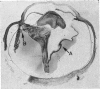
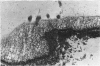
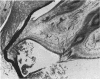
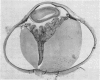
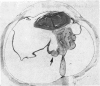
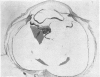
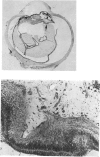
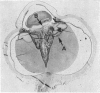
Full text
PDF


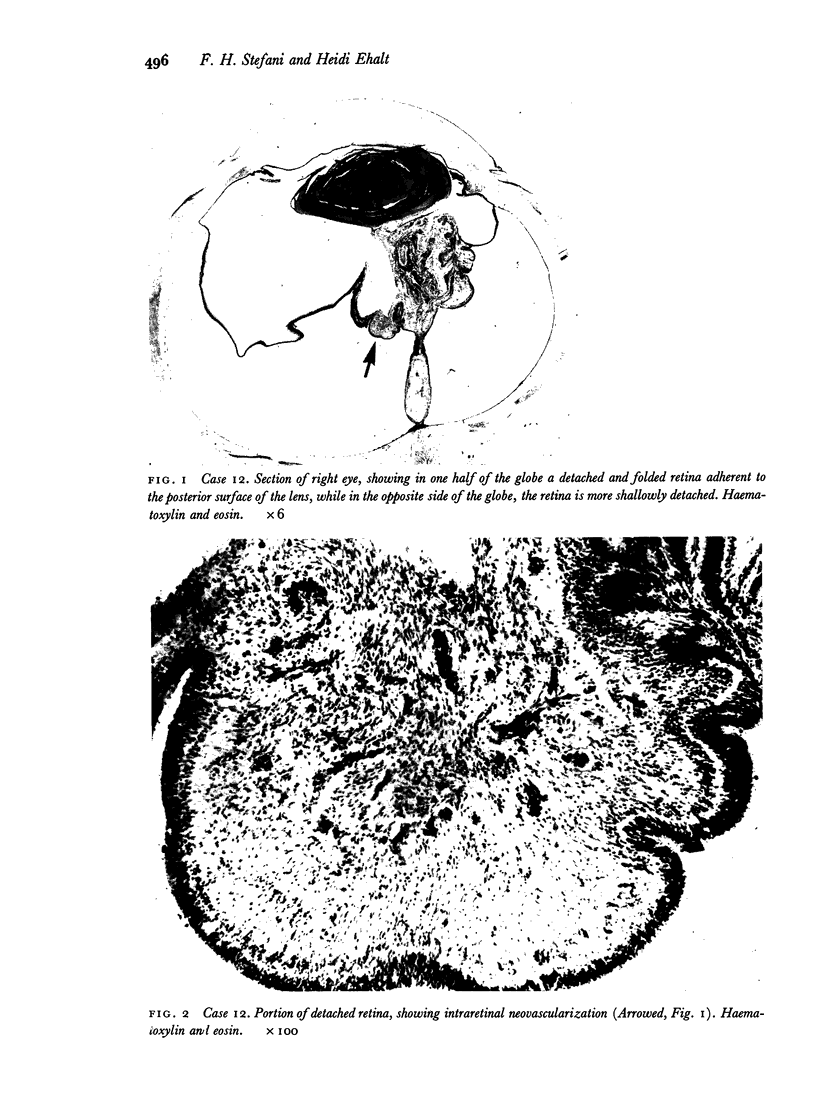
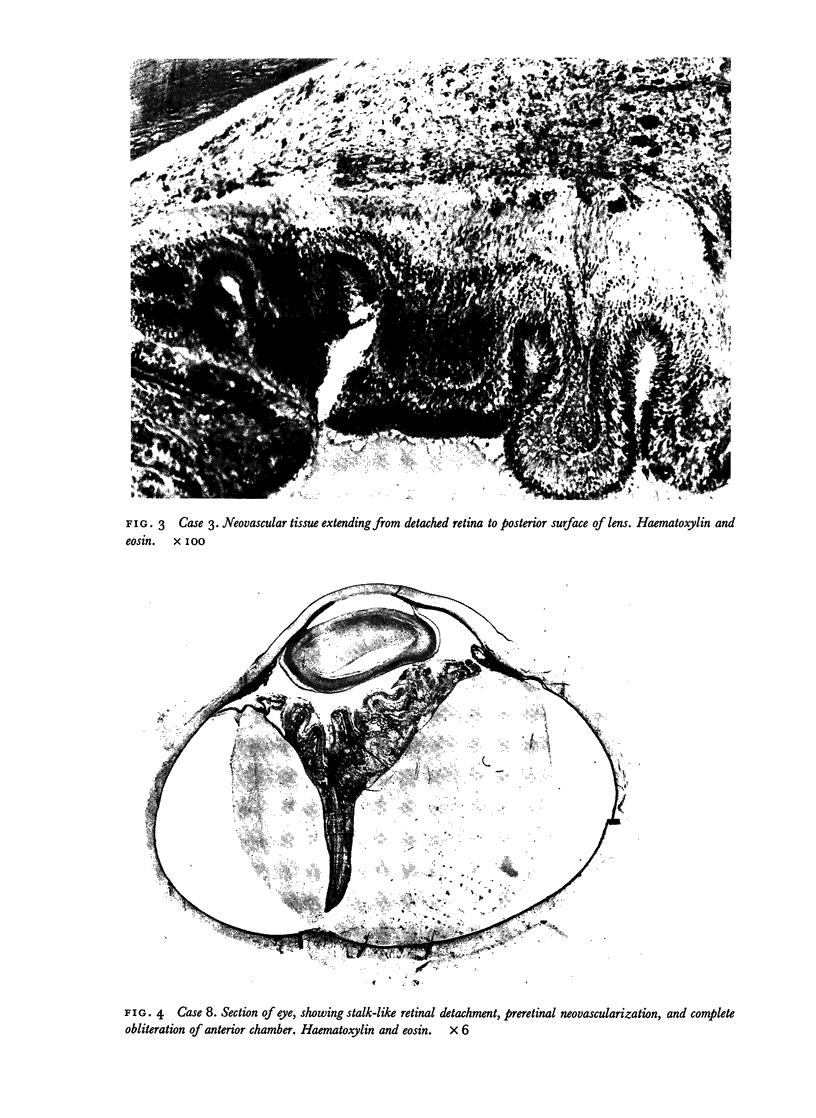


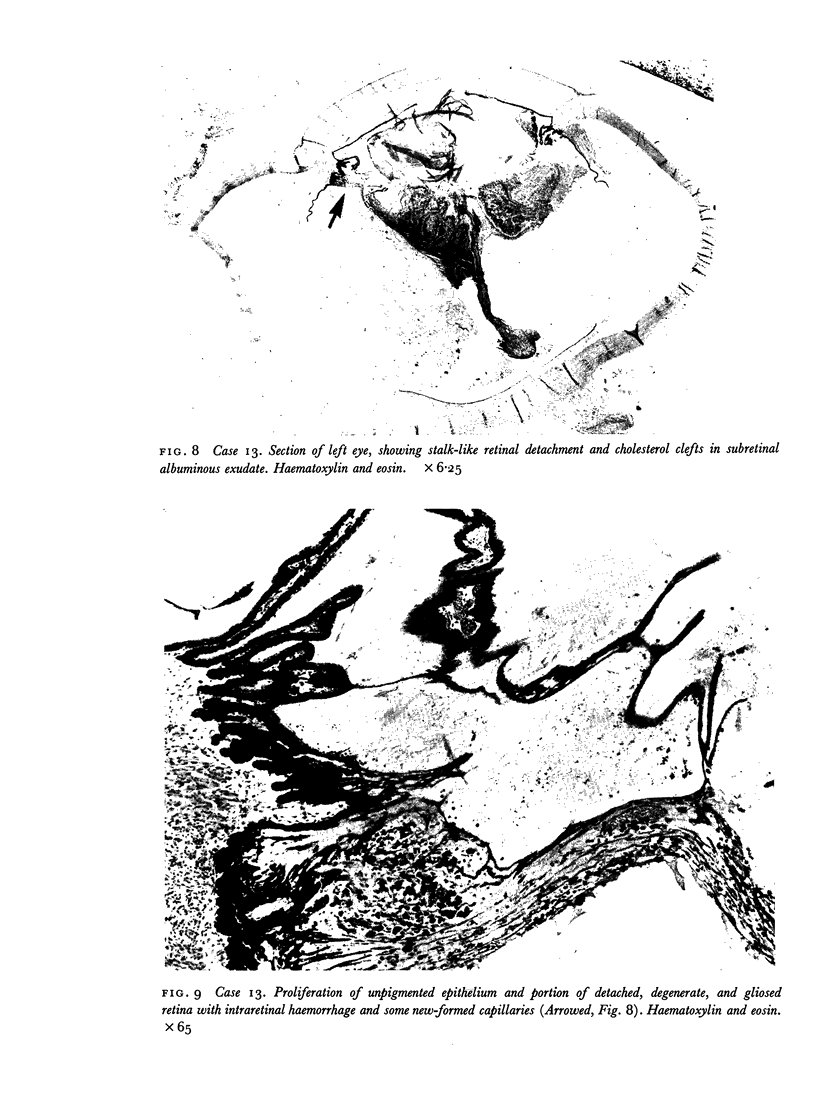


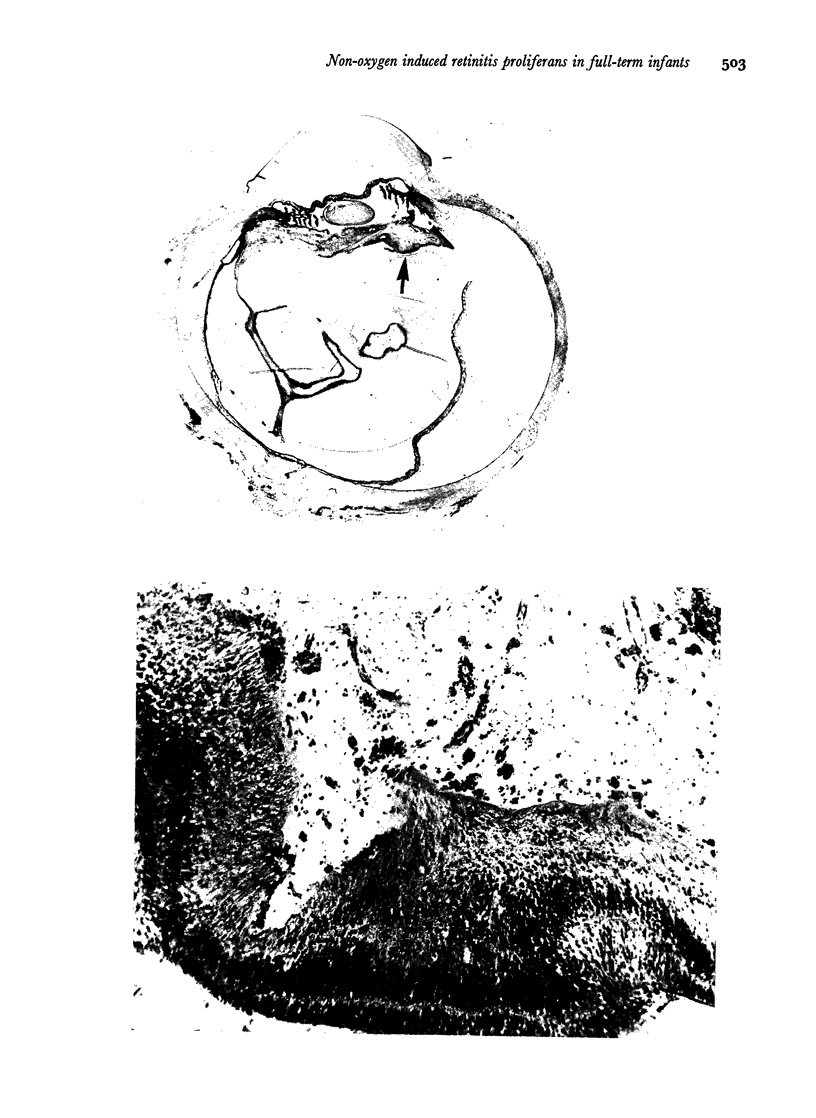






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHTON N. Neovascularization in ocular disease. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1961;81:145–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASHTON N., WARD B., SERPELL G. Role of oxygen in the genesis of retrolental fibroplasia; a preliminary report. Br J Ophthalmol. 1953 Sep;37(9):513–520. doi: 10.1136/bjo.37.9.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blodi F. C., Hunter W. S. Norrie's disease in North America. Doc Ophthalmol. 1969;26:434–450. doi: 10.1007/BF00944002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckner H. L. Retrolental fibroplasia--associated with intrauterine anoxia? Arch Ophthalmol. 