Abstract
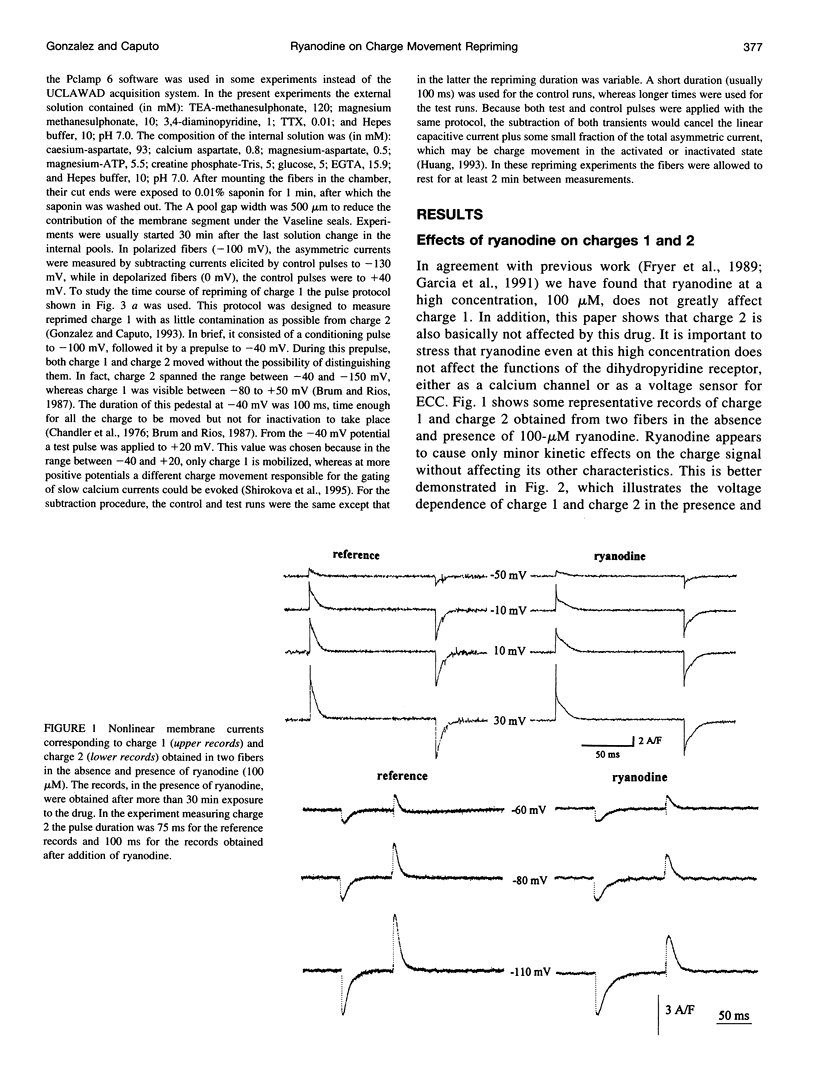
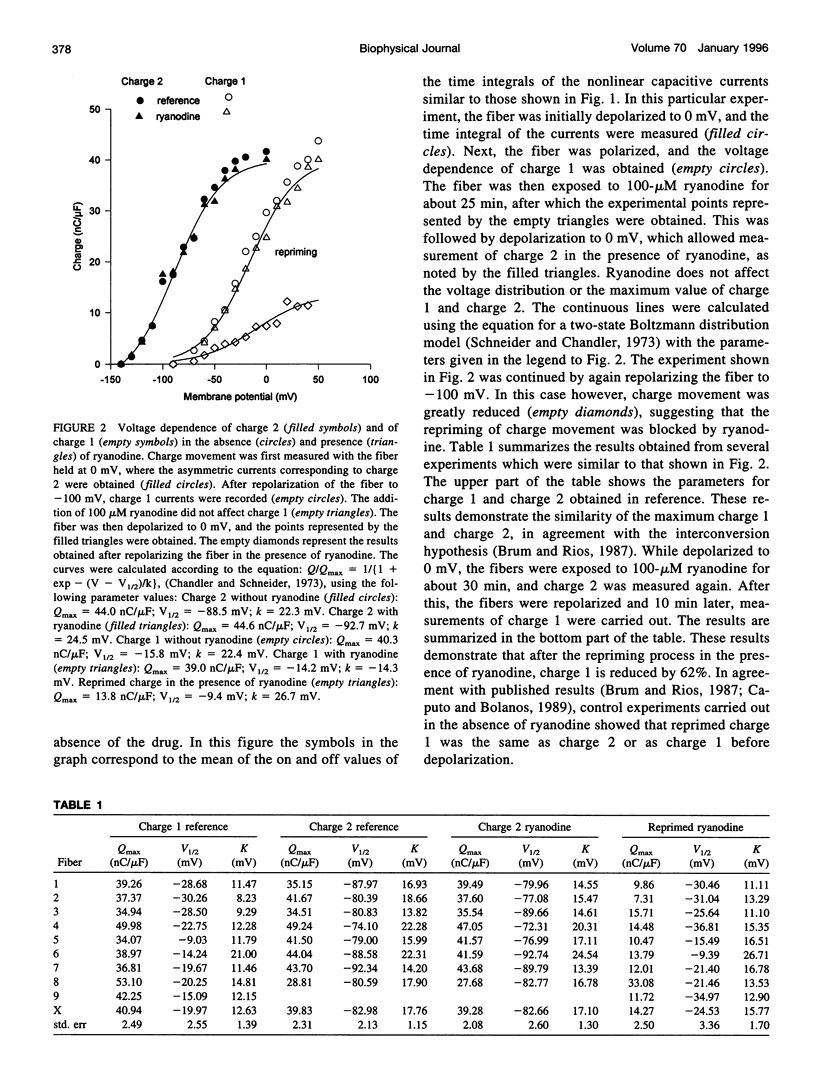
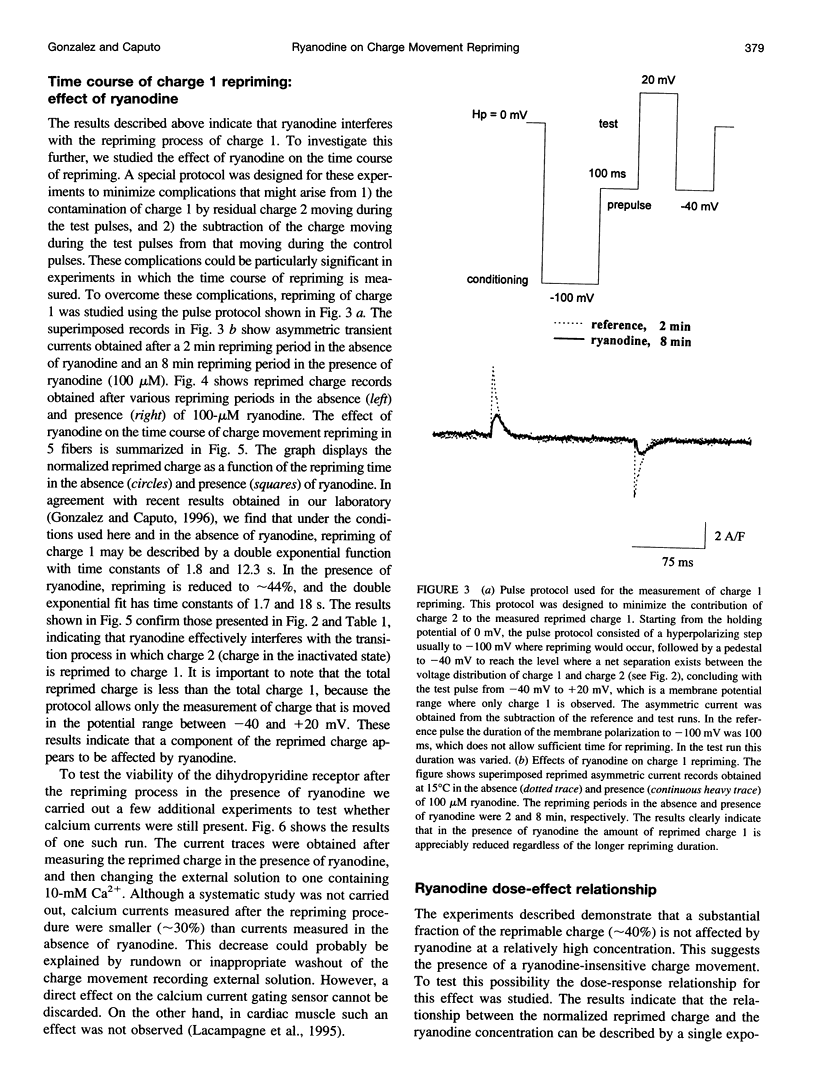
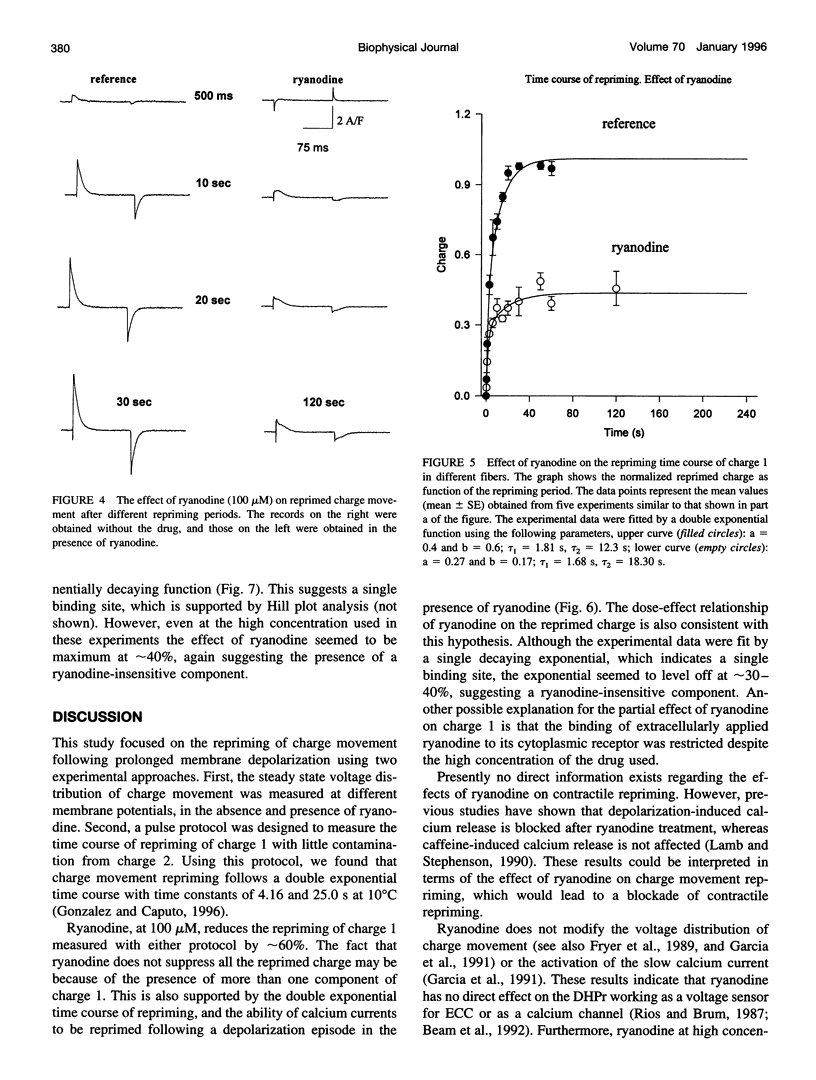
Cut twitch muscle fibers mounted in a triple Vaseline-gap chamber were used to study the effects of ryanodine on intramembranous charge movement, and in particular on the repriming of charge 1. Charge 1 repriming was measured either under steady-state conditions or by using a pulse protocol designed to study the time course of repriming. This protocol consisted of repolarizing the fibers to -100 mV from a holding potential of 0 mV, and then measuring the reprimed charge moving in the potential range between -40 and +20 mV. Ryanodine at a high concentration (100 microM) did not affect the maximum amount of movable charge 1 and charge 2, or their voltage dependence. This indicates that the alkaloid does not interact with the voltage sensor molecules. However, ryanodine did reduce the amount of reprimed charge 1 by approximately 60% suggesting the possibility of a retrograde interaction between ryanodine receptors and voltage sensors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Charge movement in the membrane of striated muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):339–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F. Charge movement and mechanical repriming in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):361–388. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam K. G., Adams B. A., Niidome T., Numa S., Tanabe T. Function of a truncated dihydropyridine receptor as both voltage sensor and calcium channel. Nature. 1992 Nov 12;360(6400):169–171. doi: 10.1038/360169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Stiffel V. M. Ratio of ryanodine to dihydropyridine receptors in cardiac and skeletal muscle and implications for E-C coupling. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jun;264(6 Pt 1):C1587–C1593. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.6.C1587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block B. A., Imagawa T., Campbell K. P., Franzini-Armstrong C. Structural evidence for direct interaction between the molecular components of the transverse tubule/sarcoplasmic reticulum junction in skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2587–2600. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt N. R., Caswell A. H., Wen S. R., Talvenheimo J. A. Molecular interactions of the junctional foot protein and dihydropyridine receptor in skeletal muscle triads. J Membr Biol. 1990 Feb;113(3):237–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01870075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brum G., Rios E. Intramembrane charge movement in frog skeletal muscle fibres. Properties of charge 2. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:489–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C., Bolaños P. Effects of D-600 on intramembrane charge movement of polarized and depolarized frog muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jul;94(1):43–64. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. Effects of glycerol treatment and maintained depolarization on charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):285–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Inui M. Biochemistry and biophysics of excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:333–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., Jaimovich E., Delpont E., Lazdunski M. [3H]nitrendipine receptors in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6086–6092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryer M. W., Lamb G. D., Neering I. R. The action of ryanodine on rat fast and slow intact skeletal muscles. J Physiol. 1989 Jul;414:399–413. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García J., Avila-Sakar A. J., Stefani E. Differential effects of ryanodine and tetracaine on charge movement and calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1991;440:403–417. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González A., Ríos E. Perchlorate enhances transmission in skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Sep;102(3):373–421. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Campbell D. T. An improved vaseline gap voltage clamp for skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):265–293. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Charge inactivation in the membrane of intact frog striated muscle fibers. J Physiol. 1993 Aug;468:107–124. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Purification of the ryanodine receptor and identity with feet structures of junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1740–1747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb G. D., Posterino G. S., Stephenson D. G. Effects of heparin on excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle toad and rat. J Physiol. 1994 Jan 15;474(2):319–329. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb G. D., Stephenson D. G. Control of calcium release and the effect of ryanodine in skinned muscle fibres of the toad. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:519–542. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Xu L., Meissner G. Activation of the skeletal muscle calcium release channel by a cytoplasmic loop of the dihydropyridine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6511–6516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Gottschalk G., Kovács L., Fuxreiter M. How perchlorate improves excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):247–249. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84346-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Anderson K., Shirokov R., Levis R., González A., Karhanek M., Hosey M. M., Meissner G., Ríos E. Effects of perchlorate on the molecules of excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal and cardiac muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Sep;102(3):423–448. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty I., Robert M., Villaz M., De Jongh K., Lai Y., Catterall W. A., Ronjat M. Biochemical evidence for a complex involving dihydropyridine receptor and ryanodine receptor in triad junctions of skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2270–2274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., el-Hashem A. Ryanodine as a functional probe of the skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release channel. Mol Cell Biochem. 1992 Sep 8;114(1-2):119–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00240306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rios E., Brum G. Involvement of dihydropyridine receptors in excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):717–720. doi: 10.1038/325717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Karhanek M., Ma J., González A. An allosteric model of the molecular interactions of excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Sep;102(3):449–481. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.3.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Pizarro G. Voltage sensor of excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jul;71(3):849–908. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.3.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirokova N., González A., Ma J., Shirokov R., Ríos E. Properties and roles of an intramembranous charge mobilized at high voltages in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1995 Jul 15;486(Pt 2):385–400. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Beam K. G., Adams B. A., Niidome T., Numa S. Regions of the skeletal muscle dihydropyridine receptor critical for excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):567–569. doi: 10.1038/346567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


