Full text
PDF


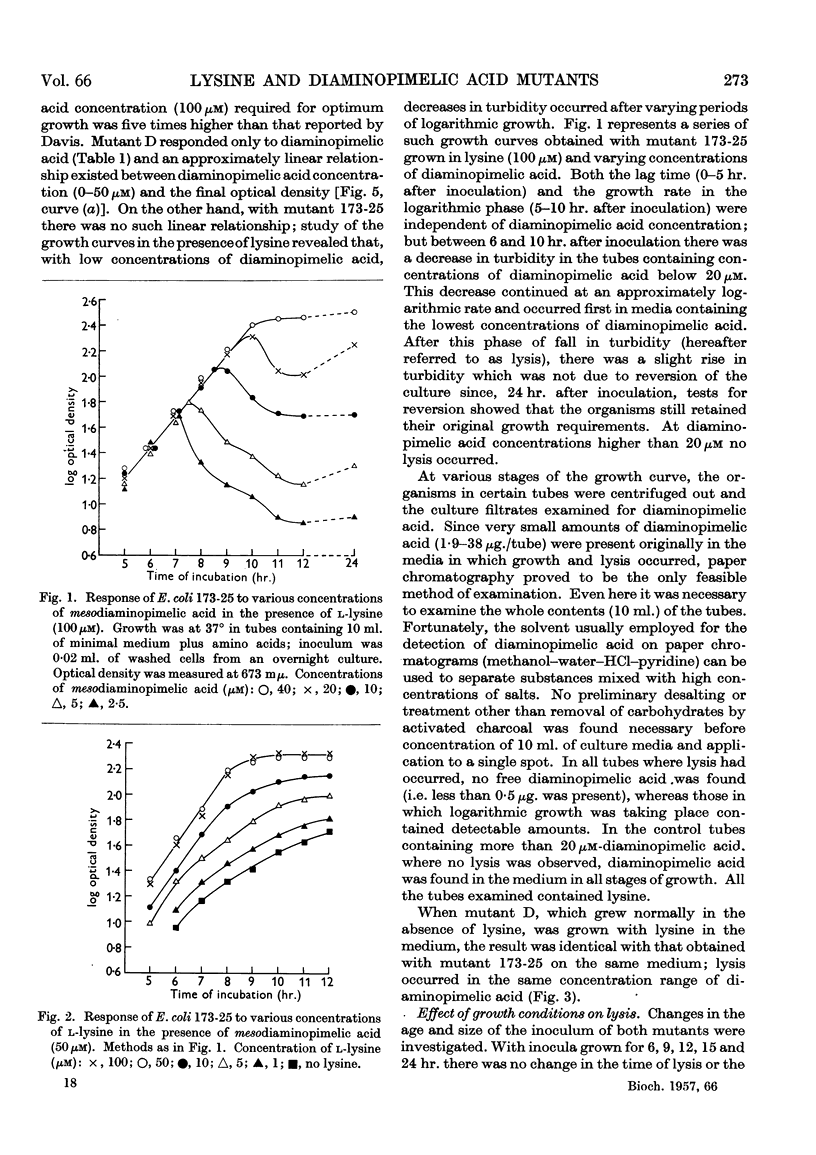
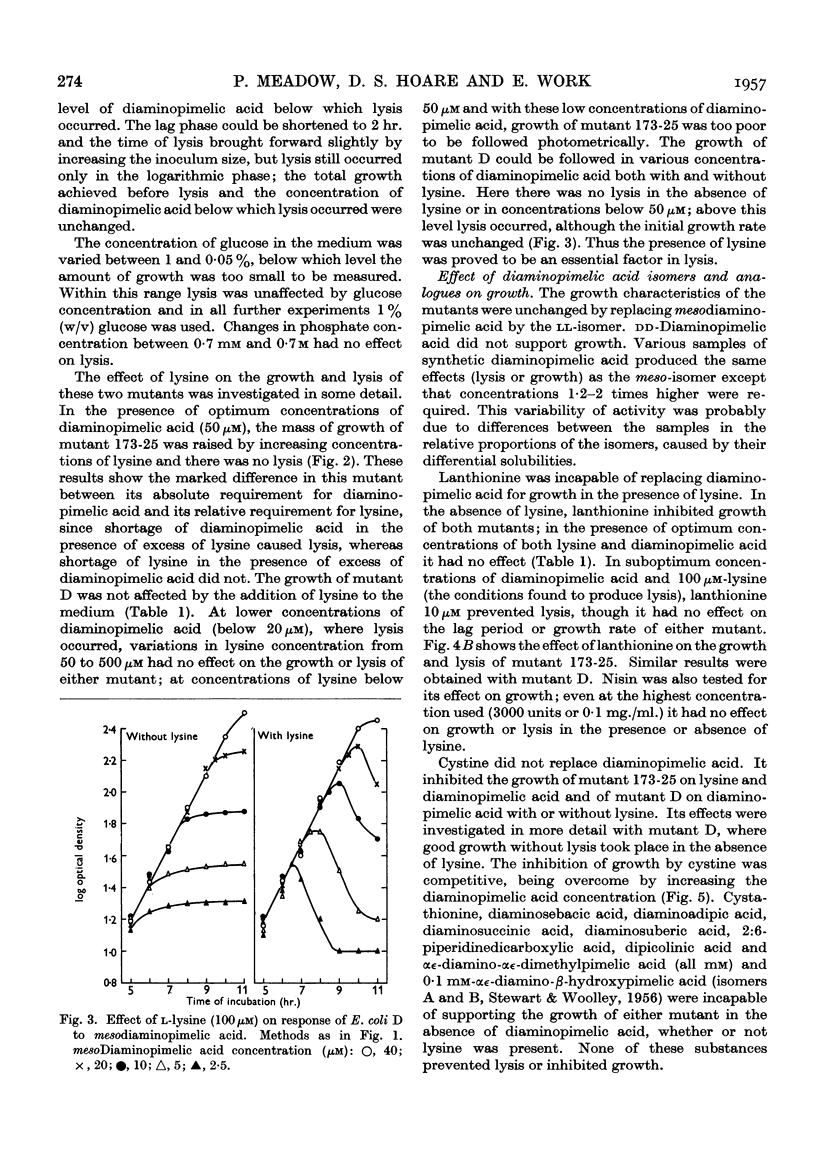
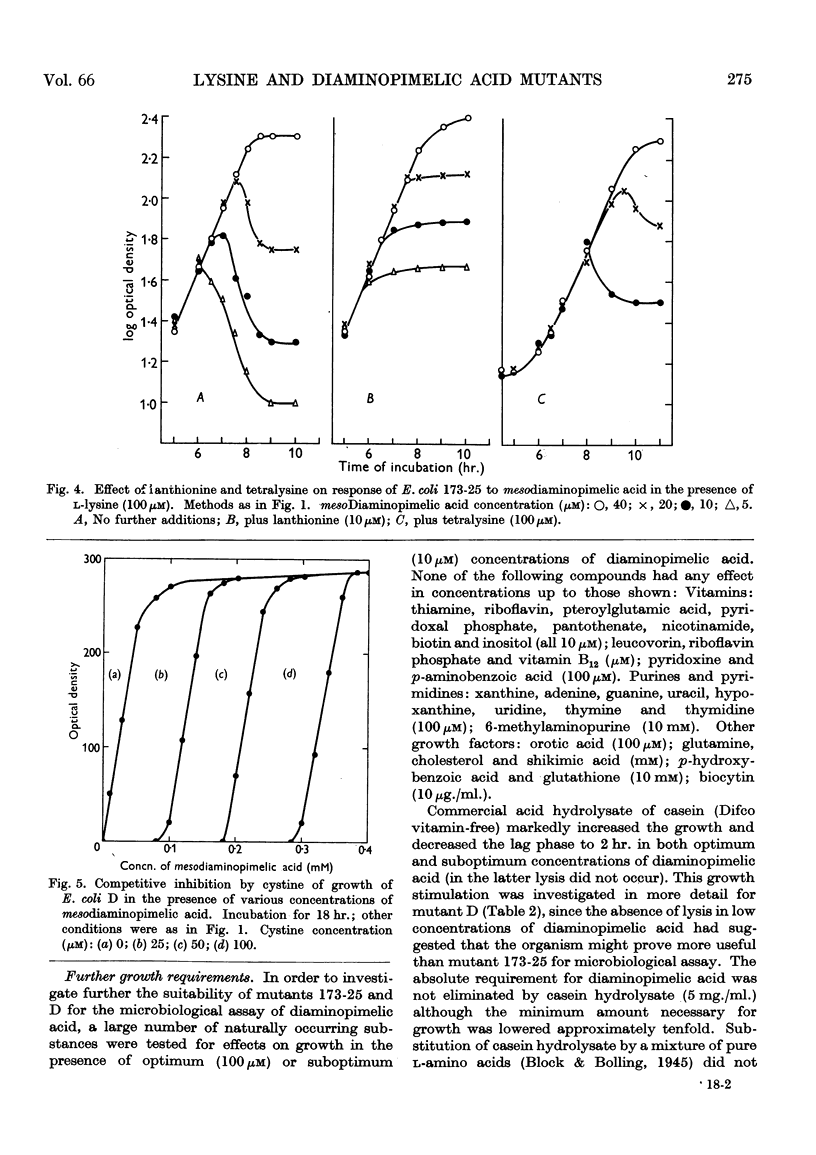
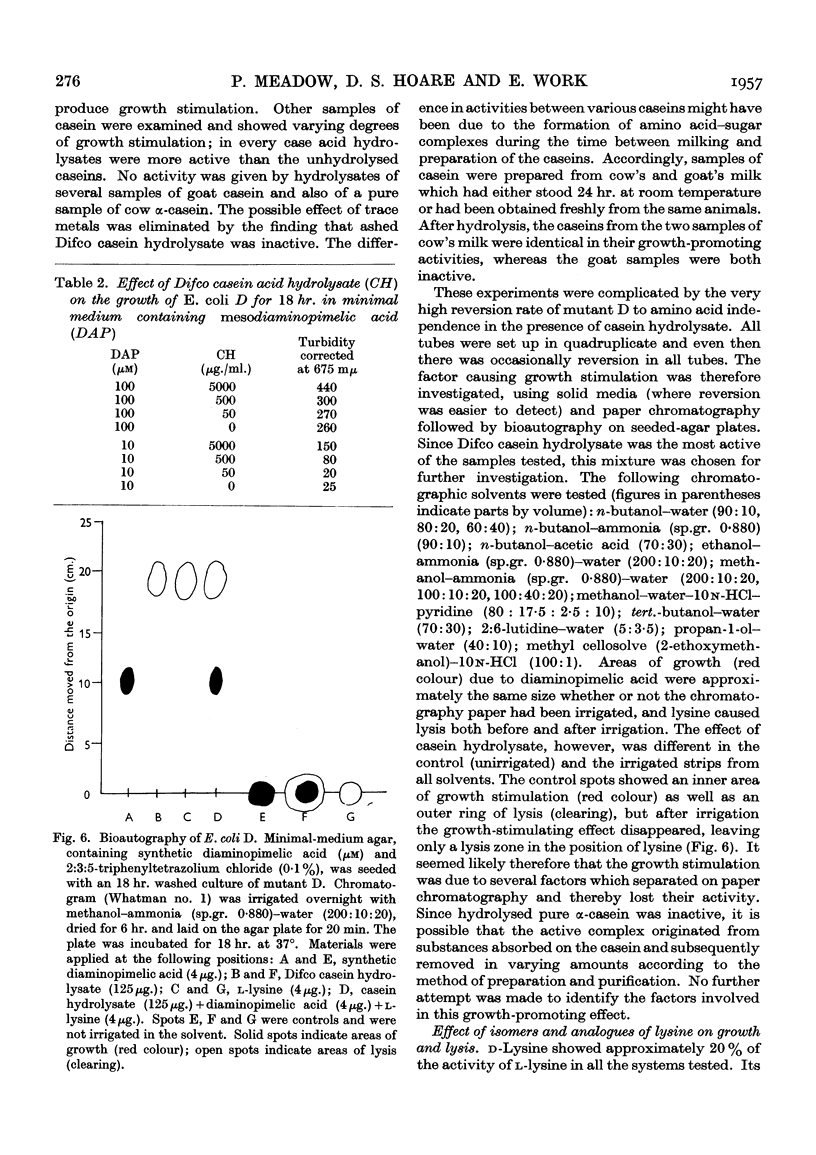





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTIA M., HOARE D. S., WORK E. The stereoisomers of alpha epsilon-diaminopimelic acid. III. Properties and distribution of diaminopimelic acid racemase, an enzyme causing interconversion of the LL and meso isomers. Biochem J. 1957 Mar;65(3):448–459. doi: 10.1042/bj0650448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASKONAS B. A., CAMPBELL P. N., WORK T. S. The biosynthesis of proteins. II. Synthesis of milk proteins by the goat. Biochem J. 1954 Oct;58(2):326–331. doi: 10.1042/bj0580326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRNBAUM S. M., LEVINTOW L., KINGSLEY R. B., GREENSTEIN J. P. Specificity of amino acid acylases. J Biol Chem. 1952 Jan;194(1):455–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINS C. S., HARRIS H. The chemical composition of the cell wall in some gram-positive bacteria and its possible value as a taxonomic character. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Jul;14(3):583–600. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-3-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D. Biosynthetic interrelations of lysine, diaminopimelic acid, and threonine in mutants of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1952 Mar 29;169(4300):534–536. doi: 10.1038/169534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWEY D. L., HOARE D. S., WORK E. Diaminopimelic acid decarboxylase in cells and extracts of Escherichia coli and Aerobacter