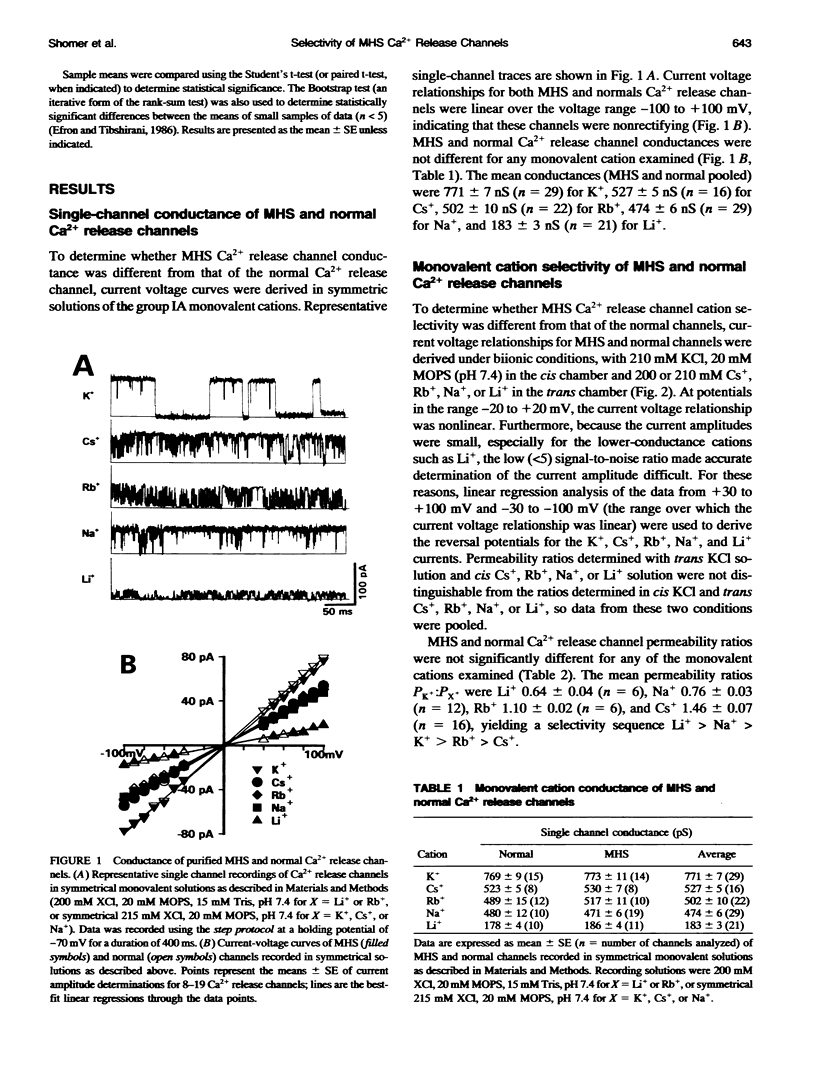
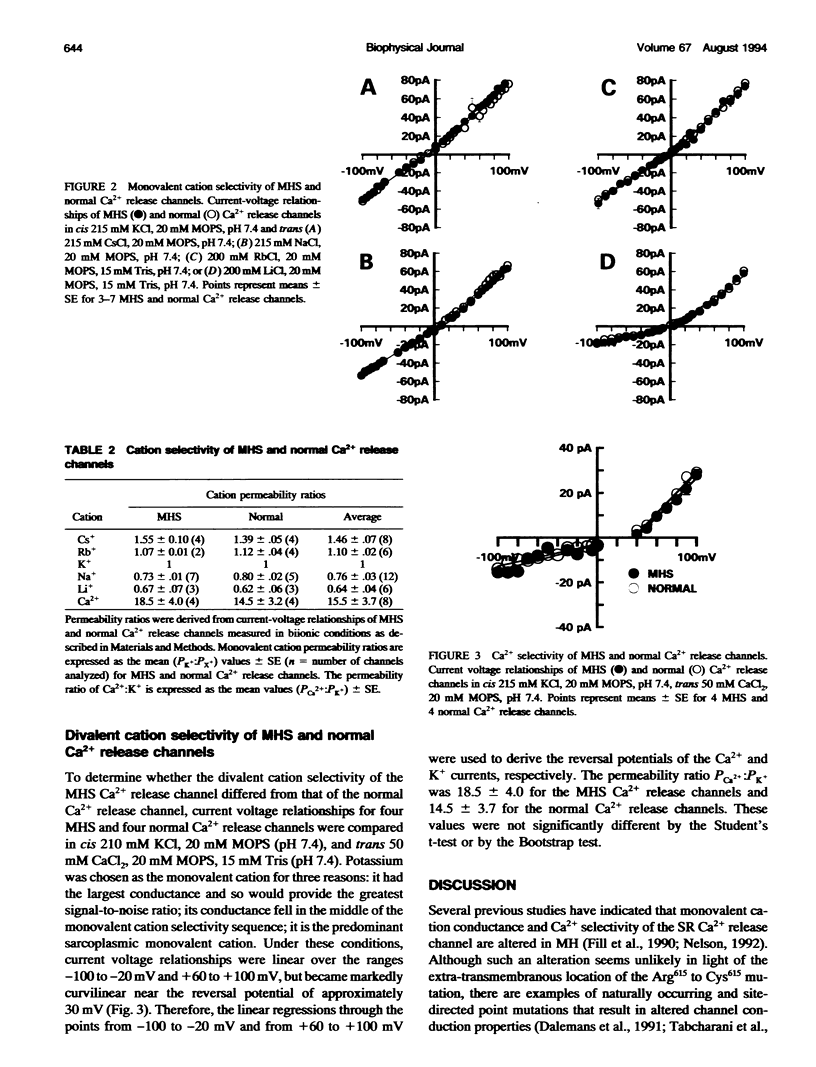
Abstract
The Arg615 to Cys615 mutation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ release channel of malignant hyperthermia susceptible (MHS) pigs results in a decreased sensitivity of the channel to inhibitory Ca2+ concentrations. To investigate whether this mutation also affects the ion selectivity filter of the channel, the monovalent cation conductances and ion permeability ratios of single Ca2+ release channels incorporated into planar lipid bilayers were compared. Monovalent cation conductances in symmetrical solutions were: Li+, 183 pS +/- 3 (n = 21); Na+, 474 pS +/- 6 (n = 29); K+, 771 pS +/- 7 (n = 29); Rb+, 502 pS +/- 10 (n = 22); and Cs+, 527 pS +/- 5 (n = 16). The single-channel conductances of MHS and normal Ca2+ release channel were not significantly different for any of the monovalent cations tested. Permeability ratios measured under biionic conditions had the permeability sequence Ca2+ >> Li+ > Na+ > K+ > or Rb+ > Cs+, with no significant difference noted between MHS and normal channels. This systematic examination of the conduction properties of the pig skeletal muscle Ca2+ release channel indicated a higher Ca2+ selectivity (PCa2+:Pk+ approximately 15.5) than the sixfold Ca2+ selectivity previously reported for rabbit skeletal (Smith et al., 1988) or sheep cardiac muscle (Tinker et al., 1992) Ca2+ release channels. These results also indicate that although Ca2+ regulation of Ca2+ release channel activity is altered, the Arg615 to Cys615 mutation of the porcine Ca2+ release channel does not affect the conductance or ion selectivity properties of the channel.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dalemans W., Barbry P., Champigny G., Jallat S., Dott K., Dreyer D., Crystal R. G., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Lazdunski M. Altered chloride ion channel kinetics associated with the delta F508 cystic fibrosis mutation. Nature. 1991 Dec 19;354(6354):526–528. doi: 10.1038/354526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fill M., Coronado R., Mickelson J. R., Vilven J., Ma J. J., Jacobson B. A., Louis C. F. Abnormal ryanodine receptor channels in malignant hyperthermia. Biophys J. 1990 Mar;57(3):471–475. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82563-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fill M., Stefani E., Nelson T. E. Abnormal human sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release channels in malignant hyperthermic skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1991 May;59(5):1085–1090. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82323-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard E. F., Otsu K., Fujii J., Duff C., de Leon S., Khanna V. K., Britt B. A., Worton R. G., MacLennan D. H. Polymorphisms and deduced amino acid substitutions in the coding sequence of the ryanodine receptor (RYR1) gene in individuals with malignant hyperthermia. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1247–1254. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90042-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard E. F., Otsu K., Fujii J., Khanna V. K., de Leon S., Derdemezi J., Britt B. A., Duff C. L., Worton R. G., MacLennan D. H. A substitution of cysteine for arginine 614 in the ryanodine receptor is potentially causative of human malignant hyperthermia. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):751–755. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90084-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan K., Couch F., Powers P. A., Gregg R. G. A cysteine-for-arginine substitution (R614C) in the human skeletal muscle calcium release channel cosegregates with malignant hyperthermia. Anesth Analg. 1992 Sep;75(3):441–448. doi: 10.1213/00000539-199209000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis C. F., Zualkernan K., Roghair T., Mickelson J. R. The effects of volatile anesthetics on calcium regulation by malignant hyperthermia-susceptible sarcoplasmic reticulum. Anesthesiology. 1992 Jul;77(1):114–125. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199207000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Fill M., Knudson C. M., Campbell K. P., Coronado R. Ryanodine receptor of skeletal muscle is a gap junction-type channel. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):99–102. doi: 10.1126/science.2459777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelson J. R., Litterer L. A., Jacobson B. A., Louis C. F. Stimulation and inhibition of [3H]ryanodine binding to sarcoplasmic reticulum from malignant hyperthermia susceptible pigs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Apr;278(1):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90255-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T. E., Lin M., Volpe P. Evidence for intraluminal Ca++ regulatory site defect in sarcoplasmic reticulum from malignant hyperthermia pig muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Feb;256(2):645–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu K., Khanna V. K., Archibald A. L., MacLennan D. H. Cosegregation of porcine malignant hyperthermia and a probable causal mutation in the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor gene in backcross families. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):744–750. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90083-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Pinkos J. pH modulates conducting and gating behaviour of single calcium release channels. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Feb;415(5):645–647. doi: 10.1007/BF02583520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker A., Lindsay A. R., Williams A. J. A model for ionic conduction in the ryanodine receptor channel of sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Sep;100(3):495–517. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzato F., Fujii J., Otsu K., Phillips M., Green N. M., Lai F. A., Meissner G., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human and rabbit forms of the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2244–2256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


