Abstract
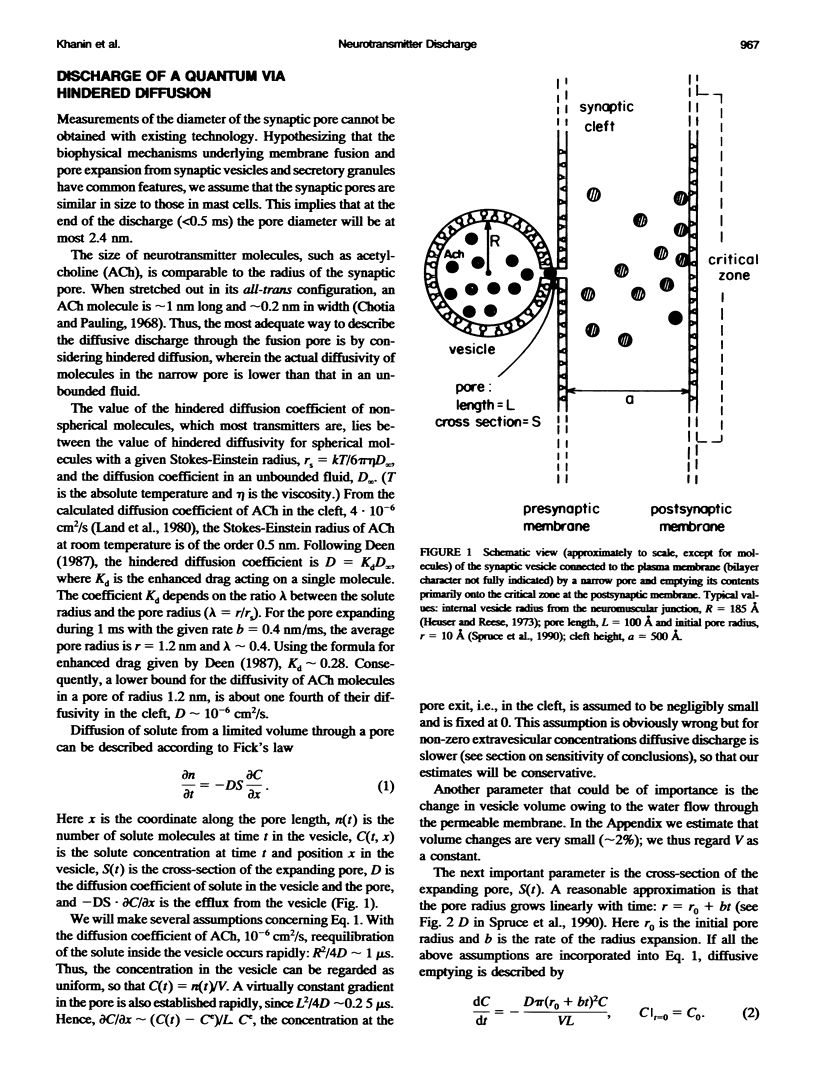
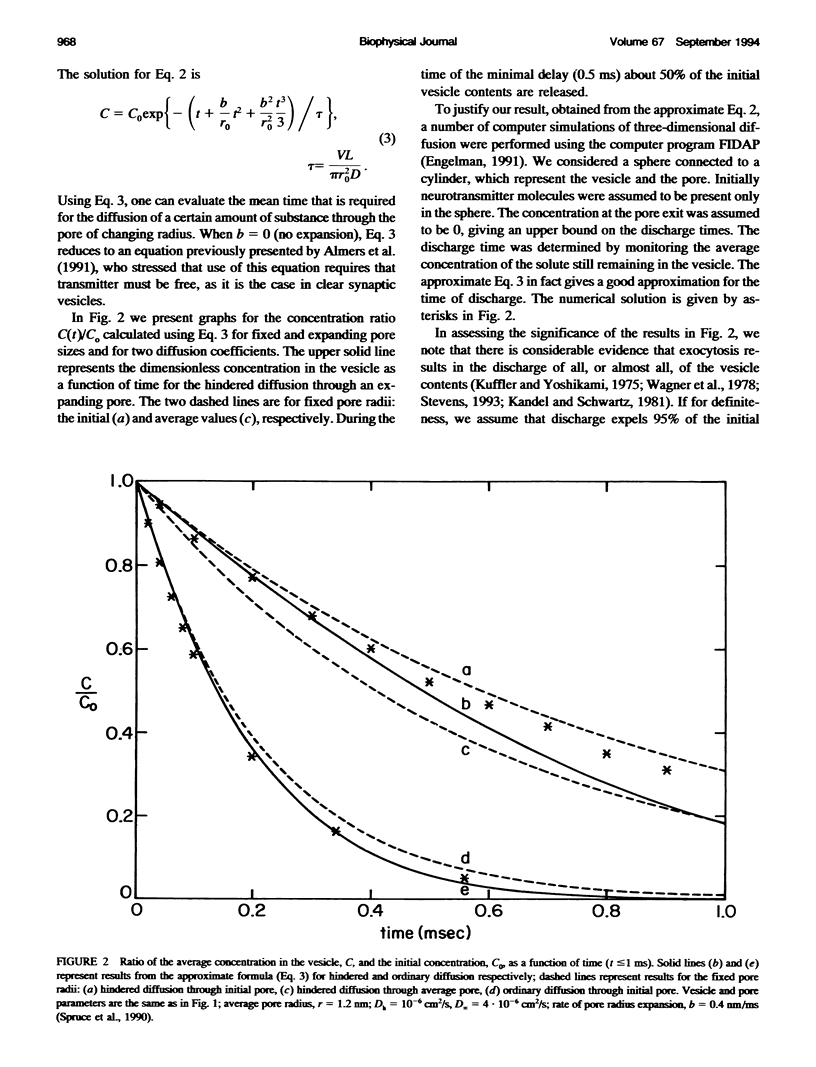
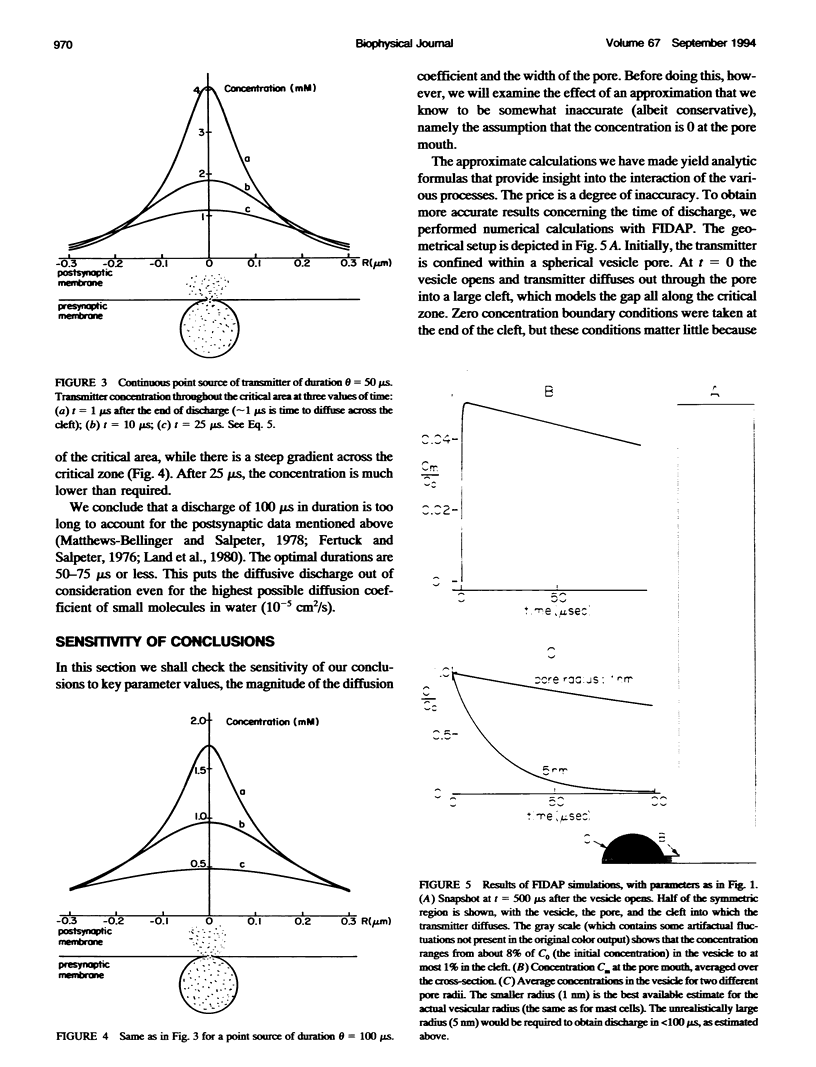
In the present work we show that diffusion cannot provide the observed fast discharge of neurotransmitter from a synaptic vesicle during neurotransmitter release, mainly because it is not sufficiently rapid nor is it sufficiently temperature-dependent. Modeling the discharge from the vesicle into the cleft as a continuous point source, we have determined that discharge should occur in 50-75 microseconds, to provide the observed high concentrations of transmitter at the critical zone.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W., Breckenridge L. J., Iwata A., Lee A. K., Spruce A. E., Tse F. W. Millisecond studies of single membrane fusion events. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;635:318–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb36502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow R. H., von Rüden L., Neher E. Delay in vesicle fusion revealed by electrochemical monitoring of single secretory events in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):60–63. doi: 10.1038/356060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran M. J., Brodwick M. S. Ionic control of the size of the vesicle matrix of beige mouse mast cells. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Oct;98(4):771–790. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.4.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datyner N. B., Gage P. W. Phasic secretion of acetylcholine at a mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:299–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. Control of quantal transmitter release at frog's motor nerve terminals. II. Modulation by de- or hyperpolarizing pulses. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Nov;402(3):235–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00585505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S. Evidence for recycling of synaptic vesicle membrane during transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Cell Biol. 1973 May;57(2):315–344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of temperature on the synaptic delay at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):656–670. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. The number of transmitter molecules in a quantum: an estimate from iontophoretic application of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):465–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land B. R., Harris W. V., Salpeter E. E., Salpeter M. M. Diffusion and binding constants for acetylcholine derived from the falling phase of miniature endplate currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1594–1598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land B. R., Salpeter E. E., Salpeter M. M. Acetylcholine receptor site density affects the rising phase of miniature endplate currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3736–3740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Simon S. M. Transmission by presynaptic spike-like depolarization in the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2415–2419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig C., Parnas H., Segel L. Release kinetics as a tool to describe drug effects on neurotransmitter release. J Theor Biol. 1990 May 22;144(2):225–248. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(05)80322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews-Bellinger J., Salpeter M. M. Distribution of acetylcholine receptors at frog neuromuscular junctions with a discussion of some physiological implications. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:197–213. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Hovav G., Parnas I. Effect of Ca2+ diffusion on the time course of neurotransmitter release. Biophys J. 1989 May;55(5):859–874. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82885-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumplin D. W., Reese T. S., Llinás R. Are the presynaptic membrane particles the calcium channels? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7210–7213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruce A. E., Breckenridge L. J., Lee A. K., Almers W. Properties of the fusion pore that forms during exocytosis of a mast cell secretory vesicle. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):643–654. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90192-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uvnäs B., Aborg C. H., Lyssarides L., Thyberg J. Cation exchanger properties of isolated rat peritoneal mast cell granules. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Sep;125(1):25–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. A., Carlson S. S., Kelly R. B. Chemical and physical characterization of cholinergic synaptic vesicles. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1199–1206. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathey J. C., Nass M. M., Lester H. A. Numerical reconstruction of the quantal event at nicotinic synapses. Biophys J. 1979 Jul;27(1):145–164. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85208-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]