Abstract
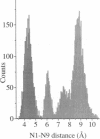
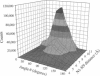
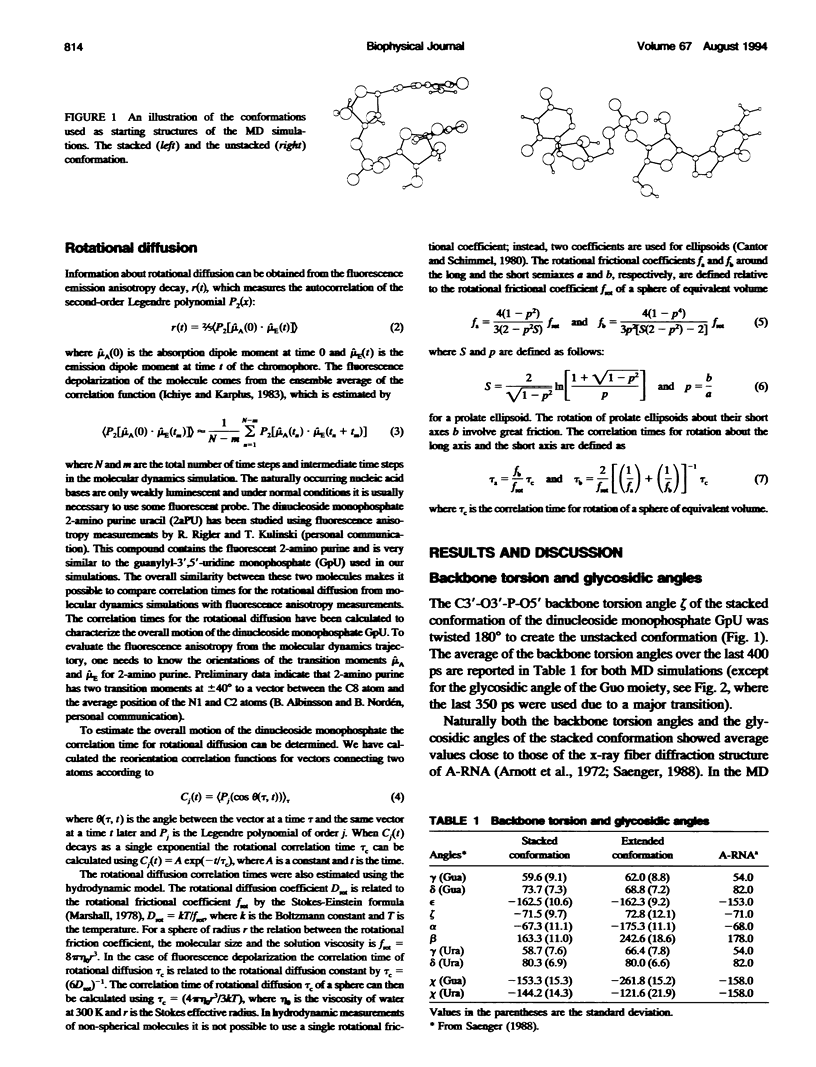
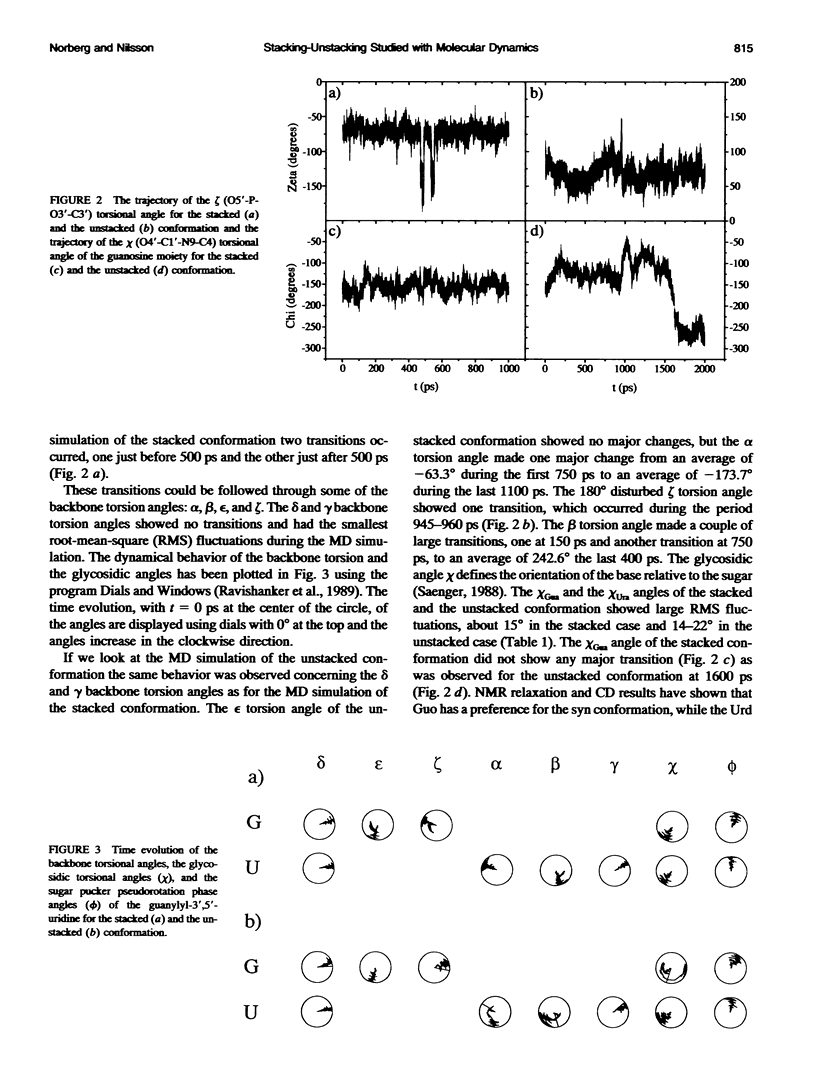
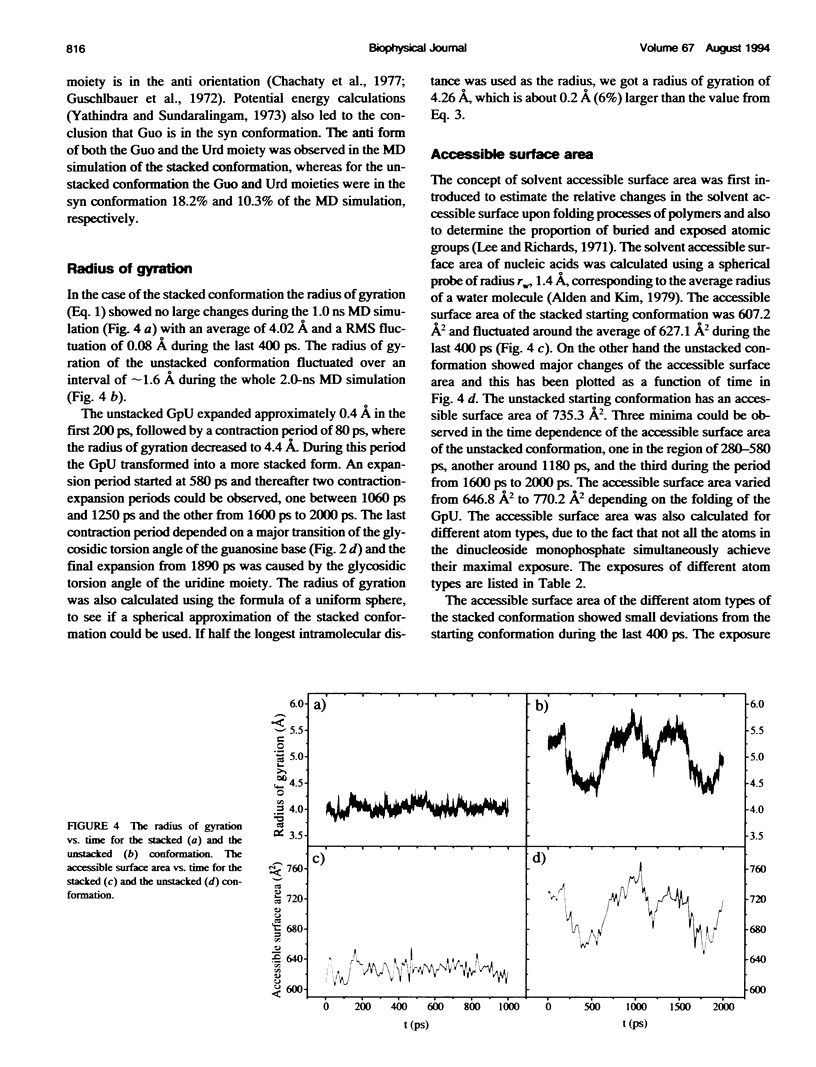
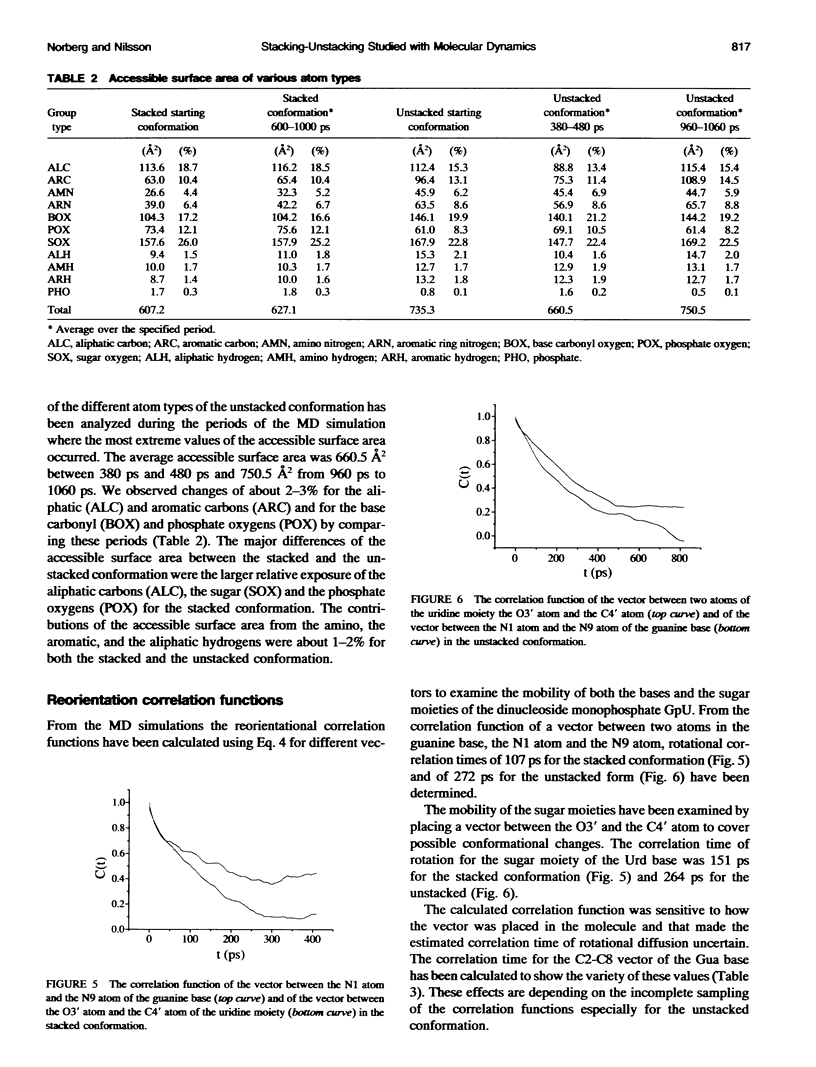
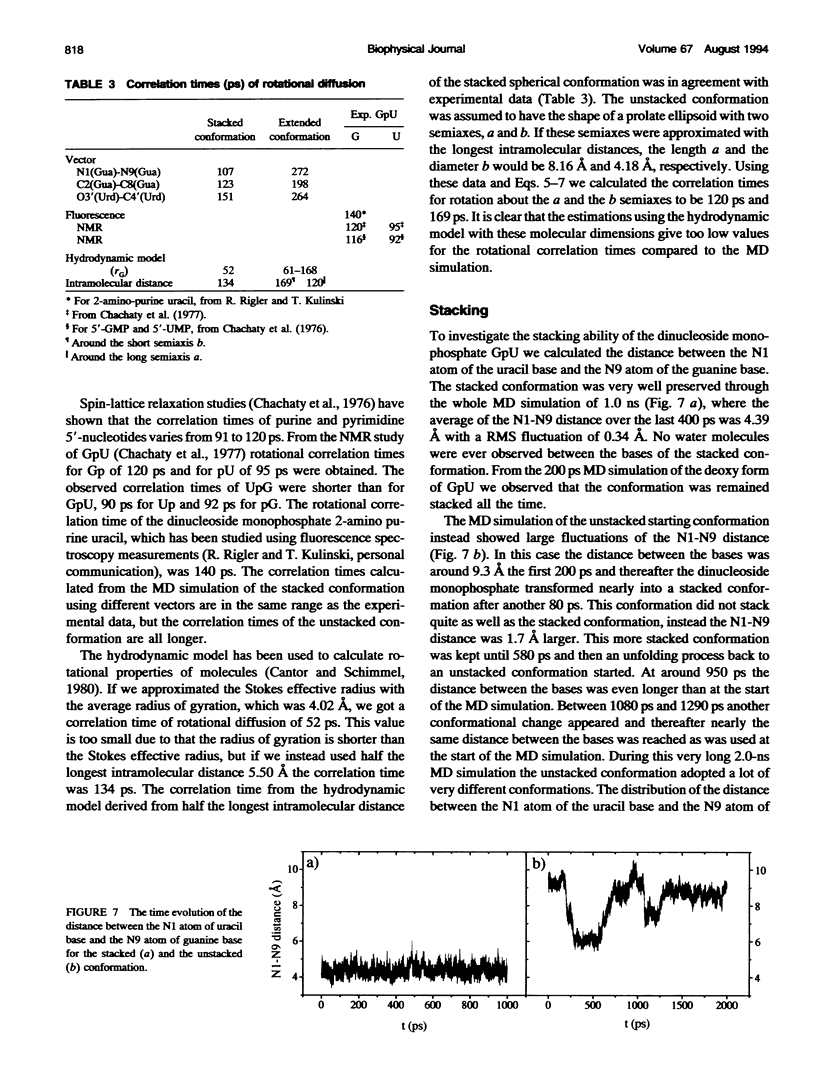
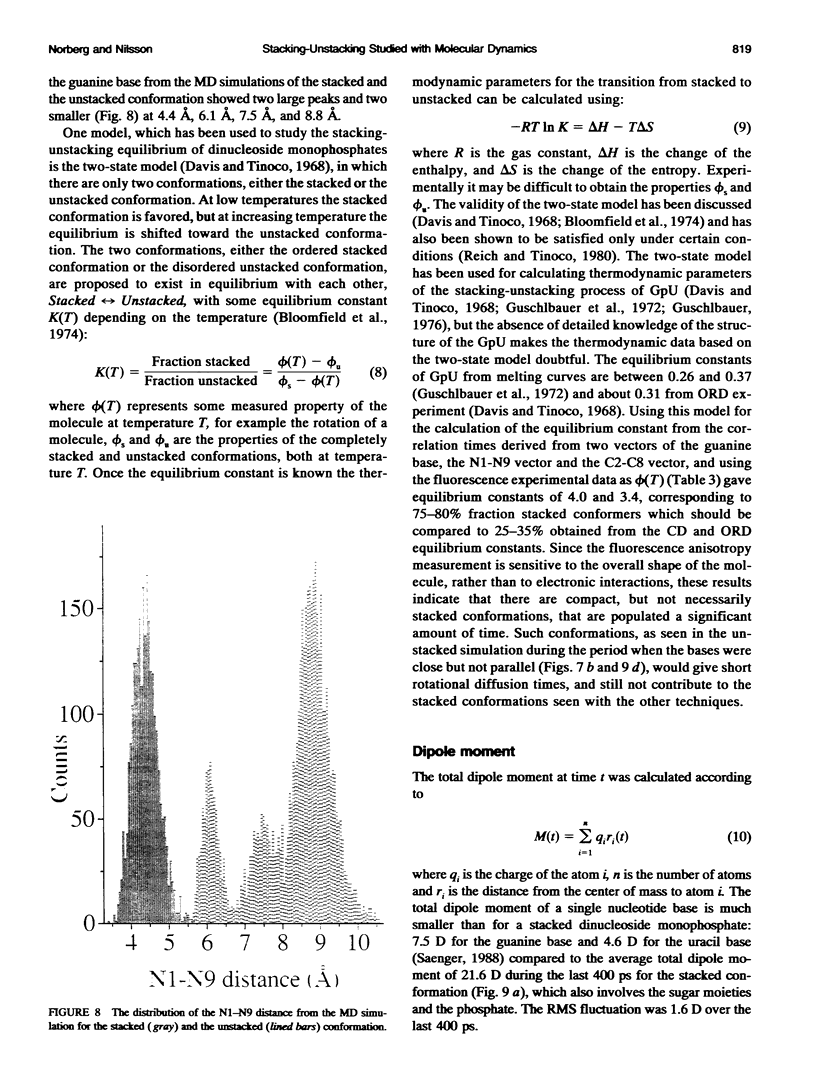
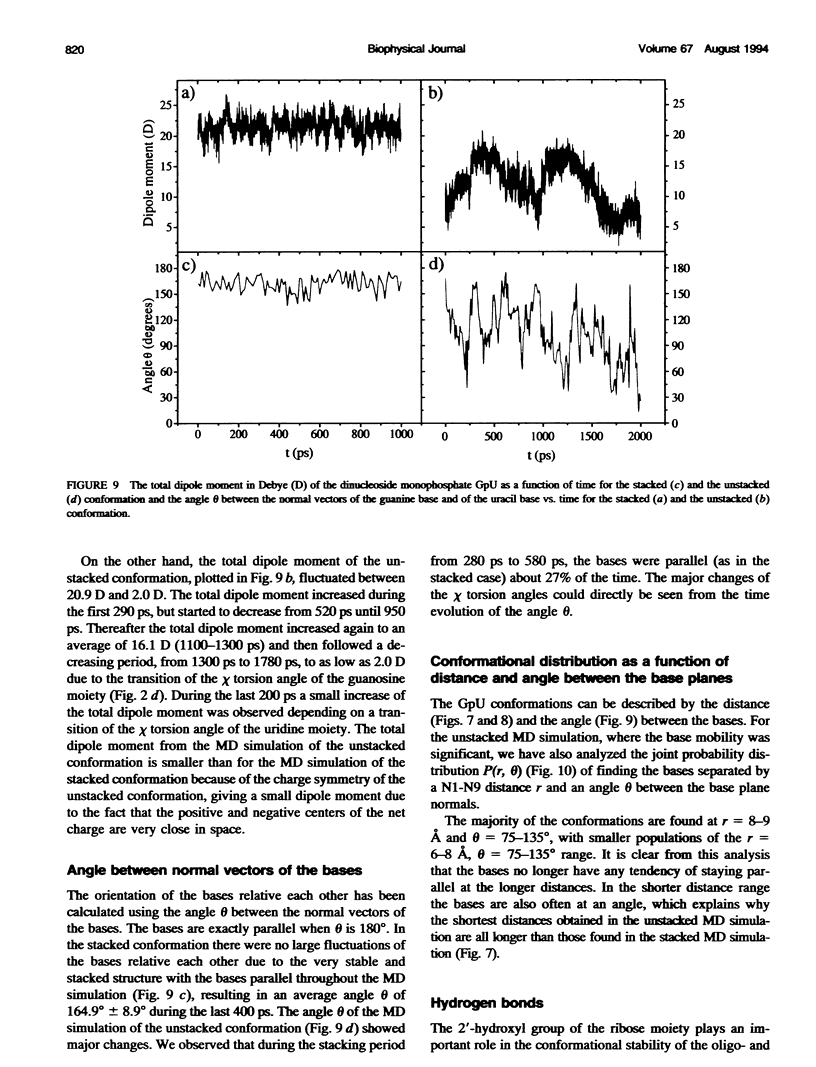
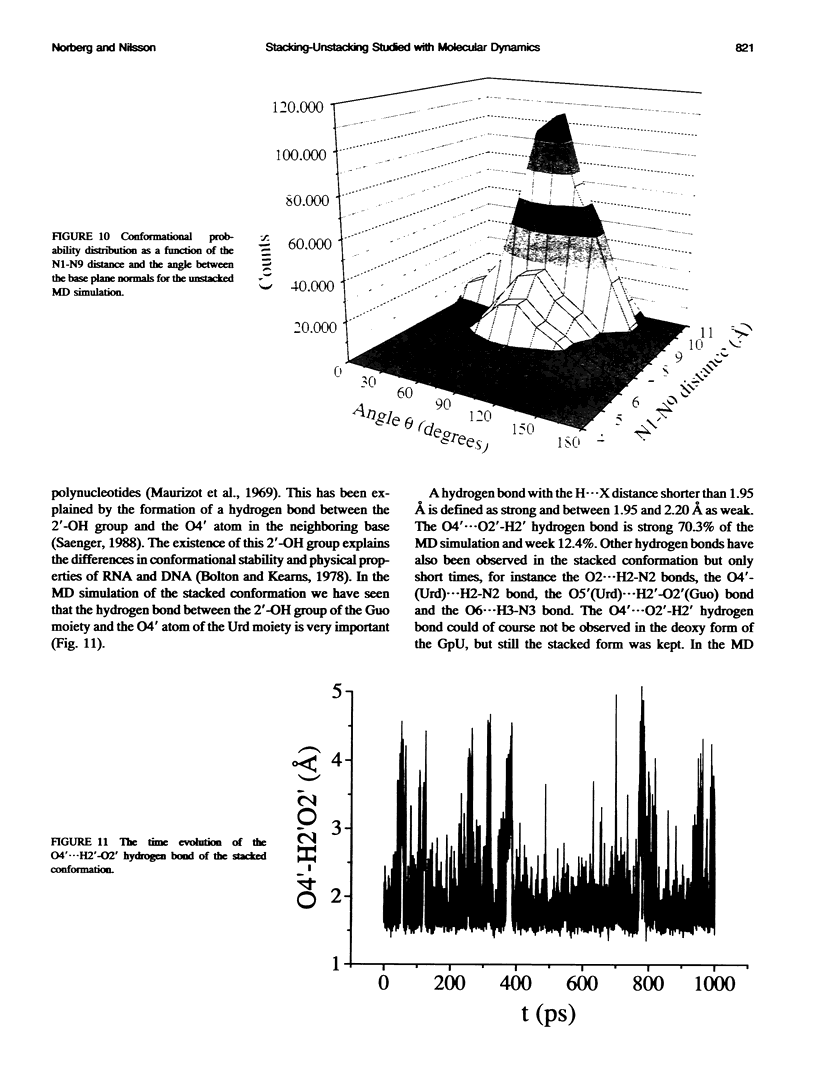
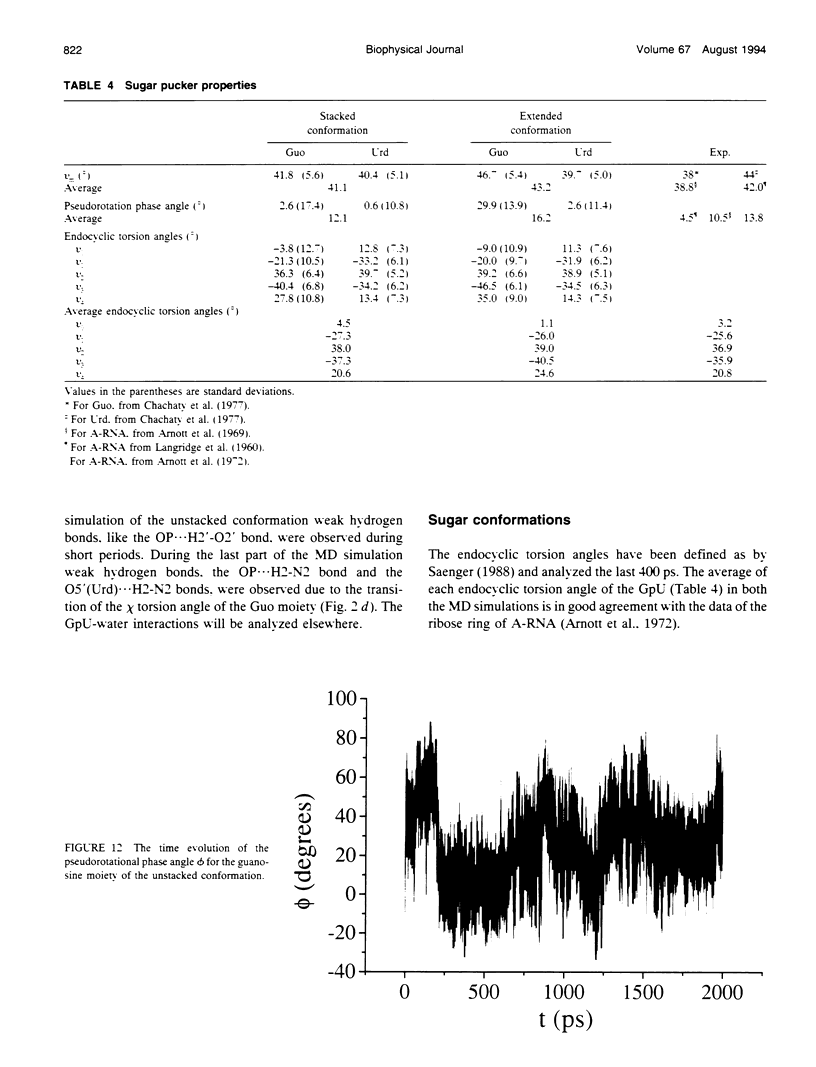
Molecular dynamics simulations were carried out on two conformations of the dinucleoside monophosphate guanylyl-3',5'-uridine (GpU) in aqueous solution with one sodium counterion. One stacked conformation and one with the C3'-O3'-P-O5' backbone torsion angle twisted 180 degrees