Abstract
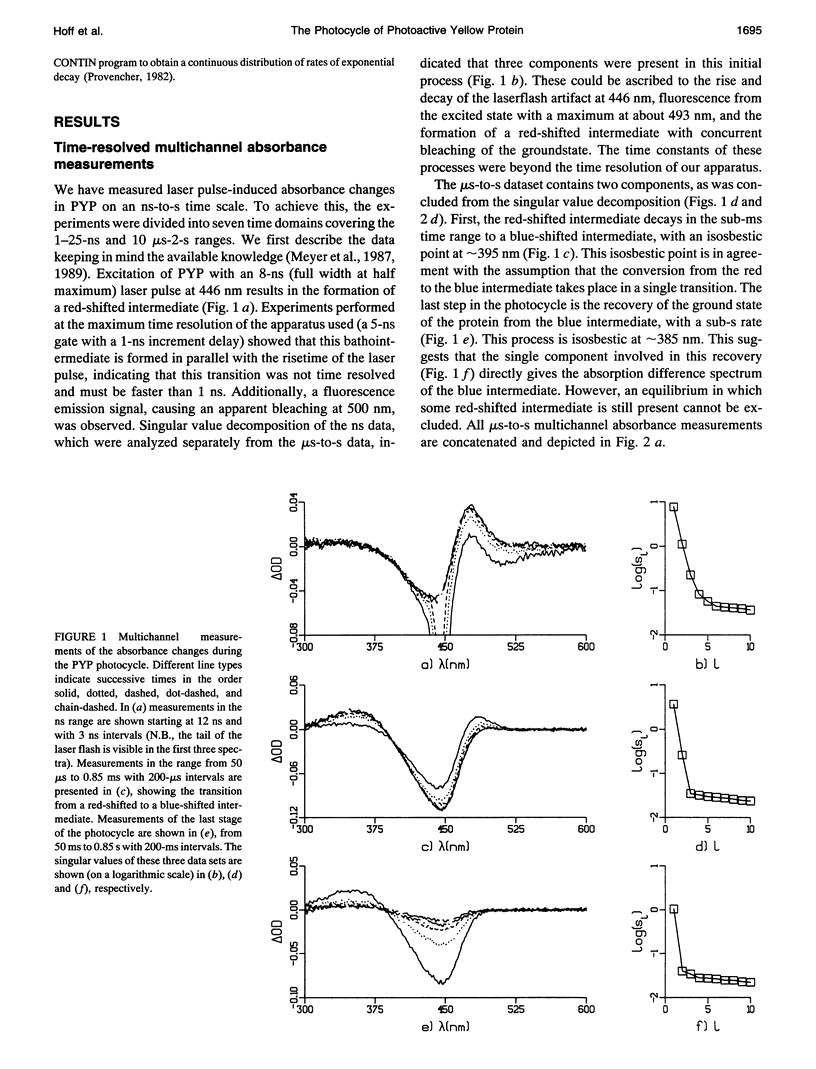
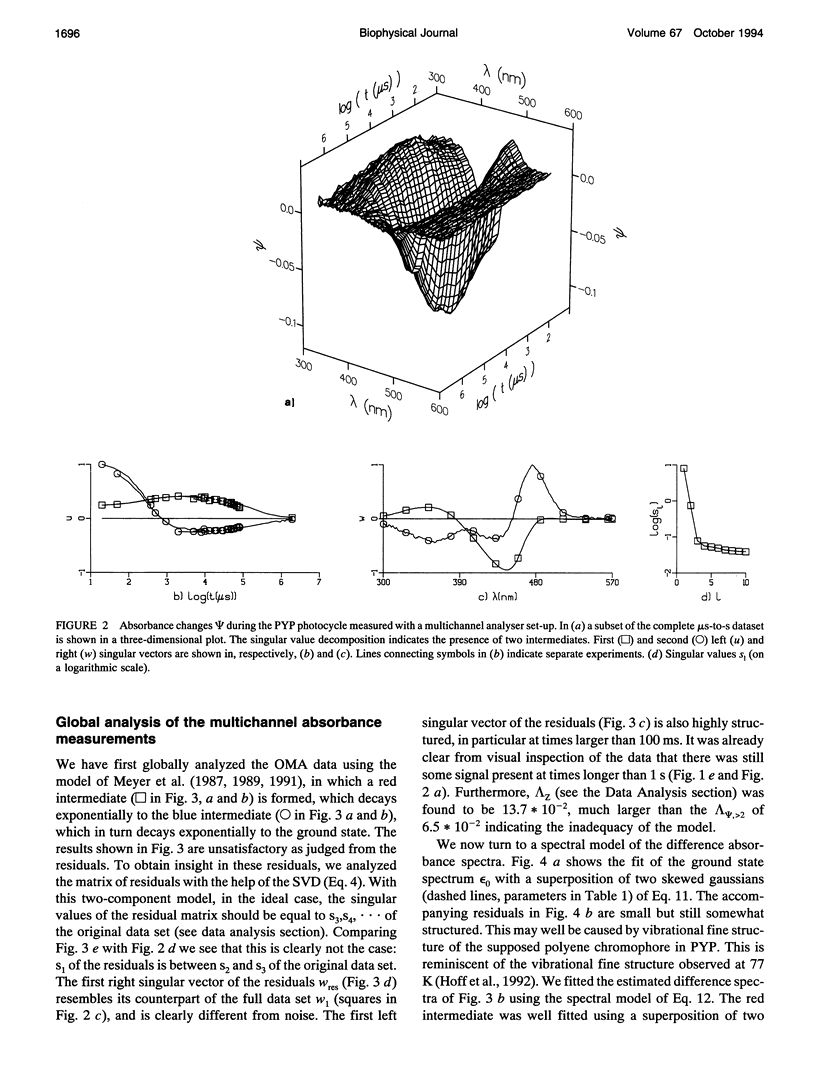
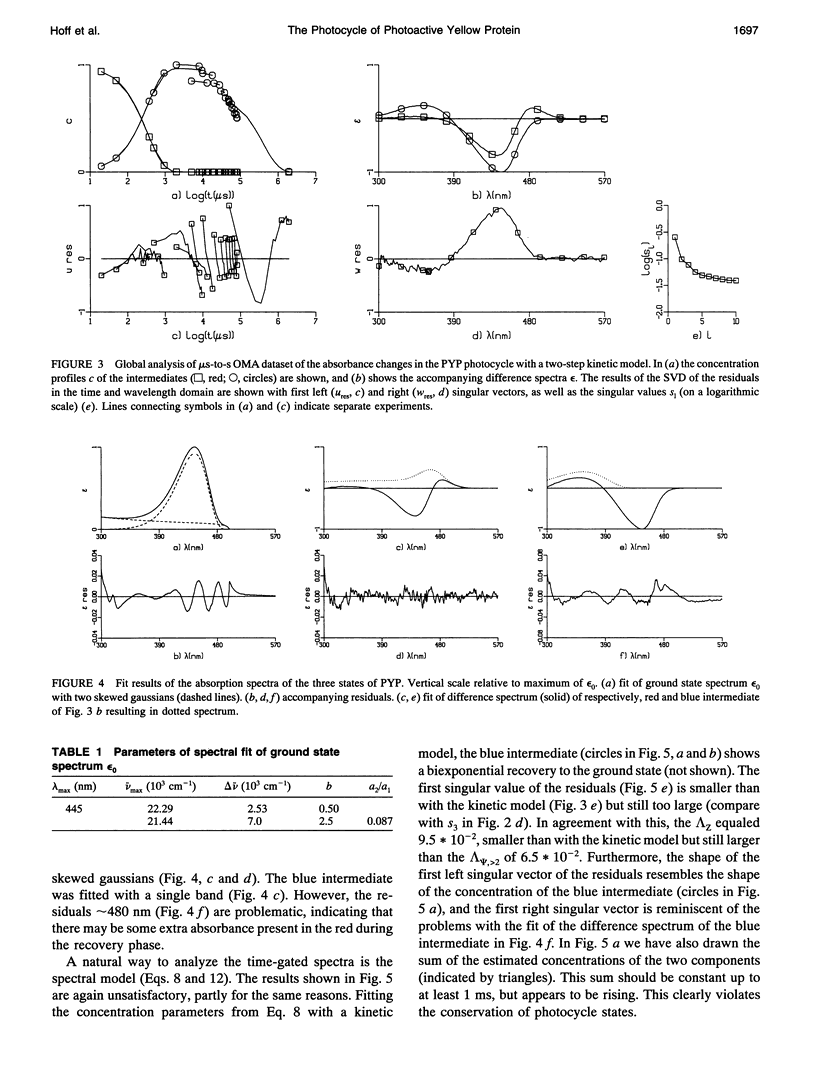
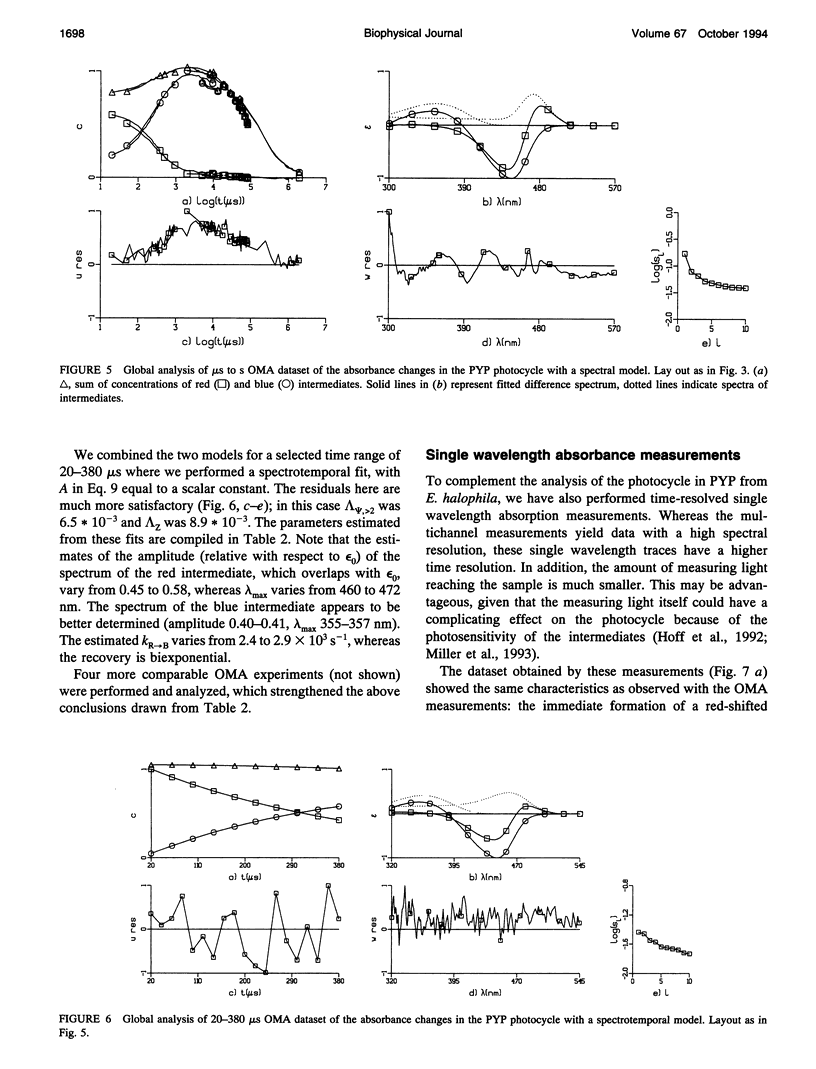
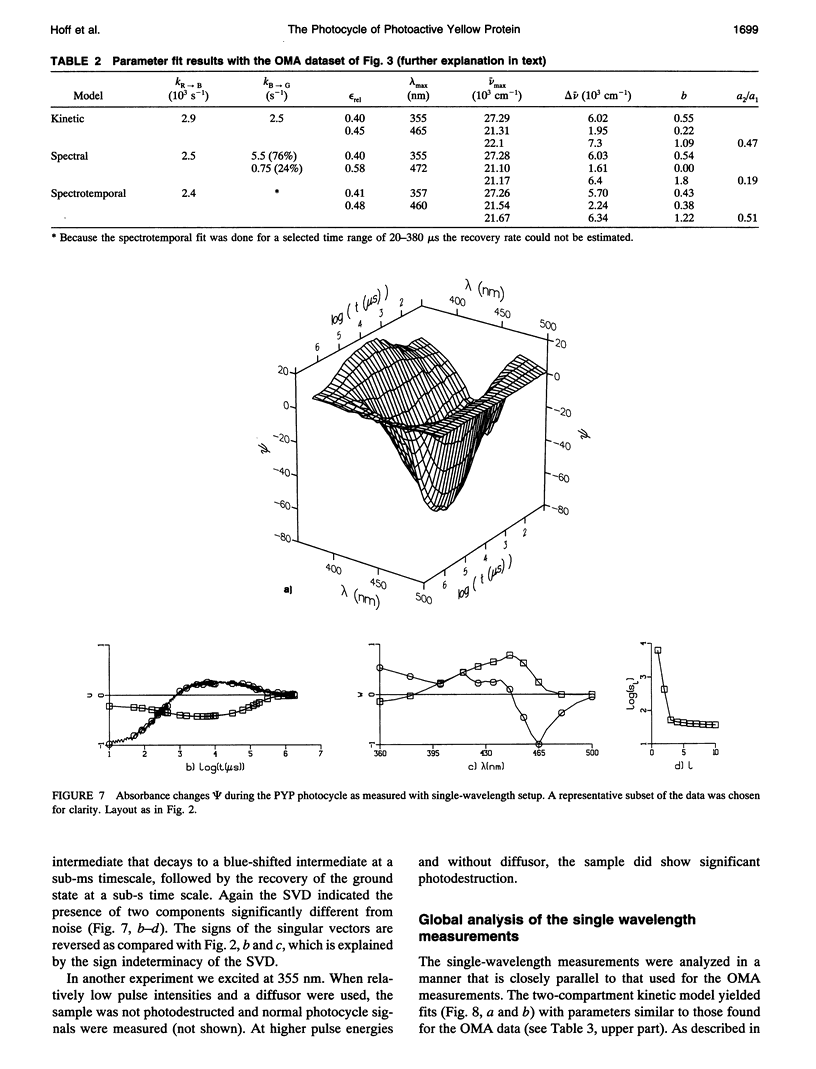
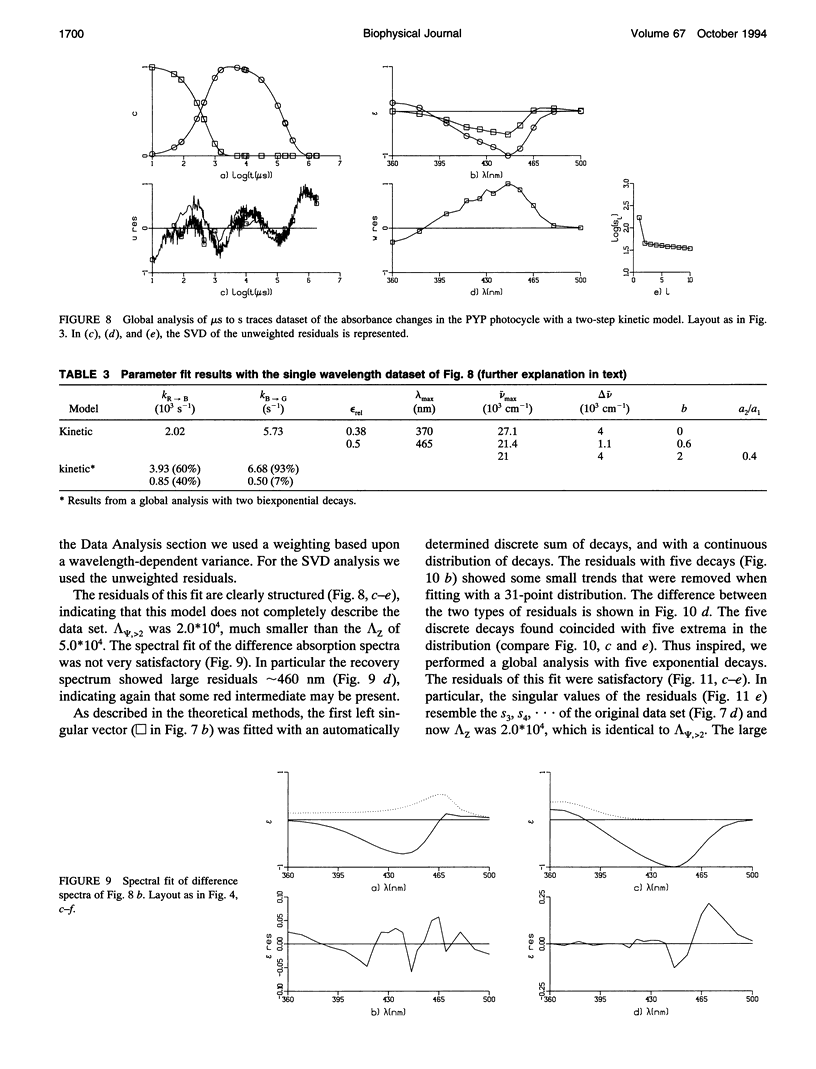
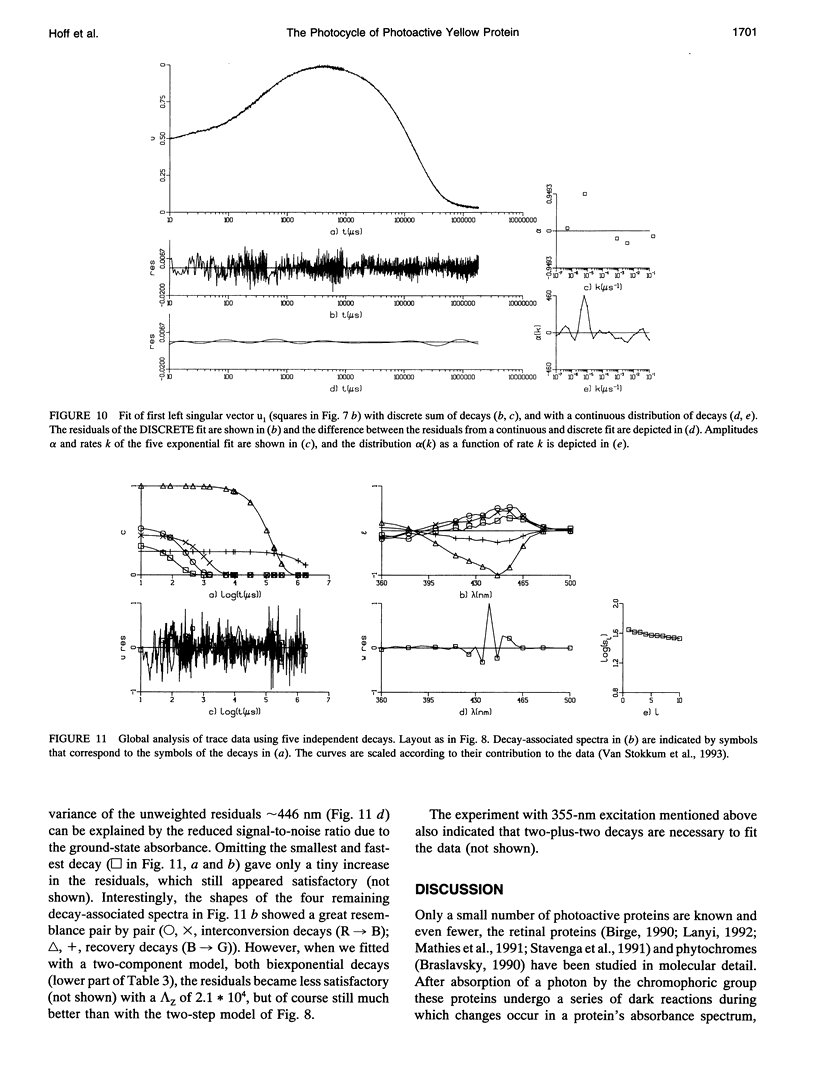
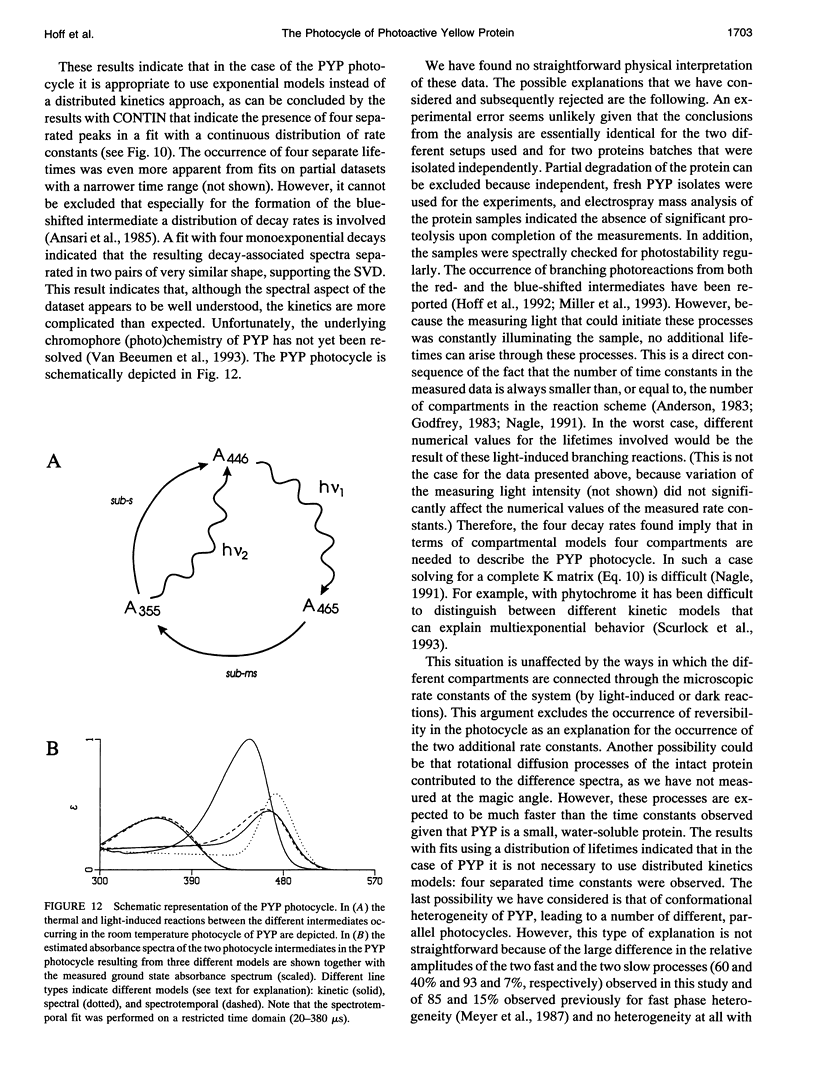
The photocycle of the photoactive yellow protein (PYP) from Ectothiorhodospira halophila was examined by time-resolved difference absorption spectroscopy in the wavelength range of 300-600 nm. Both time-gated spectra and single wavelength traces were measured. Global analysis of the data established that in the time domain between 5 ns and 2 s only two intermediates are involved in the room temperature photocycle of PYP, as has been proposed before (Meyer T.E., E. Yakali, M. A. Cusanovich, and G. Tollin. 1987. Biochemistry. 26:418-423; Meyer, T. E., G. Tollin, T. P. Causgrove, P. Cheng, and R. E. Blankenship. 1991. Biophys. J. 59:988-991). The first, red-shifted intermediate decays biexponentially (60% with tau = 0.25 ms and 40% with tau = 1.2 ms) to a blue-shifted intermediate. The last step of the photocycle is the biexponential (93% with tau = 0.15 s and 7% with tau = 2.0 s) recovery to the ground state of the protein. Reconstruction of the absolute spectra