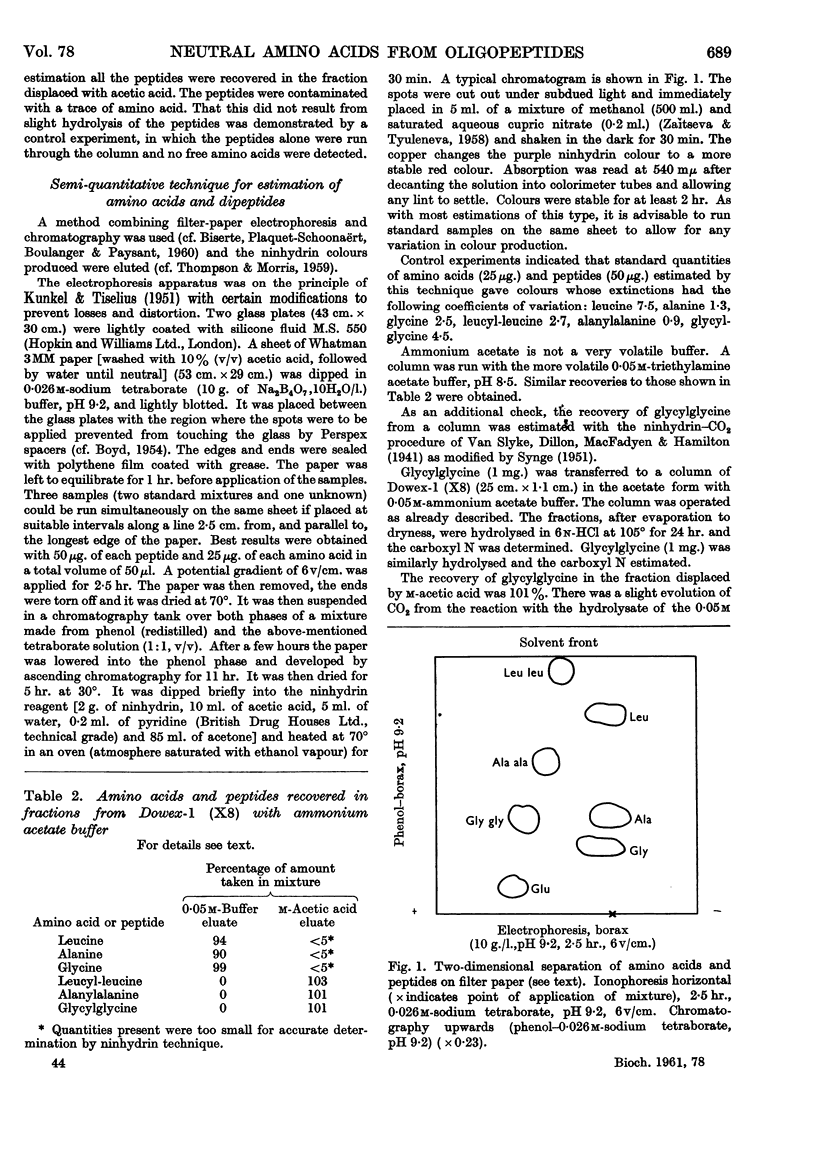
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYD G. S. The estimation of serum lipoproteins; a micromethod based on zone electrophoresis and cholesterol estimations. Biochem J. 1954 Dec;58(4):680–685. doi: 10.1042/bj0580680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARNEGIE P. R. Bound amino acids of ryegrass: the isolation of amphoteric peptide-like substances of low molecular weight. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;78:697–707. doi: 10.1042/bj0780697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROOK E. M., MATHIAS A. P., RABIN B. R. The preparation and purification of cytidine 2':3'-phosphate. Biochem J. 1960 Feb;74:230–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0740230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consden R., Gordon A. H., Martin A. J. Ionophoresis in silica jelly: A method for the separation of animo-acids and peptides. Biochem J. 1946;40(1):33–41. doi: 10.1042/bj0400033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. W. The fractionation of weak electrolyte mixtures by ion-exchange resins. Biochem J. 1949;45(1):38–41. doi: 10.1042/bj0450038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKOVITZ A., STEINBERG D. A method for the determination of peptides in the presence of free amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1957 Sep;228(1):285–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUBERG C., GRAUER A., KREIDL M. The basis of the carbamate reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Sep;58(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge S. M., Brimley R. C. Displacement chromatography on synthetic ion-exchange resins. 2. The separation of organic acids and acidic amino-acids by the use of anion-exchange resins. Biochem J. 1949;44(5):513–521. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYNGE R. L. M. Non-protein nitrogenous constituents of rye grass; ionophoretic fractionation and isolation of a 'bound amino-acid' fraction. Biochem J. 1951 Oct;49(5):642–650. doi: 10.1042/bj0490642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYNGE R. L., WOOD J. C. Bound amino acids in protein-free extracts of Italian ryegrass. Biochem J. 1958 Oct;70(2):321–339. doi: 10.1042/bj0700321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Synge R. L., Youngson M. A. Metabolic incorporation of l-[C]valine into protein and bound non-protein forms in Italian ryegrass. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;78(4):708–714. doi: 10.1042/bj0780708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALEY S. G. Acidic peptides of the lens. Biochem J. 1956 Dec;64(4):715–726. doi: 10.1042/bj0640715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIELAND T., PFLEIDERER G. Aktivierung von Aminosäuren. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1957;19:235–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


