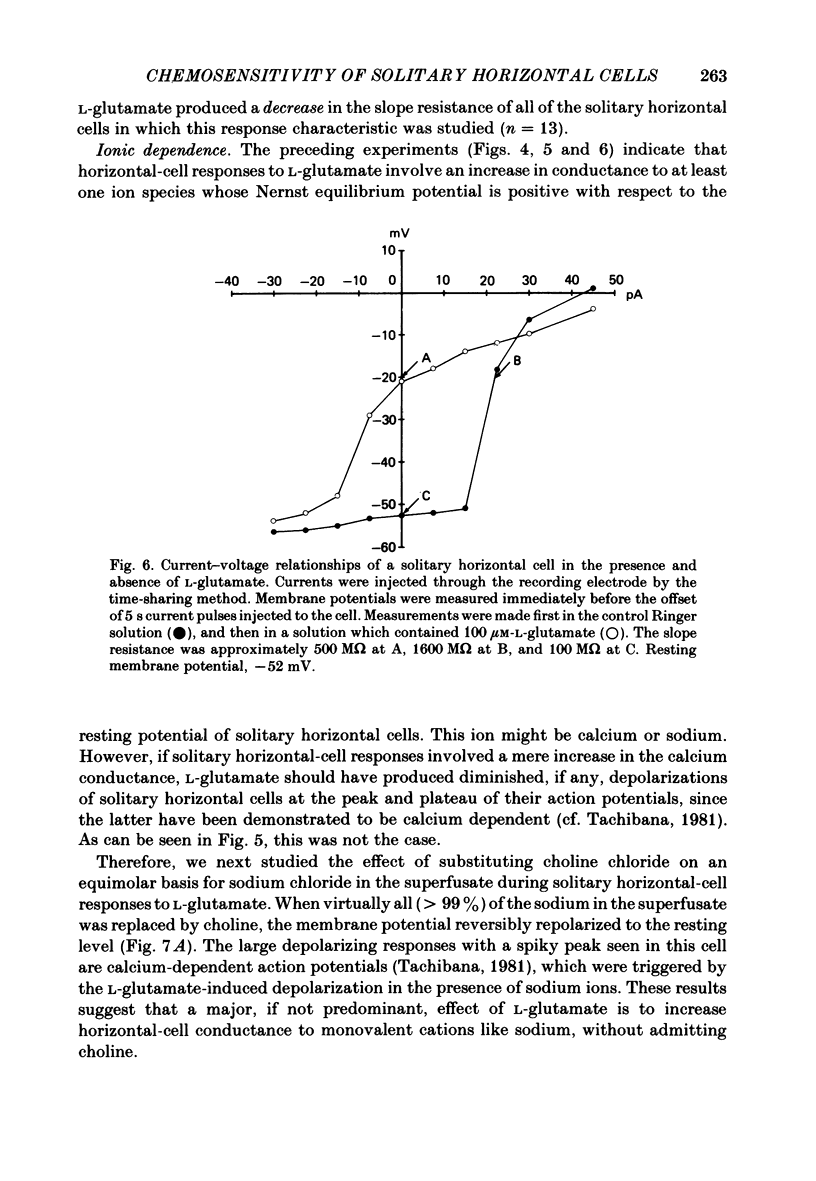
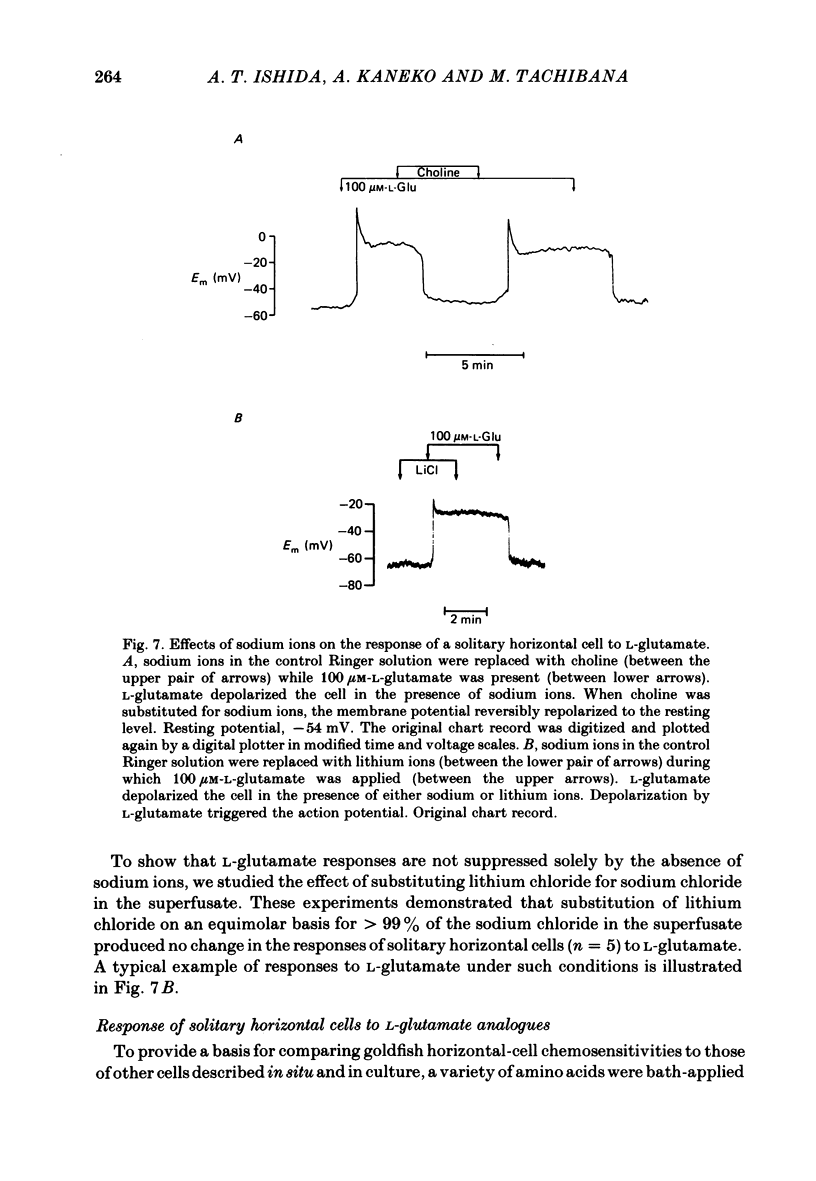
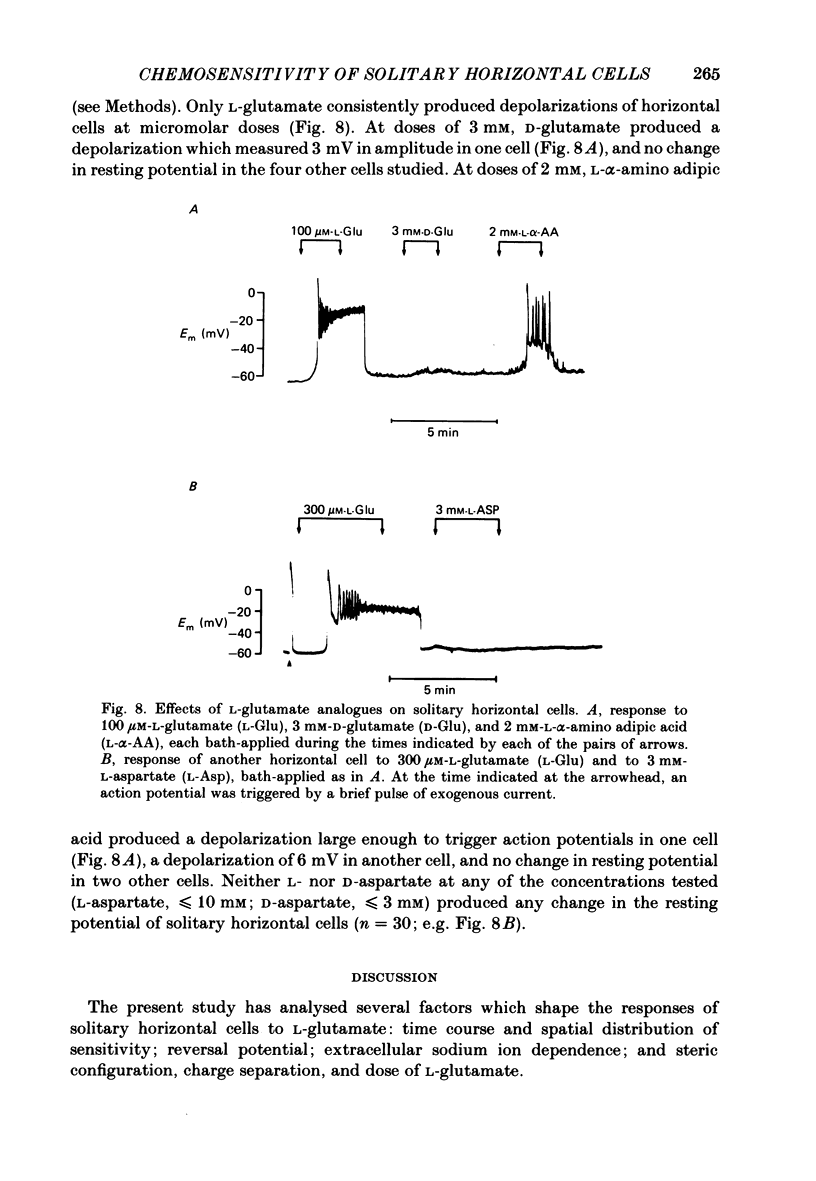
Effects of L-glutamate and its analogues on membrane potentials of solitary horizontal cells were studied by intracellular recording. L-glutamate depolarized these cells at micromolar concentrations (greater than or equal to 10 microM), while D-glutamate and L-alpha-amino adipic acid produced slight depolarizations only at millimolar concentrations. Neither L- nor D-aspartate, even at millimolar doses, produced any change in solitary horizontal-cell resting potential. Solitary horizontal-cell responses to L-glutamate did not desensitize detectably. Responses to pairs of brief, ionophoretic pulses of L-glutamate were nearly equal in amplitude at inter-pulse intervals as short as 50 ms. Responses to maintained applications of low doses of L-glutamate did not decline for as long as 2 min. Depolarizing responses were produced by ionophoretic applications of L-glutamate near cell somata as well as dendrites. The mean sensitivity was 1.4 +/- 1.5 mV/nC with a maximum of 5.1 mV/nC. Depolarizing responses to L-glutamate reversed in polarity at membrane potentials between 0 and -20 mV, were accompanied by a decrease in membrane slope resistance, and were suppressed by replacement of extracellular sodium ions with choline. These results demonstrate that chemosensitivity of retinal horizontal cells to acidic amino acids persists after dissociation protocols, and in several respects resembles that found in horizontal cells in situ. These findings are consistent with the notion that retinal horizontal cells receive a synaptic input involving L-glutamate or a similar substance.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmann H., ten Bruggencate G., Pickelmann P., Steinberg R. Effects of glutamate, aspartate, and two-presumed antagonists on feline rubrospinal neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Aug 24;364(3):249–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00581763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anis N. A., Clark R. B., Gration K. A., Usherwood P. N. Influence of agonists on desensitization of glutamate receptors on locust muscle. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:345–364. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwyl R. Permeability of the post-synaptic membrane of an excitatory glutamate synapse to sodium and potassium. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):367–388. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwyl R. The effect of foreign cations, pH and pharmacological agents on the ionic permeability of an excitatory glutamate synapse. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):389–404. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Potashner S. J. The dependence of glutamate uptake by crab nerve on external Na + and K + . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 3;249(2):616–622. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. P., Jr, Logan W. J., Snyder S. H. Amino acid neurotransmitter candidates: sodium-dependent high-affinity uptake by unique synaptosomal fractions. Science. 