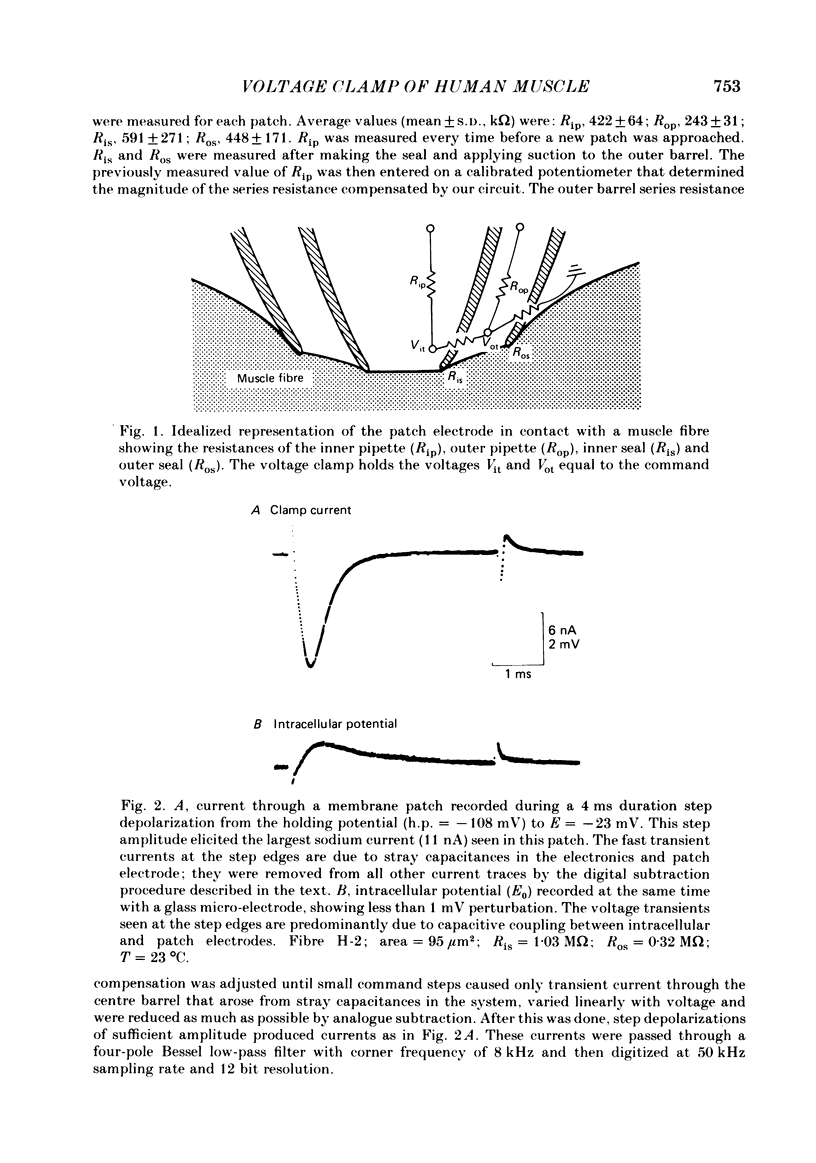
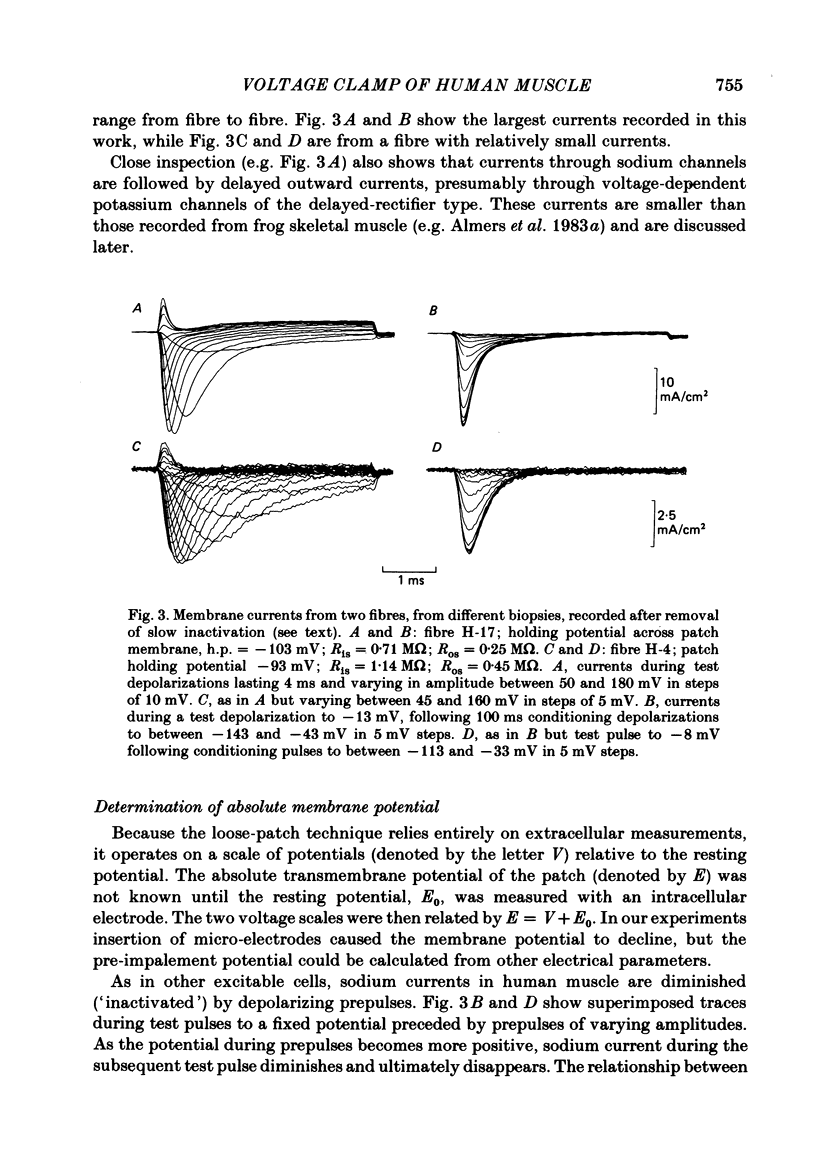
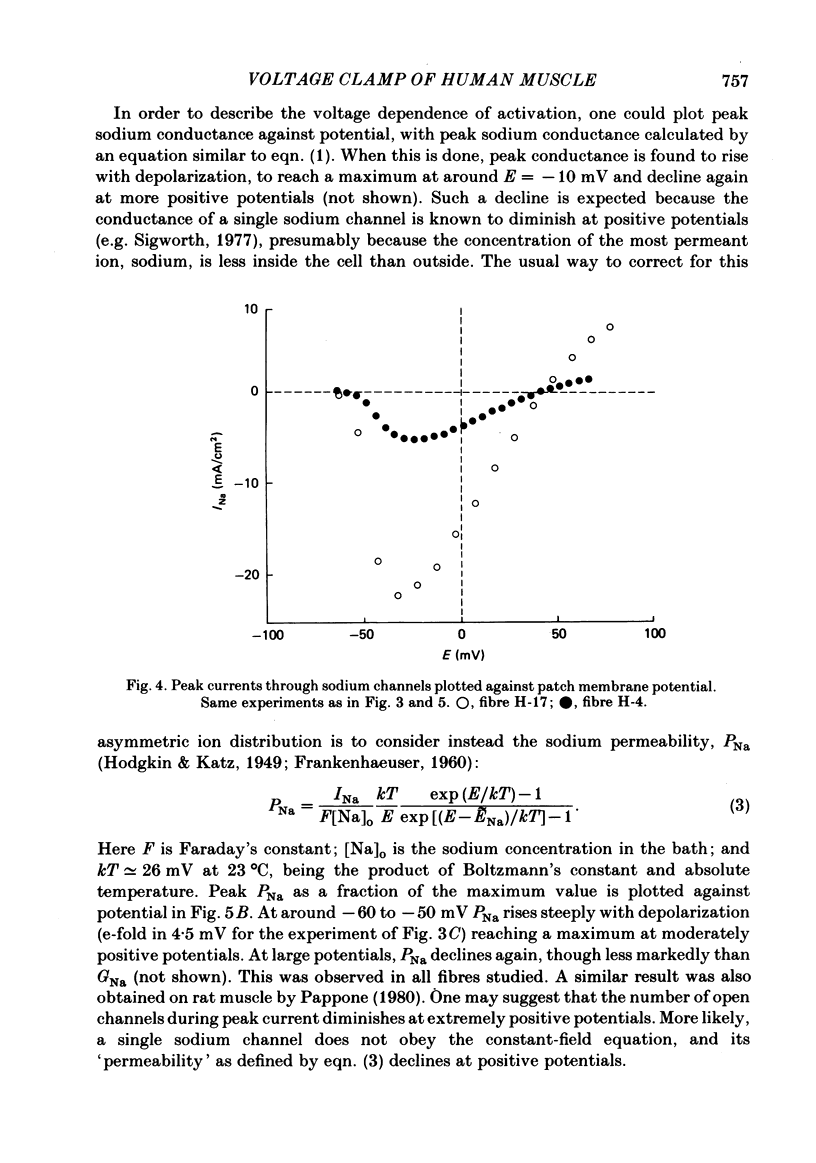
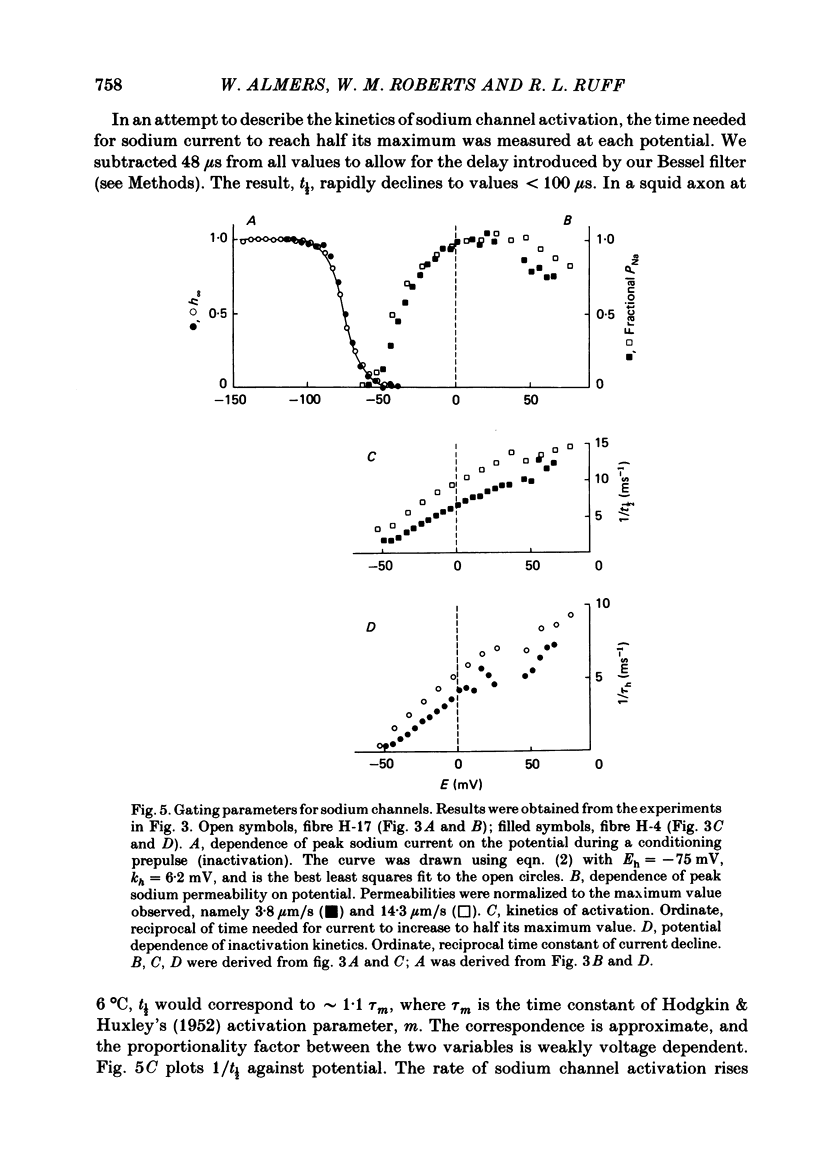
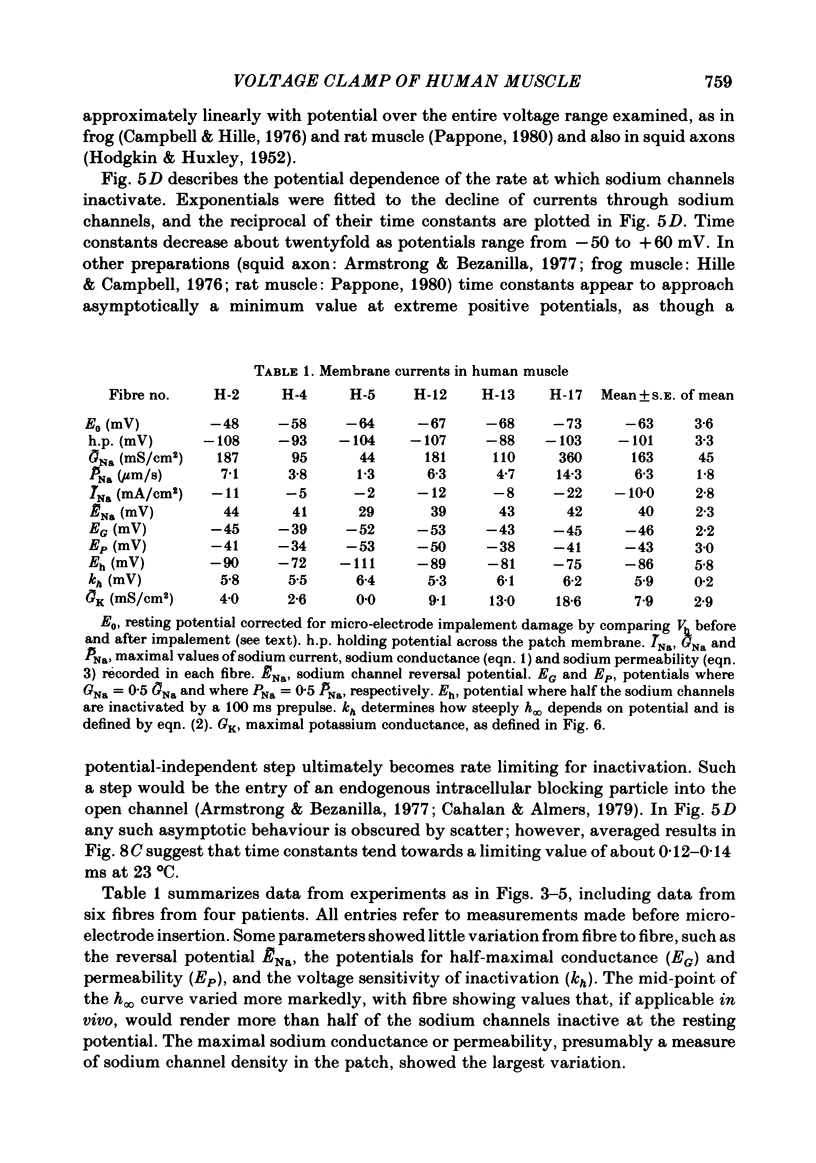