of these photointermediates yielded absorbance maxima of about 465 and 355 nm for the red- and blue-shifted intermediate with an epsilon max at about 50% and 40% relative to the epsilon max of the ground state. The quantitative analysis of the photocycle in PYP described here paves the way to a detailed biophysical analysis of the processes occurring in this photoreceptor molecule.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansari A., Berendzen J., Bowne S. F., Frauenfelder H., Iben I. E., Sauke T. B., Shyamsunder E., Young R. D. Protein states and proteinquakes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5000–5004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge R. R. Photophysics and molecular electronic applications of the rhodopsins. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1990;41:683–733. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pc.41.100190.003343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogomolni R. A., Spudich J. L. The photochemical reactions of bacterial sensory rhodopsin-I. Flash photolysis study in the one microsecond to eight second time window. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):1071–1075. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83301-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisfeld W., Pusch C., Diller R., Lohrmann R., Stockburger M. Resonance Raman and optical transient studies on the light-induced proton pump of bacteriorhodopsin reveal parallel photocycles. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 20;32(28):7196–7215. doi: 10.1021/bi00079a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindjee R., Becher B., Ebrey T. G. The fluorescence from the chromophore of the purple membrane protein. Biophys J. 1978 Apr;22(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85471-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessling B., Souvignier G., Gerwert K. A model-independent approach to assigning bacteriorhodopsin's intramolecular reactions to photocycle intermediates. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):1929–1941. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81264-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff W. D., Sprenger W. W., Postma P. W., Meyer T. E., Veenhuis M., Leguijt T., Hellingwerf K. J. The photoactive yellow protein from Ectothiorhodospira halophila as studied with a highly specific polyclonal antiserum: (intra)cellular localization, regulation of expression, and taxonomic distribution of cross-reacting proteins. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jul;176(13):3920–3927. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.13.3920-3927.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Proton transfer and energy coupling in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Apr;24(2):169–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00762675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A., Spoonhower J. P., Perreault G. J. Observation of light emission from a rhodopsin. Nature. 1976 Apr 22;260(5553):675–678. doi: 10.1038/260675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Xie A., Hofrichter J., Clore G. M. Reversible steps in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3610–3614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathies R. A., Lin S. W., Ames J. B., Pollard W. T. From femtoseconds to biology: mechanism of bacteriorhodopsin's light-driven proton pump. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:491–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRee D. E., Tainer J. A., Meyer T. E., Van Beeumen J., Cusanovich M. A., Getzoff E. D. Crystallographic structure of a photoreceptor protein at 2.4 A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6533–6537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Cusanovich M. A., Tollin G. Transient proton uptake and release is associated with the photocycle of the photoactive yellow protein from the purple phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halophila. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Nov 1;306(2):515–517. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Fitch J. C., Bartsch R. G., Tollin G., Cusanovich M. A. Soluble cytochromes and a photoactive yellow protein isolated from the moderately halophilic purple phototrophic bacterium, Rhodospirillum salexigens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 26;1016(3):364–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E. Isolation and characterization of soluble cytochromes, ferredoxins and other chromophoric proteins from the halophilic phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halophila. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 23;806(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(85)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Tollin G., Causgrove T. P., Cheng P., Blankenship R. E. Picosecond decay kinetics and quantum yield of fluorescence of the photoactive yellow protein from the halophilic purple phototrophic bacterium, Ectothiorhodospira halophila. Biophys J. 1991 May;59(5):988–991. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82313-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Tollin G., Hazzard J. H., Cusanovich M. A. Photoactive yellow protein from the purple phototrophic bacterium, Ectothiorhodospira halophila. Quantum yield of photobleaching and effects of temperature, alcohols, glycerol, and sucrose on kinetics of photobleaching and recovery. Biophys J. 1989 Sep;56(3):559–564. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82703-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Yakali E., Cusanovich M. A., Tollin G. Properties of a water-soluble, yellow protein isolated from a halophilic phototrophic bacterium that has photochemical activity analogous to sensory rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 27;26(2):418–423. doi: 10.1021/bi00376a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F. Solving complex photocycle kinetics. Theory and direct method. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):476–487. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82241-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Tittor J. Two pumps, one principle: light-driven ion transport in halobacteria. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger W. W., Hoff W. D., Armitage J. P., Hellingwerf K. J. The eubacterium Ectothiorhodospira halophila is negatively phototactic, with a wavelength dependence that fits the absorption spectrum of the photoactive yellow protein. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(10):3096–3104. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.3096-3104.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Sensory rhodopsins of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:193–215. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beeumen J. J., Devreese B. V., Van Bun S. M., Hoff W. D., Hellingwerf K. J., Meyer T. E., McRee D. E., Cusanovich M. A. Primary structure of a photoactive yellow protein from the phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halophila, with evidence for the mass and the binding site of the chromophore. Protein Sci. 1993 Jul;2(7):1114–1125. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Lanyi J. K. Thermodynamics and energy coupling in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biochemistry. 1991 May 21;30(20):5016–5022. doi: 10.1021/bi00234a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimányi L., Lanyi J. K. Deriving the intermediate spectra and photocycle kinetics from time-resolved difference spectra of bacteriorhodopsin. The simpler case of the recombinant D96N protein. Biophys J. 1993 Jan;64(1):240–251. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81360-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


