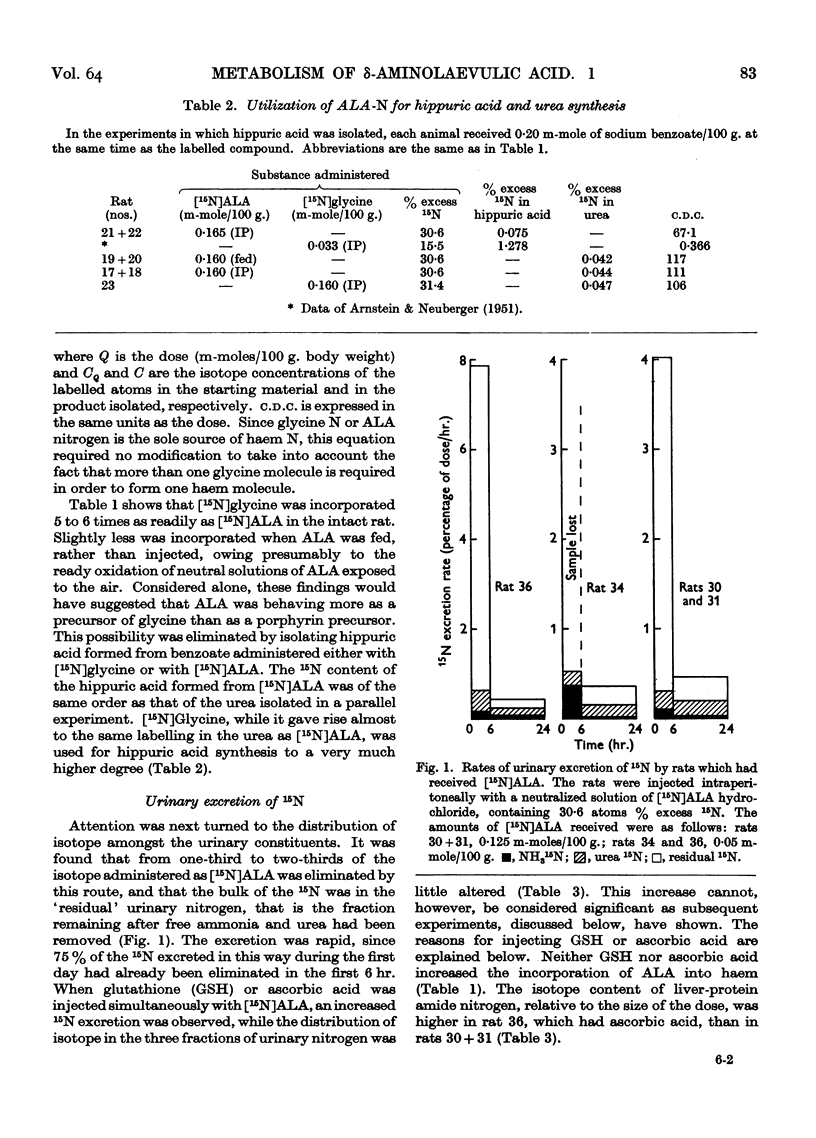
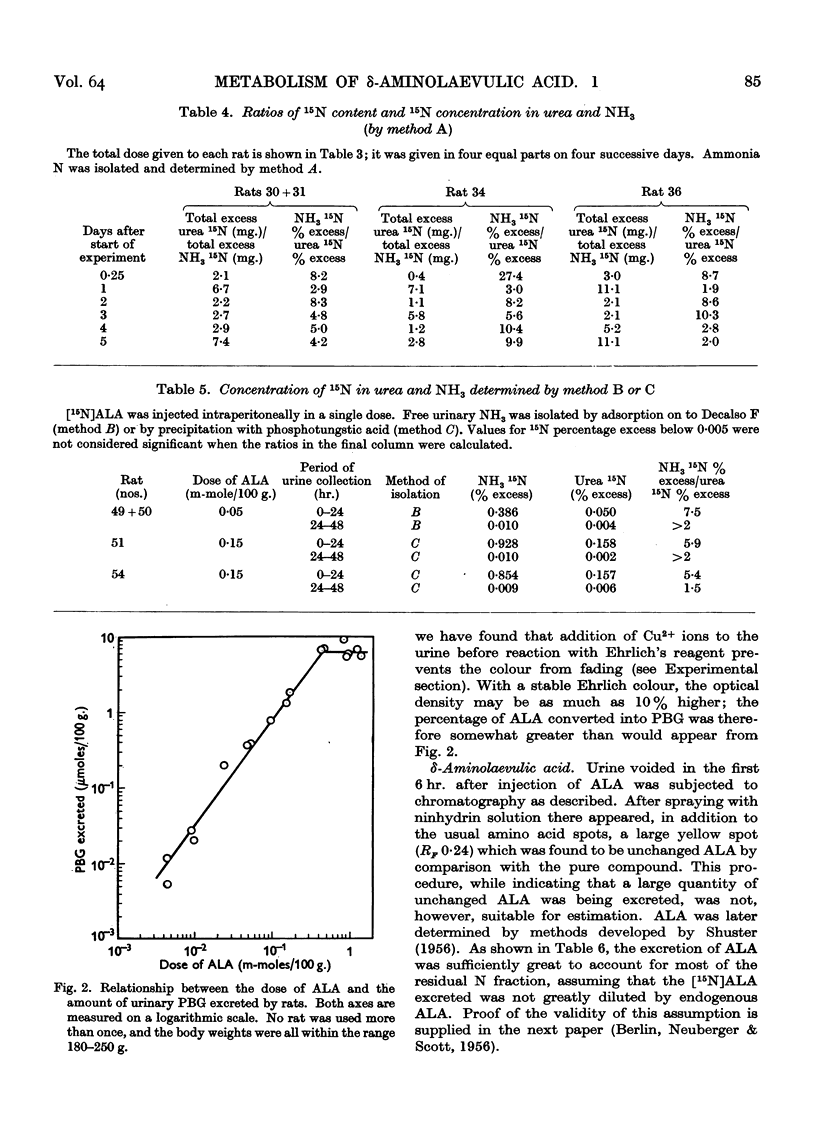
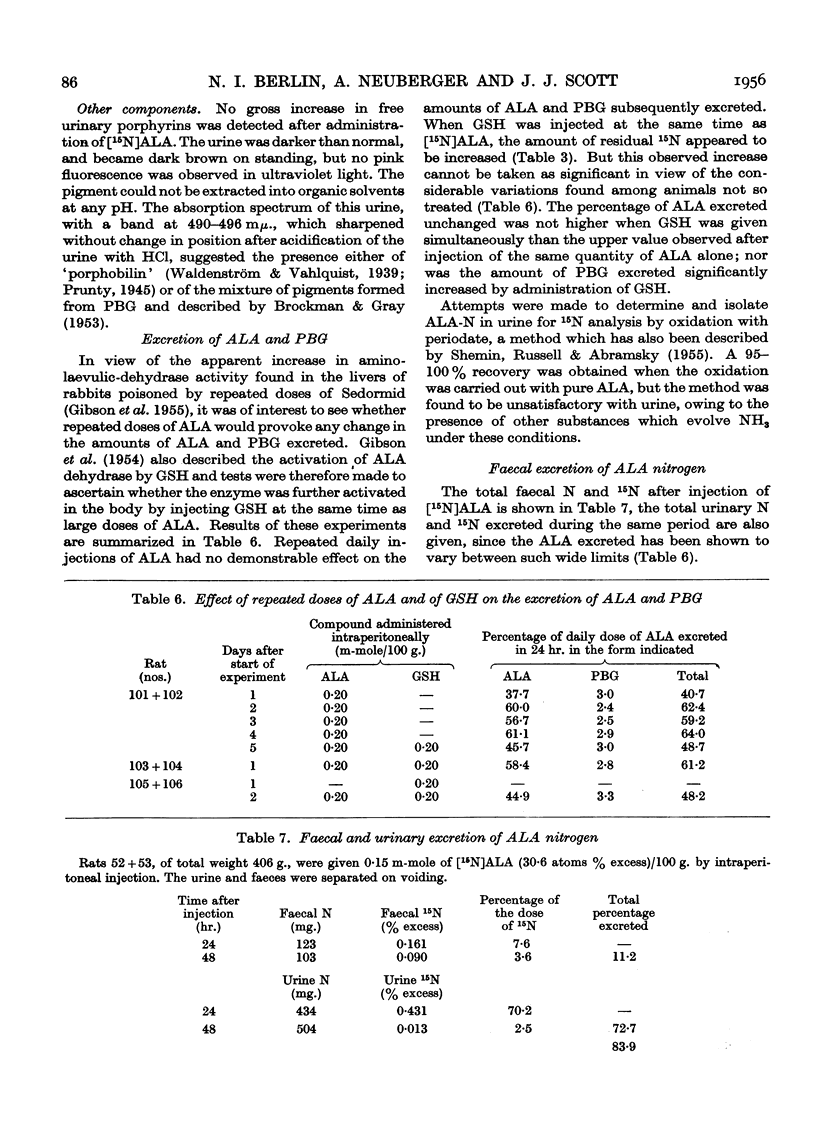
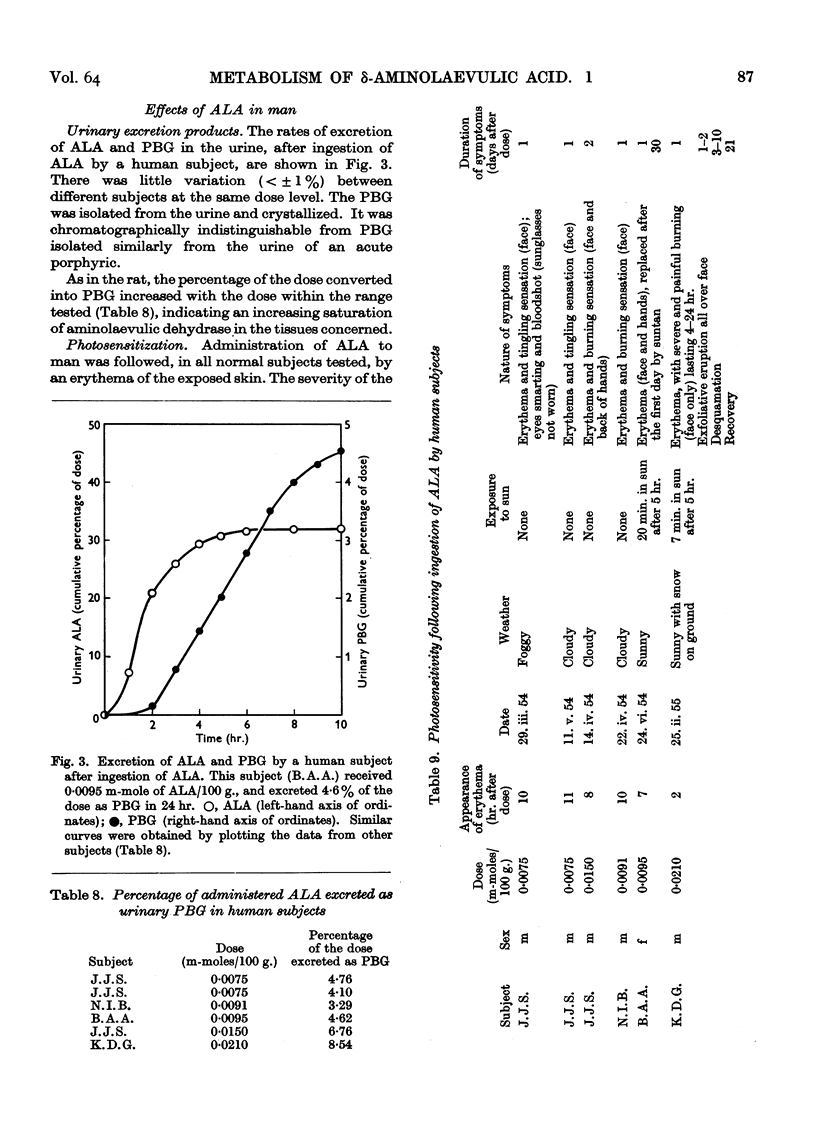
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARNSTEIN H. R. V., NEUBERGER A. Hippuric acid synthesis in the rat. Biochem J. 1951 Dec;50(2):154–162. doi: 10.1042/bj0500154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERLIN N. I., GRAY C. H., NEUBERGER A., SCOTT J. J. The metabolism of the porphyrin precursor, delta-aminolaevulic acid, in normal man and in the rat. Biochem J. 1954 Sep 24;58(332ND):xxx–xxx. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERLIN N. I., NEUBERGER A., SCOTT J. J. The metabolism of delta -aminolaevulic acid. 2. Normal pathways, studied with the aid of 14C. Biochem J. 1956 Sep;64(1):90–100. doi: 10.1042/bj0640090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKMAN P. E., GRAY C. H. Studies on porphobilinogen. Biochem J. 1953 Apr;54(1):22–29. doi: 10.1042/bj0540022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOKSON G. H., RIMINGTON C. Porphobilinogen. Biochem J. 1954 Jul;57(3):476–484. doi: 10.1042/bj0570476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRESEL E. I., FALK J. E. Conversion of alpha-aminolaevulinic acid to porphobilinogen in a tissue system. Nature. 