Abstract
We have investigated why fura-2 and Ca(2+)-sensitive microelectrodes report different values for the intracellular free calcium ion concentration ([Ca(2+)]i or its negative log, pCa(i)) of snail neurons voltage-clamped to -50 or -60 mV. Both techniques were initially calibrated in vitro, using calcium calibration solutions that had ionic concentrations similar to those of snail neuron cytoplasm. Pressure injections of the same solutions at resting and elevated [Ca(2+)]i were used to calibrate both methods in vivo. In fura-2-loaded cells these pressure injections generated changes in [Ca(2+)]i that agreed well with those expected from the in vitro calibration. Thus, using fura-2 calibrated in vitro, the average resting [Ca(2+)]i was found to be 38 nM (pCa(i) 7.42 +/- 0.05). With Ca(2+)-sensitive microelectrodes, the first injection of calibration solutions always caused a negative shift in the recorded microelectrode potential, as if the injection lowered [Ca2+]i. No such effects were seen on the fura-2 ratio. When calibrated in vivo the Ca(2+)-sensitive microelectrode gave an average resting [Ca2+]i of approximately 25 nM (pCa(i) 7.6 +/- 0.1), much lower than when calibrated in vitro. We conclude that [Ca(2+)]i in snail neurons is approximately 40 nM and that Ca(2+)-sensitive microelectrodes usually cause a leak at the point of insertion. The effects of the leak were minimized by injection of a mobile calcium buffer.
Full text
PDF

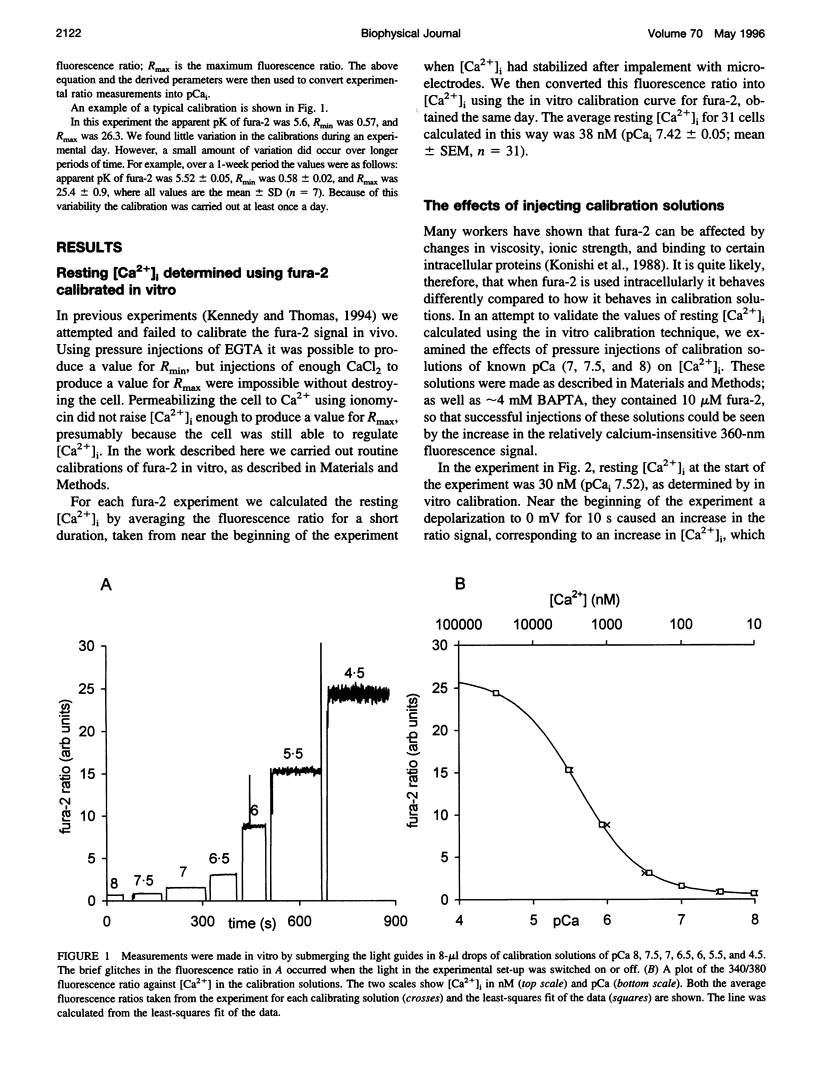
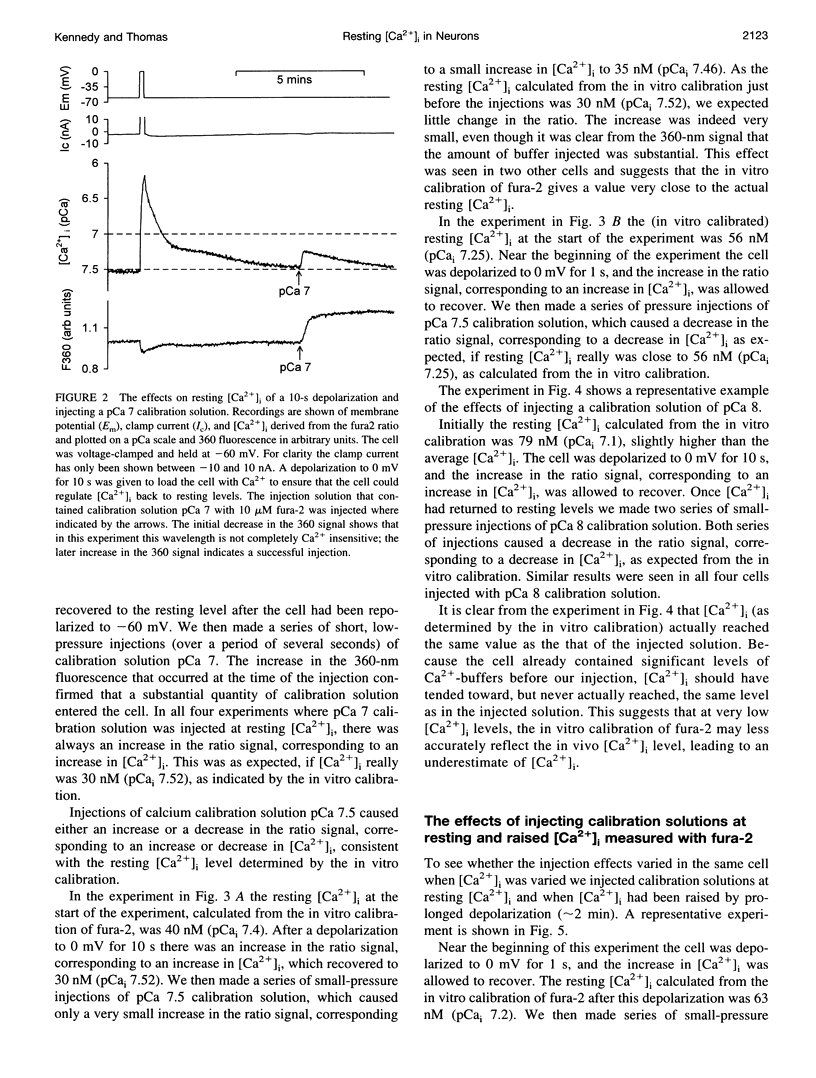
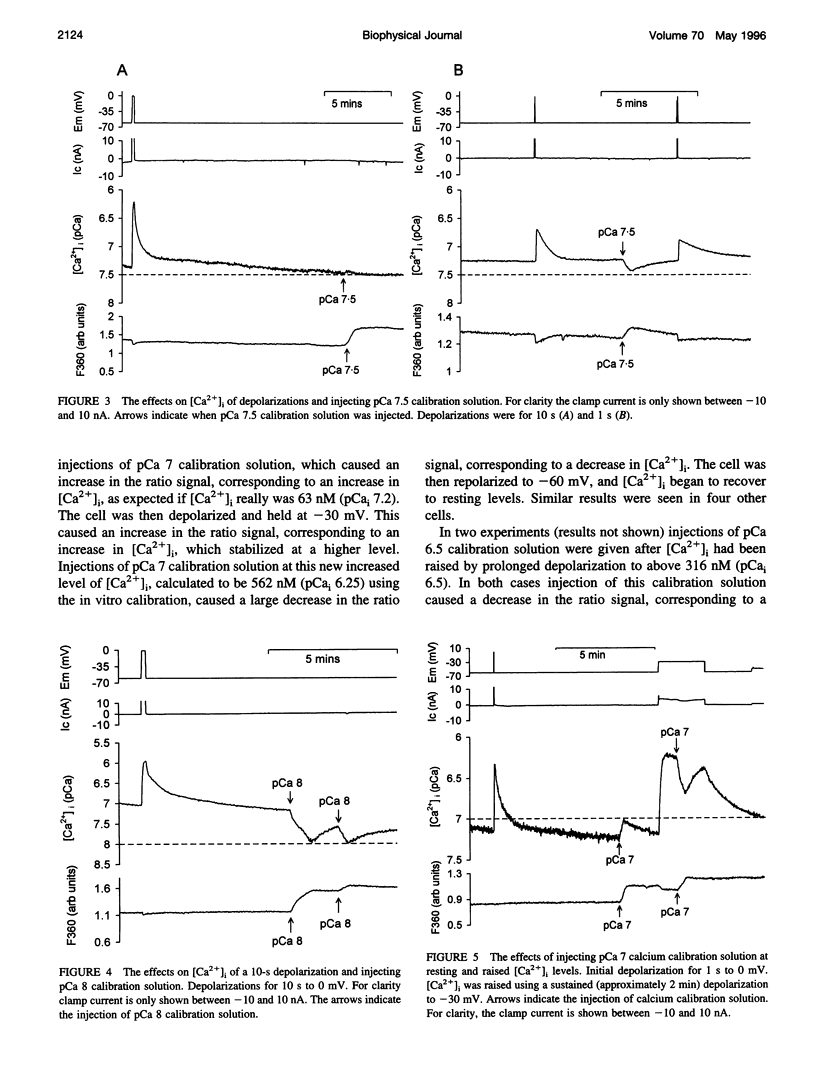