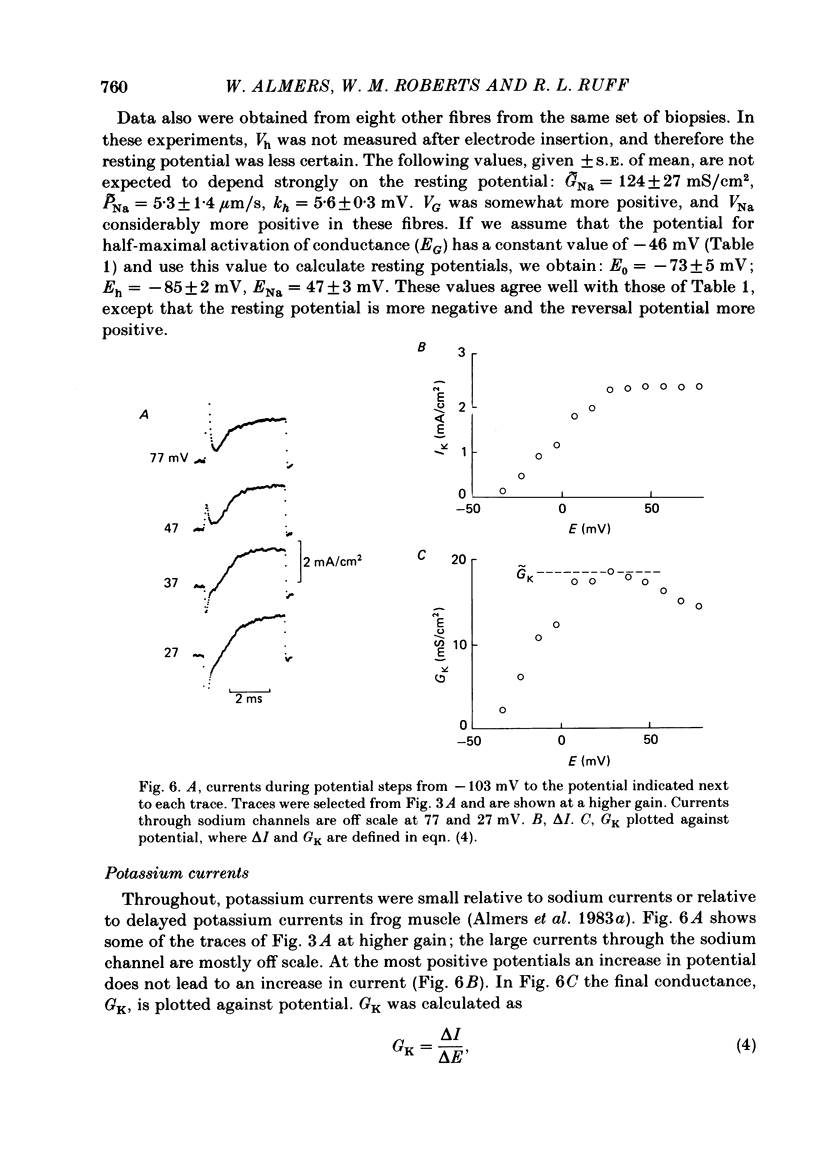
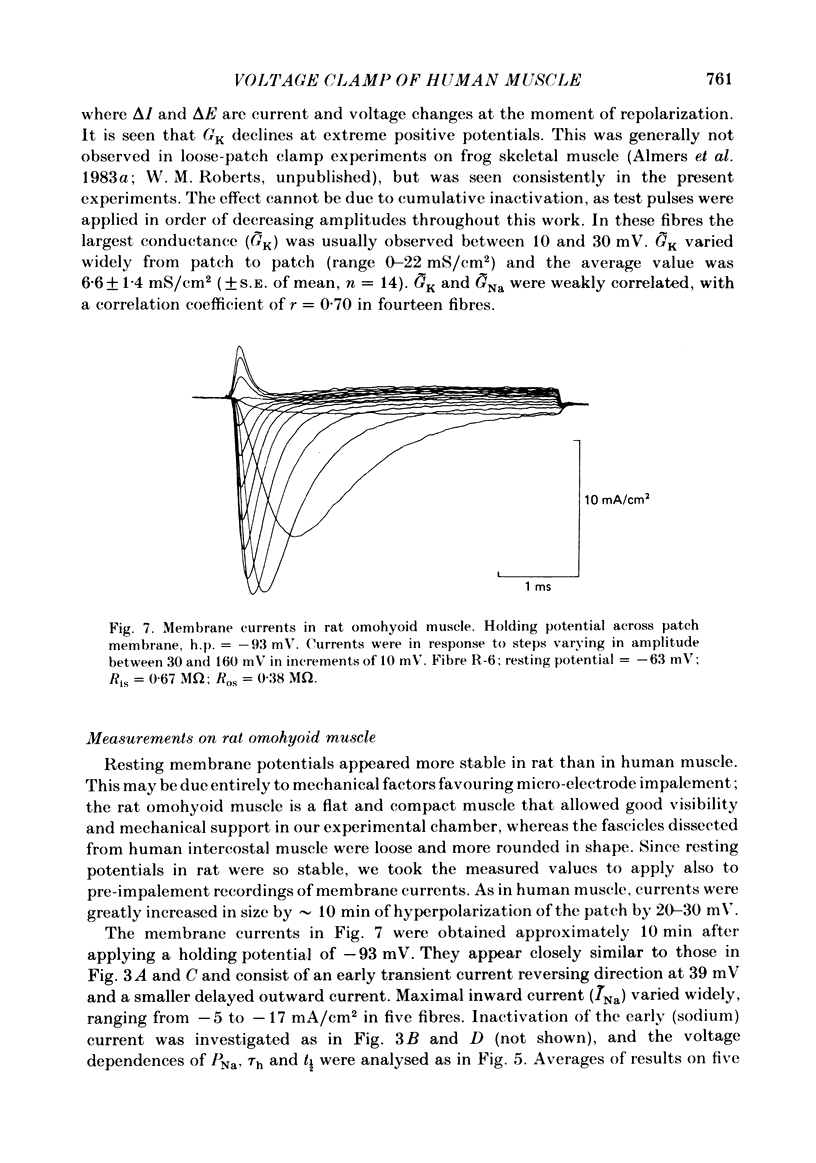
Abstract
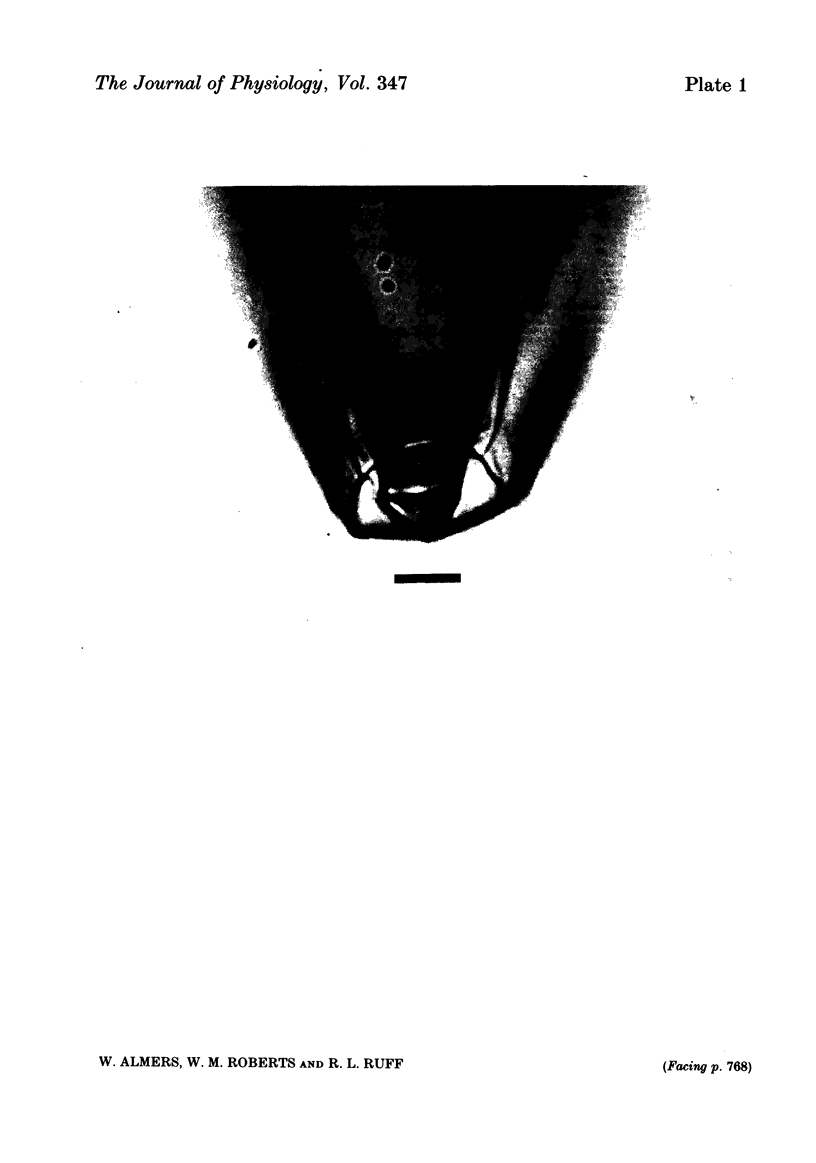
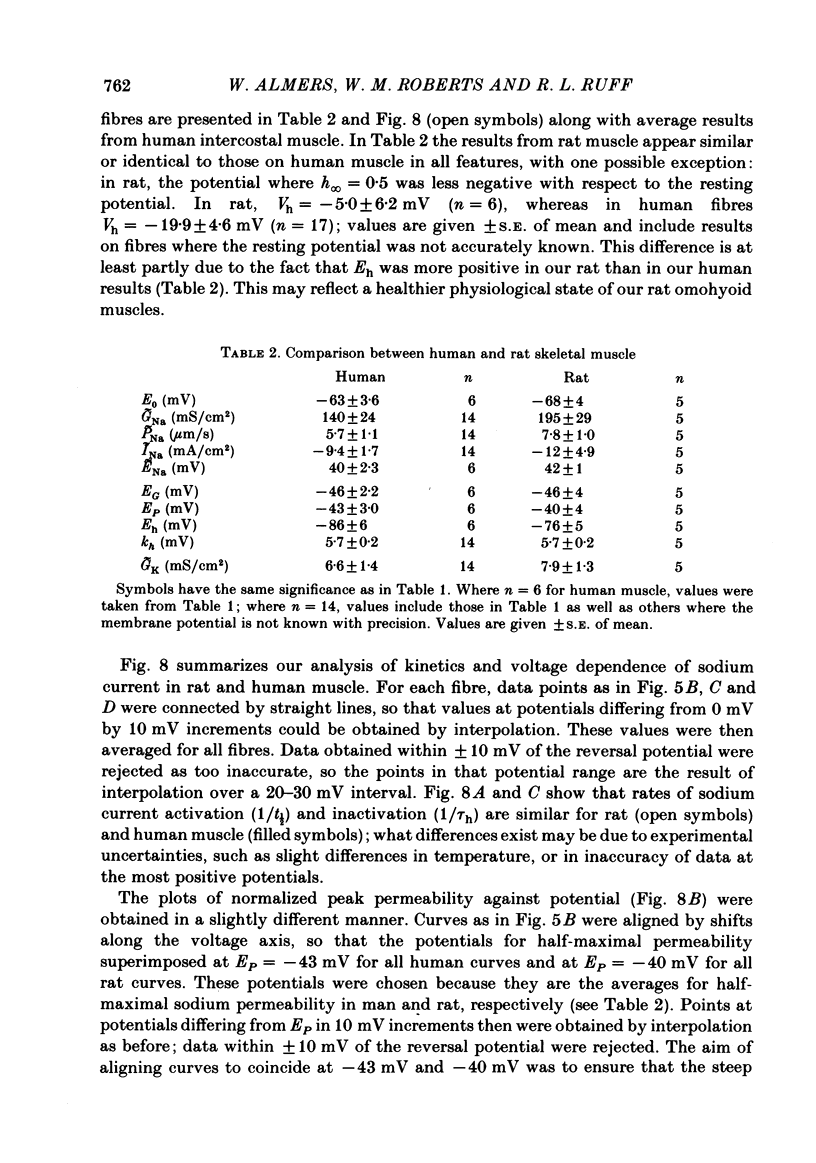
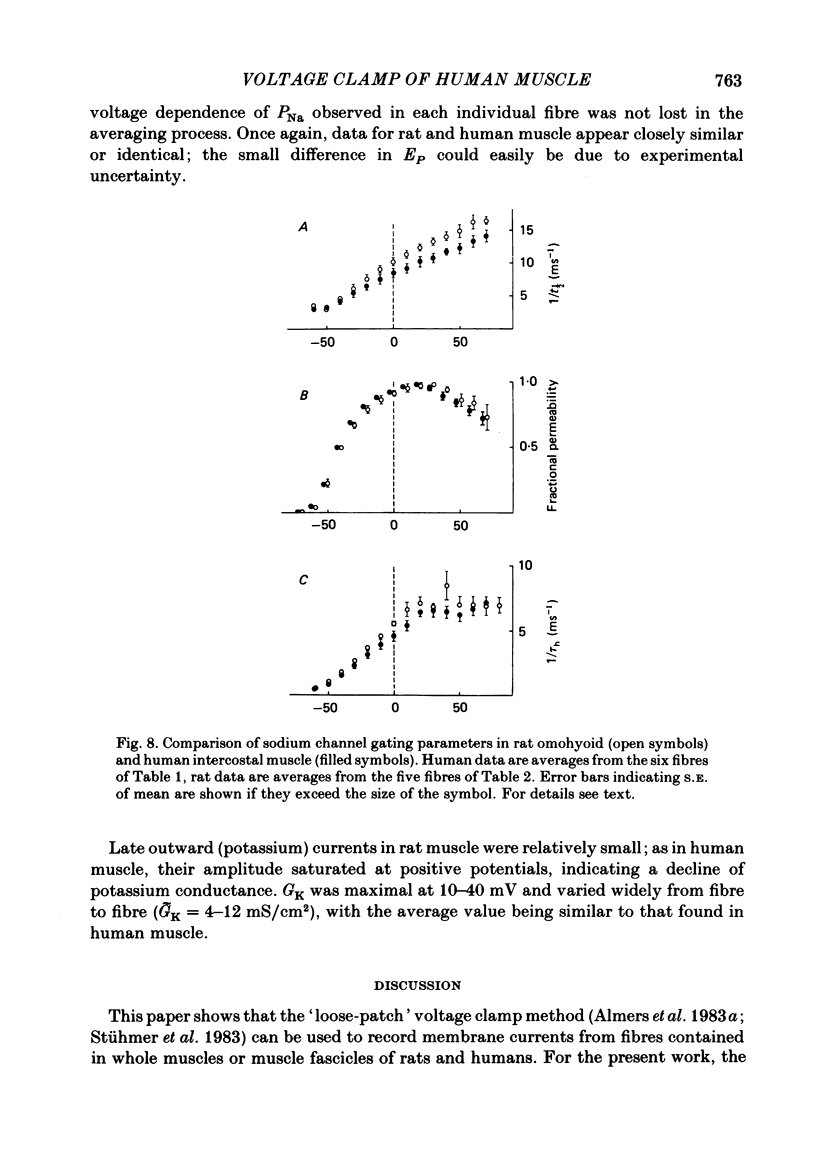
Intact fibres of human intercostal and rat omohyoid muscles were studied at 23 degree C with a loose-patch voltage-clamp technique that employed two concentric micropipettes to electrically isolate small-diameter (10-15 microns) patches of sarcolemma. This method allows investigation of membrane excitability under highly physiological conditions. Step depolarizations to 0 mV elicited sodium inward currents that reached peak values of up to 20 mA/cm2 within 250 microseconds, and then declined. In human muscle, the reversal potential (ENa) was approximately 40 mV, and maximal conductances (GNa) ranged from 44 to 360 mS/cm2. In rat muscle, ENa was 42 mV and GNa ranged from 100 to 250 mS/cm2. Sodium channels in rat and human muscle were indistinguishable in most aspects of their kinetic behaviour and voltage dependence. Outward potassium currents were small by comparison (usually less than 2 mA/cm2) and saturated at positive potentials. The maximum potassium conductance (GK) ranged from 0 to 19 mS/cm2 (human) and from 4 to 12 mS/cm2 (rat muscle).
