Abstract
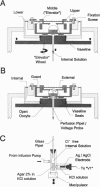
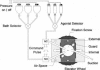
The study of whole-cell currents from ion channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes with conventional two-electrode voltage clamp has two major limitations. First, the large diameter and spherical geometry of oocytes prevent extremely fast solution changes. Second, the internal medium is not controlled, which limits the experimental versatility of the oocyte expression system. For example, because the internal medium is not controlled, endogenous calcium-activated chloride conductances can contaminate currents measured with channels that are permeable to calcium. We describe a new technique that combines vaseline-gap voltage clamp for oocytes with a fast superfusion system. The vaseline-gap procedure is simplified by having the micropipette that monitors voltage serve a dual role as a perfusion micropipette that controls the internal solution. In addition, the technique provides fast external solution changes that are complete in 30-50 ms. We applied the approach to measure the calcium permeability of a muscle and a neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Very fast agonist induced currents were measured without contamination by the secondary activation of calcium-dependent chloride channels.
Full text
PDF
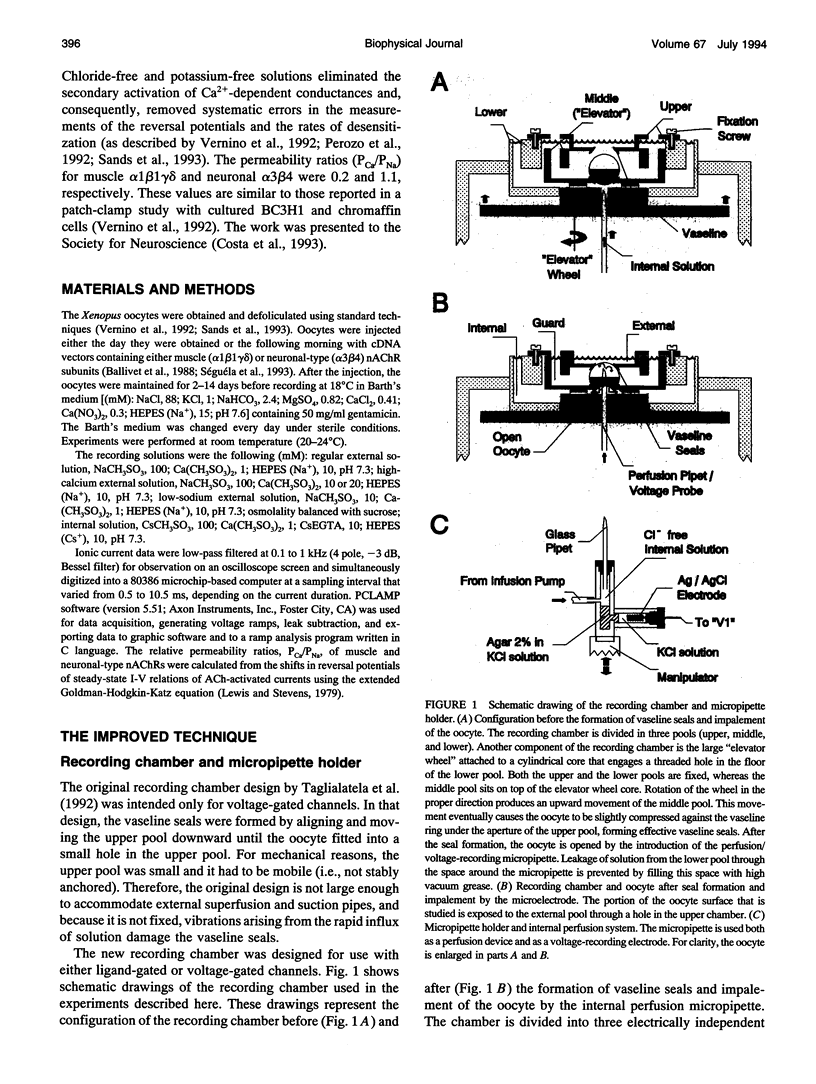
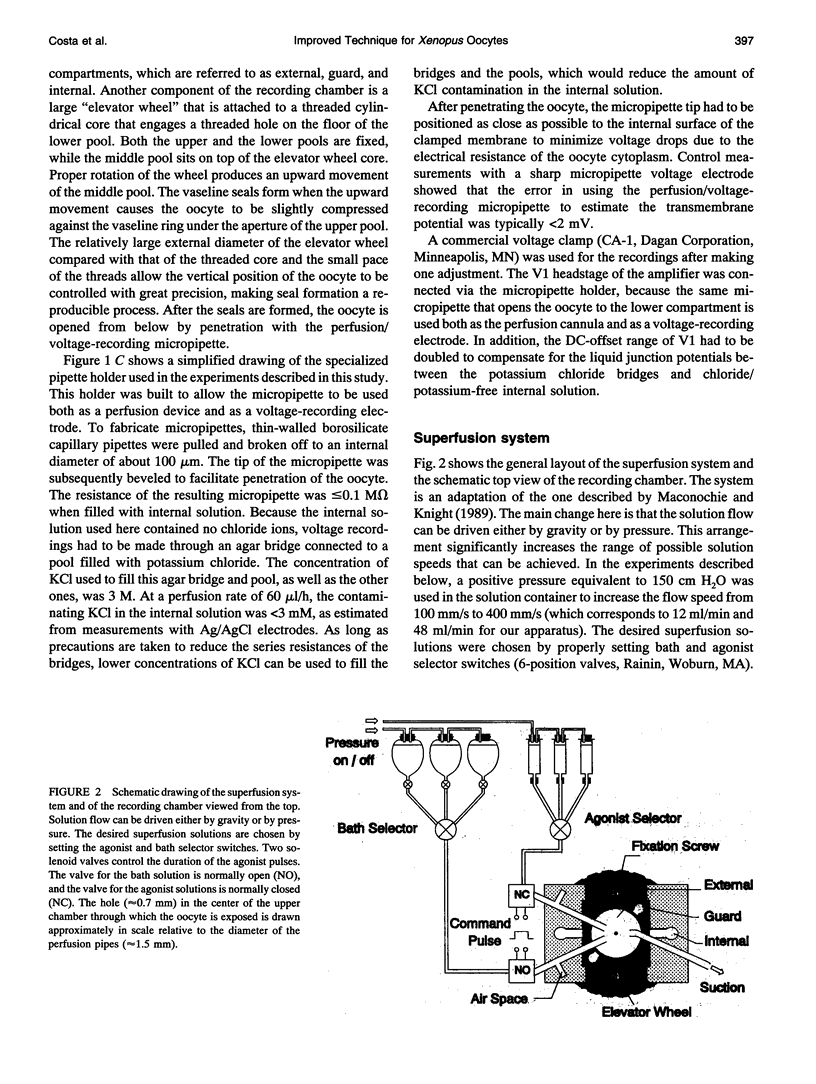

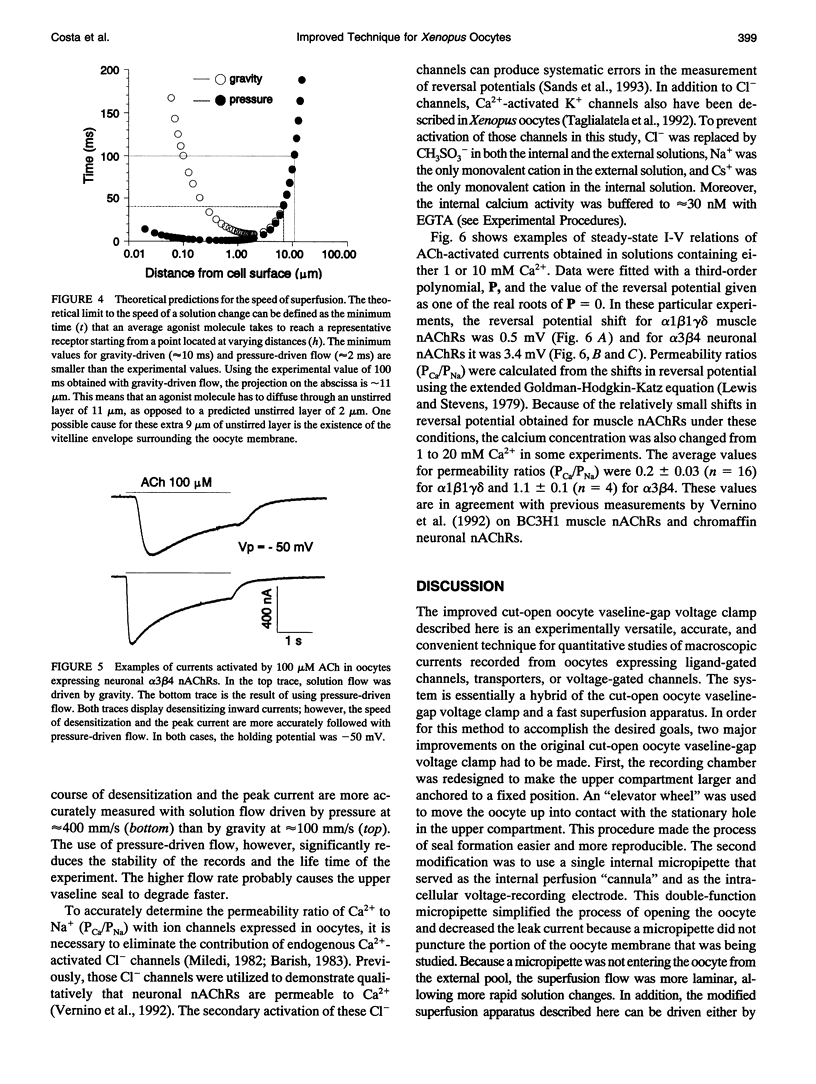
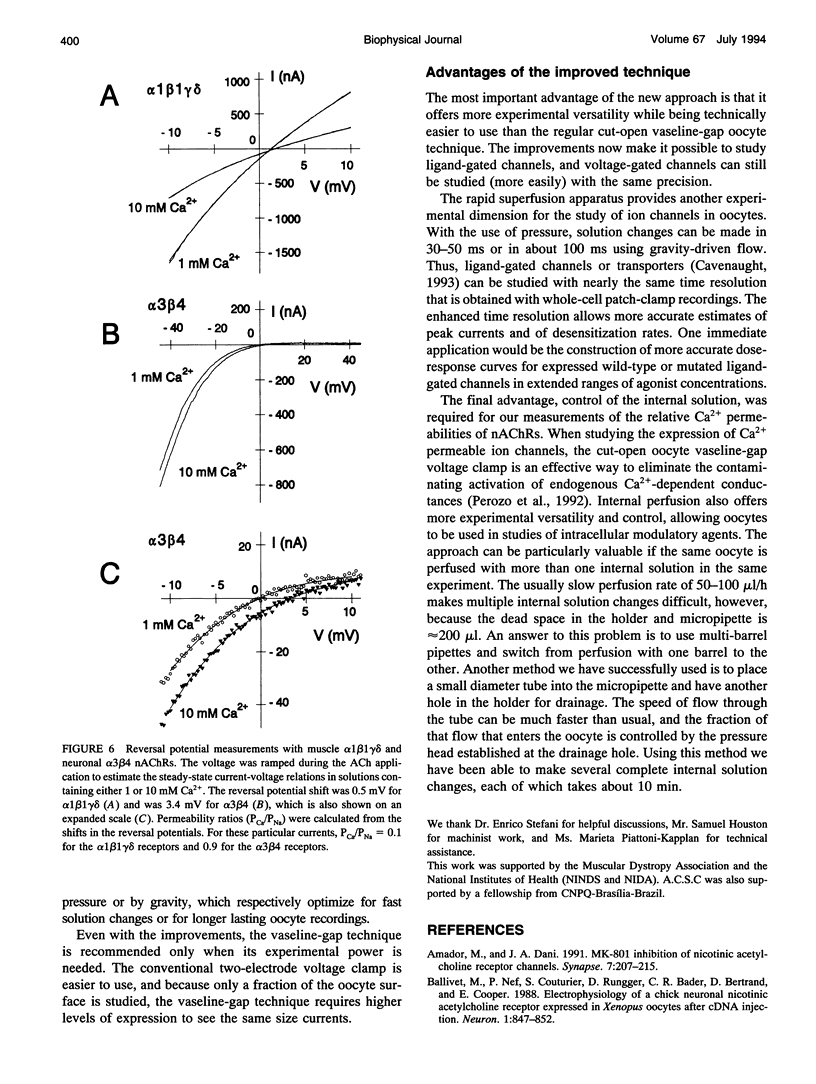