1968 Oct;80(4):504–505. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1968.00980050506020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAPELLA J. A., KAUFMAN H. E., LILL F. J. HEREDITARY CATARACTS AND MICROPHTHALMIA. Am J Ophthalmol. 1963 Sep;56:454–458. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(63)93132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE J. G., COLE H. G. Incontinentia pigmenti associated with changes in the posterior chamber of the eye. Am J Ophthalmol. 1959 Mar;47(3):321–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUKE J. R., WOODS A. C. COATS'S DISEASE. II. STUDIES ON THE IDENTITY OF THE LIPIDS CONCERNED, AND THE PROBABLE ROLE OF MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES IN ITS PATHOGENESIS. Br J Ophthalmol. 1963 Jul;47:413–434. doi: 10.1136/bjo.47.7.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORRESTER R. M. THE SYNDROMES OF PSEUDOGLIOMA. Proc R Soc Med. 1963 Nov;56:994–995. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GYLLENSTEN L. J., HELLSTROM B. E. Experimental approach to the pathogenesis of retrolental fibroplasia. III. Changes in the eye induced by exposure of newborn mice to general hypoxia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1955 Jul;39(7):409–415. doi: 10.1136/bjo.39.7.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. S., ZIMMERMAN L. E. UNILATERAL RETINAL DYSPLASIA. Arch Ophthalmol. 1965 Jul;74:23–30. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1965.00970040025006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKENSEN G. Angeborene Netzhautfalten und Persistenz der Glaskörpergefässe. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd Augenarztl Fortbild. 1953;123(4):417–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAUMENEE A. E. Further observations on the pathogenesis of congenital glaucoma. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1962;60:140–146. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann I. CONGENITAL RETINAL FOLD. Br J Ophthalmol. 1935 Dec;19(12):641–658. doi: 10.1136/bjo.19.12.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushin A., Morgan G. Ocular injury in the battered baby syndrome. Report of two cases. Br J Ophthalmol. 1971 May;55(5):343–347. doi: 10.1136/bjo.55.5.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATZ A. Retrolental fibroplasia; experimental studies. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1955 Jan-Feb;59(1):25-34; discussion, 40-1. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT J. G., FRIEDMANN A. I., CHITTERS M., PEPLER W. J. Ocular changes in the Bloch-Sulzberger syndrome (Incontinentia pigmenti) Br J Ophthalmol. 1955 May;39(5):276–282. doi: 10.1136/bjo.39.5.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNSWORTH A. C. Retrolental fibroplasia or ophthalmic dysplasia of premature infants. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1949;47:738–771. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISE G. N. Factors influencing retinal new vessel formation. Am J Ophthalmol. 1961 Nov;52:637–650. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(61)90149-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburg M. Norrie's disease. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1965;85:391–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]