Abstract
Glucose-embedded bacteriorhodopsin shows M-intermediates with different Amide I infrared bands when samples are illuminated at 240 or 260 K, in contrast with fully hydrated samples where a single M-intermediate is formed at all temperatures. In hydrated, but not in glucose-embedded specimens, the N intermediate is formed together with M at 260 K. Both Fourier transform infrared and electron diffraction data from glucose-embedded bacteriorhodopsin suggest that at 260 K a mixture is formed of the M-state that is trapped at 240 K, and a different M-intermediate (MN) that is also formed by mutant forms of bacteriorhodopsin that lack a carboxyl group at the 96 position, necessary for the M to N transition. The fact that an MN species is trapped in glucose-embedded, wild-type bacteriorhodopsin suggests that the glucose samples lack functionally important water molecules that are needed for the proton transfer aspartate 96 to the Schiff base (and, thus, to form the N-intermediate); thus, aspartate 96 is rendered ineffective as a proton donor.
Full text
PDF
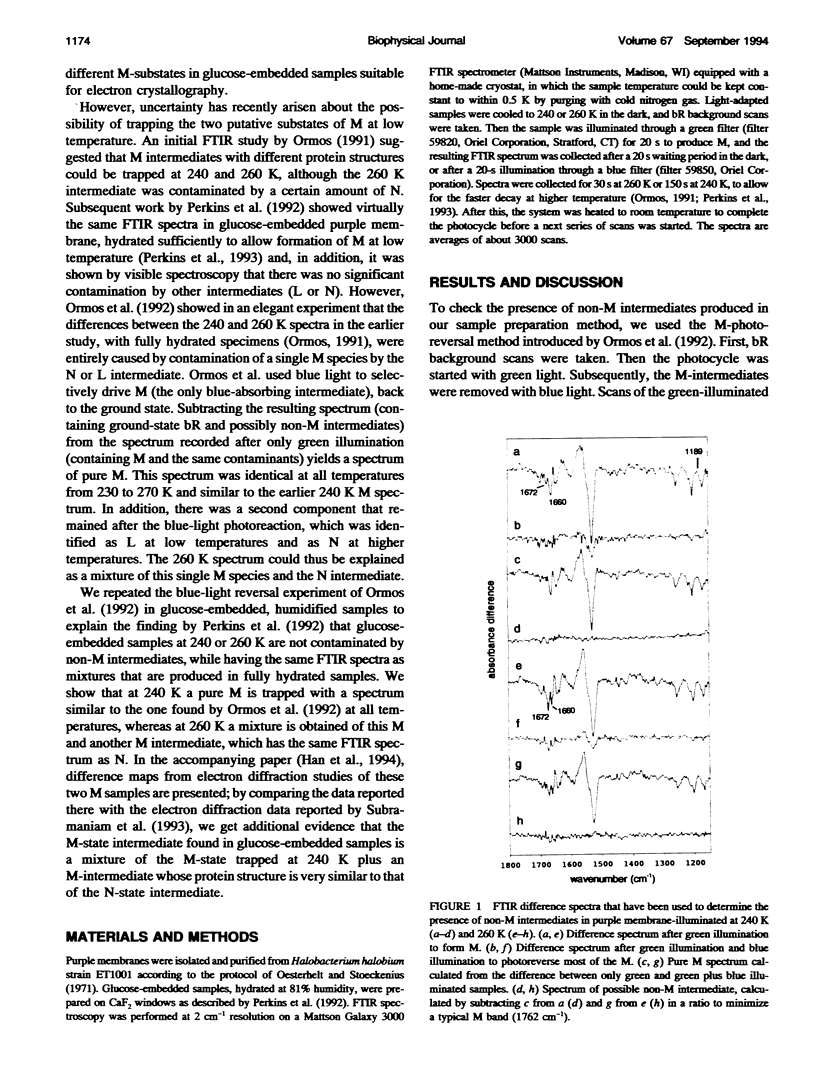

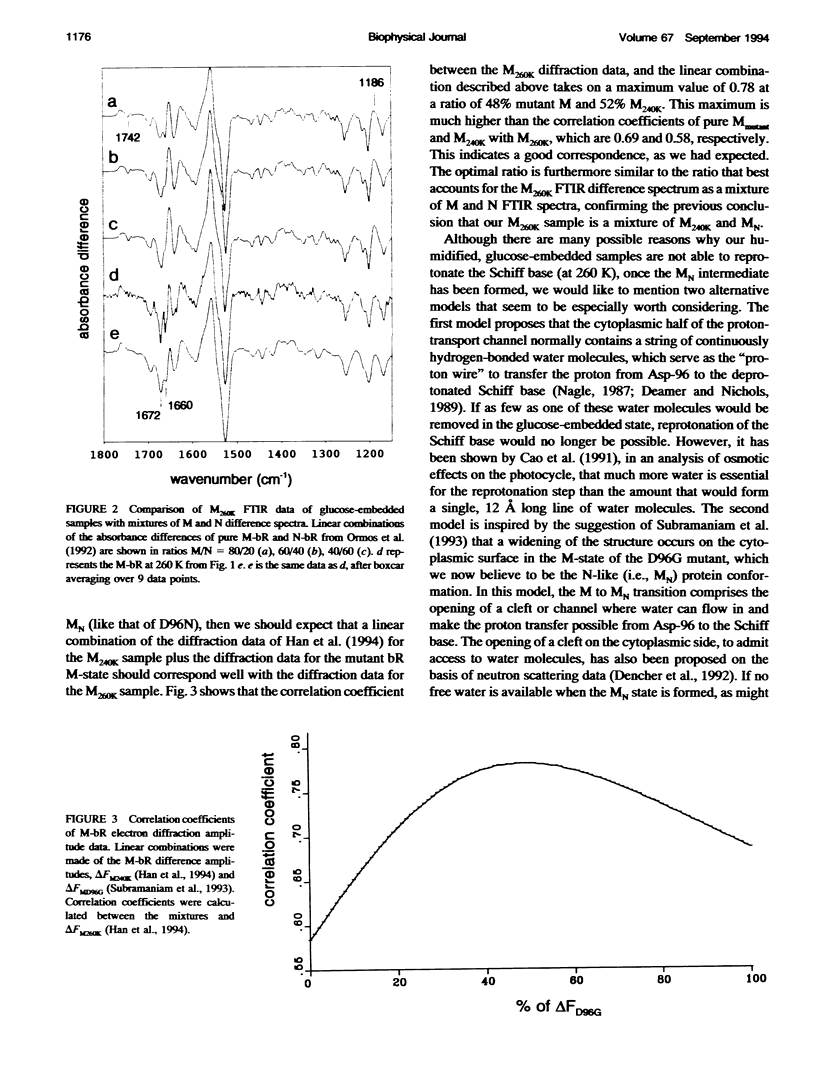


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braiman M. S., Bousché O., Rothschild K. J. Protein dynamics in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle: submillisecond Fourier transform infrared spectra of the L, M, and N photointermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2388–2392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Marti T., Stern L. J., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: light-driven proton transport involves protonation changes of aspartic acid residues 85, 96, and 212. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8516–8520. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M., Mathies R. Resonance Raman spectra of bacteriorhodopsin's primary photoproduct: evidence for a distorted 13-cis retinal chromophore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):403–407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Y., Váró G., Chang M., Ni B. F., Needleman R., Lanyi J. K. Water is required for proton transfer from aspartate-96 to the bacteriorhodopsin Schiff base. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 12;30(45):10972–10979. doi: 10.1021/bi00109a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Y., Váró G., Klinger A. L., Czajkowsky D. M., Braiman M. S., Needleman R., Lanyi J. K. Proton transfer from Asp-96 to the bacteriorhodopsin Schiff base is caused by a decrease of the pKa of Asp-96 which follows a protein backbone conformational change. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 2;32(8):1981–1990. doi: 10.1021/bi00059a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W., Nichols J. W. Proton flux mechanisms in model and biological membranes. J Membr Biol. 1989 Feb;107(2):91–103. doi: 10.1007/BF01871715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencher N. A., Dresselhaus D., Zaccai G., Büldt G. Structural changes in bacteriorhodopsin during proton translocation revealed by neutron diffraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7876–7879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaeser R. M., Baldwin J., Ceska T. A., Henderson R. Electron diffraction analysis of the M412 intermediate of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):913–920. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83532-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han B. G., Vonck J., Glaeser R. M. The bacteriorhodopsin photocycle: direct structural study of two substrates of the M-intermediate. Biophys J. 1994 Sep;67(3):1179–1186. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80586-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz M., Drachev L. A., Mogi T., Otto H., Kaulen A. D., Heyn M. P., Skulachev V. P., Khorana H. G. Replacement of aspartic acid-96 by asparagine in bacteriorhodopsin slows both the decay of the M intermediate and the associated proton movement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Rhodopsin-like protein from the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):149–152. doi: 10.1038/newbio233149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormos P. Infrared spectroscopic demonstration of a conformational change in bacteriorhodopsin involved in proton pumping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):473–477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto H., Marti T., Holz M., Mogi T., Stern L. J., Engel F., Khorana H. G., Heyn M. P. Substitution of amino acids Asp-85, Asp-212, and Arg-82 in bacteriorhodopsin affects the proton release phase of the pump and the pK of the Schiff base. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1018–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki J., Shichida Y., Lanyi J. K., Maeda A. Protein changes associated with reprotonation of the Schiff base in the photocycle of Asp96-->Asn bacteriorhodopsin. The MN intermediate with unprotonated Schiff base but N-like protein structure. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20782–20786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souvignier G., Gerwert K. Proton uptake mechanism of bacteriorhodopsin as determined by time-resolved stroboscopic-FTIR-spectroscopy. Biophys J. 1992 Nov;63(5):1393–1405. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81722-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Lanyi J. K. Distortions in the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin at moderate dehydration. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82225-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Lanyi J. K. Kinetic and spectroscopic evidence for an irreversible step between deprotonation and reprotonation of the Schiff base in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biochemistry. 1991 May 21;30(20):5008–5015. doi: 10.1021/bi00234a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Lanyi J. K. Thermodynamics and energy coupling in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biochemistry. 1991 May 21;30(20):5016–5022. doi: 10.1021/bi00234a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimányi L., Cao Y., Chang M., Ni B., Needleman R., Lanyi J. K. The two consecutive M substates in the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin are affected specifically by the D85N and D96N residue replacements. Photochem Photobiol. 1992 Dec;56(6):1049–1055. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1992.tb09728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimányi L., Tokaji Z., Dollinger G. Circular dichroic spectrum of the L form and the blue light product of the m form of purple membrane. Biophys J. 1987 Jan;51(1):145–148. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83319-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


