Abstract
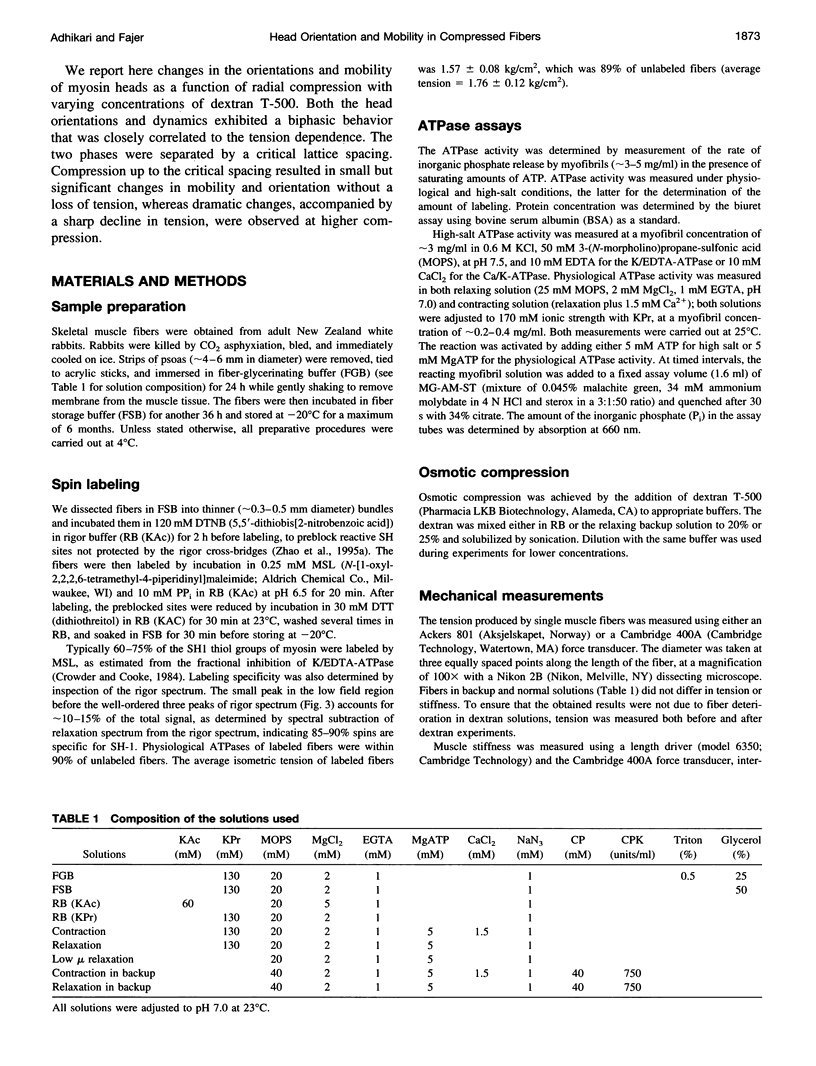
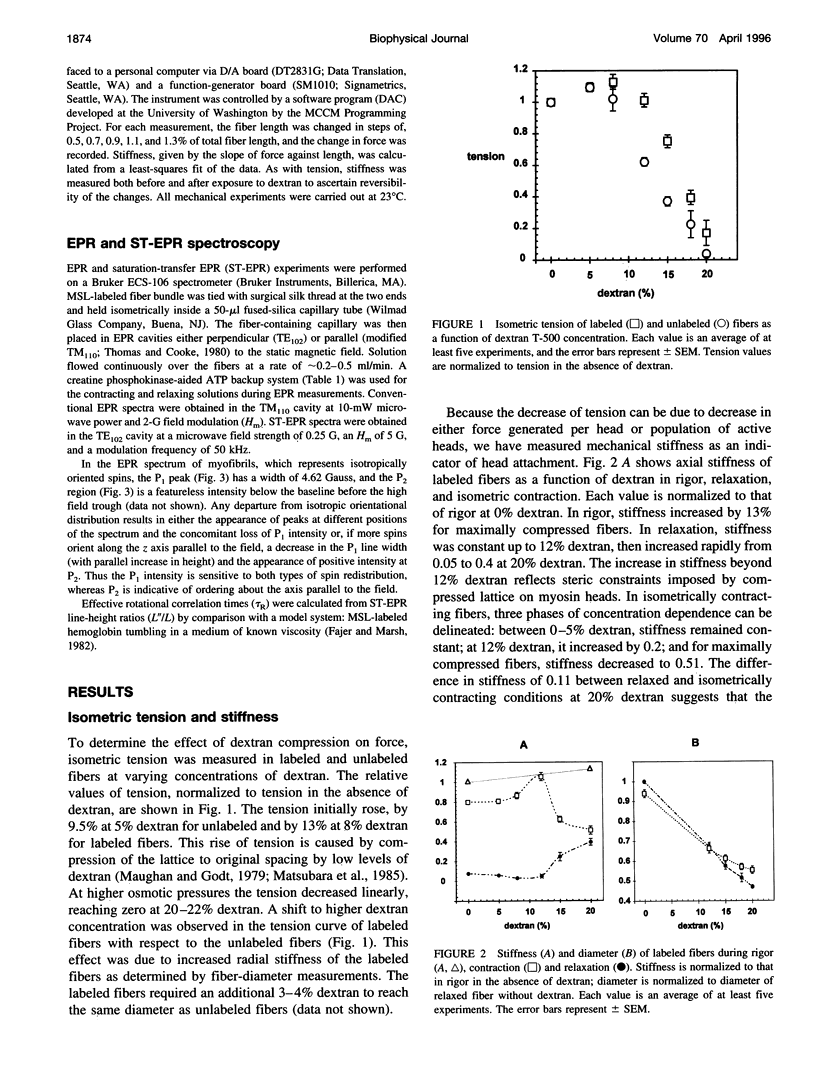
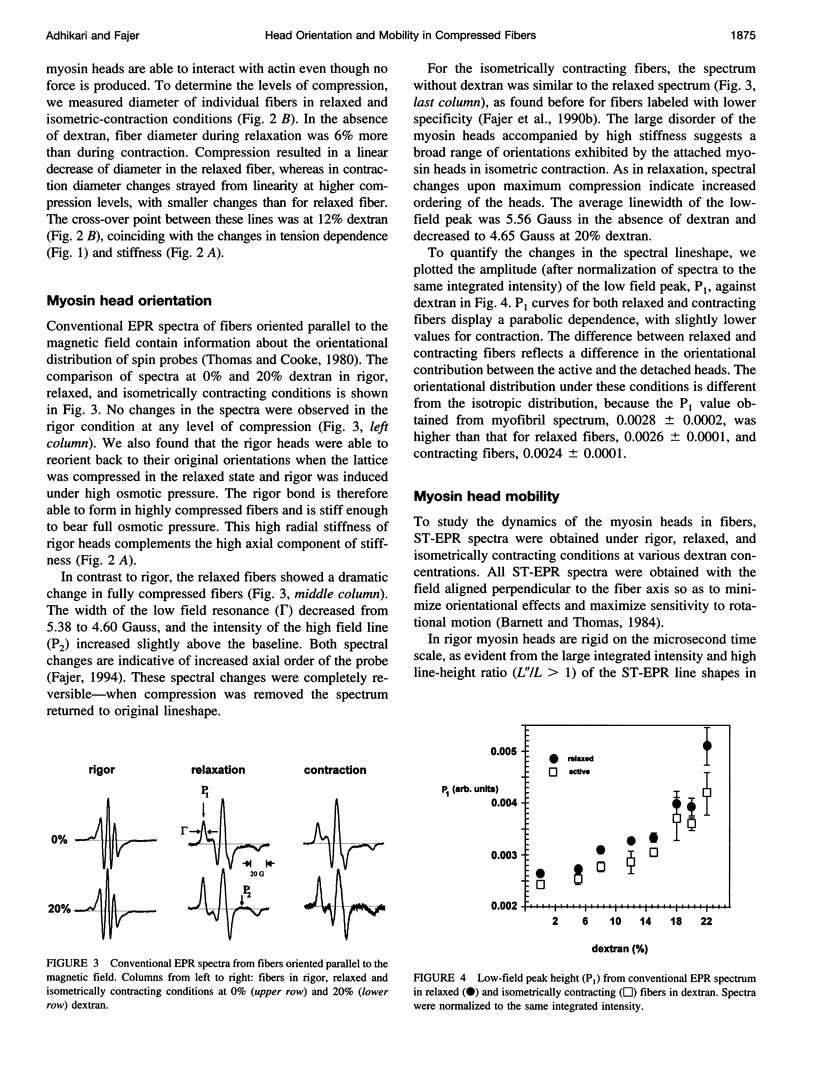
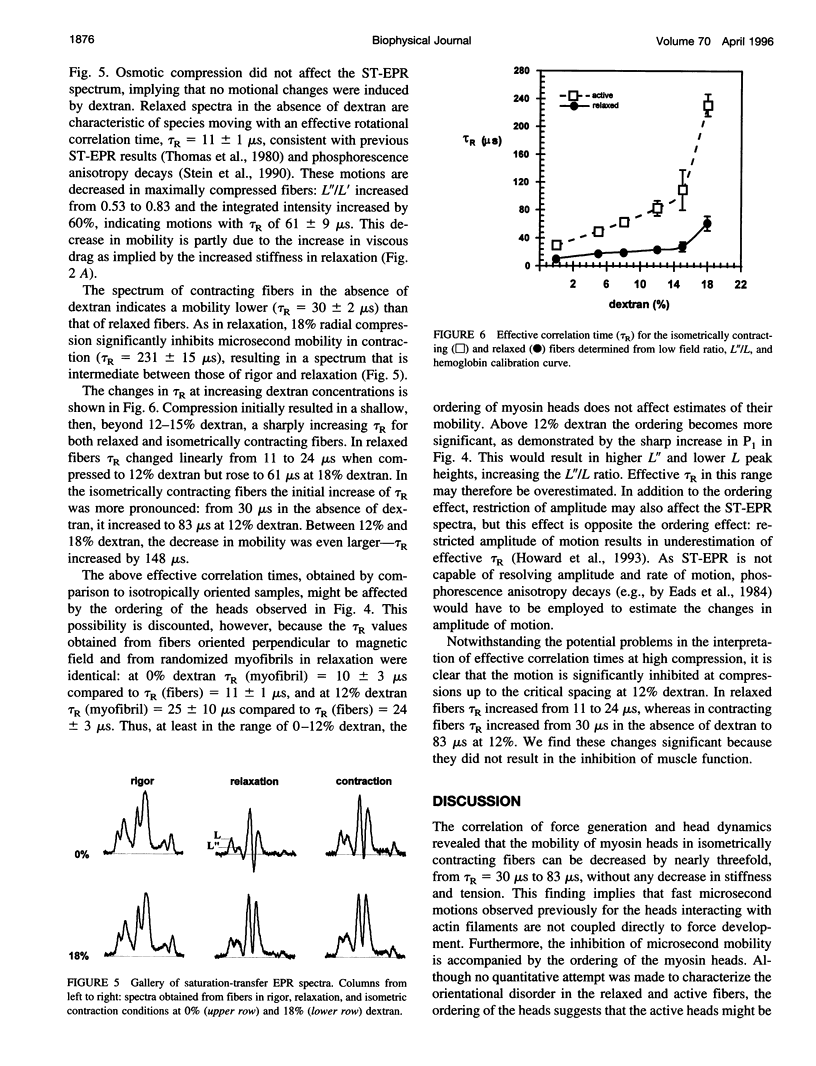
We have correlated the mobility and the generation of force of myosin heads by applying radial compression to isometrically contracting muscle fibers. Osmotic pressure was produced by dextran T-500, and its effect on the orientation and mobility of myosin heads labeled with N-(1-oxy-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-4-pyperidinyl)maleimide was observed by conventional and saturation-transfer electron paramagnetic resonance methods. A biphasic behavior is spectral changes coinciding with the tension dependence was observed as the fibers were compressed. At diameters above the equilibrium spacing, the large myosin head disorder characteristic during contraction in the absence of compression was largely maintained, whereas the mobility decreased threefold, from tauR approximately 25 microseconds to approximately 80-90 microseconds. The inhibition of fast microsecond motions was not accompanied by tension loss, implying that these motions are not necessary for force generation. At diameters below the equilibrium spacing, both the disorder and the mobility decreased dramatically in parallel with the tension inhibition, suggesting that slower microsecond motions and the disorder of the myosin head are necessary for muscle function.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnett V. A., Thomas D. D. Microsecond rotational motion of spin-labeled myosin heads during isometric muscle contraction. Saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance. Biophys J. 1989 Sep;56(3):517–523. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82698-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett V. A., Thomas D. D. Saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance of spin-labeled muscle fibers. Dependence of myosin head rotational motion on sarcomere length. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):83–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90307-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Svensson E. C., Thomas D. D. Photolysis of a photolabile precursor of ATP (caged ATP) induces microsecond rotational motions of myosin heads bound to actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8753–8757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of actin-bound intermediates in the myosin ATPase cycle. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 19;30(46):11036–11045. doi: 10.1021/bi00110a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of actin-bound intermediates of the myosin adenosine triphosphatase cycle in myofibrils. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):250–261. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80476-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of actin-bound myosin heads in active myofibrils. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 13;32(14):3812–3821. doi: 10.1021/bi00065a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Yu L. C. Characterization of radial force and radial stiffness in Ca(2+)-activated skinned fibres of the rabbit psoas muscle. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:703–718. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock J. A., Cunnane T. C. Relationship between the nerve action potential and transmitter release from sympathetic postganglionic nerve terminals. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):605–607. doi: 10.1038/326605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghardt T. P., Ajtai K. Effect of negative mechanical stress on the orientation of myosin cross-bridges in muscle fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5366–5370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Crowder M. S., Thomas D. D. Orientation of spin labels attached to cross-bridges in contracting muscle fibres. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):776–778. doi: 10.1038/300776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. Stress does not alter the conformation of a domain of the myosin cross-bridge in rigor muscle fibres. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):570–571. doi: 10.1038/294570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowder M. S., Cooke R. The effect of myosin sulphydryl modification on the mechanics of fibre contraction. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Apr;5(2):131–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00712152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dos Remedios C. G., Millikan R. G., Morales M. F. Polarization of tryptophan fluorescence from single striated muscle fibers. A molecular probe of contractile state. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jan;59(1):103–120. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eads T. M., Thomas D. D., Austin R. H. Microsecond rotational motions of eosin-labeled myosin measured by time-resolved anisotropy of absorption and phosphorescence. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):55–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90306-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Hill T. L. Muscle contraction and free energy transduction in biological systems. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):999–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.3156404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer P. G., Fajer E. A., Brunsvold N. J., Thomas D. D. Effects of AMPPNP on the orientation and rotational dynamics of spin-labeled muscle cross-bridges. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):513–524. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83131-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer P. G., Fajer E. A., Matta J. J., Thomas D. D. Effect of ADP on the orientation of spin-labeled myosin heads in muscle fibers: a high-resolution study with deuterated spin labels. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5865–5871. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer P. G., Fajer E. A., Schoenberg M., Thomas D. D. Orientational disorder and motion of weakly attached cross-bridges. Biophys J. 1991 Sep;60(3):642–649. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82093-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer P. G., Fajer E. A., Thomas D. D. Myosin heads have a broad orientational distribution during isometric muscle contraction: time-resolved EPR studies using caged ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5538–5542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer P. G. Method for the determination of myosin head orientation from EPR spectra. Biophys J. 1994 Jun;66(6):2039–2050. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80998-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godt R. E., Maughan D. W. Swelling of skinned muscle fibers of the frog. Experimental observations. Biophys J. 1977 Aug;19(2):103–116. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85573-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulati J., Babu A. Critical dependence of calcium-activated force on width in highly compressed skinned fibers of the frog. Biophys J. 1985 Nov;48(5):781–787. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83836-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulati J., Babu A. Tonicity effects on intact single muscle fibers: relation between force and cell volume. Science. 1982 Feb 26;215(4536):1109–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.6977845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada Y., Sakurada K., Aoki T., Thomas D. D., Yanagida T. Mechanochemical coupling in actomyosin energy transduction studied by in vitro movement assay. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 5;216(1):49–68. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H., Yanagida T., Goldman Y. E. Compliance of thin filaments in skinned fibers of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1995 Sep;69(3):1000–1010. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79975-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose K., Lenart T. D., Murray J. M., Franzini-Armstrong C., Goldman Y. E. Flash and smash: rapid freezing of muscle fibers activated by photolysis of caged ATP. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):397–408. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81061-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E. C., Lindahl K. M., Polnaszek C. F., Thomas D. D. Simulation of saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance spectra for rotational motion with restricted angular amplitude. Biophys J. 1993 Mar;64(3):581–593. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81417-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):533–538. doi: 10.1038/233533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E., Stewart A., Sosa H., Irving T. X-ray diffraction measurements of the extensibility of actin and myosin filaments in contracting muscle. Biophys J. 1994 Dec;67(6):2411–2421. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80728-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. The mechanism of muscular contraction. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1356–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. The working stroke of myosin crossbridges. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):55S–58S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving T. C., Millman B. M. Changes in thick filament structure during compression of the filament lattice in relaxed frog sartorius muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1989 Oct;10(5):385–394. doi: 10.1007/BF01758435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Wray J. S., Zhao Y. The effect of lattice spacing change on cross-bridge kinetics in chemically skinned rabbit psoas muscle fibers. I. Proportionality between the lattice spacing and the fiber width. Biophys J. 1993 Jan;64(1):187–196. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81356-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lymn R. W., Taylor E. W. Mechanism of adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis by actomyosin. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 7;10(25):4617–4624. doi: 10.1021/bi00801a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara I., Elliott G. F. X-ray diffraction studies on skinned single fibres of frog skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):657–669. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90183-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara I., Umazume Y., Yagi N. Lateral filamentary spacing in chemically skinned murine muscles during contraction. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:135–148. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maughan D. W., Godt R. E. Stretch and radial compression studies on relaxed skinned muscle fibers of the frog. Biophys J. 1979 Dec;28(3):391–402. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85188-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor G. R., Podolsky R. J. X-ray diffraction of strained muscle fibers in rigor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5559–5563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Cooke R. Energetics of the actomyosin bond in the filament array of muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):561–573. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83136-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raucher D., Fajer E. A., Sár C., Hideg K., Zhao Y., Kawai M., Fajer P. G. A novel electron paramagnetic resonance spin label and its application to study the cross-bridge cycle. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):128S–134S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raucher D., Fajer P. G. Orientation and dynamics of myosin heads in aluminum fluoride induced pre-power stroke states: an EPR study. Biochemistry. 1994 Oct 4;33(39):11993–11999. doi: 10.1021/bi00205a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raucher D., Sár C. P., Hideg K., Fajer P. G. Myosin catalytic domain flexibility in MgADP. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 29;33(47):14317–14323. doi: 10.1021/bi00251a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Rypniewski W. R., Schmidt-Bäse K., Smith R., Tomchick D. R., Benning M. M., Winkelmann D. A., Wesenberg G., Holden H. M. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8316857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. A., Ludescher R. D., Dahlberg P. S., Fajer P. G., Bennett R. L., Thomas D. D. Time-resolved rotational dynamics of phosphorescent-labeled myosin heads in contracting muscle fibers. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 30;29(43):10023–10031. doi: 10.1021/bi00495a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Cooke R. Orientation of spin-labeled myosin heads in glycerinated muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1980 Dec;32(3):891–906. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85024-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Ishiwata S., Seidel J. C., Gergely J. Submillisecond rotational dynamics of spin-labeled myosin heads in myofibrils. Biophys J. 1980 Dec;32(3):873–889. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85023-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Ramachandran S., Roopnarine O., Hayden D. W., Ostap E. M. The mechanism of force generation in myosin: a disorder-to-order transition, coupled to internal structural changes. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):135S–141S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi K., Sugimoto Y., Tanaka H., Ueno Y., Takezawa Y., Amemiya Y. X-ray diffraction evidence for the extensibility of actin and myosin filaments during muscle contraction. Biophys J. 1994 Dec;67(6):2422–2435. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80729-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S., Brenner B., Yu L. C. State-dependent radial elasticity of attached cross-bridges in single skinned fibres of rabbit psoas muscle. J Physiol. 1993 Feb;461:283–299. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida T., Arata T., Oosawa F. Sliding distance of actin filament induced by a myosin crossbridge during one ATP hydrolysis cycle. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):366–369. doi: 10.1038/316366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L. C., Brenner B. Structures of actomyosin crossbridges in relaxed and rigor muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1989 Mar;55(3):441–453. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82838-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao L., Naber N., Cooke R. Muscle cross-bridges bound to actin are disordered in the presence of 2,3-butanedione monoxime. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1980–1990. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80375-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y., Kawai M. The effect of the lattice spacing change on cross-bridge kinetics in chemically skinned rabbit psoas muscle fibers. II. Elementary steps affected by the spacing change. Biophys J. 1993 Jan;64(1):197–210. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81357-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


