Abstract
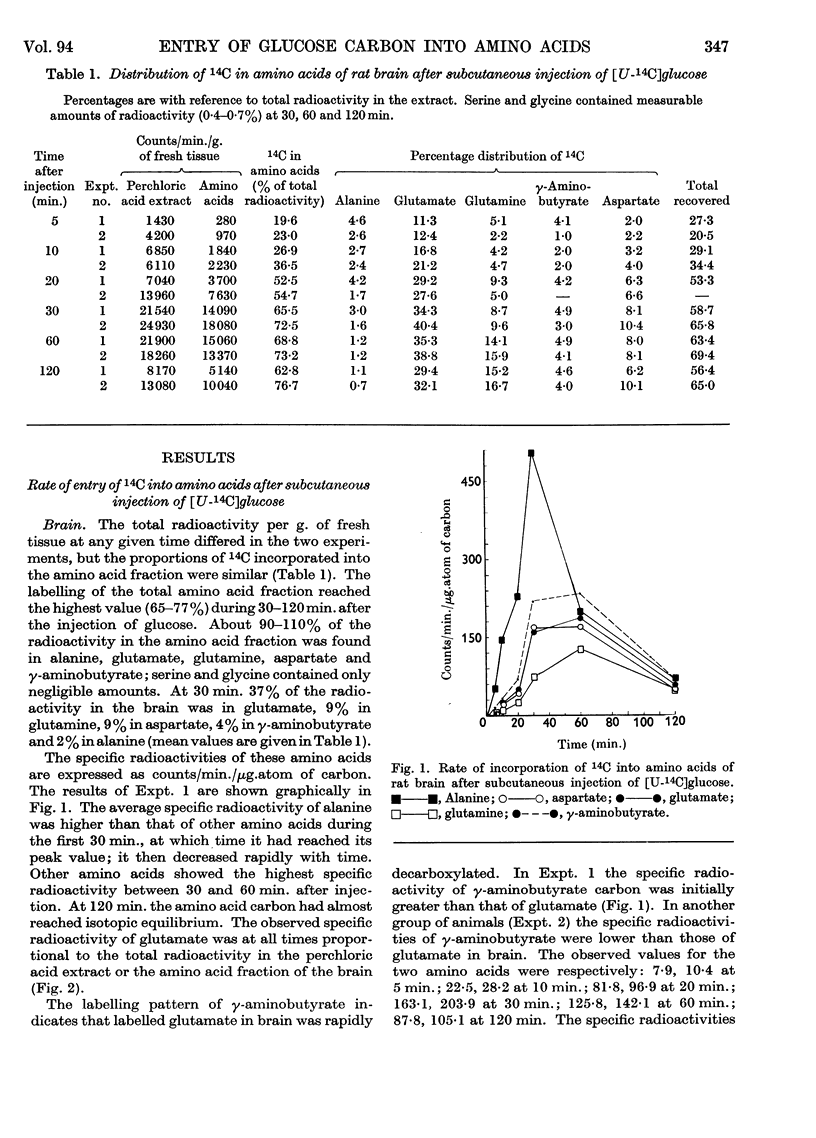
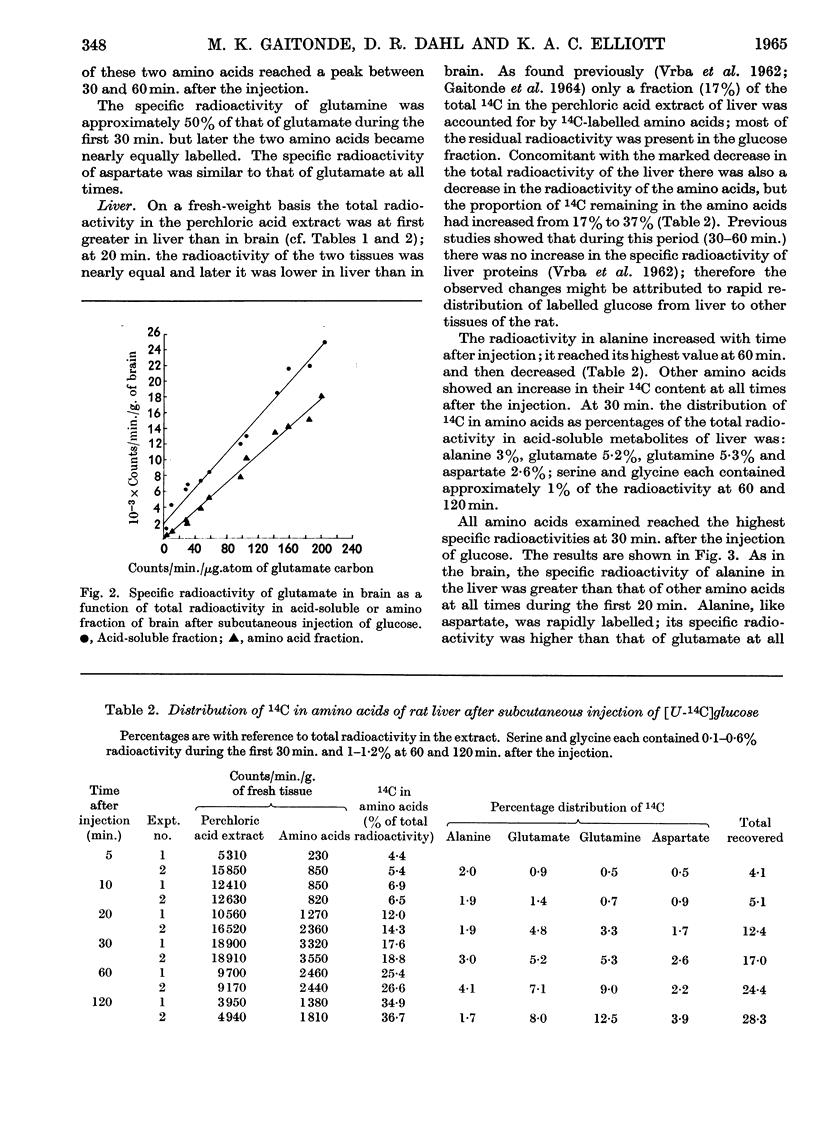
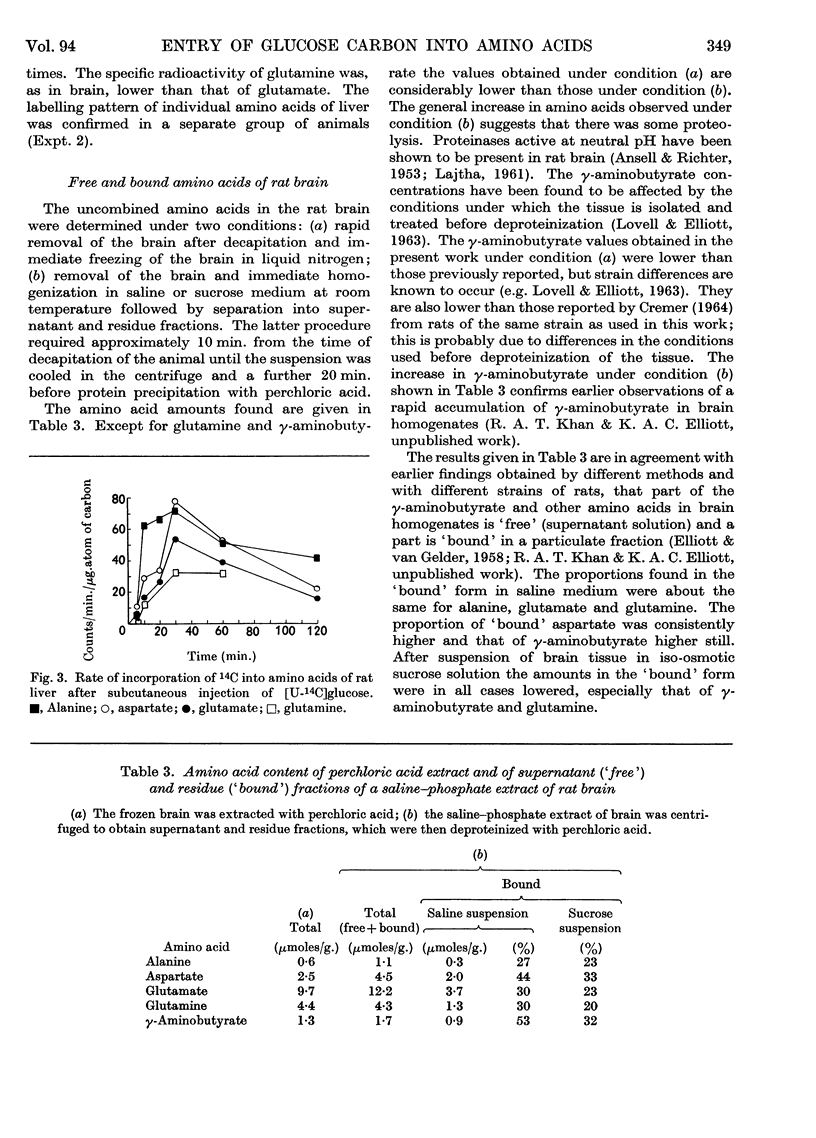
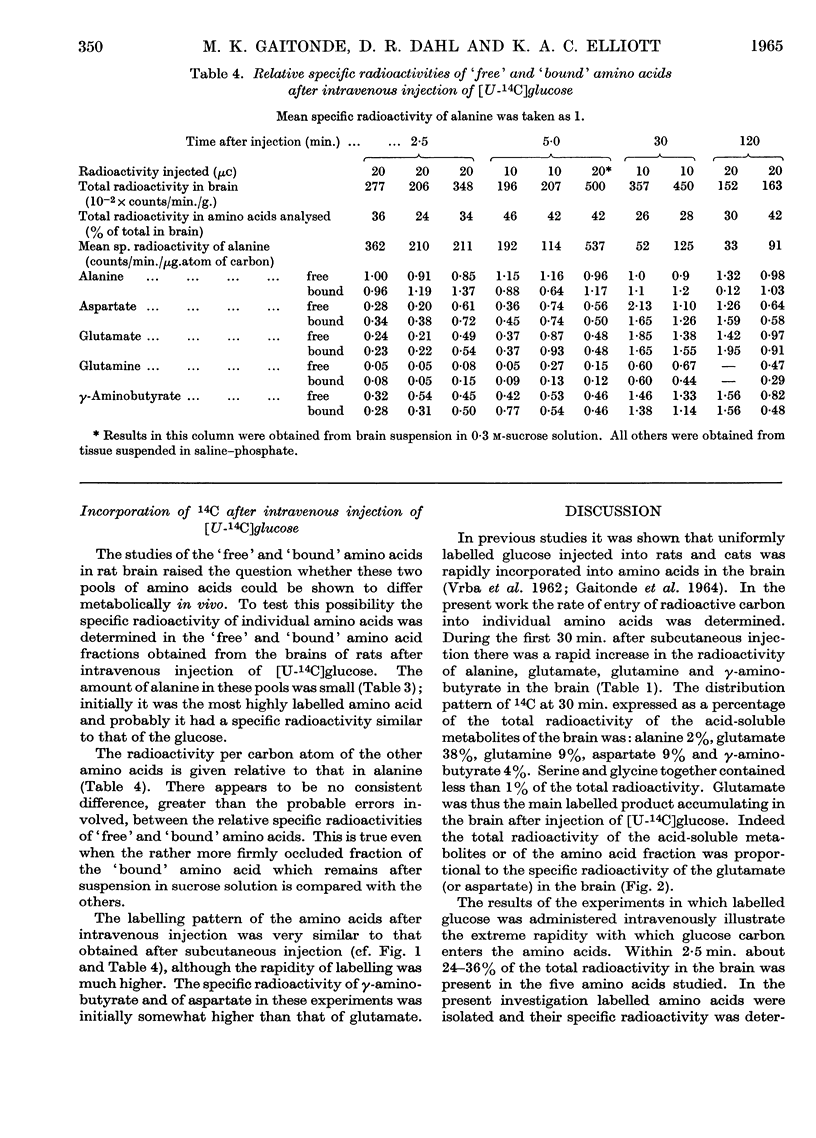
1. Measurements were made of the rate of incorporation of 14C from uniformly 14C-labelled glucose into individual amino acids of rat brain and liver. 2. At 2·5 min. after intravenous injection of uniformly 14C-labelled glucose, about 30% of the total radioactivity in the brain was present in the five amino acids studied. At 30 min. after subcutaneous injection the distribution of 14C in amino acids was: in brain, alanine 2%, γ-aminobutyrate 4%, aspartate 9%, glutamine 9% and glutamate 37% (total 69%); in liver, alanine 3%, aspartate 2·6%, glutamine 5·3% and glutamate 5·2% (total 18%). About 1% of the total radioactivity was in serine and glycine. 3. In both organs the specific radioactivity of alanine was initially higher than that of the other amino acids examined. The specific radioactivity of γ-aminobutyrate in the brain was about the same as or higher than that of glutamate. 4. Amino acids of the rat brain were separated into `free' and `bound' fractions from brain dispersions in saline (or sucrose) media. Definite differences in the specific activities of the `bound' and `free' forms were not apparent.