1953 Dec 26;172(4391):1185–1185. doi: 10.1038/1721185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALK J. E., DRESEL E. I., RIMINGTON C. Porphobilinogen as a porphyrin precursor, and interconversion of porphyrins, in a tissue system. Nature. 1953 Aug 15;172(4372):292–294. doi: 10.1038/172292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON K. D., NEUBERGER A., SCOTT J. J. The purification and properties of delta-aminolaevulic acid dehydrase. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):618–629. doi: 10.1042/bj0610618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG A., RIMINGTON C. Fate of porphobilinogen in the rat: relation to acute porphyria in man. Lancet. 1954 Jul 24;267(6830):172–173. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(54)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANICK S., VANDEN SCHRIECK H. G. Porphobilinogen and delta-amino levulinic acid in acute porphyria. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Feb;88(2):270–273. doi: 10.3181/00379727-88-21560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir H. M., Neuberger A. The biogenesis of porphyrins. The distribution of N in the ring system. Biochem J. 1949;45(2):163–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUBERGER A., SCOTT J. J. Aminolaevulinic acid and porphyrin biosynthesis. Nature. 1953 Dec 12;172(4389):1093–1094. doi: 10.1038/1721093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prunty F. T. Acute porphyria: Some properties of porphobilinogen. Biochem J. 1945;39(5):446–451. doi: 10.1042/bj0390446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEMIN D., RUSSELL C. S., ABRAMSKY T. The succinate-glycine cycle. I. The mechanism of pyrrole synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1955 Aug;215(2):613–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUSTER L. The determination of delta -aminolaevulic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Sep;64(1):101–106. doi: 10.1042/bj0640101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WU H. Relative concentrations of N15 in urinary ammonia N and urea N after feeding N15-labeled compounds. J Gen Physiol. 1951 Mar 20;34(4):403–409. doi: 10.1085/jgp.34.4.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