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amador M., Dani J. A. MK-801 inhibition of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channels. Synapse. 1991 Mar;7(3):207–215. doi: 10.1002/syn.890070305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballivet M., Nef P., Couturier S., Rungger D., Bader C. R., Bertrand D., Cooper E. Electrophysiology of a chick neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes after cDNA injection. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):847–852. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barish M. E. A transient calcium-dependent chloride current in the immature Xenopus oocyte. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:309–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Khodorova A., Jonas P., Helm P. J., Wisden W., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Calcium-permeable AMPA-kainate receptors in fusiform cerebellar glial cells. Science. 1992 Jun 12;256(5063):1566–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.1317970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dascal N. The use of Xenopus oocytes for the study of ion channels. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1987;22(4):317–387. doi: 10.3109/10409238709086960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilger J. P., Brett R. S. Direct measurement of the concentration- and time-dependent open probability of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channel. Biophys J. 1990 Apr;57(4):723–731. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82593-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Hume R. I., Heinemann S. F. Structural determinants of barium permeation and rectification in non-NMDA glutamate receptor channels. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):4080–4087. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-04080.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Heinemann S. F. Ca2+ permeability of unedited and edited versions of the kainate selective glutamate receptor GluR6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavanaugh M. P. Voltage dependence of facilitated arginine flux mediated by the system y+ basic amino acid transporter. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 8;32(22):5781–5785. doi: 10.1021/bi00073a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maconochie D. J., Knight D. E. A method for making solution changes in the sub-millisecond range at the tip of a patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Sep;414(5):589–596. doi: 10.1007/BF00580996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maconochie D. J., Knight D. E. A study of the bovine adrenal chromaffin nicotinic receptor using patch clamp and concentration-jump techniques. J Physiol. 1992 Aug;454:129–153. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. A calcium-dependent transient outward current in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jul 22;215(1201):491–497. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulle C., Choquet D., Korn H., Changeux J. P. Calcium influx through nicotinic receptor in rat central neurons: its relevance to cellular regulation. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90115-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perozo E., Papazian D. M., Stefani E., Bezanilla F. Gating currents in Shaker K+ channels. Implications for activation and inactivation models. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):160–171. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81802-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands S. B., Costa A. C., Patrick J. W. Barium permeability of neuronal nicotinic receptor alpha 7 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Biophys J. 1993 Dec;65(6):2614–2621. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81296-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguéla P., Wadiche J., Dineley-Miller K., Dani J. A., Patrick J. W. Molecular cloning, functional properties, and distribution of rat brain alpha 7: a nicotinic cation channel highly permeable to calcium. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):596–604. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00596.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taglialatela M., Toro L., Stefani E. Novel voltage clamp to record small, fast currents from ion channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Biophys J. 1992 Jan;61(1):78–82. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81817-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernino S., Amador M., Luetje C. W., Patrick J., Dani J. A. Calcium modulation and high calcium permeability of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90114-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]