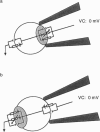
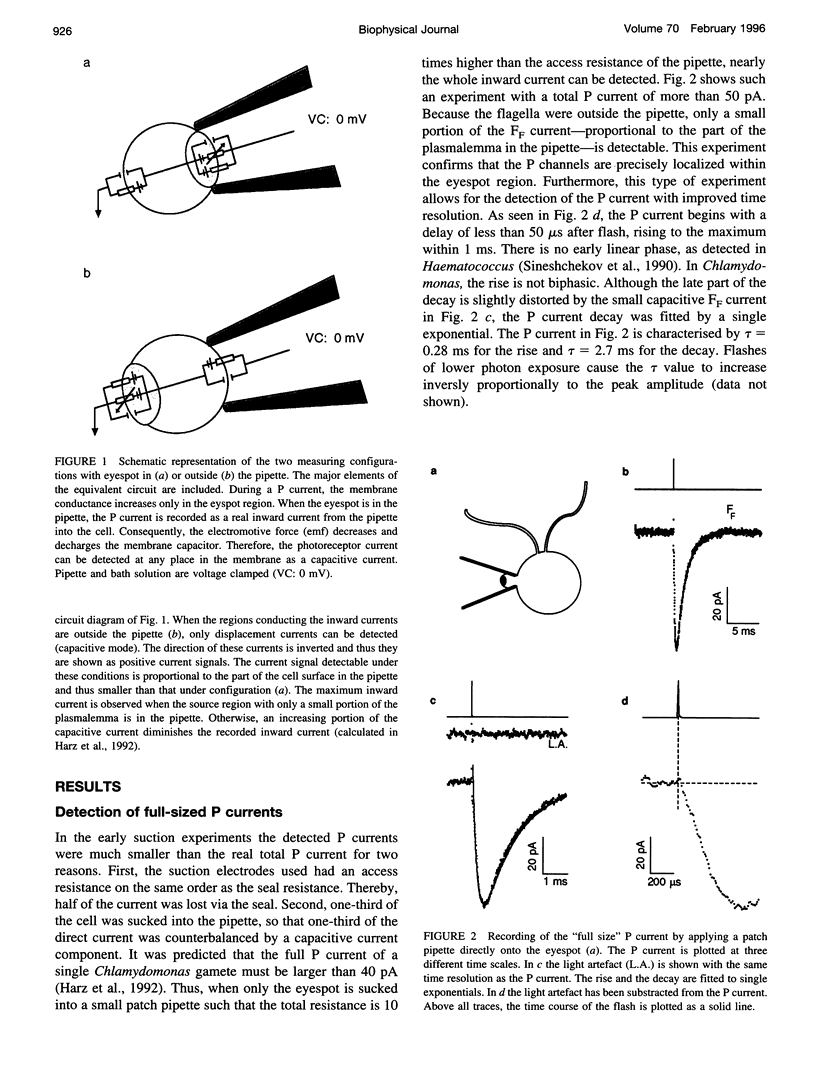
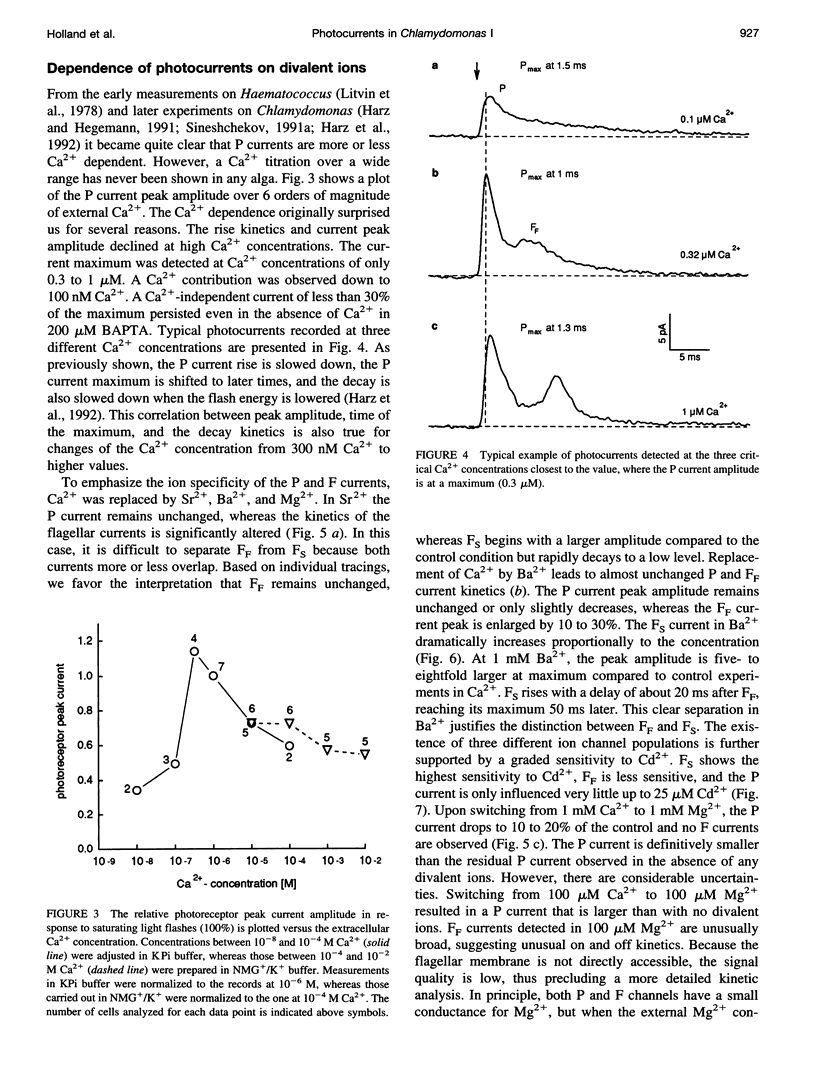
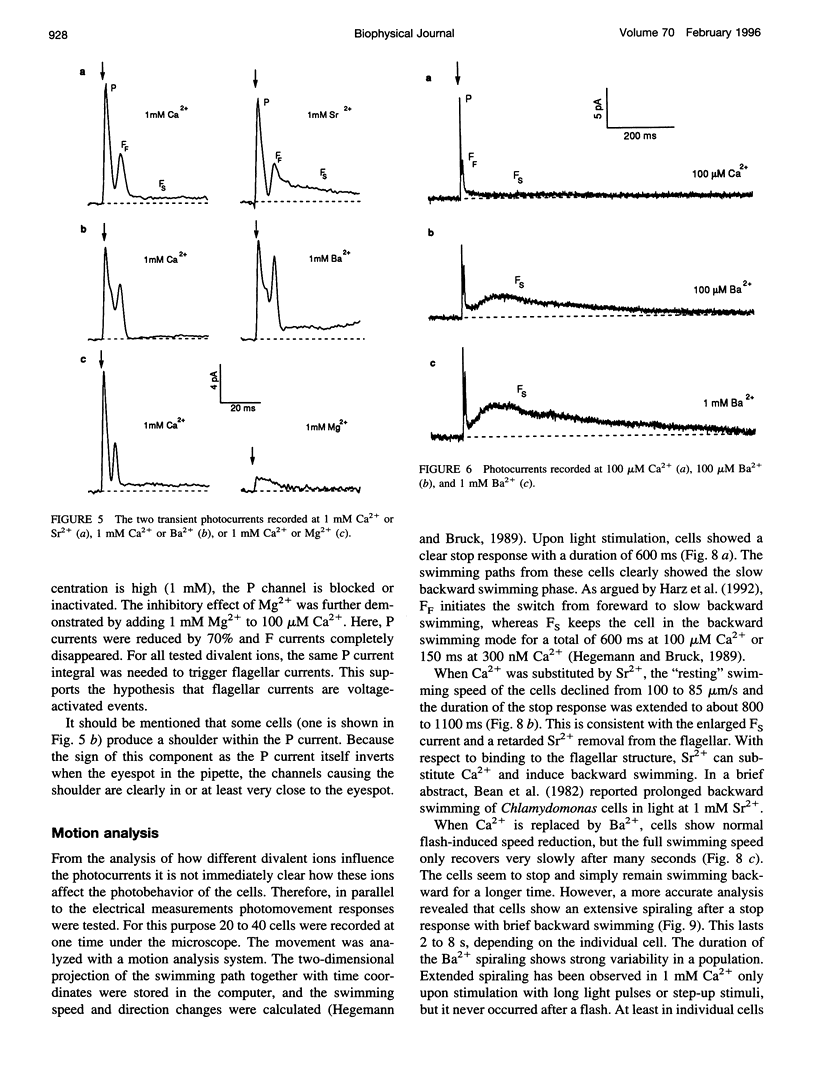
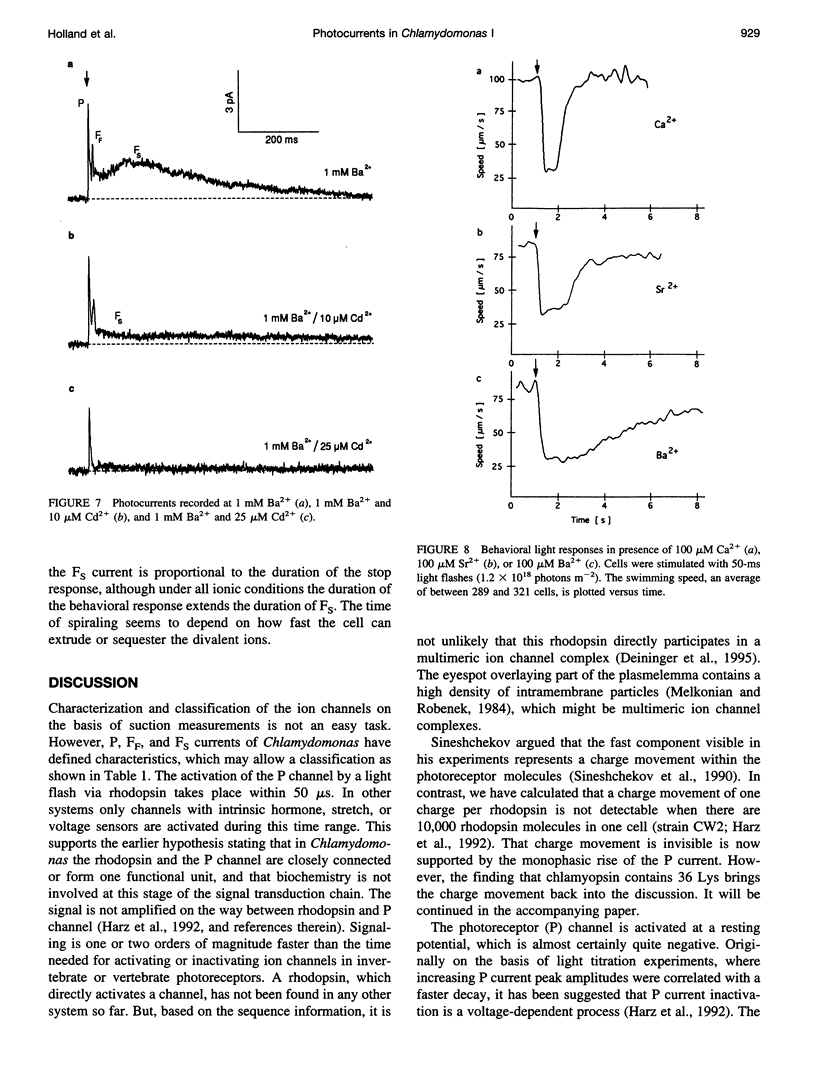
Abstract
In the green alga Chlamydomonas chlamyrhodopsin fulfills its role as a light sensor by absorbing light and activating photoreceptor channels within the eyespot area. At intense light stimuli, the photoreceptor (P) current triggers a fast and a slow flagellar current that finally leads to backward swimming (stop response). Here we report about probing the photoreceptor current directly at the eyespot. This allows the detection of the whole P current with a size of above 50 pA. The P current appears with a delay of less than 50 microseconds, suggesting that rhodopsin and the P channel are closely coupled or form one ion channel complex. The Ca2+ dependence of the P current has been demonstrated with the established suction technique in a capacitive mode. The P current shows the maximum amplitude at only 300 nM Ca2+, and it gradually declines at higher Ca2+. In addition to Ca2+, the photoreceptor and the fast flagellar current can be carried by Sr2+ and Ba2+. Mg2+ is conducted less efficiently and at high concentrations blocks the photoreceptor channel. A motion analysis of the cells shows that only Ca2+ and Sr2+ can induce physiological stop responses, whereas the large Ba2+ currents cause abnormal long-lasting cell spiraling.