Abstract
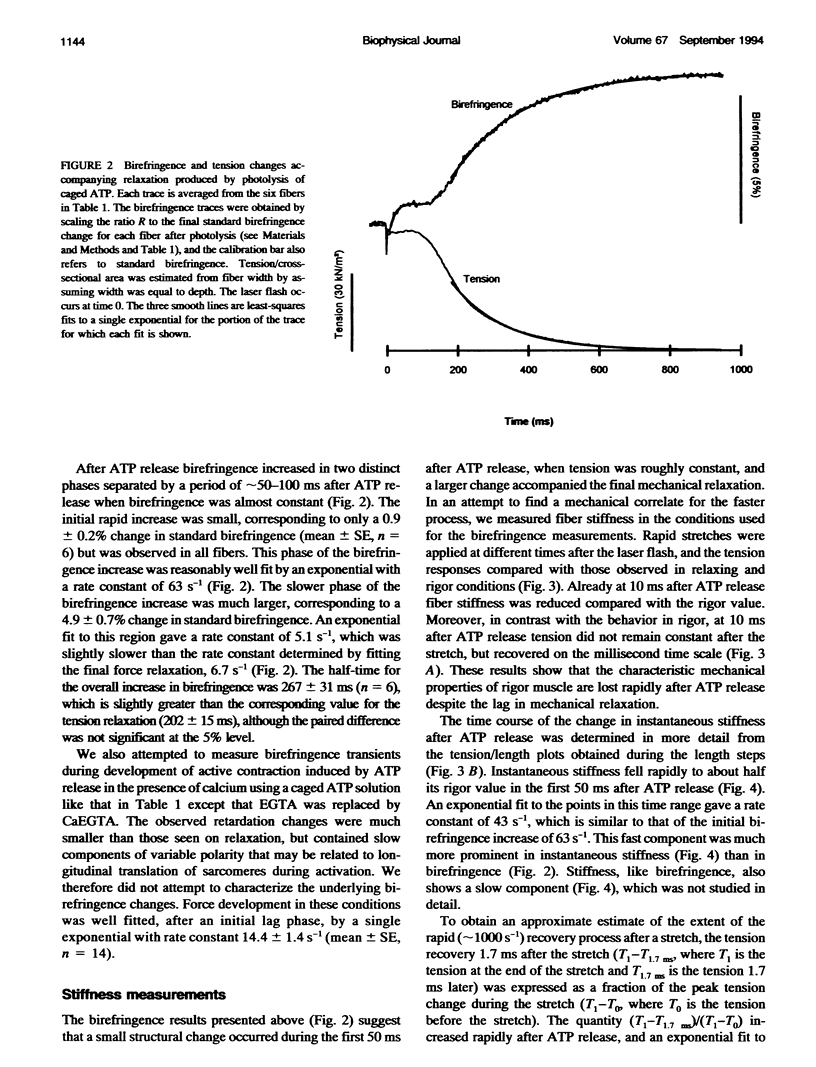
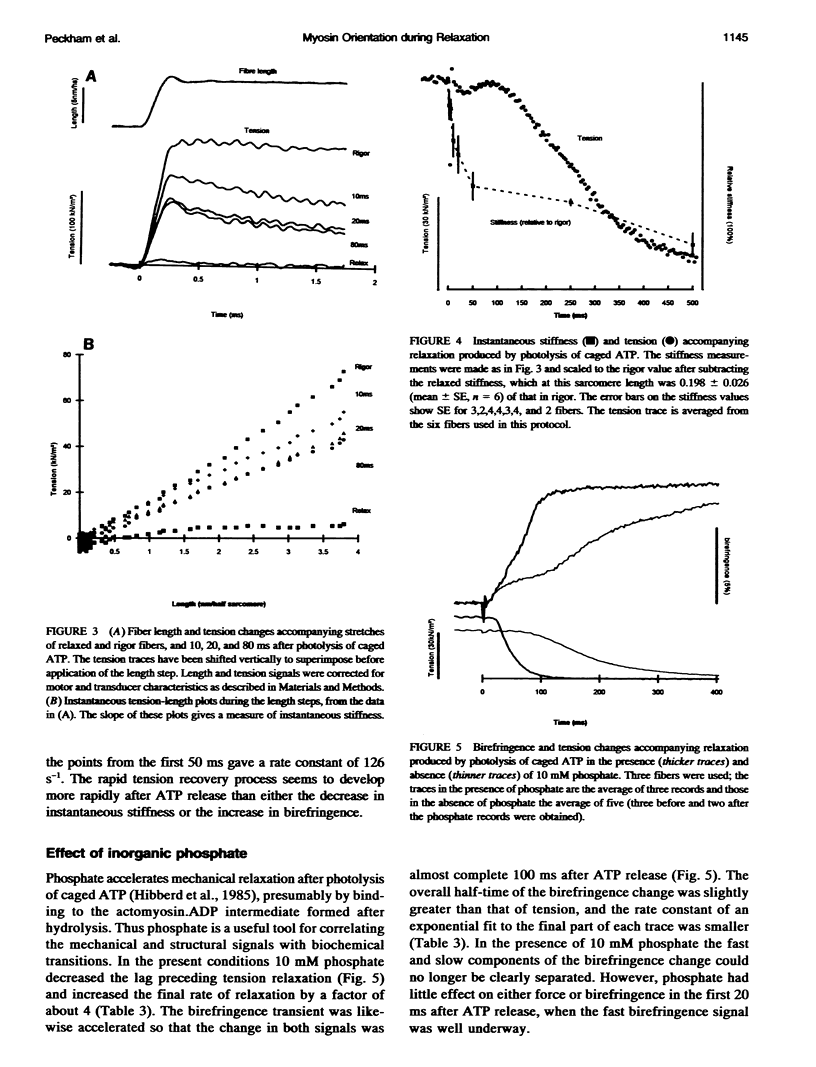
The birefringence of isolated skinned fibers from rabbit psoas muscle was measured continuously during relaxation from rigor produced by photolysis of caged ATP at sarcomere length 2.8-2.9 microns, ionic strength 0.1 M, 15 degrees C. Birefringence, the difference in refractive index between light components polarized parallel and perpendicular to the fiber axis, depends on the average degree of alignment of the myosin head domain with the fiber axis. After ATP release birefringence increased by 5.8 +/- 0.7% (mean +/- SE, n = 6) with two temporal components. A small fast component had an amplitude of 0.9 +/- 0.2% and rate constant of 63 s-1. By the completion of this component, the instantaneous stiffness had decreased to about half the rigor value, and the force response to a step stretch showed a rapid (approximately 1000 s-1) recovery phase. Subsequently a large slow birefringence component with rate constant 5.1 s-1 accompanied isometric force relaxation. Inorganic phosphate (10 mM) did not affect the fast birefringence component but accelerated the slow component and force relaxation. The fast birefringence component was probably caused by formation of myosin.ATP or myosin.ADP.Pi states that are weakly bound to actin. The average myosin head orientation at the end of this component is slightly more parallel to the fiber axis than in rigor.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barabás K., Keszthelyi L. Temperature dependence of ATP release from "caged" ATP. Acta Biochim Biophys Acad Sci Hung. 1984;19(3-4):305–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of actin-bound myosin heads in active myofibrils. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 13;32(14):3812–3821. doi: 10.1021/bi00065a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Schoenberg M., Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Evidence for cross-bridge attachment in relaxed muscle at low ionic strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7288–7291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Yu L. C., Podolsky R. J. X-ray diffraction evidence for cross-bridge formation in relaxed muscle fibers at various ionic strengths. Biophys J. 1984 Sep;46(3):299–306. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84026-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig J. A., Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R., Goldman Y. E. Cross-bridge kinetics in the presence of MgADP investigated by photolysis of caged ATP in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:639–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer P. G., Fajer E. A., Schoenberg M., Thomas D. D. Orientational disorder and motion of weakly attached cross-bridges. Biophys J. 1991 Sep;60(3):642–649. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82093-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer P. G., Fajer E. A., Thomas D. D. Myosin heads have a broad orientational distribution during isometric muscle contraction: time-resolved EPR studies using caged ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5538–5542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenczi M. A. Phosphate burst in permeable muscle fibers of the rabbit. Biophys J. 1986 Sep;50(3):471–477. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83484-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Tension responses to sudden length change in stimulated frog muscle fibres near slack length. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(2):441–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Hibberd M. G., McCray J. A., Trentham D. R. Relaxation of muscle fibres by photolysis of caged ATP. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):701–705. doi: 10.1038/300701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R. Relaxation of rabbit psoas muscle fibres from rigor by photochemical generation of adenosine-5'-triphosphate. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:577–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E. Kinetics of the actomyosin ATPase in muscle fibers. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:637–654. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Simmons R. M. The stiffness of frog skinned muscle fibres at altered lateral filament spacing. J Physiol. 1986 Sep;378:175–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskell R. C., Carlson F. D., Blank P. S. Form birefringence of muscle. Biophys J. 1989 Aug;56(2):401–413. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82686-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibberd M. G., Dantzig J. A., Trentham D. R., Goldman Y. E. Phosphate release and force generation in skeletal muscle fibers. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.3159090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving M. Birefringence changes associated with isometric contraction and rapid shortening steps in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:127–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peckham M., Irving M. Myosin crossbridge orientation in demembranated muscle fibres studied by birefringence and X-ray diffraction measurements. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):113–126. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole K. J., Maeda Y., Rapp G., Goody R. S. Dynamic X-ray diffraction measurements following photolytic relaxation and activation of skinned rabbit psoas fibres. Adv Biophys. 1991;27:63–75. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(91)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. W., Thomas D. D., Goldman Y. E. Transients in orientation of a fluorescent cross-bridge probe following photolysis of caged nucleotides in skeletal muscle fibres. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 5;223(1):185–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90725-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toylor D. L. Quantitative studies on the polarization optical properties of striated muscle. I. Birefringence changes of rabbit psoas muscle in the transition from rigor to relaxed state. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):497–511. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. D., Taylor E. W. Energetics and mechanism of actomyosin adenosine triphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 28;15(26):5818–5826. doi: 10.1021/bi00671a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


