Abstract
We have investigated the effect of different zwitterionic compounds on DNA precipitation induced by spermine4+. Glycine, beta-alanine, 4-aminobutyric acid, and 6-aminocaproic acid have shown an increasing capacity to attenuate DNA precipitation. This protection effect has been correlated with the dielectric constant increase of their corresponding solutions. Calculations based on these experimental data and counter-ion condensation theory have confirmed the importance of this parameter for DNA-ion interactions and precipitation mechanisms. We have also observed a resolubilization of DNA in the presence of 6-aminocaproic acid at high spermine4+ concentration and in the presence of glycine at high spermidine3+ concentration. This could be explained by an increase of screening effect with polyamine concentration.
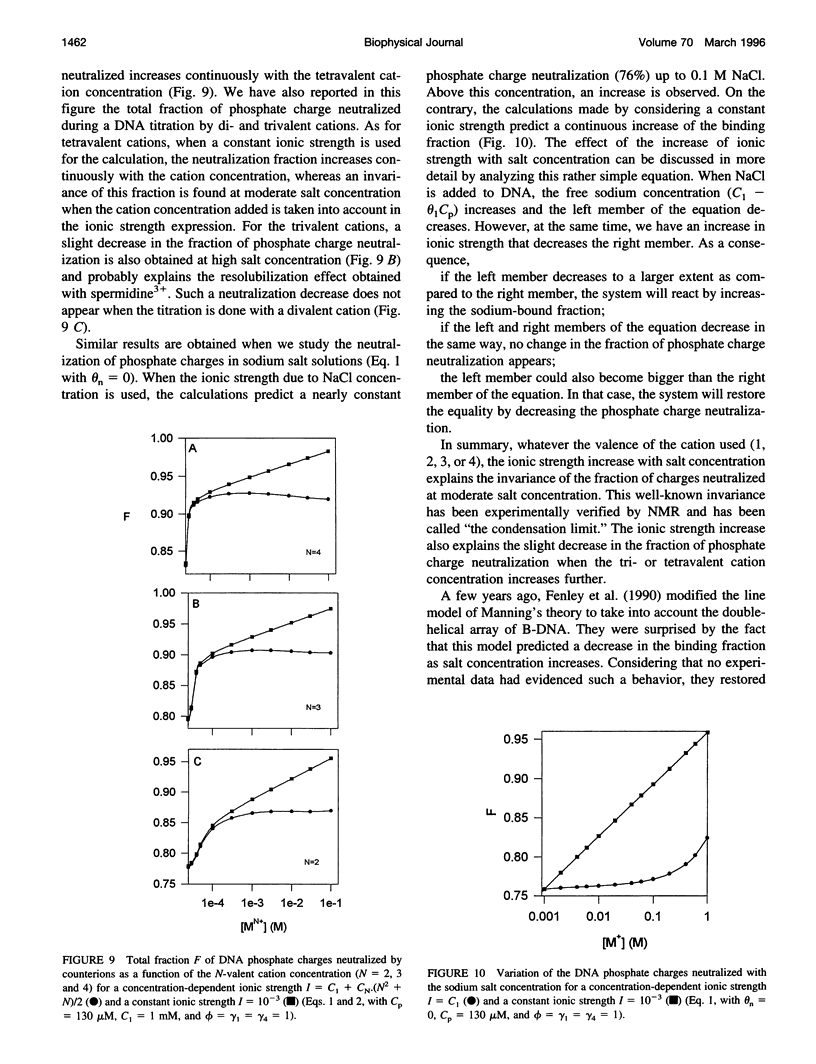
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATCHLEY W. A., BHAGAVAN N. V. SALINE-SOLUBLE PREPARATIONS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEOPROTEINS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul 20;106:505–515. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr Ion distributions around DNA and other cylindrical polyions: theoretical descriptions and physical implications. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:423–465. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.002231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasson B., Nordenskiöld L., Braunlin W. H., Schultz J., Stilbs P. Localized interaction of the polyamine methylspermidine with double-helical DNA as monitored by 1H NMR self-diffusion measurements. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 26;32(3):961–967. doi: 10.1021/bi00054a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arscott P. G., Ma C., Wenner J. R., Bloomfield V. A. DNA condensation by cobalt hexaammine (III) in alcohol-water mixtures: dielectric constant and other solvent effects. Biopolymers. 1995 Sep;36(3):345–364. doi: 10.1002/bip.360360309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausio J., Borochov N., Seger D., Eisenberg H. Interaction of chromatin with NaCl and MgCl2. Solubility and binding studies, transition to and characterization of the higher-order structure. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 15;177(3):373–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90291-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleam M. L., Anderson C. F., Record M. T. Relative binding affinities of monovalent cations for double-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3085–3089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield V. A. Condensation of DNA by multivalent cations: considerations on mechanism. Biopolymers. 1991 Nov;31(13):1471–1481. doi: 10.1002/bip.360311305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunlin W. H., Strick T. J., Record M. T., Jr Equilibrium dialysis studies of polyamine binding to DNA. Biopolymers. 1982 Jul;21(7):1301–1314. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunlin W. H., Xu Q. Hexaamminecobalt(III) binding environments on double-helical DNA. Biopolymers. 1992 Dec;32(12):1703–1711. doi: 10.1002/bip.360321212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buche A., Colson P., Houssier C. Effect of organic effectors on chromatin solubility, DNA-histone H1 interactions, DNA and histone H1 structures. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1993 Aug;11(1):95–119. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1993.10508712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buche A., Colson P., Houssier C. Organic osmotic effectors and chromatin structure. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1990 Dec;8(3):601–618. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1990.10507831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buche A., Ouassaidi A., Hacha R., Delpire E., Gilles R., Houssier C. Glycine and other amino compounds prevent chromatin precipitation at physiological ionic strength. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81372-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattoraj D. K., Gosule L. C., Schellman A. DNA condensation with polyamines. II. Electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90367-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J., Kimura T. Electrostatic mechanism of chromatin folding. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):883–896. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90081-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J., Thomas J. O. Salt-dependent co-operative interaction of histone H1 with linear DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):569–580. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90335-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpire E., Duchêne C., Goessens G., Gilles R. Effects of osmotic shocks on the ultrastructure of different tissues and cell types. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Sep;160(1):106–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenley M. O., Manning G. S., Olson W. K. Approach to the limit of counterion condensation. Biopolymers. 1990;30(13-14):1191–1203. doi: 10.1002/bip.360301305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flock S., Labarbe R., Houssier C. Osmotic effectors and DNA structure: effect of glycine on precipitation of DNA by multivalent cations. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1995 Aug;13(1):87–102. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1995.10508823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredericq E., Hacha R., Colson P., Houssier C. Condensation and precipitation of chromatin by multivalent cations. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Feb;8(4):847–865. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gersanovski D., Colson P., Houssier C., Fredericq E. Terbium(3+) as a probe of nucleic acids structure. Does it alter the DNA conformation in solution? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 19;824(4):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilles R. Comparative aspects of cell osmoregulation and volume control. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1988 May-Oct;11(3-5):277–288. doi: 10.1159/000173167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosule L. C., Schellman J. A. DNA condensation with polyamines I. Spectroscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90366-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leikin S., Parsegian V. A., Rau D. C., Rand R. P. Hydration forces. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1993;44:369–395. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pc.44.100193.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma C., Bloomfield V. A. Gel electrophoresis measurement of counterion condensation on DNA. Biopolymers. 1995 Feb;35(2):211–216. doi: 10.1002/bip.360350209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. Self-attraction and natural curvature in null DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1989 Aug;7(1):41–61. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1989.10507751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquet R., Colson P., Houssier C. The condensation of chromatin and histone H1-depleted chromatin by spermine. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Oct;4(2):205–218. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10506340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquet R., Colson P., Matton A. M., Houssier C., Thiry M., Goessens G. Comparative study of the condensation of chicken erythrocyte and calf thymus chromatins by di- and multivalent cations. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1988 Feb;5(4):839–857. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1988.10506430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquet R., Houssier C., Fredericq E. An electro-optical study of the mechanisms of DNA condensation induced by spermine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 21;825(4):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquet R., Houssier C. Thermodynamics of cation-induced DNA condensation. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Aug;9(1):159–167. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattai J., Kwak J. C. A dye spectrophotometric method for binding studies of Zn2+ and Mn2+ by biopolyelectrolytes. Biophys Chem. 1981 Sep;14(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(81)87006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post C. B., Zimm B. H. Theory of DNA condensation: collapse versus aggregation. Biopolymers. 1982 Nov;21(11):2123–2137. doi: 10.1002/bip.360211104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riemer S. C., Bloomfield V. A. Packaging of DNA in bacteriophage heads: some considerations on energetics. Biopolymers. 1978 Mar;17(3):785–794. doi: 10.1002/bip.1978.360170317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellman J. A., Parthasarathy N. X-ray diffraction studies on cation-collapsed DNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 25;175(3):313–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90351-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajmir-Riahi H. A., Ahmad R., Naoui M. Interaction of calf-thymus DNA with trivalent La, Eu, and Tb ions. Metal ion binding, DNA condensation and structural features. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1993 Apr;10(5):865–877. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1993.10508680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wemmer D. E., Srivenugopal K. S., Reid B. R., Morris D. R. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of polyamine binding to a defined DNA sequence. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):457–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90418-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widom J., Baldwin R. L. Cation-induced toroidal condensation of DNA studies with Co3+(NH3)6. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 25;144(4):431–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widom J., Baldwin R. L. Monomolecular condensation of lambda-DNA induced by cobalt hexamine. Biopolymers. 1983 Jun;22(6):1595–1620. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widom J. Physicochemical studies of the folding of the 100 A nucleosome filament into the 300 A filament. Cation dependence. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):411–424. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. W., Bloomfield V. A. Counterion-induced condesation of deoxyribonucleic acid. a light-scattering study. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2192–2196. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong H. G., Lyklema J., van Leeuwen H. P. Conductometric analysis of the competition between monovalent and divalent counterions in their interaction with polyelectrolytes. Biophys Chem. 1987 Aug;27(2):173–182. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(87)80056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


