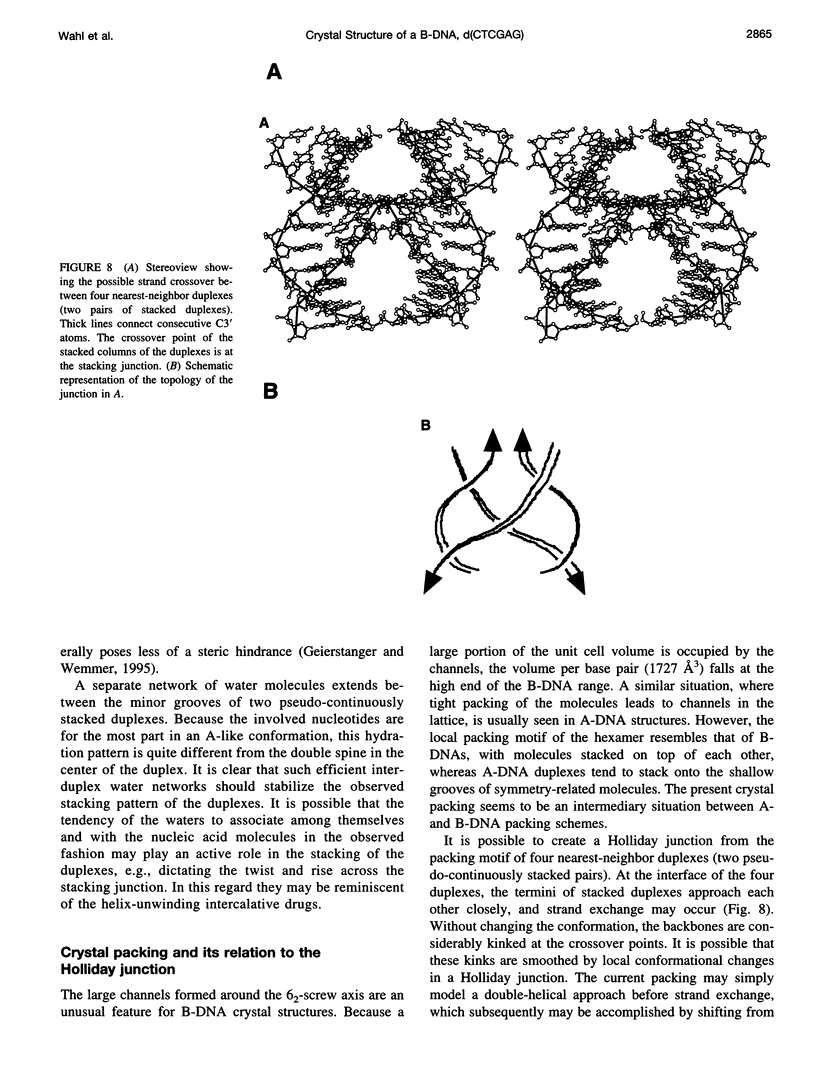
Abstract
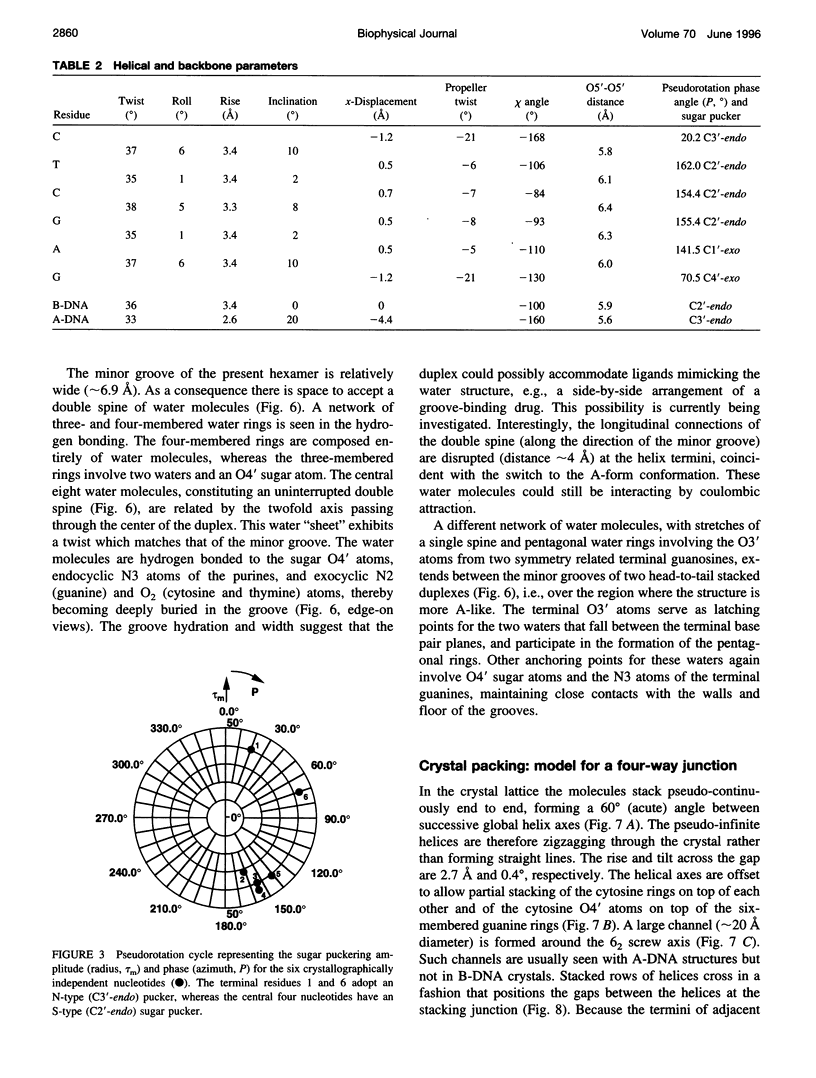
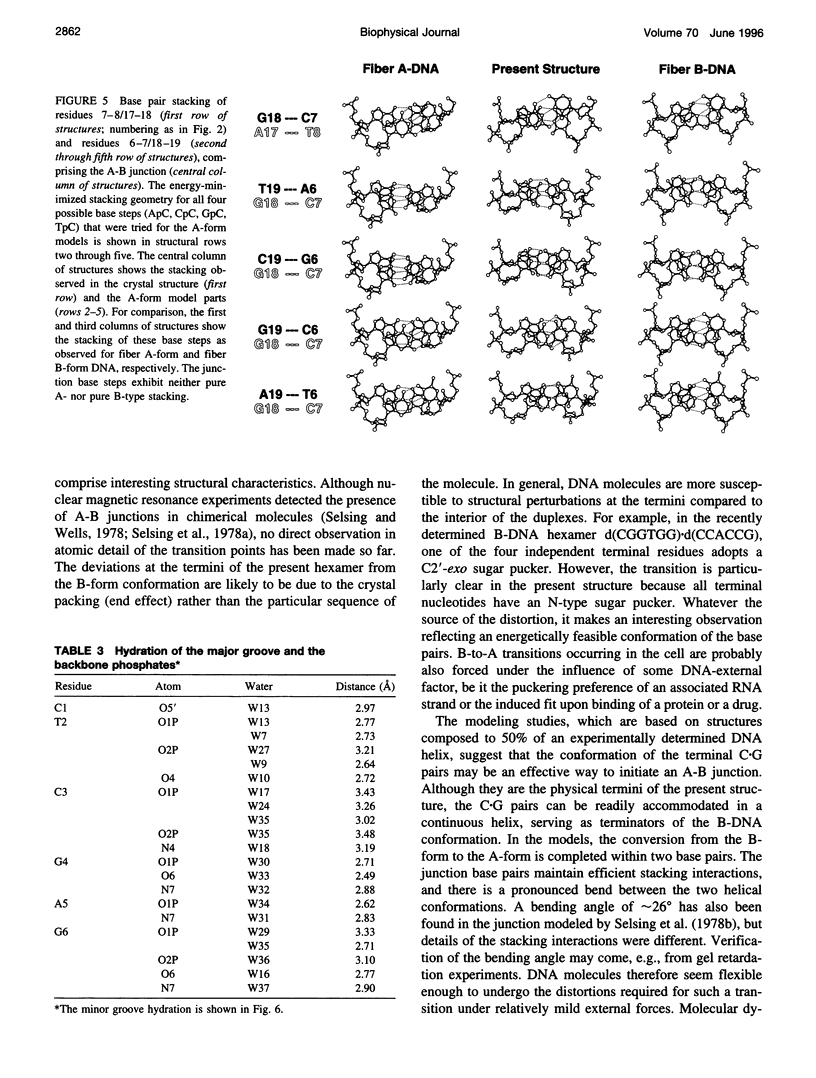
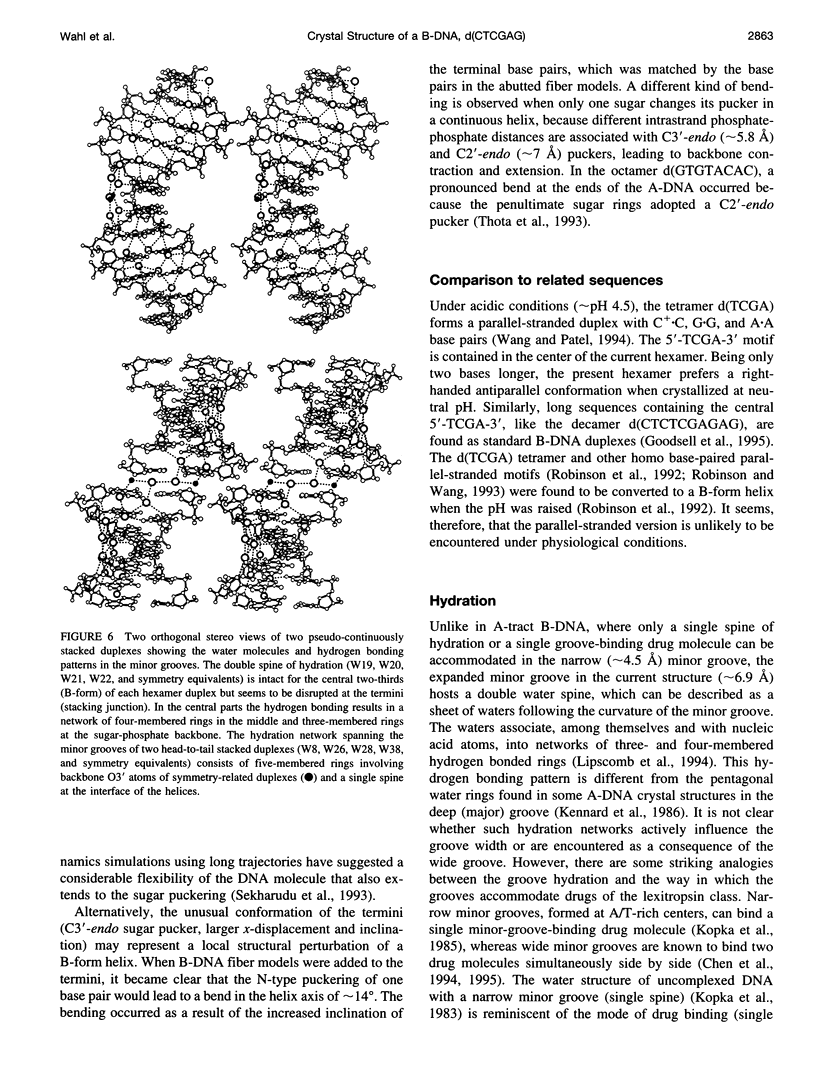
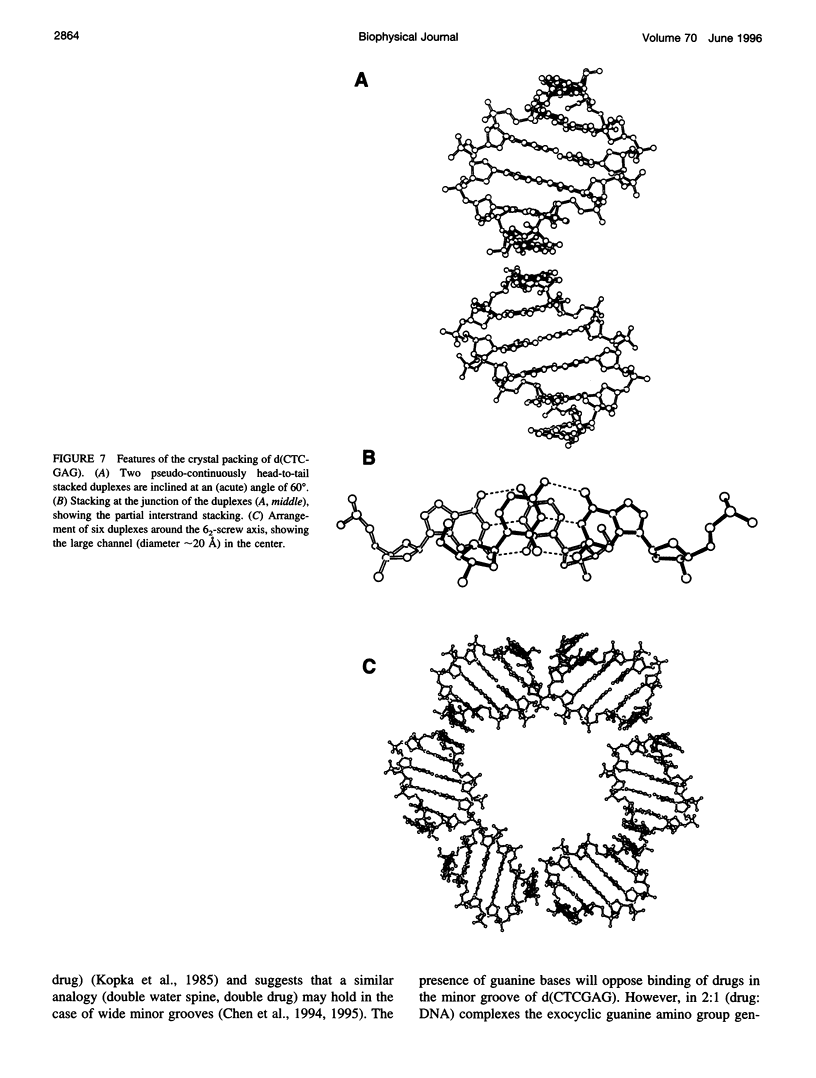
The crystal structure of the B-DNA hexamer d(CTCGAG) has been solved at 1.9 A resolution by iterative single isomorphous replacement, using the brominated derivative d(CG5BrCGAG), and refined to an R-factor of 18.6% for 120 nonhydrogen nucleic acid atoms and 32 water molecules. Although the central four base pairs form a typical B-form helix, several parameters suggest a transition to an A-like conformation at the termini. Based on this observation, a B-to-A transition was modeled, maintaining efficient base stacking across the junction. The wide minor groove (approximately 6.9 A) is reminiscent of that in the side-by-side double drug-DNA complexes and hosts a double spine of hydration. The global helix axes of the pseudo-continuous helices are at an acute angle of 60 degrees. The pseudocontinuous stacking is reinforced by the minor groove water structure extending between the two duplexes. The crossover point of two pairs of stacked duplexes is at the stacking junction, unlike that observed in the B-DNA decamers and dodecamers. This arrangement may have implications for the structure of a four-way DNA junction. The duplexes are arranged around a large (approximately 20 A diameter) channel centered on a 6(2) screw axis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharyya D., Bansal M. Local variability and base sequence effects in DNA crystal structures. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1990 Dec;8(3):539–572. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1990.10507828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Ramakrishnan B., Rao S. T., Sundaralingam M. Binding of two distamycin A molecules in the minor groove of an alternating B-DNA duplex. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Mar;1(3):169–175. doi: 10.1038/nsb0394-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruse W. B., Salisbury S. A., Brown T., Cosstick R., Eckstein F., Kennard O. Chiral phosphorothioate analogues of B-DNA. The crystal structure of Rp-d[Gp(S)CpGp(S)CpGp(S)C]. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 20;192(4):891–905. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geierstanger B. H., Wemmer D. E. Complexes of the minor groove of DNA. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1995;24:463–493. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.24.060195.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodsell D. S., Grzeskowiak K., Dickerson R. E. Crystal structure of C-T-C-T-C-G-A-G-A-G. Implications for the structure of the Holliday junction. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 24;34(3):1022–1029. doi: 10.1021/bi00003a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennard O., Cruse W. B., Nachman J., Prange T., Shakked Z., Rabinovich D. Ordered water structure in an A-DNA octamer at 1.7 A resolution. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Feb;3(4):623–647. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Nikolov D. B., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):520–527. doi: 10.1038/365520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Geiger J. H., Hahn S., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of a yeast TBP/TATA-box complex. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):512–520. doi: 10.1038/365512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Fratini A. V., Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Ordered water structure around a B-DNA dodecamer. A quantitative study. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 5;163(1):129–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Yoon C., Goodsell D., Pjura P., Dickerson R. E. The molecular origin of DNA-drug specificity in netropsin and distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1376–1380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavery R., Sklenar H. The definition of generalized helicoidal parameters and of axis curvature for irregular nucleic acids. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1988 Aug;6(1):63–91. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1988.10506483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb L. A., Peek M. E., Zhou F. X., Bertrand J. A., VanDerveer D., Williams L. D. Water ring structure at DNA interfaces: hydration and dynamics of DNA-anthracycline complexes. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 29;33(12):3649–3659. doi: 10.1021/bi00178a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooers B. H., Schroth G. P., Baxter W. W., Ho P. S. Alternating and non-alternating dG-dC hexanucleotides crystallize as canonical A-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1995 Jun 16;249(4):772–784. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H., Wang A. H. 5'-CGA sequence is a strong motif for homo base-paired parallel-stranded DNA duplex as revealed by NMR analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5224–5228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Wang A. H. Unusual DNA conformation at low pH revealed by NMR: parallel-stranded DNA duplex with homo base pairs. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 3;31(43):10510–10517. doi: 10.1021/bi00158a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekharudu C. Y., Yathindra N., Sundaralingam M. Molecular dynamics investigations of DNA triple helical models: unique features of the Watson-Crick duplex. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1993 Oct;11(2):225–244. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1993.10508723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsing E., Wells R. D., Alden C. J., Arnott S. Bent DNA: visualization of a base-paired and stacked A-B conformational junction. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5417–5422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsing E., Wells R. D., Early T. A., Kearns D. R. Two contiguous conformations in a nucleic acid duplex. Nature. 1978 Sep 21;275(5677):249–250. doi: 10.1038/275249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsing E., Wells R. D. Polynucleotide block polymers consisting of a DNA.RNA hybrid joined to a DNA.DNA duplex. Synthesis and characterization of dGn.rCidCk duplexes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5410–5416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tari L. W., Secco A. S. Base-pair opening and spermine binding--B-DNA features displayed in the crystal structure of a gal operon fragment: implications for protein-DNA recognition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Jun 11;23(11):2065–2073. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.11.2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thota N., Li X. H., Bingman C., Sundaralingam M. High-resolution refinement of the hexagonal A-DNA octamer d(GTGTACAC) at 1.4 A. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1993 Mar 1;49(Pt 2):282–291. doi: 10.1107/S0907444992007522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timsit Y., Moras D. Groove-backbone interaction in B-DNA. Implication for DNA condensation and recombination. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 5;221(3):919–940. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80184-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Patel D. J. Solution structure of the d(T-C-G-A) duplex at acidic pH. A parallel-stranded helix containing C+ .C, G.G and A.A pairs. J Mol Biol. 1994 Sep 30;242(4):508–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


