Abstract
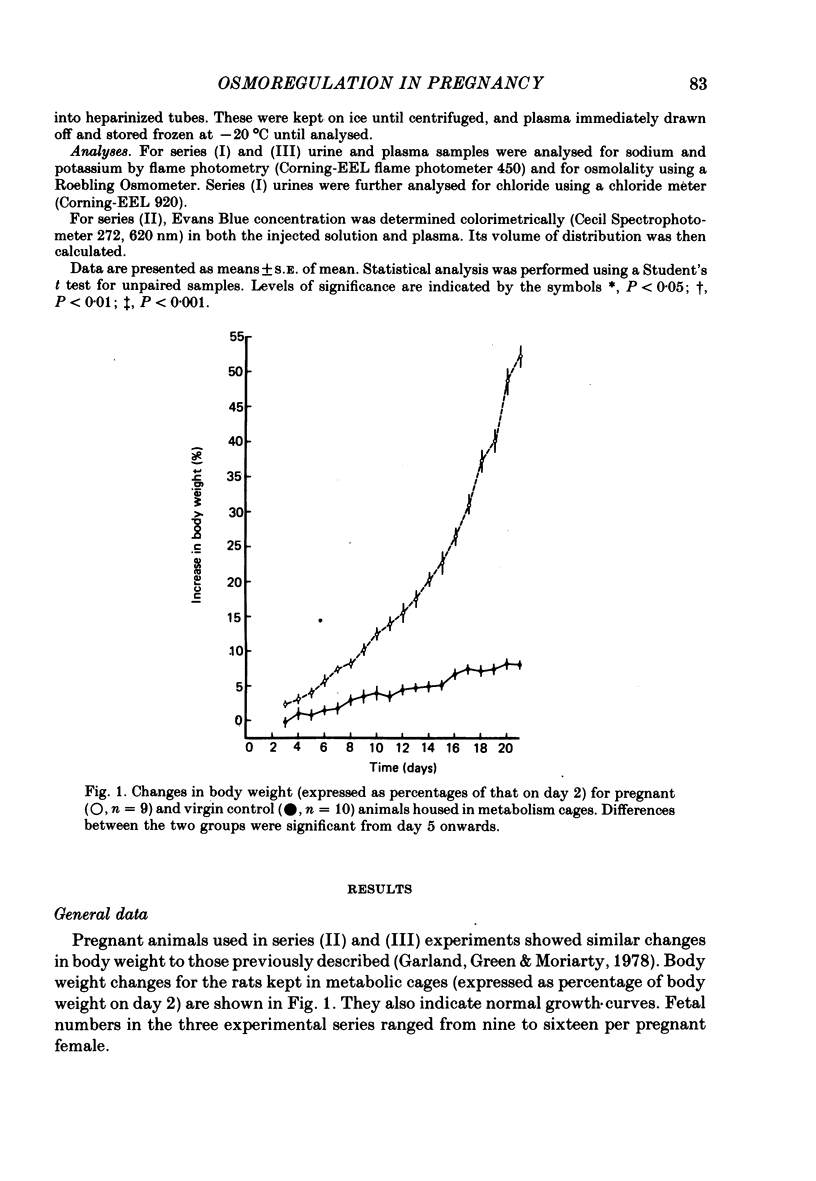
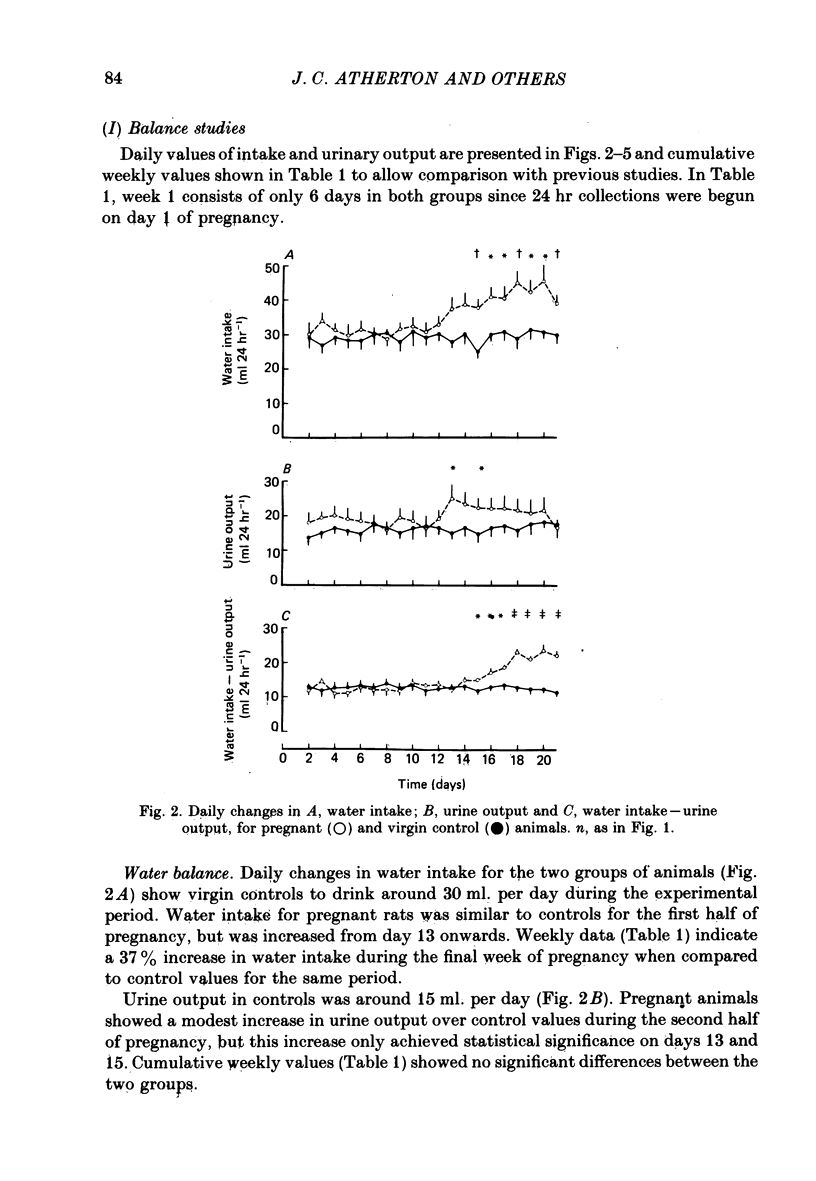
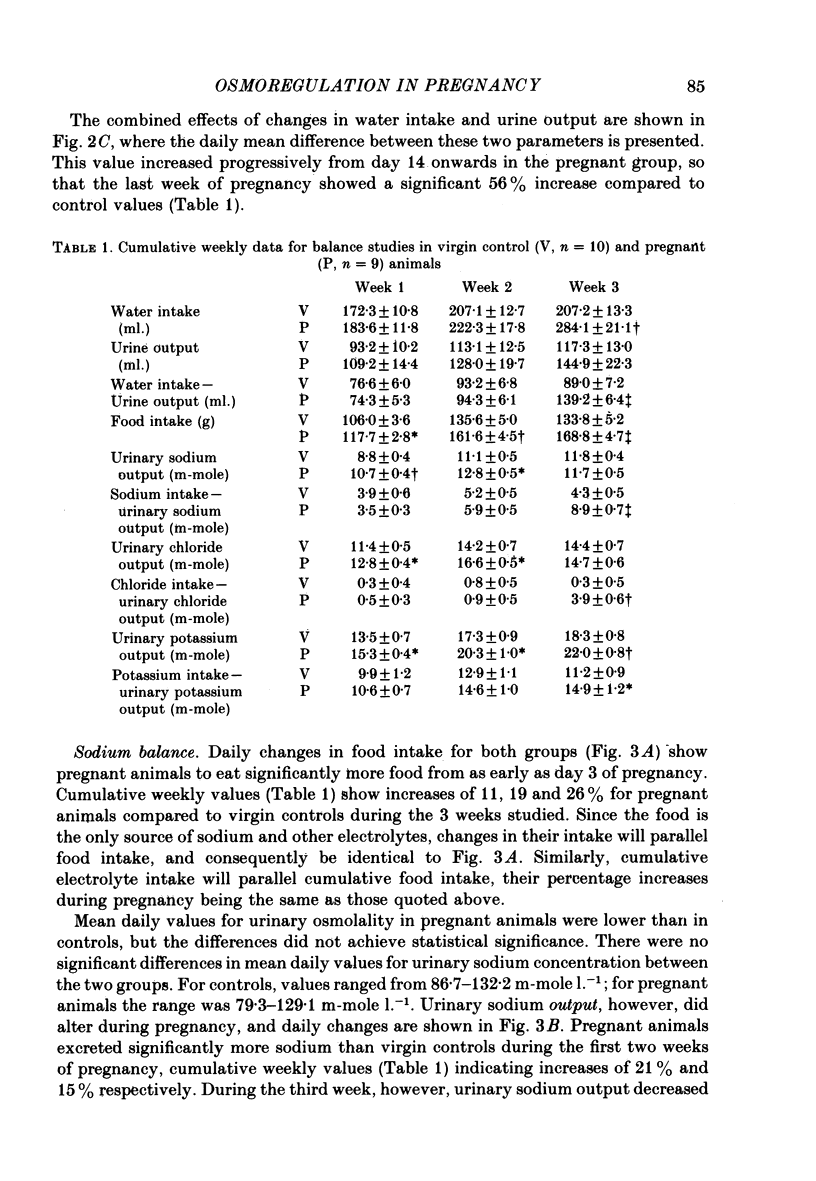
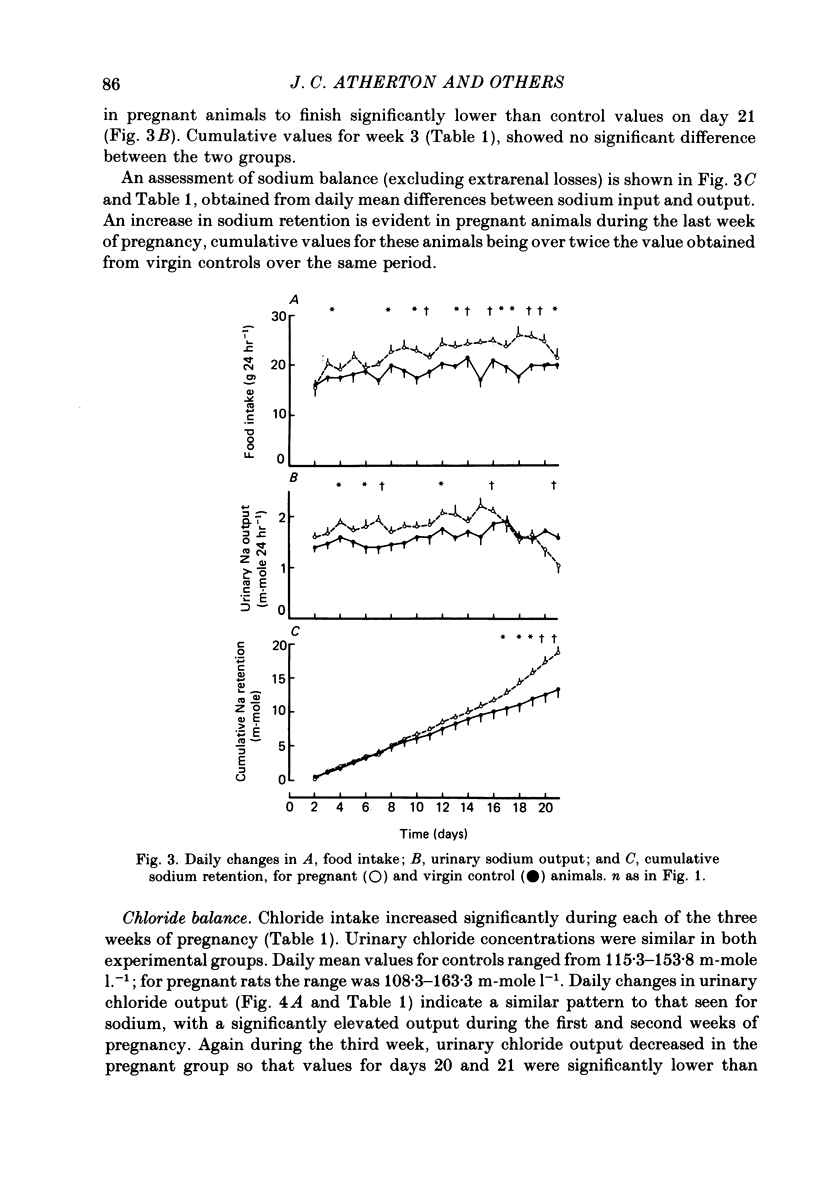
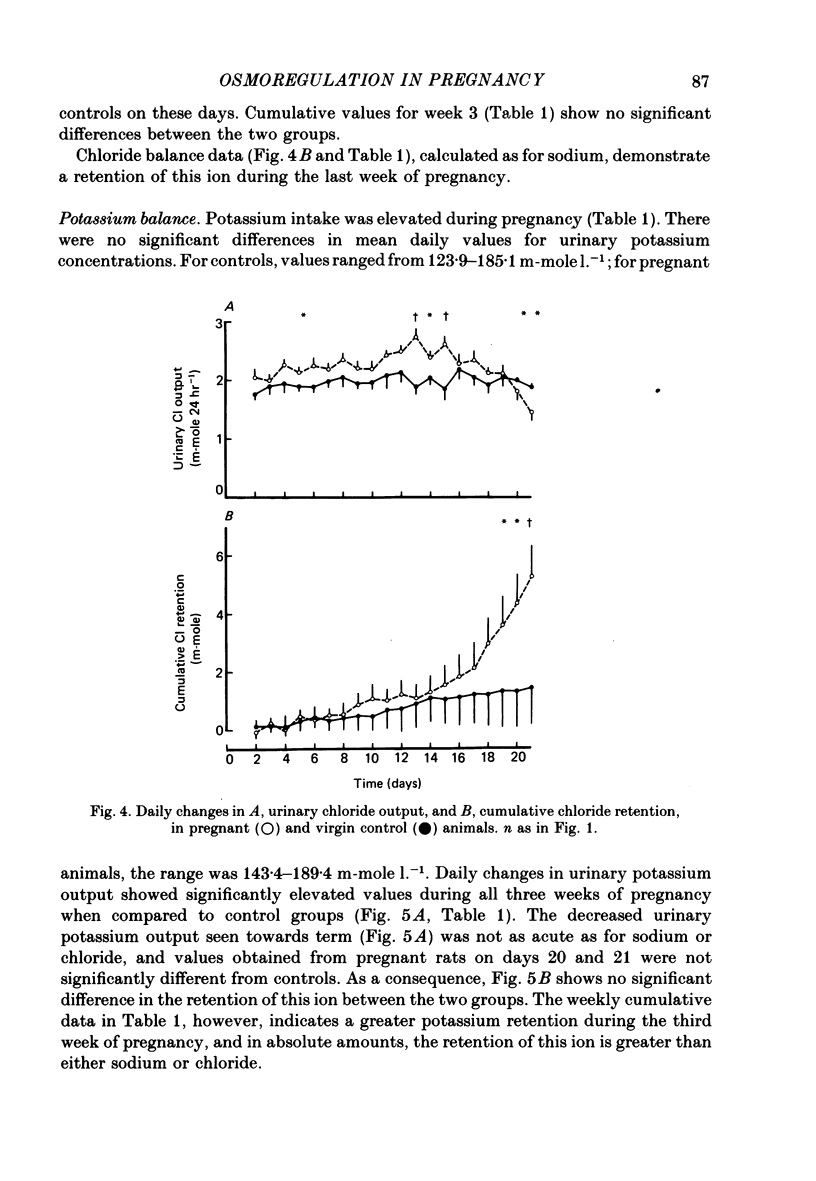
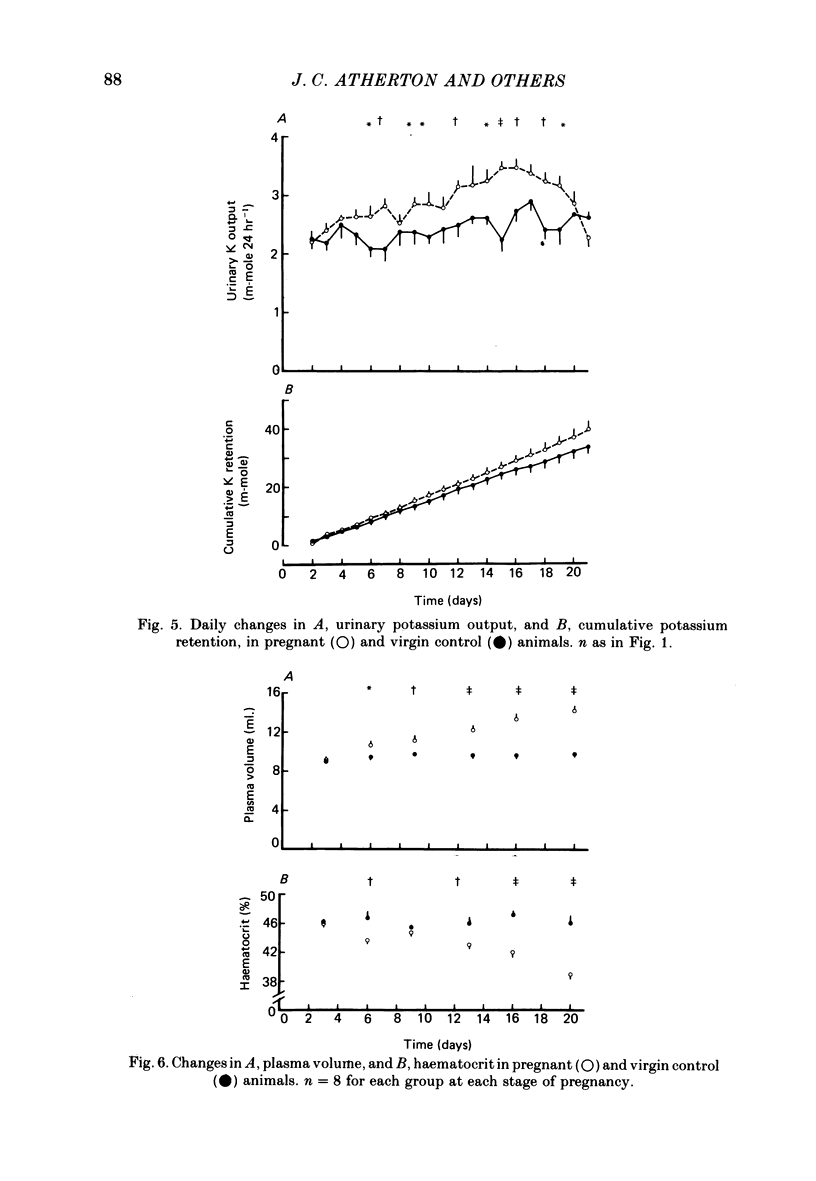
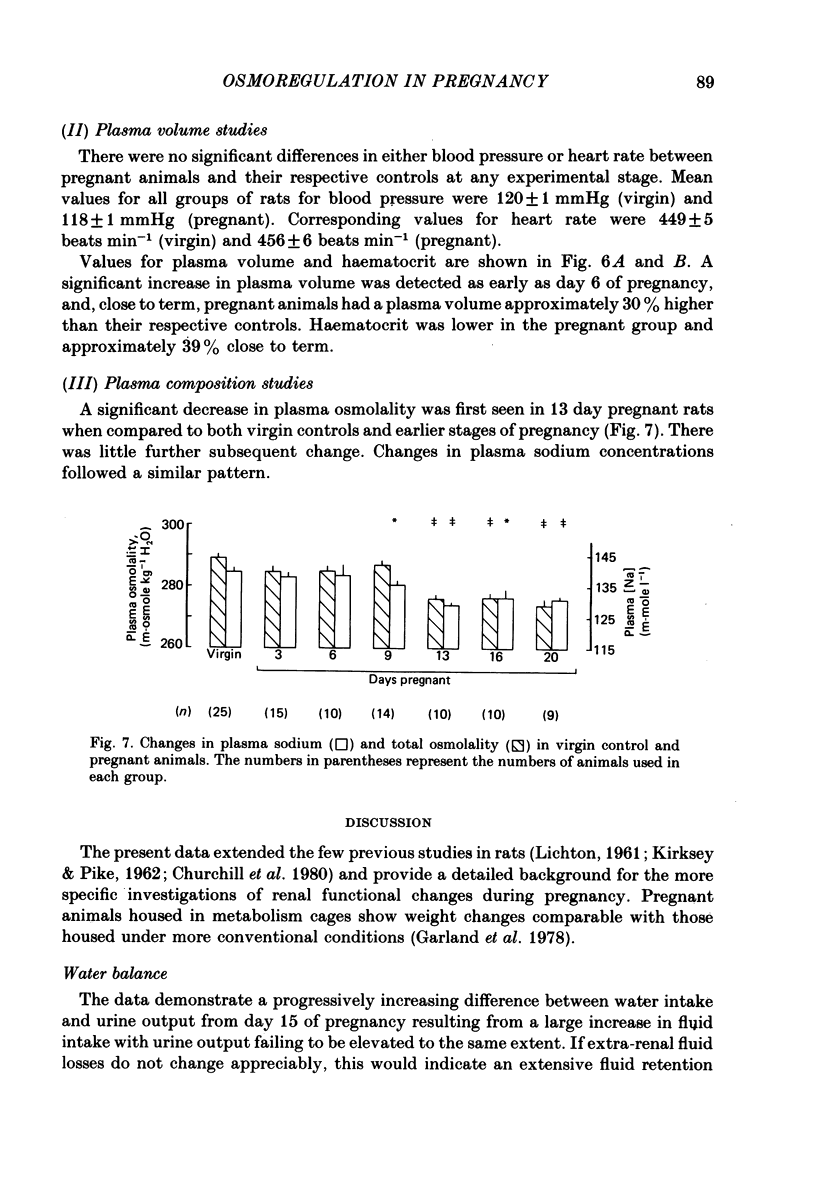
1. Daily changes in water and electrolyte balance during pregnancy were investigated in rats housed in metabolism cages. 2. Fluid intake was significantly elevated above control values from day 13 of pregnancy, with urine output failing to be raised to the same extent. This would result in an extensive fluid retention if extrarenal fluid losses were not substantially altered. 3. Electrolyte intake increased from as early as the third day after mating with an accompanying increase in renal ionic excretion. A net retention of Na, Cl and K did not occur until the final week of pregnancy when the urinary output of these ions was reduced. 4. In a parallel study, changes in plasma volume and composition throughout pregnancy were investigated. 