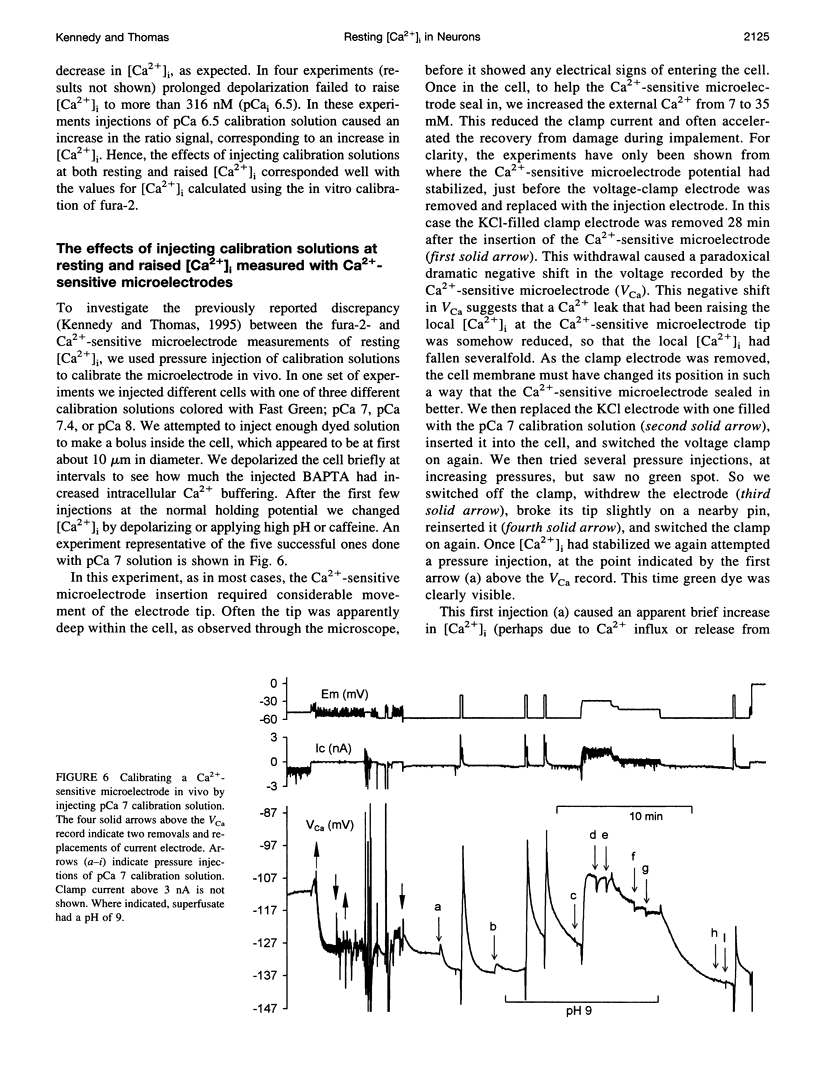



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez-Leefmans F. J., Rink T. J., Tsien R. Y. Free calcium ions in neurones of Helix aspersa measured with ion-selective micro-electrodes. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:531–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
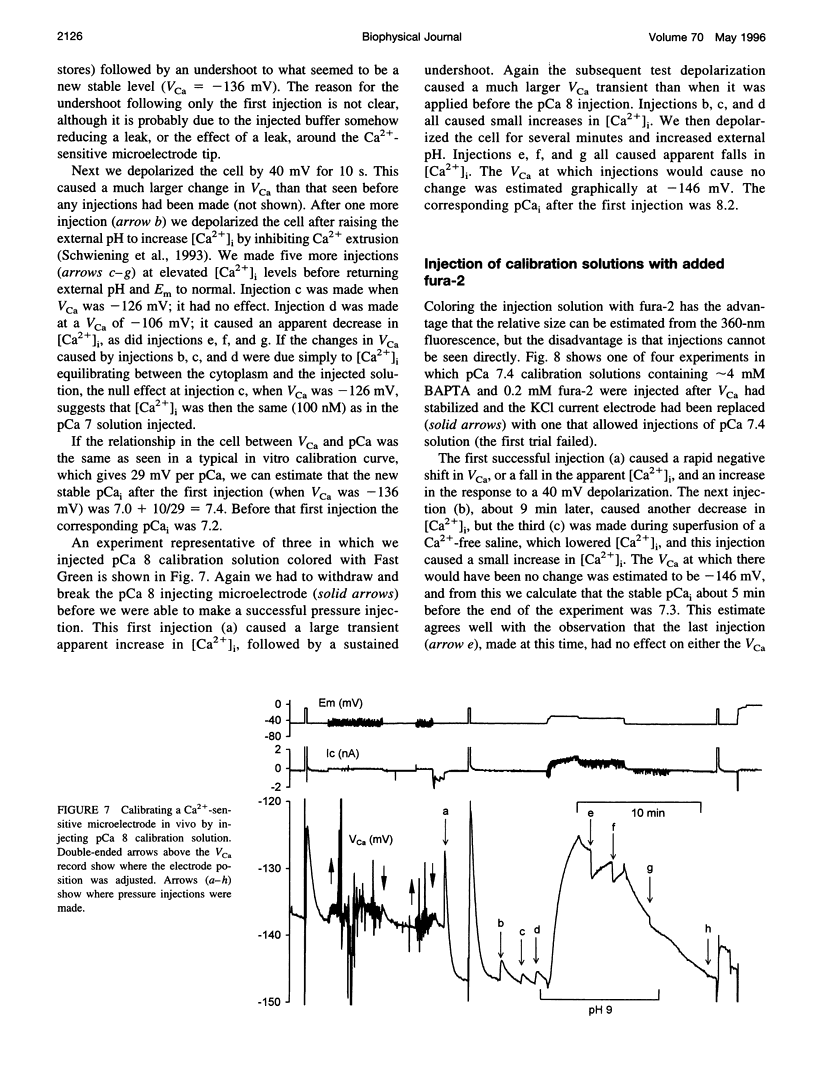
- Ammann D., Bührer T., Schefer U., Müller M., Simon W. Intracellular neutral carrier-based Ca2+ microelectrode with subnanomolar detection limit. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Jul;409(3):223–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00583469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
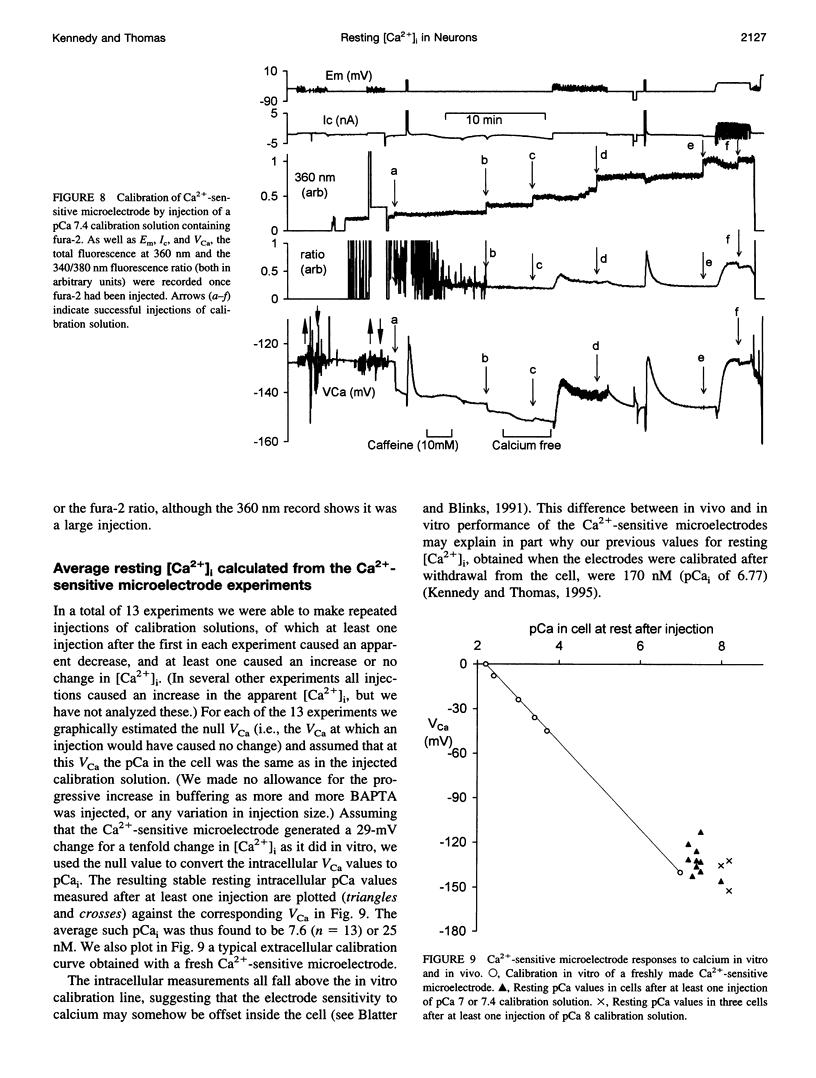
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassani J. W., Bassani R. A., Bers D. M. Calibration of indo-1 and resting intracellular [Ca]i in intact rabbit cardiac myocytes. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4):1453–1460. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80318-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter L. A., Blinks J. R. Simultaneous measurement of Ca2+ in muscle with Ca electrodes and aequorin. Diffusible cytoplasmic constituent reduces Ca(2+)-independent luminescence of aequorin. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Dec;98(6):1141–1160. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.6.1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleakman D., Roback J. D., Wainer B. H., Miller R. J., Harrison N. L. Calcium homeostasis in rat septal neurons in tissue culture. Brain Res. 1993 Jan 15;600(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91381-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D., Tsien R. W. A caffeine- and ryanodine-sensitive Ca2+ store in bullfrog sympathetic neurones modulates effects of Ca2+ entry on [Ca2+]i. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:217–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Levy S., Nasi E., Tillotson D. Intracellular calcium measured with calcium-sensitive micro-electrodes and Arsenazo III in voltage-clamped Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:127–142. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. M., Bers D. M. Correction of proton and Ca association constants of EGTA for temperature and ionic strength. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):C1250–C1256. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.6.C1250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingworth S., Harkins A. B., Kurebayashi N., Konishi M., Baylor S. M. Excitation-contraction coupling in intact frog skeletal muscle fibers injected with mmolar concentrations of fura-2. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):224–234. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81599-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenouchi H., Peeters G. A., Barry W. H. Evidence that binding of Indo-1 to cardiac myocyte protein does not markedly change Kd for Ca2+. Cell Calcium. 1991 Jun;12(6):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(91)90067-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy H. J., Thomas R. C. Intracellular calcium and its sodium-independent regulation in voltage-clamped snail neurones. J Physiol. 1995 May 1;484(Pt 3):533–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Olson A., Hollingworth S., Baylor S. M. Myoplasmic binding of fura-2 investigated by steady-state fluorescence and absorbance measurements. Biophys J. 1988 Dec;54(6):1089–1104. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83045-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S., Tillotson D. Effects of Na+ and Ca2+ gradients on intracellular free Ca2+ in voltage-clamped Aplysia neurons. Brain Res. 1988 Dec 6;474(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90447-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuigan J. A., Lüthi D., Buri A. Calcium buffer solutions and how to make them: a do it yourself guide. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;69(11):1733–1749. doi: 10.1139/y91-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller T. H., Partridge L. D., Swandulla D. Calcium buffering in bursting Helix pacemaker neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Dec;425(5-6):499–505. doi: 10.1007/BF00374877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Augustine G. J. Calcium gradients and buffers in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:273–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohmi M., Hua S. Y., Kuba K. Basal Ca2+ and the oscillation of Ca2+ in caffeine-treated bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:513–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkand R. K., Thomas R. C. Effects of low doses of caffeine on [Ca2+]i in voltage-clamped snail (Helix aspersa) neurones. J Physiol. 