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N., EMERY R. C., STREET B. W. A tissue homogenizer. Biochem J. 1960 Nov;77:326–327. doi: 10.1042/bj0770326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLWEIS C., MAGNES J. The uptake and oxidation of glucose by the perfused cat brain. J Neurochem. 1958;2(4):326–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANSELL G. B., RICHTER D. Evidence for a neutral proteinase in brain tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Jan;13(1):92–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERL S., TAKAGAKI G., CLARKE D. D., WAELSCH H. Carbon dioxide fixation in the brain. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2570–2573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSCH H., FUJIWARA E., KEER L. M. Metabolic patterns for glucose-1-C14 in tissues of tumor-bearing rats. Cancer Res. 1960 Jan;20:50–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREMER J. E. AMINO ACID METABOLISM IN RAT BRAIN STUDIED WITH 14C-LABELLED GLUCOSE. J Neurochem. 1964 Mar;11:165–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1964.tb06127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODT E., WALTHER J. B. Fluorescence of the crystalline lens and electroretinographic sensitivity determinations. Nature. 1958 Jan 24;181(4604):286–287. doi: 10.1038/181286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT K. A., VAN GELDER N. M. Occlusion and metabolism of gamma-aminobutyric acid by brain tissue. J Neurochem. 1958 Oct;3(1):28–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROHMAN C. E., ORTEN J. M., SMITH A. H. Chromatographic determination of the acids of the citric acid cycle in tissues. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):277–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAITONDE M. K., MARCHI S. A., RICHTER D. THE UTILIZATION OF GLUCOSE IN THE BRAIN AND OTHER ORGANS OF THE CAT. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Apr 14;160:124–136. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVELL R. A., ELLIOTT S. J., ELLIOTT K. A. THE GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID AND FACTOR I CONTENT OF BRAIN. J Neurochem. 1963 Jul;10:479–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb09850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCMILLAN P. J., MORTENSEN R. A. The metabolism of brain pyruvate and acetate in the tricarboxylic acid cycle. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:91–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLDAVE K., WINZLER R. J., PEARSON H. E. The incorporation in vitro of C14 into amino acids of control and virus-infected mouse brain. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jan;200(1):357–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTSUKI S., GEIGER A., GOMBOS G. The metabolic pattern of the brain in brain perfusion experiments in vivo. I. The quantitative significance of CO2 assimilation in the metabolism of the brain. J Neurochem. 1963 Jun;10:397–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb13667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS R. B., FLEXNER J. B., FLEXNER L. B. Biochemical and physiological differentiation during morphogenesis. XXIII. Further observations relating to the synthesis of amino acids and proteins by the cerebral cortex and liver of the mouse. J Neurochem. 1959 Apr;4(1):78–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1959.tb13176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACKS W. Cerebral metabolism of isotopic glucose in normal human subjects. J Appl Physiol. 1957 Jan;10(1):37–44. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.10.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VRBA R., GAITONDE M. K., RICHTER D. The conversion of glucose carbon into protein in the brain and other organs of the rat. J Neurochem. 1962 Sep-Oct;9:465–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1962.tb04199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