1972 Dec 1;178(4064):997–999. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4064.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., WATKINS J. C. Acidic amino acids with strong excitatory actions on mammalian neurones. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:1–14. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Gration K. A., Usherwood P. N. Desensitization of glutamate receptors on innervated and denervated locust muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):551–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Connor J. D., Galvan M., Nistri A. Intracellularly-recorded effects of glutamate and aspartate on neurones in the guinea-pig olfactory cortex slice. Brain Res. 1980 Aug 18;195(2):403–420. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J., Roper S. Analysis of Mauthner cell responses to iontophoretically delivered pulses of GABA, glycine and L-glutamate. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):113–128. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. E., Ehinger B. The interplexiform cell system. I. Synapses of the dopaminergic neurons of the goldfish retina. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978 Apr 13;201(1142):7–26. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1978.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. E., Ripps H. Effect of magnesium on horizontal cell activity in the skate retina. Nature. 1973 Mar 9;242(5393):101–103. doi: 10.1038/242101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. Aspartate and other inhibitors of excitatory synaptic transmission in crayfish muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1977 May 6;369(1):7–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00580803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W. The differential sensitivity to L-glutamate and L-aspartate of spinal interneurones and Renshaw cells. Exp Brain Res. 1974 Mar 29;19(5):522–528. doi: 10.1007/BF00236115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Watkins J. C. Effects of monovalent cations on the responses of motoneurones to different groups to amino acid excitants in frog and rat spinal cord. Experientia. 1977 Feb 15;33(2):246–248. doi: 10.1007/BF02124092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman A. R., Shank R. P., Kephart J., Dekin M., Wang M. A model for excitatory transmission at a glutamate synapse. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1981;27:227–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glitsch H. G., Pott L. Effects of acetylcholine and parasympathetic nerve stimulation on membrane potential in quiescent guinea-pig atria. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:655–668. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., McLennan H., Wheal H. V. The actions of certain amino acids as neuronal excitants [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;272(1):52P–53P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz L. Functional interactions between neurons and astrocytes I. Turnover and metabolism of putative amino acid transmitters. Prog Neurobiol. 