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck C., Uhl R. On the localization of voltage-sensitive calcium channels in the flagella of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(5):1119–1125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.5.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann M., Hegemann P. In vitro identification of rhodopsin in the green alga Chlamydomonas. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 16;30(15):3692–3697. doi: 10.1021/bi00229a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessen M., Fay R. B., Witman G. B. Calcium control of waveform in isolated flagellar axonemes of Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):446–455. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster K. W., Saranak J., Patel N., Zarilli G., Okabe M., Kline T., Nakanishi K. A rhodopsin is the functional photoreceptor for phototaxis in the unicellular eukaryote Chlamydomonas. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):756–759. doi: 10.1038/311756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegemann P., Gärtner W., Uhl R. All-trans retinal constitutes the functional chromophore in Chlamydomonas rhodopsin. Biophys J. 1991 Dec;60(6):1477–1489. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82183-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya R., Witman G. B. Submicromolar levels of calcium control the balance of beating between the two flagella in demembranated models of Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):97–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson M. A., Zacks D. N., Derguini F., Nakanishi K., Spudich J. L. Retinal analog restoration of photophobic responses in a blind Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutant. Evidence for an archaebacterial like chromophore in a eukaryotic rhodopsin. Biophys J. 1991 Dec;60(6):1490–1498. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82184-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litvin F. F., Sineshchekov O. A., Sineshchekov V. A. Photoreceptor electric potential in the phototaxis of the alga Haematococcus pluvialis. Nature. 1978 Feb 2;271(5644):476–478. doi: 10.1038/271476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols K. M., Rikmenspoel R. Control of flagellar motion in Chlamydomonas and Euglena by mechanical microinjection of Mg2+ and Ca2+ and by electric current injection. J Cell Sci. 1978 Feb;29:233–247. doi: 10.1242/jcs.29.1.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. A., Eckert R. Calcium couples flagellar reversal to photostimulation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):713–715. doi: 10.1038/262713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sineshchekov O. A., Litvin F. F., Keszthelyi L. Two components of photoreceptor potential in phototaxis of the flagellated green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. Biophys J. 1990 Jan;57(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82504-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Yoshihara K., Watanabe M., Kubota M., Johnson R., Derguini F., Nakanishi K. Photoisomerization of retinal at 13-ene is important for phototaxis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: simultaneous measurements of phototactic and photophobic responses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):1273–1279. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl R., Hegemann P. Probing visual transduction in a plant cell: Optical recording of rhodopsin-induced structural changes from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biophys J. 1990 Nov;58(5):1295–1302. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82469-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B. Chlamydomonas phototaxis. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;3(11):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90091-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan B., Nakanishi K., Spudich J. L. Mechanism of activation of sensory rhodopsin I: evidence for a steric trigger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9412–9416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Calcium channels. Structure and selectivity. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):109–110. doi: 10.1038/366109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacks D. N., Derguini F., Nakanishi K., Spudich J. L. Comparative study of phototactic and photophobic receptor chromophore properties in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):508–518. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81067-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]