Abstract
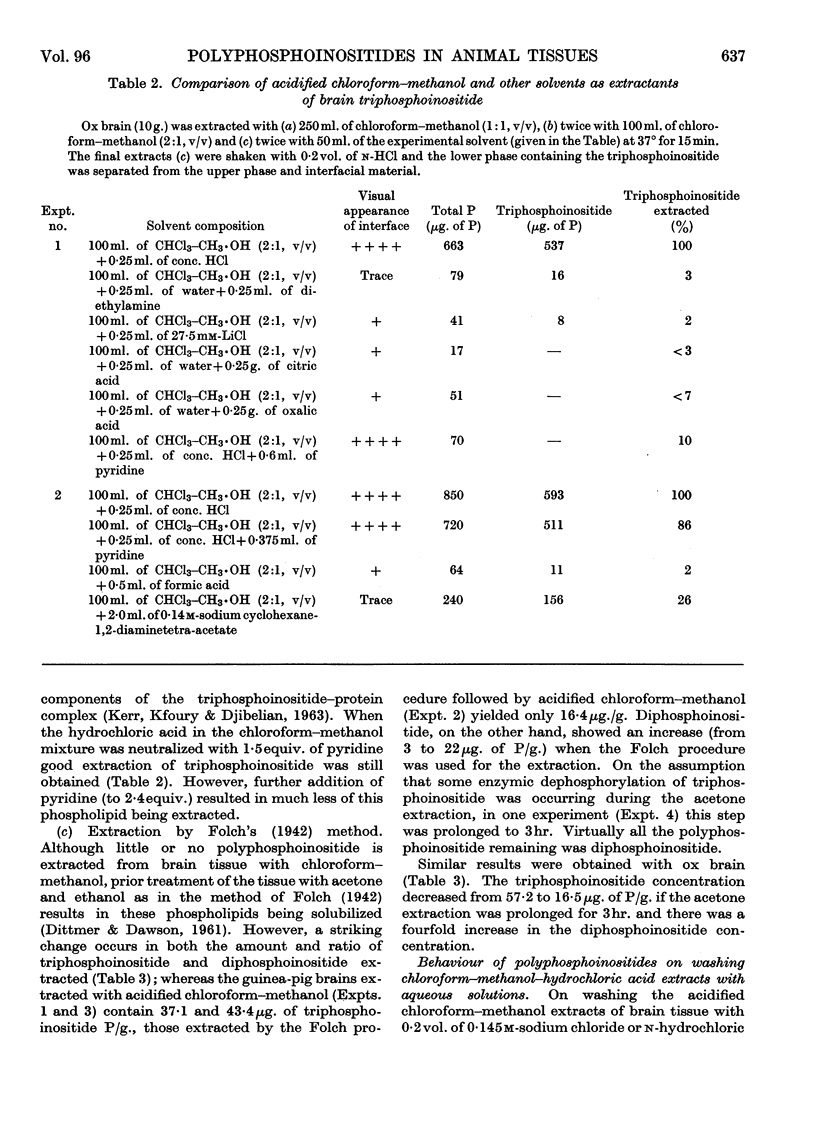
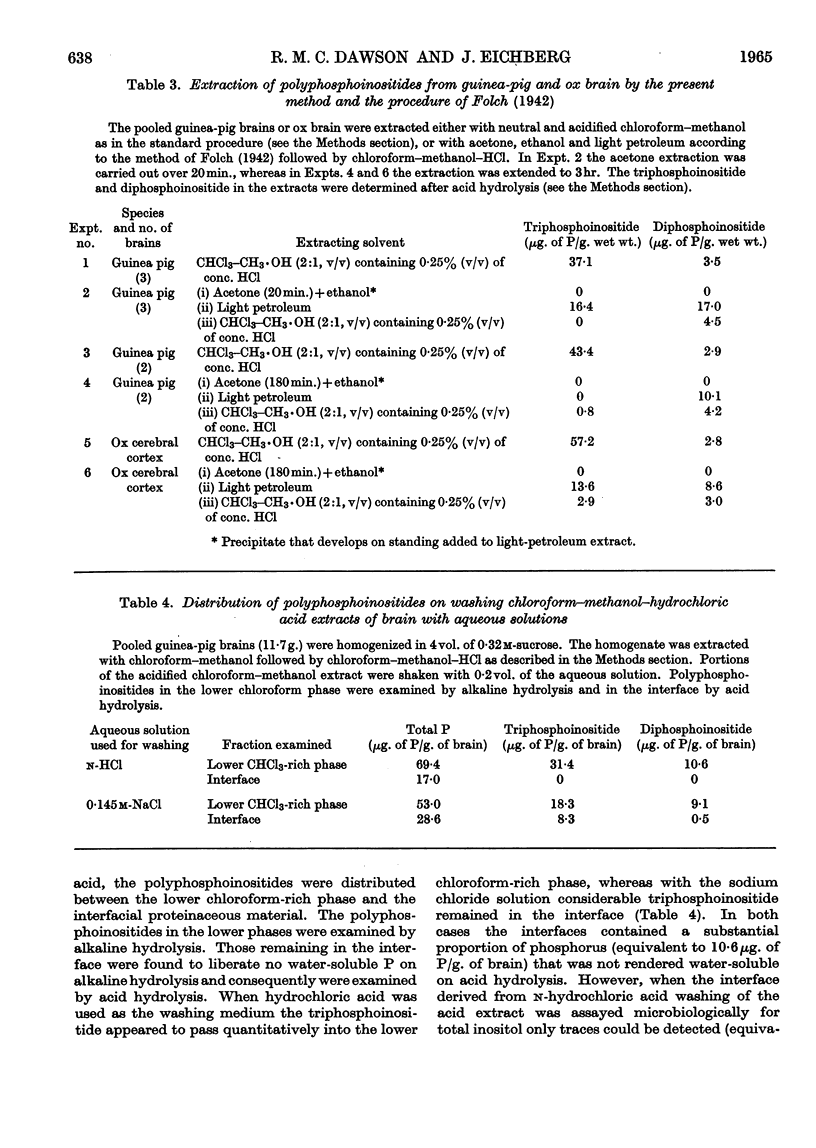
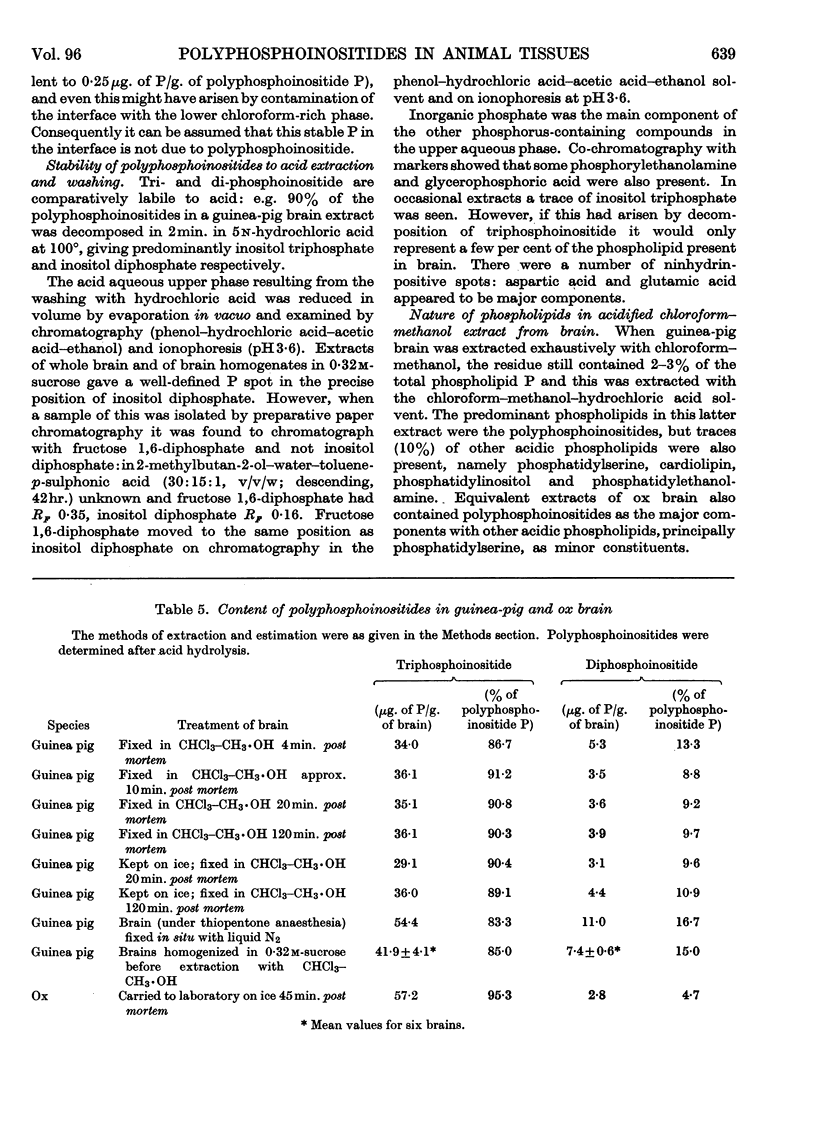
1. A method is presented for the determination of the di- and tri-phosphoinositide in animal tissues. 2. The polyphosphoinositides are quantitatively extracted into chloroform–methanol–hydrochloric acid solvent after a preliminary chloroform–methanol (1:1, v/v) extraction to remove the bulk of the other phospholipids. On washing this extract with n-hydrochloric acid the polyphosphoinositides pass completely into the lower chloroform-rich phase. Their concentrations in the lower phase are determined by chromatography on formaldehyde-treated paper or chromatography and ionophoresis of the acid hydrolysis products. 3. When guinea-pig brain is extracted by the method of Folch (1942), considerable hydrolysis of the triphosphoinositide and accumulation of diphosphoinositide occurs during the initial acetone extraction. 4. The tri- and di-phosphoinositide contents of rat and guinea-pig brain decline substantially within a few minutes after death. 5. The concentrations of tri- and di-phosphoinositide in rat brain are not changed by insulin-hypoglycaemia or electrical stimulation. 6. Examination of frozen rat tissues showed that the brain contained the highest concentration of polyphosphoinositides. Much smaller amounts are present in kidney, and only trace quantities in liver and lung. None could be detected in spleen, heart and skeletal muscle.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N., EMERY R. C., STREET B. W. A tissue homogenizer. Biochem J. 1960 Nov;77:326–327. doi: 10.1042/bj0770326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKERHOFF H., BALLOU C. E. Phosphate incorporation in brain phosphionositides. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:49–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPLING J. D., NIXON D. A. The inositol content of foetal blood and foetal fluids. J Physiol. 1954 Oct 28;126(1):71–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. C., RICHTER D. Effect of stimulation on the phosphate esters of the brain. Am J Physiol. 