1979;13(3):277–323. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(79)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hösli L., Andrès P. F., Hösli E. Ionic mechanisms associated with the depolarization by glutamate and aspartate on human and rat spinal neurones in tissue culture. Pflugers Arch. 1976 May 6;363(1):43–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00587400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida A. T., Fain G. L. D-aspartate potentiates the effects of L-glutamate on horizontal cells in goldfish retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5890–5894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Iontophoretic studies of neurones in the mammalian cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Feb;165:274–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A. Electrical connexions between horizontal cells in the dogfish retina. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):95–105. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A., Shimazaki H. Effects of external ions on the synaptic transmission from photorecptors to horizontal cells in the carp retina. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(2):509–522. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasater E. M., Dowling J. E. Carp horizontal cells in culture respond selectively to L-glutamate and its agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):936–940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge D., Headley P. M., Curtis D. R. Selective antagonism by D-alpha-aminoadipate of amino acid and synaptic excitation of cat spinal neurons. Brain Res. 1978 Sep 8;152(3):603–608. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc R. E., Lam D. M. Uptake of aspartic and glutamic acid by photoreceptors in goldfish retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7185–7189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall L. M., Werblin F. S. Synaptic transmission to the horizontal cells in the retina of the larval tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:321–346. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori S., Miller W. H., Tomita T. Microelectrode study of spreading depression (SD) in frog retina--general observations of field potential associated with SD. Jpn J Physiol. 1976;26(2):203–217. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.26.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Otsu K., Otsuka T. Effects of chemicals on receptors and horizontal cells in the retina. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):899–913. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naka K. I., Rushton W. A. The generation and spread of S-potentials in fish (Cyprinidae). J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):437–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera K., Takeuchi A. Ionic mechanism of the excitatory synaptic membrane of the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;252(1):295–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas I., Rahamimoff R., Sarney Tonic release of transmitter at the neuromuscular junction of the crab. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;250(2):275–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Bullock P. N., Nelson P. G. Mouse spinal cord in cell culture. III. Neuronal chemosensitivity and its relationship to synaptic activity. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Sep;40(5):1163–1177. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.5.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. S., Ruddock K. H. Depolarization of retinal horizontal cells by excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter agonists. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Jun 30;30(3):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiells R. A., Falk G., Naghshineh S. Action of glutamate and aspartate analogues on rod horizontal and bipolar cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):592–594. doi: 10.1038/294592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid: a new pharmacological tool for retina research. Science. 1981 Jan 9;211(4478):182–185. doi: 10.1126/science.6255566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallcup W. B., Bulloch K., Baetge E. E. Coupled transport of glutamate and sodium in a cerebellar nerve cell line. J Neurochem. 1979 Jan;32(1):57–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stell W. K., Lightfoot D. O. Color-specific interconnections of cones and horizontal cells in the retina of the goldfish. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Feb 15;159(4):473–502. doi: 10.1002/cne.901590404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M. Membrane properties of solitary horizontal cells isolated from goldfish retina. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:141–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waloga G., Pak W. L. Horizontal cell potentials: dependence on external sodium ion concentration. Science. 1976 Mar 5;191(4230):964–966. doi: 10.1126/science.1251211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojtowicz J. M., Gysen M., MacDonald J. F. Multiple reversal potentials for responses to L-glutamic acid. Brain Res. 1981 May 25;213(1):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. M., Dowling J. E. L-aspartate: evidence for a role in cone photoreceptor synaptic transmission in the carp retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5205–5209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada E., Ishikawa T. The fine structure of the horizontal cells in some vertebrate retinae. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:383–392. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieglgänsberger W., Puil E. A. Actions of glutamic acid on spinal neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1973 Mar 29;17(1):35–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00234562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