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):607–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Marshall M. W. Sodium currents in mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(1):223–250. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N. Intracellular ion concentration and electrical activity in potassium-depleted mammalian soleus muscle fibers. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Mar 11;362(1):15–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00588676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W. Differential effects of tetracaine on delayed potassium channels and displacement currents in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(3):613–637. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Stanfield P. R., Stühmer W. Lateral distribution of sodium and potassium channels in frog skeletal muscle: measurements with a patch-clamp technique. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:261–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Stanfield P. R., Stühmer W. Slow changes in currents through sodium channels in frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:253–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Inactivation of the sodium channel. II. Gating current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):567–590. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLTE H. D., RIECKER G., ROHL D. [Measurements of the membrane potential of single cross-striated muscles of man in situ. Normal values]. Klin Wochenschr. 1963 Apr 15;41:356–359. doi: 10.1007/BF01487862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bay C. M., Strichartz G. R. Saxitoxin binding to sodium channels of rat skeletal muscles. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:89–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam K. G., Donaldson P. L. A quantitative study of potassium channel kinetics in rat skeletal muscle from 1 to 37 degrees C. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Apr;81(4):485–512. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.4.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Almers W. Block of sodium conductance and gating current in squid giant axons poisoned with quaternary strychnine. Biophys J. 1979 Jul;27(1):57–73. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85202-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. T., Hille B. Kinetic and pharmacological properties of the sodium channel of frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):309–323. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y., Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B., Stagg D. A quantitative description of membrane currents in rabbit myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:149–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCoursey T. E., Bryant S. H., Lipicky R. J. Sodium currents in human skeletal muscle fibers. Muscle Nerve. 1982 Oct;5(8):614–618. doi: 10.1002/mus.880050805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval A., Léoty C. Ionic currents in mammalian fast skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:403–423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval A., Léoty C. Ionic currents in slow twitch skeletal muscle in the rat. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:23–41. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B. Quantitative description of sodium currents in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151:491–501. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French R. J., Wells J. B. Sodium ions as blocking agents and charge carriers in the potassium channel of the squid giant axon. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Dec;70(6):707–724. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.6.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodgold J., Eberstein A. Transmembrane potentials of human muscle cells in vivo. Exp Neurol. 1966 Jul;15(3):338–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(66)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hencek M., Nonner W., Stämpfli R. Voltage clamp of a small muscle membrane area by means of a circular sucrose gap arrangement. Pflugers Arch. 1969;313(1):71–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00586330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Campbell D. T. An improved vaseline gap voltage clamp for skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):265–293. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ildefonse M., Rougier O. Voltage-clamp analysis of the early current in frog skeletal muscle fibre using the double sucrose-gap method. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):373–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Horn F., Rüdel R., Dengler R., Lorković H., Haass A., Ricker K. Membrane defects in paramyotonia congenita with and without myotonia in a warm environment. Muscle Nerve. 1981 Sep-Oct;4(5):396–406. doi: 10.1002/mus.880040508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Horn F., Rüdel R., Ricker K., Lorković H., Dengler R., Hopf H. C. Two cases of adynamia episodica hereditaria: in vitro investigation of muscle cell membrane and contraction parameters. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Feb;6(2):113–121. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipicky R. J., Bryant S. H., Salmon J. H. Cable parameters, sodium, potassium, chloride, and water content, and potassium efflux in isolated external intercostal muscle of normal volunteers and patients with myotonia congenita. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2091–2103. doi: 10.1172/JCI106703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludin H. P. Microelectrode study of normal human skeletal muscle. Eur Neurol. 1969;2(6):340–347. doi: 10.1159/000113810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappone P. A. Voltage-clamp experiments in normal and denervated mammalian skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:377–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B. The binding of labelled saxitoxin to the sodium channels in normal and denervated mammalian muscle, and in amphibian muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(2):341–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L., Martyn D., Gordon A. M. Glucocorticoid-induced atrophy is not due to impaired excitability of rat muscle. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):E512–E521. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.6.E512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J., Neher E. Single Na+ channel currents observed in cultured rat muscle cells. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):447–449. doi: 10.1038/287447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. Sodium channels in nerve apparently have two conductance states. Nature. 1977 Nov 17;270(5634):265–267. doi: 10.1038/270265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. The effect of zinc ions on the gating of the delayed potassium conductance of frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(3):711–735. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Almers W. Photobleaching through glass micropipettes: sodium channels without lateral mobility in the sarcolemma of frog skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):946–950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]