5. A significant increase in plasma volume occurred from day 6 of pregnancy at a time well before fluid intake or urine output were altered. This indicates either an altered extrarenal output or a shift of fluid between body fluid compartments. 6. Maternal plasma sodium and total osmolality were reduced during the last week of pregnancy despite the salt retention, suggesting an increased fetal usage. 7. Such findings are related to the known renal and endocrine changes of rat pregnancy.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atherton J. C., Hai M. A., Thomas S. Effects of water diuresis and osmotic (mannitol) diuresis on urinary solute excretion by the conscious rat. J Physiol. 1968 Jul;197(2):395–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton J. C., Pirie S. C. The effect of pregnancy on glomerular filtration rate and salt and water reabsorption in the rat. J Physiol. 1981;319:153–164. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylis C. The mechanism of the increase in glomerular filtration rate in the twelve-day pregnant rat. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:405–414. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. H., Green R. Effects of pregnancy on glucose handling by rat kidneys. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:491–502. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher R. L., Fugo N. W., Collins W. E. Semicircadian rhythm in plasma levels of prolactin during early gestation in the rat. Endocrinology. 1972 Apr;90(4):1125–1127. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-4-1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchi-l S. E., Bengele H. H., Alexander E. A. Sodium balance during pregnancy in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jul;239(1):R143–R148. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1980.239.1.R143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill P. C. Calcium dependency of the inhibitory effect of antidiuretic hormone on in vitro renin secretion in rats. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill S., Bengele H. H., Melby J. C., Alexander E. A. Role of aldosterone in sodium retention of pregnancy in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):R175–R181. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1981.240.3.R175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison J. M., Lindheimer M. D. Changes in renal haemodynamics and kidney weight during pregnancy in the unanaesthetized rat. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:129–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durr J. A., Stamoutsos B., Lindheimer M. D. Osmoregulation during pregnancy in the rat. Evidence for resetting of the threshold for vasopressin secretion during gestation. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):337–346. doi: 10.1172/JCI110261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein A. N., Fitzsimons J. T., Rolls B. J. Drinking induced by injection of angiotensin into the rain of the rat. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):457–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland H. O. A role for prolactin in increasing proximal tubule length during pregnancy in the rat [proceedings]. J Endocrinol. 1979 Oct;83(1):28P–29P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland H. O., Green R. Micropuncture study of changes in glomerular filtration and ion and water handling by the rat kidney during pregnancy. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:389–409. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRKSEY A., PIKE R. L., CALLAHAN J. A. Some effects of high and low sodium intakes during pregnancy in the rat. II. Electrolyte concentrations of maternal plasma, muscle, bone and brain and of placenta, amniotic fluid, fetal plasma and total fetus in normal pregnancy. J Nutr. 1962 May;77:43–51. doi: 10.1093/jn/77.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRKSEY A., PIKE R. L. Some effects of high and low sodium intakes during pregnancy in the rat. I. Food consumption, weight gain, reproductive performance, electrolyte balances, plasma total protein and protein fractions in normal pregnancy. J Nutr. 1962 May;77:33–42. doi: 10.1093/jn/77.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. The dipsogenic activity of prolactin in male and female rats. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:435–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTON I. J. Salt saving in the pregnant rat. Am J Physiol. 1961 Nov;201:765–768. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.5.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTON I. J. Urinary excretion of water, sodium, and total solutes by the pregnant rat. Am J Physiol. 1963 Apr;204:563–567. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.4.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichton I. J., Hugh J. E. Renal clearance of water and solutes by pregnant rats treated with spironolactone. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Oct;129(1):312–315. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichton I. J., Rasa A. P., Hugh J. E. Effects of vasopressin and spironolactone on excretion of water and solutes by the pregnant rat. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jun;214(6):1468–1474. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.6.1468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindheimer M. D., Katz A. I. Kidney function in the pregnant rat. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Oct;78(4):633–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishige W. K., Pepe G. J., Rothchild I. Serum luteinizing hormone, prolactin and progesterone levels during pregnancy in the rat. Endocrinology. 1973 May;92(5):1527–1530. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-5-1527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. S., Neill J. D. Termination at midpregnancy of the two daily surges of plasma prolactin initiated by mating in the rat. Endocrinology. 1976 Mar;98(3):696–701. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-3-696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp G. T., Coghlan J. P., Shulkes A. A., Skinner S. L., Wintour E. M. Regulation of aldosterone in the rat. Effect of oestrous cycle, pregnancy, and sodium status. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1978 Oct;56(5):545–551. doi: 10.1038/icb.1978.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