to create an unstacked conformation. We observed a relatively stable behavior of the stacked conformation, which remained stacked throughout the simulation, whereas the unstacked conformation showed major changes in the backbone torsion and glycosidic angles. During the simulation the unstacked conformation transformed into a more stacked form and then back again to an unstacked one. The calculated correlation times for rotational diffusion from the molecular dynamics simulations are in agreement with fluorescence anisotropy and nuclear magnetic resonance data. As expected, the correlation times for rotational diffusion of the unstacked conformation were observed to be longer than for the stacked conformation. The 2'OH group may contribute in stabilizing the stacked conformation, where the O2'-H...O4' hydrogen bond occurred in 82.7% of the simulation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alden C. J., Kim S. H. Solvent-accessible surfaces of nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):411–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90268-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altona C., Sundaralingam M. Conformational analysis of the sugar ring in nucleosides and nucleotides. A new description using the concept of pseudorotation. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Nov 15;94(23):8205–8212. doi: 10.1021/ja00778a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W., Dover S. D. Optimised parameters for RNA double-helices. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 26;48(6):1392–1399. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90867-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton P. H., Kearns D. R. Hydrogen bonding of the 2' OH in RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 16;517(2):329–337. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chachaty C., Yokono T., Tran-Dinh S., Guschlbauer W. Oligonucleotide conformations. (5) NMR and relaxation studies on GpU and UpG at neutral pH. Biophys Chem. 1977 Jan;6(2):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(77)87004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chachaty C., Zemb T., Langlet G., Tran Dinh Son, Buc