Abstract
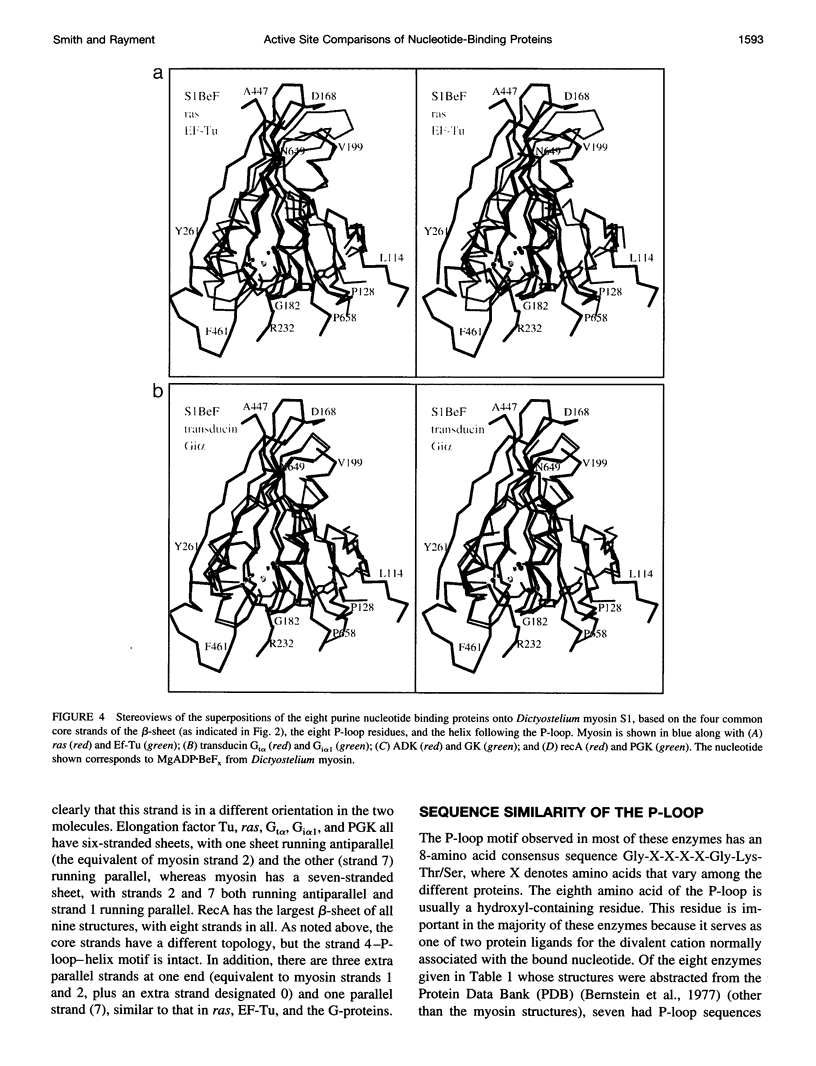
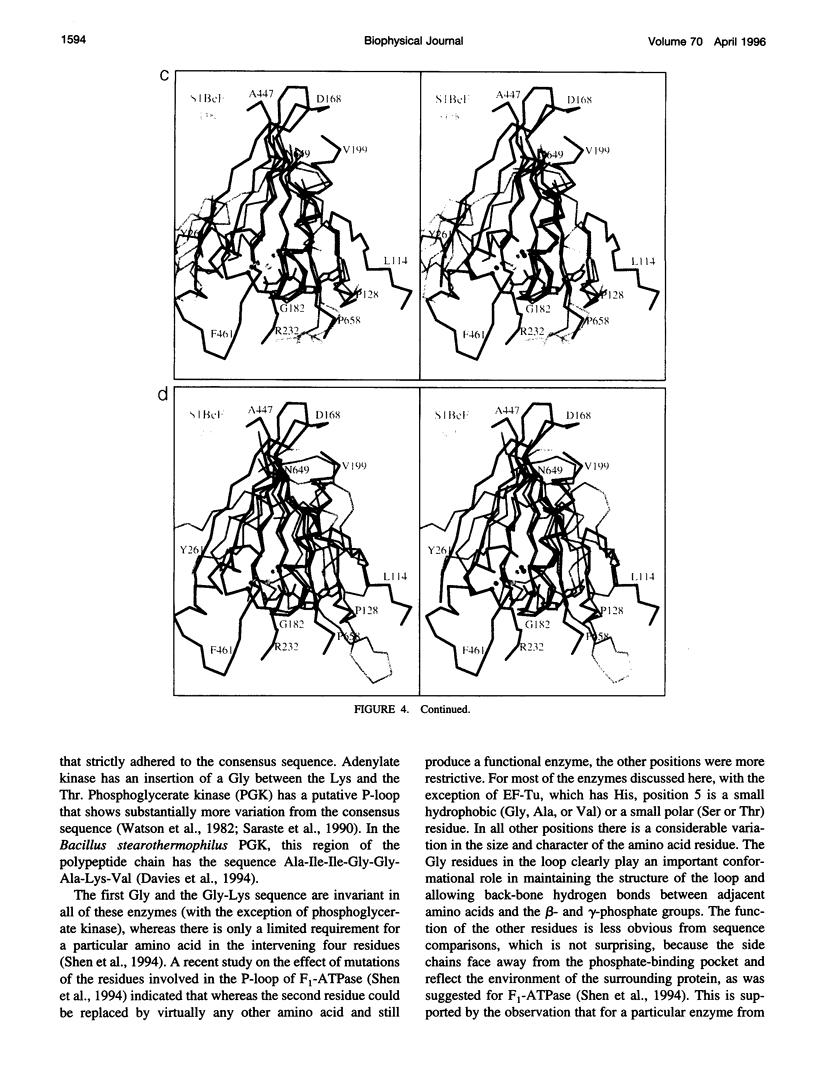
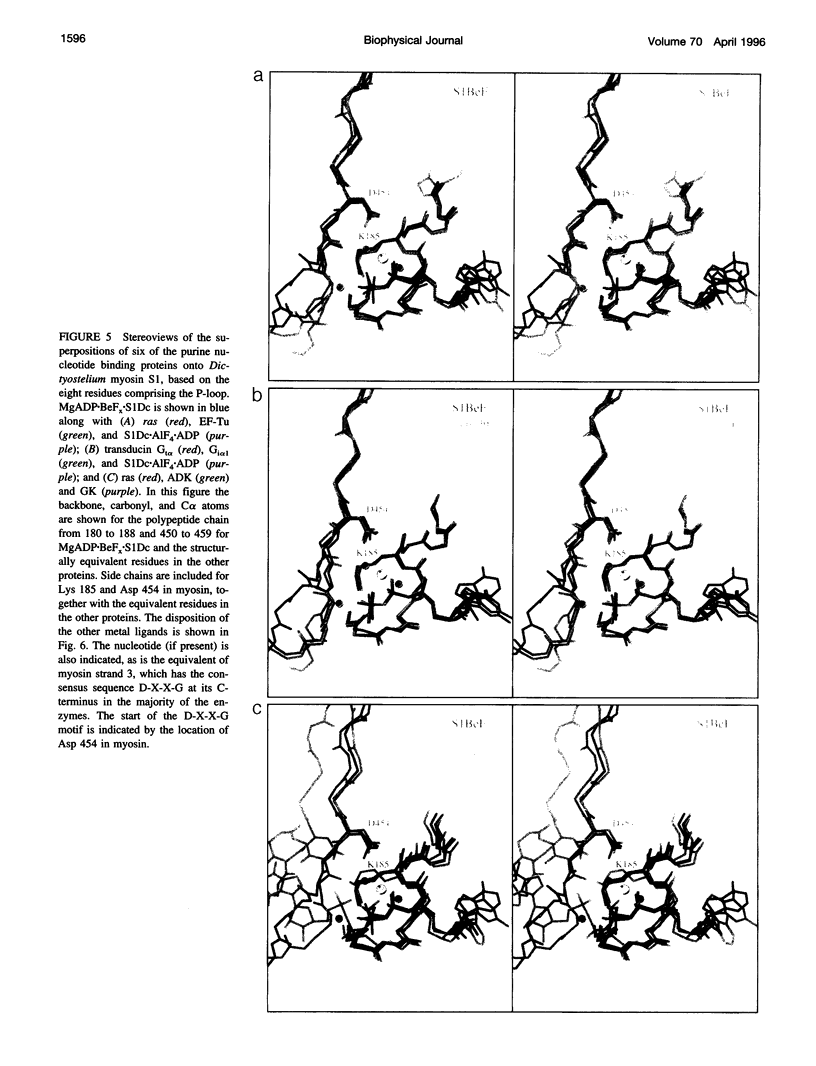
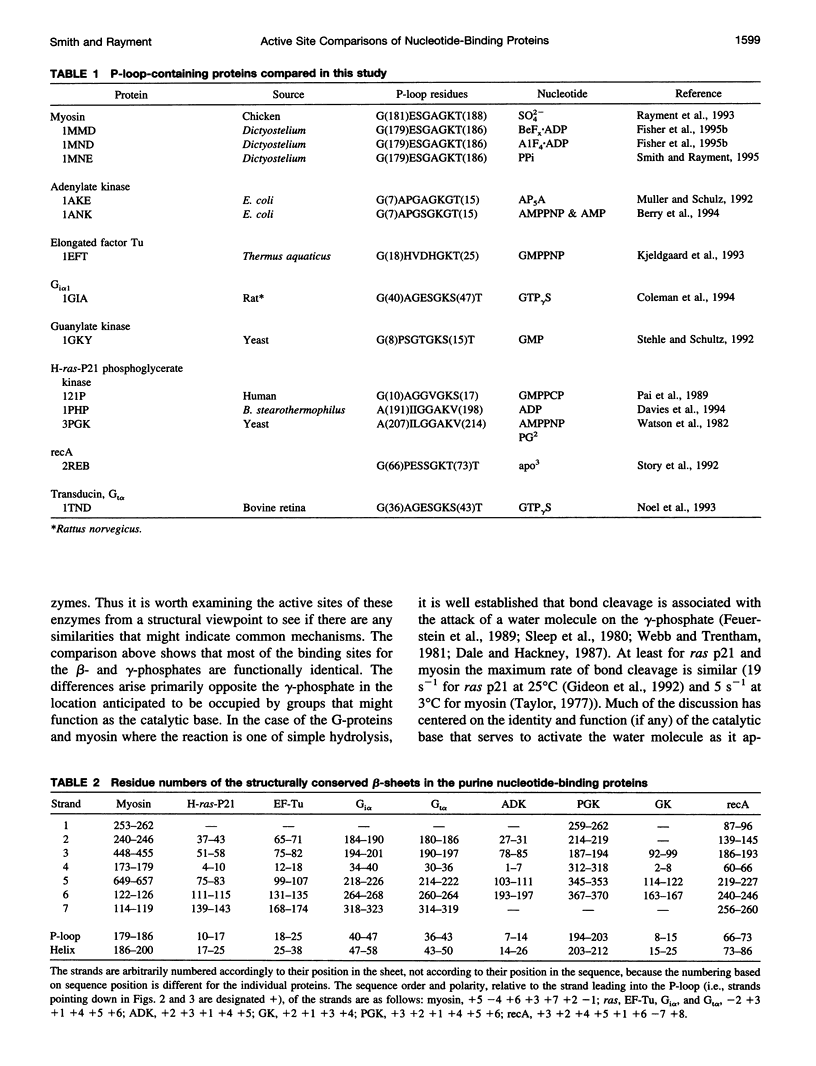
The phosphate binding loop (P-loop) is a common feature of a large number of enzymes that bind nucleotide whose consensus sequence is often used as a fingerprint for identifying new members of this group. We review here the binding sites of nine purine nucleotide binding proteins, with a focus on their relationship to the active site of myosin. This demonstrates that there is considerable conversation in the distribution and nature of the ligands that coordinate the triphosphate moiety. This comparison further suggests that at least myosin and the G-proteins utilize a similar mechanism for nucleotide hydrolysis.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AEvarsson A., Brazhnikov E., Garber M., Zheltonosova J., Chirgadze Y., al-Karadaghi S., Svensson L. A., Liljas A. Three-dimensional structure of the ribosomal translocase: elongation factor G from Thermus thermophilus. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3669–3677. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahams J. P., Leslie A. G., Lutter R., Walker J. E. Structure at 2.8 A resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature. 1994 Aug 25;370(6491):621–628. doi: 10.1038/370621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berchtold H., Reshetnikova L., Reiser C. O., Schirmer N. K., Sprinzl M., Hilgenfeld R. Crystal structure of active elongation factor Tu reveals major domain rearrangements. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):126–132. doi: 10.1038/365126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. B., Meador B., Bilderback T., Liang P., Glaser M., Phillips G. N., Jr The closed conformation of a highly flexible protein: the structure of E. coli adenylate kinase with bound AMP and AMPPNP. Proteins. 1994 Jul;19(3):183–198. doi: 10.1002/prot.340190304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bálint M., Sréter F. A., Wolf I., Nagy B., Gergely J. The substructure of heavy meromyosin. The effect of Ca2+ and Mg2+ on the tryptic fragmentation of heavy meromyosin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6168–6177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung H. H., Benson D. R., Schultz P. G. Probing the structure and mechanism of Ras protein with an expanded genetic code. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):806–809. doi: 10.1126/science.8430333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. E., Berghuis A. M., Lee E., Linder M. E., Gilman A. G., Sprang S. R. Structures of active conformations of Gi alpha 1 and the mechanism of GTP hydrolysis. Science. 1994 Sep 2;265(5177):1405–1412. doi: 10.1126/science.8073283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronet P., Bellsolell L., Sander C., Coll M., Serrano L. Investigating the structural determinants of the p21-like triphosphate and Mg2+ binding site. J Mol Biol. 1995 Jun 9;249(3):654–664. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czworkowski J., Wang J., Steitz T. A., Moore P. B. The crystal structure of elongation factor G complexed with GDP, at 2.7 A resolution. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3661–3668. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06675.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale M. P., Hackney D. D. Analysis of positional isotope exchange in ATP by cleavage of the beta P-O gamma P bond. Demonstration of negligible positional isotope exchange by myosin. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8365–8372. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. J., Gamblin S. J., Littlechild J. A., Dauter Z., Wilson K. S., Watson H. C. Structure of the ADP complex of the 3-phosphoglycerate kinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus at 1.65 A. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1994 Mar 1;50(Pt 2):202–209. doi: 10.1107/S0907444993011138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diederichs K., Schulz G. E. Three-dimensional structure of the complex between the mitochondrial matrix adenylate kinase and its substrate AMP. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 4;29(35):8138–8144. doi: 10.1021/bi00487a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreusicke D., Karplus P. A., Schulz G. E. Refined structure of porcine cytosolic adenylate kinase at 2.1 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):359–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90319-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein J., Goody R. S., Webb M. R. The mechanism of guanosine nucleotide hydrolysis by p21 c-Ha-ras. The stereochemical course of the GTPase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6188–6190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. J., Smith C. A., Thoden J. B., Smith R., Sutoh K., Holden H. M., Rayment I. X-ray structures of the myosin motor domain of Dictyostelium discoideum complexed with MgADP.BeFx and MgADP.AlF4-. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 18;34(28):8960–8972. doi: 10.1021/bi00028a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. J., Smith C. A., Thoden J., Smith R., Sutoh K., Holden H. M., Rayment I. Structural studies of myosin:nucleotide complexes: a revised model for the molecular basis of muscle contraction. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):19S–28S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. C., Kuby S. A., Mildvan A. S. ATP-binding site of adenylate kinase: mechanistic implications of its homology with ras-encoded p21, F1-ATPase, and other nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):907–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gideon P., John J., Frech M., Lautwein A., Clark R., Scheffler J. E., Wittinghofer A. Mutational and kinetic analyses of the GTPase-activating protein (GAP)-p21 interaction: the C-terminal domain of GAP is not sufficient for full activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2050–2056. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry G. D., Maruta S., Ikebe M., Sykes B. D. Observation of multiple myosin subfragment 1-ADP-fluoroberyllate complexes by 19F NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 5;32(39):10451–10456. doi: 10.1021/bi00090a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldgaard M., Nissen P., Thirup S., Nyborg J. The crystal structure of elongation factor EF-Tu from Thermus aquaticus in the GTP conformation. Structure. 1993 Sep 15;1(1):35–50. doi: 10.1016/0969-2126(93)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocabivik S., Perlin M. H. Amino acid substitutions within the analogous nucleotide binding loop (P-loop) of aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase-II. Int J Biochem. 1994 Jan;26(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(94)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambright D. G., Noel J. P., Hamm H. E., Sigler P. B. Structural determinants for activation of the alpha-subunit of a heterotrimeric G protein. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):621–628. doi: 10.1038/369621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Jullien E., Courvalin P. Nucleotide sequence of Acinetobacter baumannii aphA-6 gene: evolutionary and functional implications of sequence homologies with nucleotide-binding proteins, kinases and other aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):615–625. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta S., Henry G. D., Sykes B. D., Ikebe M. Formation of the stable myosin-ADP-aluminum fluoride and myosin-ADP-beryllium fluoride complexes and their analysis using 19F NMR. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7093–7100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Tong L., deVos A. M., Brünger A., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S., Kim S. H. Molecular switch for signal transduction: structural differences between active and inactive forms of protooncogenic ras proteins. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):939–945. doi: 10.1126/science.2406906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mixon M. B., Lee E., Coleman D. E., Berghuis A. M., Gilman A. G., Sprang S. R. Tertiary and quaternary structural changes in Gi alpha 1 induced by GTP hydrolysis. Science. 1995 Nov 10;270(5238):954–960. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5238.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. The limited tryptic cleavage of chymotryptic S-1: an approach to the characterization of the actin site in myosin heads. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91867-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Dieckmann H. J., Schulz G. E. The structure of uridylate kinase with its substrates, showing the transition state geometry. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 11;236(1):361–367. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller C. W., Schulz G. E. Structure of the complex between adenylate kinase from Escherichia coli and the inhibitor Ap5A refined at 1.9 A resolution. A model for a catalytic transition state. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 5;224(1):159–177. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90582-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel J. P., Hamm H. E., Sigler P. B. The 2.2 A crystal structure of transducin-alpha complexed with GTP gamma S. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):654–663. doi: 10.1038/366654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Kabsch W., Krengel U., Holmes K. C., John J., Wittinghofer A. Structure of the guanine-nucleotide-binding domain of the Ha-ras oncogene product p21 in the triphosphate conformation. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):209–214. doi: 10.1038/341209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Krengel U., Petsko G. A., Goody R. S., Kabsch W., Wittinghofer A. Refined crystal structure of the triphosphate conformation of H-ras p21 at 1.35 A resolution: implications for the mechanism of GTP hydrolysis. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2351–2359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Franks-Skiba K., White H., Cooke R. The use of differing nucleotides to investigate cross-bridge kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10046–10053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Rypniewski W. R., Schmidt-Bäse K., Smith R., Tomchick D. R., Benning M. M., Winkelmann D. A., Wesenberg G., Holden H. M. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8316857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Sibbald P. R., Wittinghofer A. The P-loop--a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Nov;15(11):430–434. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90281-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweins T., Geyer M., Scheffzek K., Warshel A., Kalbitzer H. R., Wittinghofer A. Substrate-assisted catalysis as a mechanism for GTP hydrolysis of p21ras and other GTP-binding proteins. Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Jan;2(1):36–44. doi: 10.1038/nsb0195-36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweins T., Langen R., Warshel A. Why have mutagenesis studies not located the general base in ras p21. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Jul;1(7):476–484. doi: 10.1038/nsb0794-476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen H., Yao B. Y., Mueller D. M. Primary structural constraints of P-loop of mitochondrial F1-ATPase from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9424–9428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleep J. A., Hackney D. D., Boyer P. D. The equivalence of phosphate oxygens for exchange and the hydrolysis characteristics revealed by the distribution of [18O]Pi species formed by myosin and actomyosin ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4094–4099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Rayment I. X-ray structure of the magnesium(II)-pyrophosphate complex of the truncated head of Dictyostelium discoideum myosin to 2.7 A resolution. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 18;34(28):8973–8981. doi: 10.1021/bi00028a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sondek J., Lambright D. G., Noel J. P., Hamm H. E., Sigler P. B. GTPase mechanism of Gproteins from the 1.7-A crystal structure of transducin alpha-GDP-AIF-4. Nature. 1994 Nov 17;372(6503):276–279. doi: 10.1038/372276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehle T., Schulz G. E. Refined structure of the complex between guanylate kinase and its substrate GMP at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 20;224(4):1127–1141. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90474-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story R. M., Steitz T. A. Structure of the recA protein-ADP complex. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):374–376. doi: 10.1038/355374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story R. M., Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. The structure of the E. coli recA protein monomer and polymer. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):318–325. doi: 10.1038/355318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E. W. Transient phase of adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis by myosin, heavy meromyosin, and subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):732–739. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasavada K. V., Kaplan J. I., Nageswara Rao B. D. Analysis of 31P NMR spectra of enzyme-bound reactants and products of adenylate kinase using density matrix theory of chemical exchange. Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 28;23(5):961–968. doi: 10.1021/bi00300a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson H. C., Walker N. P., Shaw P. J., Bryant T. N., Wendell P. L., Fothergill L. A., Perkins R. E., Conroy S. C., Dobson M. J., Tuite M. F. Sequence and structure of yeast phosphoglycerate kinase. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1635–1640. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M. R., Trentham D. R. The mechanism of ATP hydrolysis catalyzed by myosin and actomyosin, using rapid reaction techniques to study oxygen exchange. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10910–10916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








