Abstract
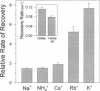
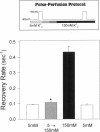
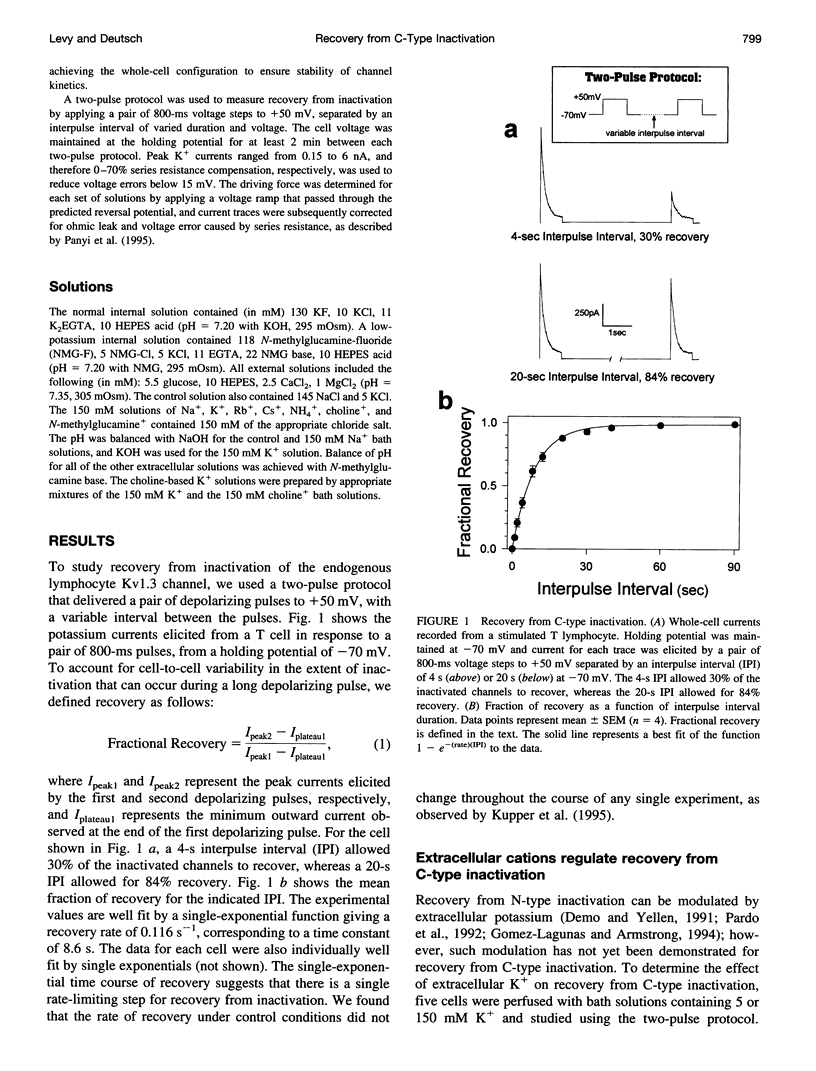
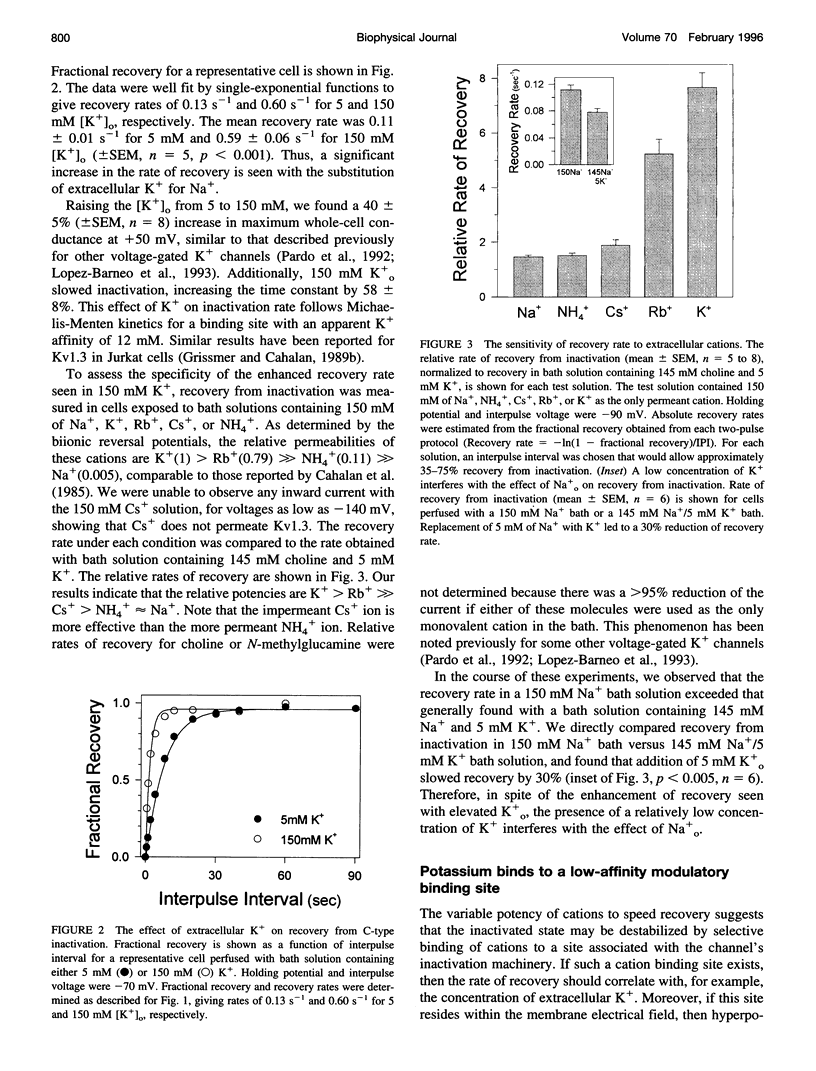
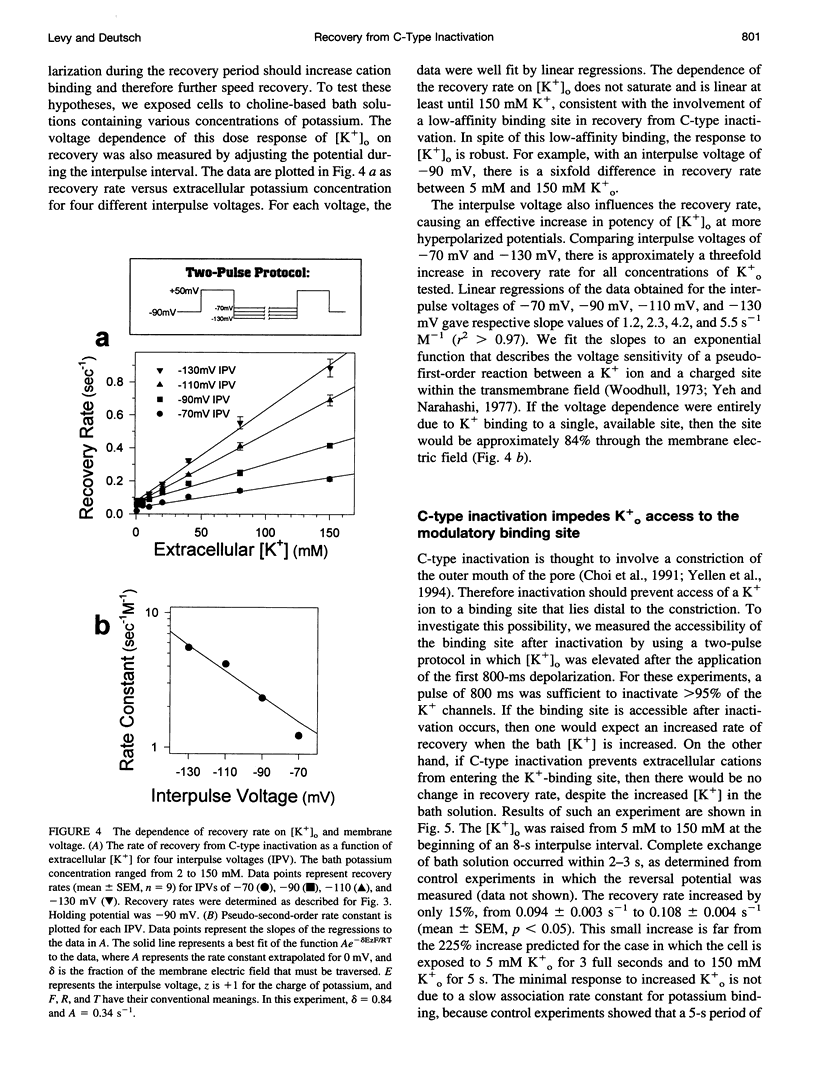
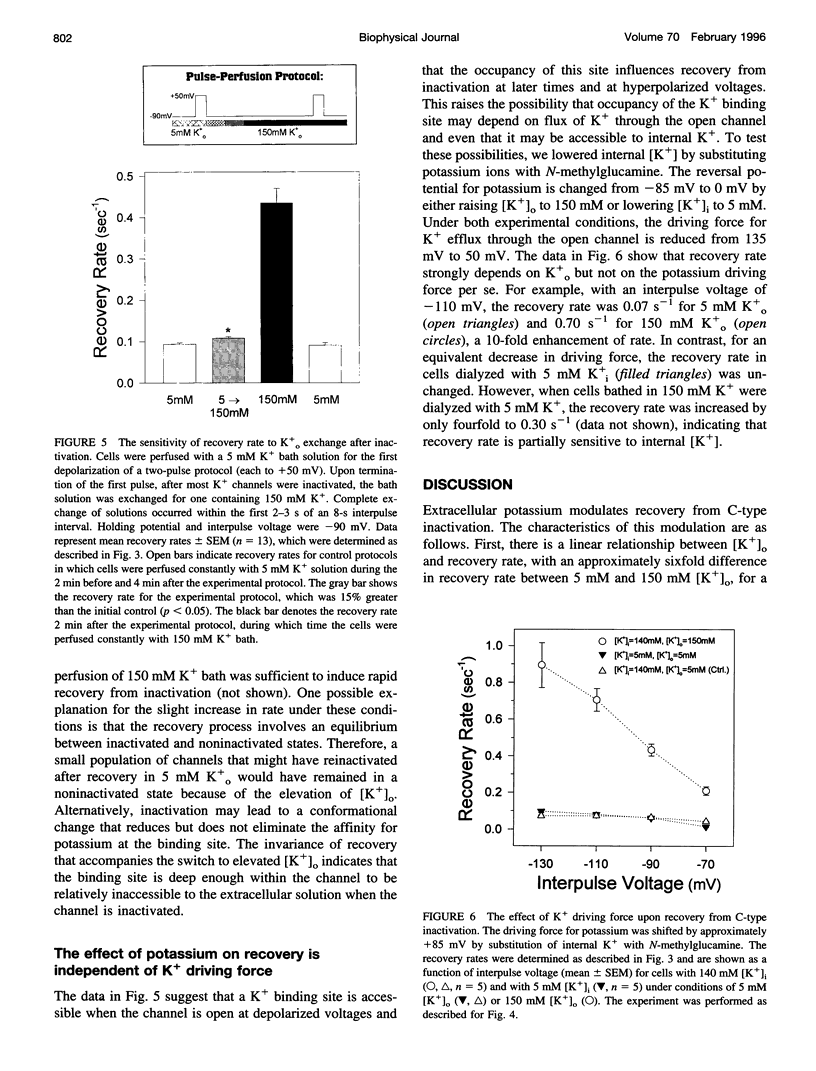
Extracellular potassium modulates recovery from C-type inactivation of Kv1.3 in human T lymphocytes. The results of whole-cell patch clamp recordings show that there is a linear increase in recovery rate with increasing [K+]o. An increase from 5 to 150 mM K+o causes a sixfold acceleration of recovery rate at a holding potential of -90 mV. Our results suggest that 1) a low-affinity K+ binding site is involved in recovery, 2) the rate of recovery increases with hyperpolarization, 3) potassium must bind to the channel before inactivation to speed its recovery, and 4) recovery rate depends on external [K+] but not on the magnitude of the driving force through open channels. We present a model in which a bound K+ ion destabilizes the inactivated state to increase the rate of recovery of C-type inactivation, thereby providing a mechanism for autoregulation of K+ channel activity. The ability of K+ to regulate its own conductance may play a role in modulating voltage-dependent immune function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):413–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attali B., Romey G., Honoré E., Schmid-Alliana A., Mattéi M. G., Lesage F., Ricard P., Barhanin J., Lazdunski M. Cloning, functional expression, and regulation of two K+ channels in human T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8650–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Chandy K. G., DeCoursey T. E., Gupta S. A voltage-gated potassium channel in human T lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:197–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. L., Aldrich R. W., Yellen G. Tetraethylammonium blockade distinguishes two inactivation mechanisms in voltage-activated K+ channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5092–5095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCoursey T. E., Chandy K. G., Gupta S., Cahalan M. D. Voltage-gated K+ channels in human T lymphocytes: a role in mitogenesis? Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):465–468. doi: 10.1038/307465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demo S. D., Yellen G. The inactivation gate of the Shaker K+ channel behaves like an open-channel blocker. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):743–753. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch C., Krause D., Lee S. C. Voltage-gated potassium conductance in human T lymphocytes stimulated with phorbol ester. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:405–423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch C., Price M., Lee S., King V. F., Garcia M. L. Characterization of high affinity binding sites for charybdotoxin in human T lymphocytes. Evidence for association with the voltage-gated K+ channel. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3668–3674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman B. D., Price M. A., Deutsch C. J. Evidence for voltage modulation of IL-2 production in mitogen-stimulated human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 15;149(12):3784–3794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Lagunas F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation in ShakerB K+ channels: a test for the number of inactivating particles on each channel. Biophys J. 1995 Jan;68(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80162-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Dixon S. J. Ion transport, membrane potential, and cytoplasmic pH in lymphocytes: changes during activation. Physiol Rev. 1989 Apr;69(2):417–481. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.2.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grissmer S., Cahalan M. D. Divalent ion trapping inside potassium channels of human T lymphocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Apr;93(4):609–630. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.4.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grissmer S., Cahalan M. TEA prevents inactivation while blocking open K+ channels in human T lymphocytes. Biophys J. 1989 Jan;55(1):203–206. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82793-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Lagunas F., Armstrong C. M. The relation between ion permeation and recovery from inactivation of ShakerB K+ channels. Biophys J. 1994 Nov;67(5):1806–1815. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80662-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen A. J., Zeuthen T. Extracellular ion concentrations during spreading depression and ischemia in the rat brain cortex. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Dec;113(4):437–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heginbotham L., MacKinnon R. The aromatic binding site for tetraethylammonium ion on potassium channels. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90276-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Biophysical and molecular mechanisms of Shaker potassium channel inactivation. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):533–538. doi: 10.1126/science.2122519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Two types of inactivation in Shaker K+ channels: effects of alterations in the carboxy-terminal region. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):547–556. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90367-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Structural elements involved in specific K+ channel functions. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:537–555. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.002541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupper J., Bowlby M. R., Marom S., Levitan I. B. Intracellular and extracellular amino acids that influence C-type inactivation and its modulation in a voltage-dependent potassium channel. Pflugers Arch. 1995 May;430(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00373833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Deutsch C. Temperature dependence of K(+)-channel properties in human T lymphocytes. Biophys J. 1990 Jan;57(1):49–62. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82506-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. S., Boltz R. C., Blake J. T., Nguyen M., Talento A., Fischer P. A., Springer M. S., Sigal N. H., Slaughter R. S., Garcia M. L. Voltage-gated potassium channels regulate calcium-dependent pathways involved in human T lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. 1993 Mar 1;177(3):637–645. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Barneo J., Hoshi T., Heinemann S. H., Aldrich R. W. Effects of external cations and mutations in the pore region on C-type inactivation of Shaker potassium channels. Receptors Channels. 1993;1(1):61–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Aldrich R. W., Lee A. W. Functional stoichiometry of Shaker potassium channel inactivation. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):757–759. doi: 10.1126/science.7694359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R. Determination of the subunit stoichiometry of a voltage-activated potassium channel. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):232–235. doi: 10.1038/350232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marom S., Levitan I. B. State-dependent inactivation of the Kv3 potassium channel. Biophys J. 1994 Aug;67(2):579–589. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80517-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Deutsch C. K channels in T lymphocytes: a patch clamp study using monoclonal antibody adhesion. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):468–471. doi: 10.1038/307468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleson D. R., DeFelice L. J., Donahoe R. M. A comparison of K+ channel characteristics in human T cells: perforated-patch versus whole-cell recording techniques. J Membr Biol. 1993 Mar;132(3):229–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00235740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyi G., Sheng Z., Deutsch C. C-type inactivation of a voltage-gated K+ channel occurs by a cooperative mechanism. Biophys J. 1995 Sep;69(3):896–903. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79963-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardo L. A., Heinemann S. H., Terlau H., Ludewig U., Lorra C., Pongs O., Stühmer W. Extracellular K+ specifically modulates a rat brain K+ channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2466–2470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver I. A. Measurement of pH and ionic composition of pericellular sites. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jul 17;271(912):261–272. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu L., Santarelli V., Deutsch C. Truncated K+ channel DNA sequences specifically suppress lymphocyte K+ channel gene expression. Biophys J. 1995 Jan;68(1):147–156. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80169-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Narahashi T. Kinetic analysis of pancuronium interaction with sodium channels in squid axon membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Mar;69(3):293–323. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G., Sodickson D., Chen T. Y., Jurman M. E. An engineered cysteine in the external mouth of a K+ channel allows inactivation to be modulated by metal binding. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):1068–1075. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80888-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Voltage-dependent gating of Shaker A-type potassium channels in Drosophila muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jan;95(1):29–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]