H., Morange M. A proton-relaxation-time study of the conformation of some purine and pyrimidine 5'-nucleotides in aqueous solution. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 2;62(1):45–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. C., Tinoco I., Jr Temperature-dependent properties of dinucleoside phosphates. Biopolymers. 1968;6(2):223–242. doi: 10.1002/bip.1968.360060206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter C. A. Sequence-dependent DNA structure. The role of base stacking interactions. J Mol Biol. 1993 Apr 5;230(3):1025–1054. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiye T., Karplus M. Fluorescence depolarization of tryptophan residues in proteins: a molecular dynamics study. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 7;22(12):2884–2893. doi: 10.1021/bi00281a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann J. M., Guschlbauer W., Tran-Dinh S. Conformation and flexibility of GpC and CpG in neutral aqueous solution using 1H nuclear-magnetic-resonance and spin-lattice-relaxation time measurements. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):141–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravishanker G., Swaminathan S., Beveridge D. L., Lavery R., Sklenar H. Conformational and helicoidal analysis of 30 PS of molecular dynamics on the d(CGCGAATTCGCG) double helix: "curves", dials and windows. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1989 Feb;6(4):669–699. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1989.10507729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibel G. L., Singh U. C., Kollman P. A. A molecular dynamics simulation of double-helical B-DNA including counterions and water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6537–6540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soman K. V., Karimi A., Case D. A. Unfolding of an alpha-helix in water. Biopolymers. 1991 Oct 15;31(12):1351–1361. doi: 10.1002/bip.360311202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidor B., Irikura K. K., Brooks B. R., Karplus M. Dynamics of DNA oligomers. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(1):231–252. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]