1950 Jan;160(1):203–211. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1949.160.1.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M., HEMINGTON N., DAVENPORT J. B. Improvements in the method of determining individual phospholipids in a complex mixture by successive chemical hydrolyses. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:497–501. doi: 10.1042/bj0840497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., DAWSON R. M. The isolation of a new lipid, triphosphoinositide, and monophosphoinositide from ox brain. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:535–540. doi: 10.1042/bj0810535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., DAWSON R. M. The isolation of a new lipid, triphosphoinositide, and monophosphoinositide from ox brain. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:535–540. doi: 10.1042/bj0810535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Thompson W. The triphosphoinositide phosphomonoesterase of brain tissue. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):244–250. doi: 10.1042/bj0910244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichberg J., Dawson R. M. Polyphosphoinositides in myelin. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):644–650. doi: 10.1042/bj0960644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLIARD T., HAWTHORNE J. N. RAPID LABELLING OF DIPHOSPHOINOSITIDE IN LIVER MITOCHONDRIA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 27;70:479–481. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90782-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M., SLAYMAN C. W., EICHBERG J., DAWSON R. M. THE ADENOSINE-TRIPHOSPHATASE SYSTEM RESPONSIBLE FOR CATION TRANSPORT IN ELECTRIC ORGAN: EXCLUSION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS AS INTERMEDIATES. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:692–699. doi: 10.1042/bj0940692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORHAMMER L., WAGNER H., RICHTER G. Zur papierchromatographischen Auftrennung von Phosphatiden. I. Biochem Z. 1959;331(3):155–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KFOURY G. A., KERR S. E. ON THE OCCURRENCE OF DIPHOSPHOINOSITOL IN THE LIPIDS OF LIVER AND PANCREAS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 5;84:391–403. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBARON F. N., HAUSER G., RUIZ E. E. The occurrence and metabolism of protein-bound phosphoinositides in several lipid-protein complexes from brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 2;60:338–349. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBARON F. N., LEES M. B. The effects of acetone, ethanol, or trichloroacetic acid on extraction of proteolipids and phosphatidopeptides from brain tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 2;60:412–414. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90419-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBARON F. N., MCDONALD C. P., RAMARAO B. S. THE AMOUNTS AND DISTRIBUTION OF FREE INOSITOL AND FREE AND PROTEIN-BOUND PHOSPHOINOSITIDES IN BRAIN TISSUES. J Neurochem. 1963 Oct;10:677–683. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb08925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBARON F. N. THE NATURE OF THE LINKAGE BETWEEN PHOSPHOINOSITIDES AND PROTEINS IN BRAIN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Dec 27;70:658–669. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90810-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANTIAGO-CALVO E., MULE S. J., HOKIN L. E. A new phosphoinositide containing four phosphates per inositol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 19;70:91–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90724-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone W. E. The effects of anaesthetics and of convulsants on the lactic acid content of the brain. Biochem J. 1938 Nov;32(11):1908–1918. doi: 10.1042/bj0321908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W., Dawson R. M. The hydrolysis of triphosphoinositide by extracts of ox brain. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):233–236. doi: 10.1042/bj0910233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]