aerogenes. Biochem J. 1954 Dec;58(4):523–531. doi: 10.1042/bj0580523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWEY D. L., WORK E. Diaminopimelic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1952 Mar 29;169(4300):533–534. doi: 10.1038/169533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOOD N., HEILBRONNER R., MITCHELL H. K. Epsilon-Hydroxynorleucine as a substitute for lysine for neurospora. Arch Biochem. 1950 Oct;28(3):464–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOARE D. S. The progressive reaction of isonicotinyl hydrazide with two bacterial amino acid decarboxylases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Jan;19(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOARE D. S., WORK E. The stereoisomers of alpha epsilon-diaminopimelic acid: their distribution in nature and behaviour towards certain enzyme preparations. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):562–568. doi: 10.1042/bj0610562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. I., Work T. S. Lysine analogues as inhibitors of bacterial growth. Biochem J. 1950 Feb;46(2):190–195. doi: 10.1042/bj0460190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATCHALSKI E., BICHOWSKI-SLOMNITZKI L., VOLCANI B. E. The action of some water-soluble poly-alpha-amino acids on bacteria. Biochem J. 1953 Nov;55(4):671–680. doi: 10.1042/bj0550671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDLEY H. A new synthetic substrate for trypsin and its application to the determination of the amino-acid sequence of proteins. Nature. 