1995 Nov 15;489(Pt 1):19–28. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp021026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou-Yang Y., Kristián T., Mellergård P., Siesjö B. K. The influence of pH on glutamate- and depolarization-induced increases of intracellular calcium concentration in cortical neurons in primary culture. Brain Res. 1994 May 16;646(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M. Alteration of intracellular Fura-2 fluorescence by viscosity: a simple correction. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90062-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. N. Calcium on the level. Biophys J. 1993 Jun;64(6):1655–1656. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81537-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwiening C. J., Kennedy H. J., Thomas R. C. Calcium-hydrogen exchange by the plasma membrane Ca-ATPase of voltage-clamped snail neurons. Proc Biol Sci. 1993 Sep 22;253(1338):285–289. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1993.0115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver I. A., Erecińska M. Intracellular and extracellular changes of [Ca2+] in hypoxia and ischemia in rat brain in vivo. J Gen Physiol. 1990 May;95(5):837–866. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.5.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuenkel E. L. Regulation of intracellular calcium and calcium buffering properties of rat isolated neurohypophysial nerve endings. J Physiol. 1994 Dec 1;481(Pt 2):251–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumi H., Katayama Y. Regulation of the intracellular free calcium concentration in acutely dissociated neurones from rat nucleus basalis. J Physiol. 1993 May;464:165–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. S., Thomas R. C. The effect of leakage on micro-electrode measurements of intracellular sodium activity in crab muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:539–550. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer S. A., Miller R. J. Regulation of the intracellular free calcium concentration in single rat dorsal root ganglion neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:85–115. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uto A., Arai H., Ogawa Y. Reassessment of Fura-2 and the ratio method for determination of intracellular Ca2+ concentrations. Cell Calcium. 1991 Jan;12(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(91)90082-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerblad H., Allen D. G. Methods for calibration of fluorescent calcium indicators in skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1994 Mar;66(3 Pt 1):926–928. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80870-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerblad H., Allen D. G. The influence of intracellular pH on contraction, relaxation and [Ca2+]i in intact single fibres from mouse muscle. J Physiol. 1993 Jul;466:611–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


