Abstract
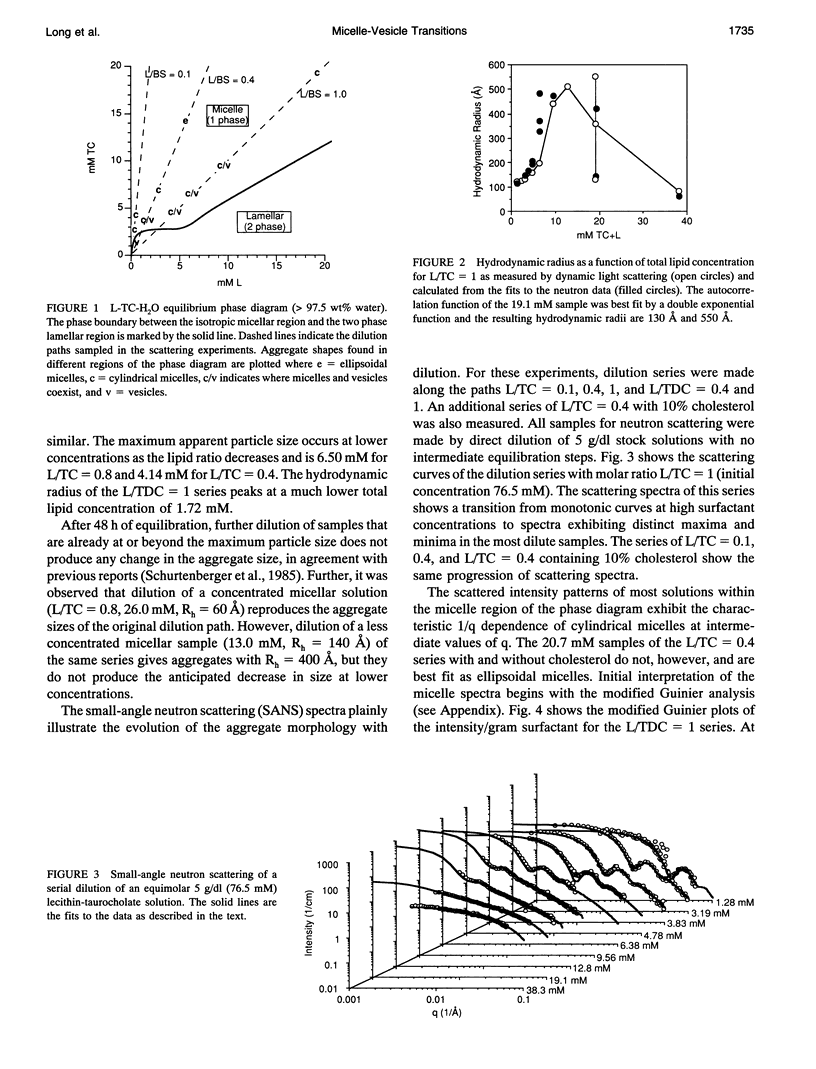
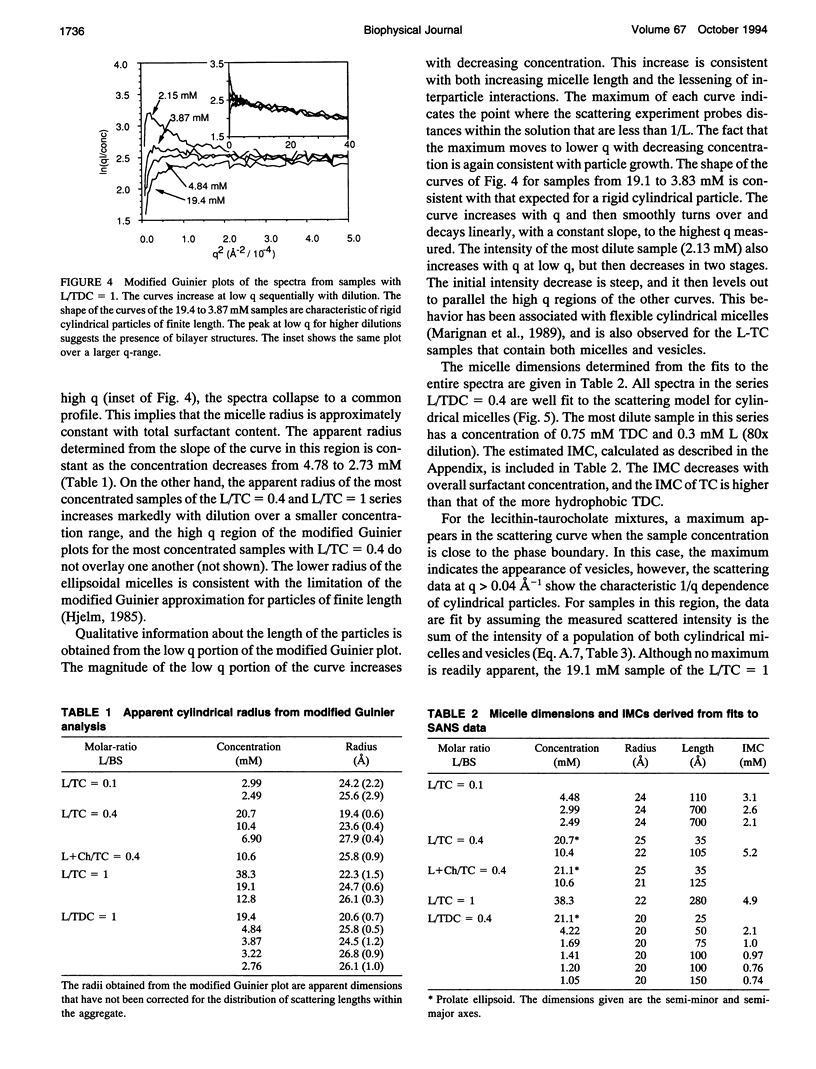
Small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and dynamic light scattering (QLS) are used to characterize the aggregates found upon dilution of mixed lecithin-bile salt micelles. Molar ratios of lecithin (L) to taurocholate (TC) studied varied from 0.1 to 1, and one series contained cholesterol (Ch). Mixed aggregates of L and taurodeoxycholate (TDC) at ratios of 0.4 and 1 were also examined. In all cases the micelles are cylindrical or globular and elongate upon dilution. The radius of the mixed micelles varies only slightly with the overall composition of lecithin and bile salt which indicates that the composition of the cylindrical micelle body is nearly constant. The transition from micelles to vesicles is a smooth transformation involving a region where micelles and vesicles coexist. SANS measurements are more sensitive to the presence of two aggregate populations than QLS. Beyond the coexistence region the vesicle size and degree of polydispersity decrease with dilution. Incorporation of a small amount of cholesterol in the lipid mixture does not affect the sequence of observed aggregate structures.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almog S., Kushnir T., Nir S., Lichtenberg D. Kinetic and structural aspects of reconstitution of phosphatidylcholine vesicles by dilution of phosphatidylcholine-sodium cholate mixed micelles. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2597–2605. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almog S., Litman B. J., Wimley W., Cohen J., Wachtel E. J., Barenholz Y., Ben-Shaul A., Lichtenberg D. States of aggregation and phase transformations in mixtures of phosphatidylcholine and octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1990 May 15;29(19):4582–4592. doi: 10.1021/bi00471a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouillette C. G., Segrest J. P., Ng T. C., Jones J. L. Minimal size phosphatidylcholine vesicles: effects of radius of curvature on head group packing and conformation. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4569–4575. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell B. A., Middlehurst J., Separovic F. The molecular packing and stability within highly curved phospholipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 23;598(2):405–410. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. M., Timofeyeva N., Carey M. C. Influence of total lipid concentration, bile salt:lecithin ratio, and cholesterol content on inter-mixed micellar/vesicular (non-lecithin-associated) bile salt concentrations in model bile. J Lipid Res. 1991 Sep;32(9):1501–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duane W. C. Taurocholate- and taurochenodeoxycholate-lecithin micelles: the equilibrium of bile salt between aqueous phase and micelle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 10;74(1):223–229. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duane W. C. The intermicellar bile salt concentration in equilibrium with the mixed-micelles of human bile. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 25;398(2):275–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia de la Torre J. G., Bloomfield V. A. Hydrodynamic properties of complex, rigid, biological macromolecules: theory and applications. Q Rev Biophys. 1981 Feb;14(1):81–139. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groen A. K., Ottenhoff R., Jansen P. L., van Marle J., Tytgat G. N. Effect of cholesterol nucleation-promoting activity on cholesterol solubilization in model bile. J Lipid Res. 1989 Jan;30(1):51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., Park H. Z., Madani H., Kaler E. W. Partial characterization of a nonmicellar system of cholesterol solubilization in bile. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 1):G374–G383. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.3.G374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberg D., Zilberman Y., Greenzaid P., Zamir S. Structural and kinetic studies on the solubilization of lecithin by sodium deoxycholate. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 7;18(16):3517–3525. doi: 10.1021/bi00583a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little T. E., Madani H., Lee S. P., Kaler E. W. Lipid vesicle fusion induced by phospholipase C activity in model bile. J Lipid Res. 1993 Feb;34(2):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazer N. A., Benedek G. B., Carey M. C. Quasielastic light-scattering studies of aqueous biliary lipid systems. Mixed micelle formation in bile salt-lecithin solutions. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):601–615. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazer N. A., Schurtenberg P., Carey M. C., Preisig R., Weigand K., Känzig W. Quasi-elastic light scattering studies of native hepatic bile from the dog: comparison with aggregative behavior of model biliary lipid systems. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 24;23(9):1994–2005. doi: 10.1021/bi00304a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller K. Structural dimorphism of bile salt/lecithin mixed micelles. A possible regulatory mechanism for cholesterol solubility in bile? X-ray structure analysis. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 20;20(2):404–414. doi: 10.1021/bi00505a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. W., Ozarowski J. Sizing of lecithin-bile salt mixed micelles by size-exclusion high-performance liquid chromatography. Biochemistry. 1990 May 15;29(19):4600–4606. doi: 10.1021/bi00471a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert R., Schmidt K. H. Structural changes in vesicle membranes and mixed micelles of various lipid compositions after binding of different bile salts. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8787–8794. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankland W. The equilibrium and structure of lecithin-cholate mixed micelles. Chem Phys Lipids. 1970 Apr;4(2):109–130. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(70)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M. Phase equilibria and structure of dry and hydrated egg lecithin. J Lipid Res. 1967 Nov;8(6):551–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. E., Gosselin G. J., Donovan J. M., Carey M. C., Roberts M. F. Influence of dilution on the physical state of model bile systems: NMR and quasi-elastic light-scattering investigations. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5599–5605. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. E., Manstein J. L., Curatolo W., Sears B. Deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance studies of bile salt/phosphatidylcholine mixed micelles. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2486–2490. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson P. K., Talmon Y., Walter A. Vesicle-micelle transition of phosphatidylcholine and octyl glucoside elucidated by cryo-transmission electron microscopy. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):669–681. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82714-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter A., Vinson P. K., Kaplun A., Talmon Y. Intermediate structures in the cholate-phosphatidylcholine vesicle-micelle transition. Biophys J. 1991 Dec;60(6):1315–1325. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82169-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