1956 Sep 22;178(4534):647–648. doi: 10.1038/178647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J. BACTERIAL PROTOPLASTS INDUCED BY PENICILLIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):574–577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Autolytic protoplast release in Bacterium coli. Nature. 1956 Nov 3;178(4540):993–993. doi: 10.1038/178993a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLAREN A. D., KNIGHT C. A. The response of Leuconostoc mesenteroides P-60 to some compounds related to lysine. J Biol Chem. 1953 Sep;204(1):417–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON G. G., ABRAHAM E. P., BERRIDGE N. J. Sulphur-containing amino-acids of nisin. Nature. 1953 Apr 4;171(4353):606–606. doi: 10.1038/171606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger A., Sanger F. The availability of the acetyl derivatives of lysine for growth. Biochem J. 1943 Oct;37(4):515–518. doi: 10.1042/bj0370515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger A., Sanger F. The metabolism of lysine. Biochem J. 1944;38(1):119–125. doi: 10.1042/bj0380119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAVEL J. M., WOODS L., FELSING B., SHIVE W. Some interrelationships of aspartic acid, threonine, and lysine. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jan;206(1):391–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. Cell structure and the enzymic lysis of bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Dec;9(3):512–523. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-3-512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. Studies of the bacterial cell wall. IV. The composition of the cell walls of some Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Apr;10(4):512–523. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90296-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWEET R. S., HOLDEN J. T., LOWY P. H. The metabolism of lysine in Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):517–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEIBERT F. B., SOTO-FIGUEROA E., MILLER E. E., SEIBERT M. V. Comparison of the amino acid composition of alcoholic extracts of neoplastic tissues with similar extracts of normal muscle. Growth. 1954 Sep;18(3):145–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMMONDS D. H. Analogues of diaminopimelic acid as inhibitors of bacterial growth. Biochem J. 1954 Dec;58(4):520–523. doi: 10.1042/bj0580520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANGE R. E., POWELL J. F. Hexosamine-containing peptides in spores of Bacillus subtilis, B. megatherium and B. cereus. Biochem J. 1954 Sep;58(1):80–85. doi: 10.1042/bj0580080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C. The isolation of protoplasts from Bacillus megaterium by controlled treatment with lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1953 Dec;66(6):688–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.6.688-695.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINSTEN W. A., EIGEN E. Bioautographic studies with use of Leuconostoc citrovorum 8081. J Biol Chem. 1950 May;184(1):155–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder N. D., Arndt W. F. PRODUCTION OF PROTOPLASTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI BY LYSOZYME TREATMENT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):586–590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


