Abstract
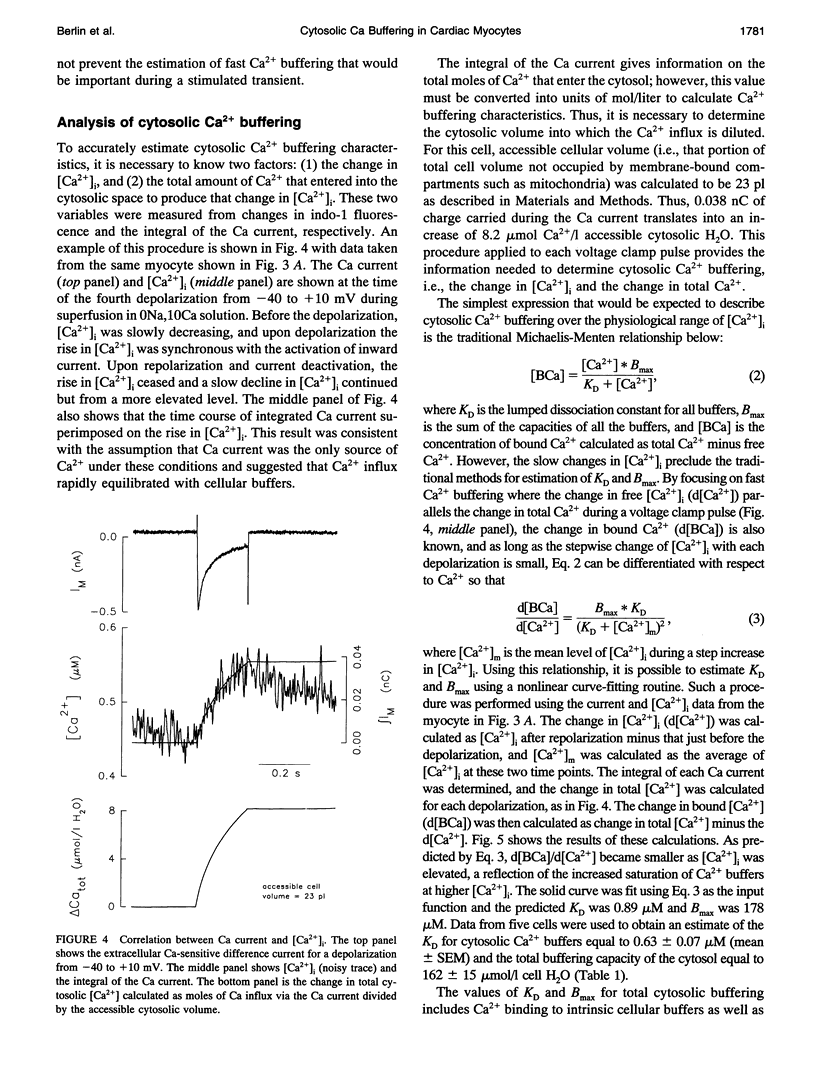
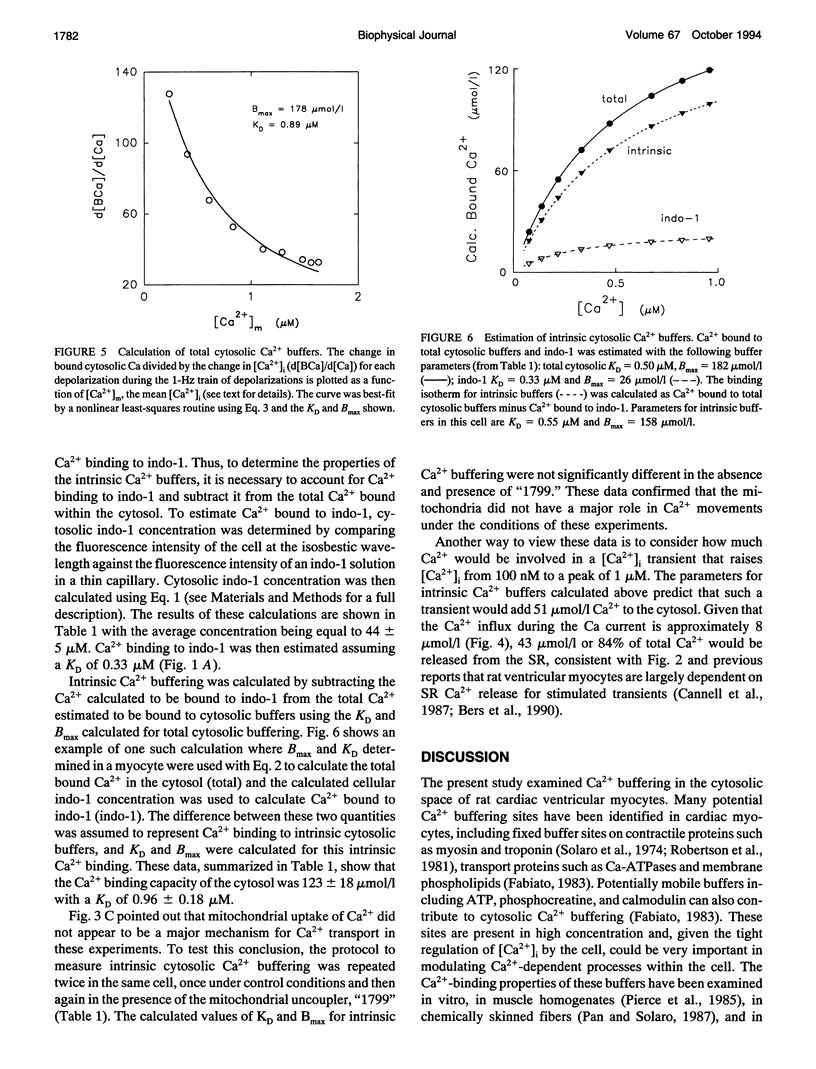
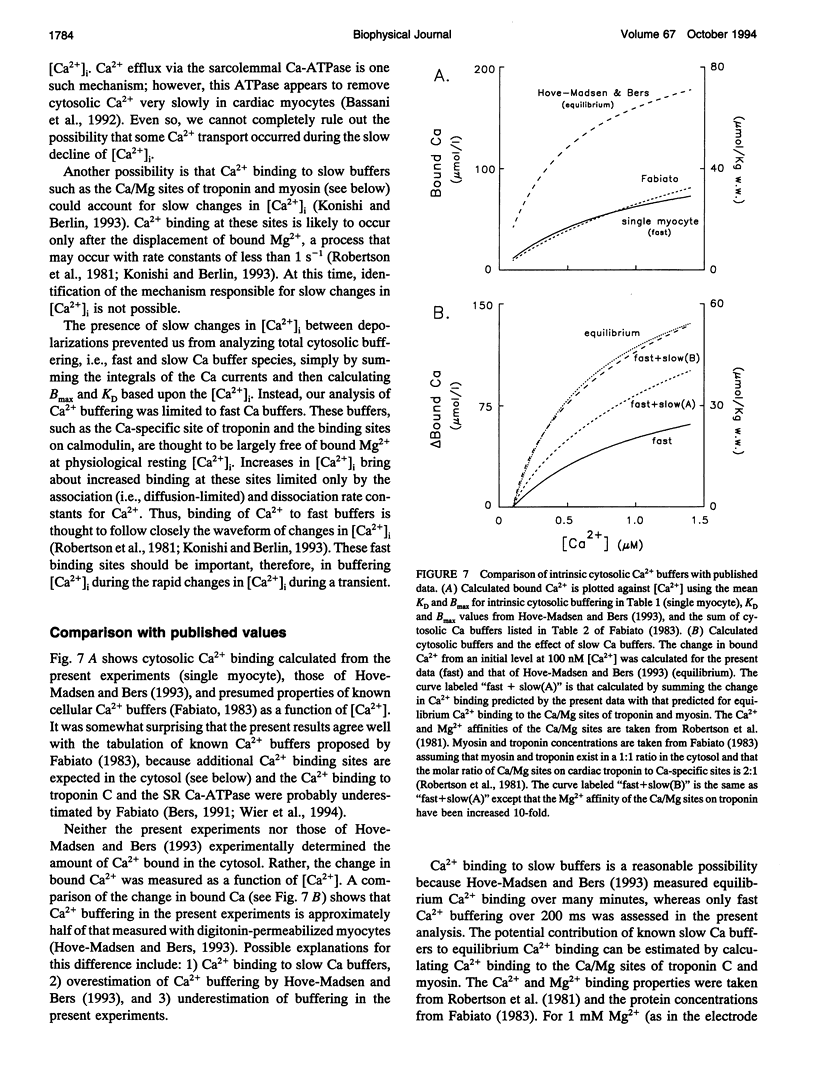
Intracellular passive Ca2+, buffering was measured in voltage-clamped rat ventricular myocytes. Cells were loaded with indo-1 (K+ salt) to an estimated cytosolic concentration of 44 +/- 5 microM (Mean +/- SEM, n = 5), and accessible cell volume was estimated to be 24.5 +/- 3.6 pl. Ca2+ transport by the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca-ATPase and sarcolemmal Na-Ca exchange was inhibited by treatment with thapsigargin and Na-free solutions, respectively. Extracellular [Ca2+] was maintained at 10 mM and, in some experiments, the mitochondrial uncoupler "1799" was used to assess the degree of mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake. To perform single cell titrations, intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) was increased progressively by a train of depolarizing voltage clamp pulses from -40 to +10 mV. The total Ca2+ gain with each pulse was calculated by integration of the Ca current and then analyzed as a function of the rapid change in [Ca2+]i during the pulse. In the range of [Ca2+]i from 0.1 to 2 microM, overall cell buffering was well described as a single lumped Michaelis-Menten type species with an apparent dissociation constant, KD, of of 0.63 +/- 0.07 microM (n = 5) and a binding capacity, Bmax, of 162 +/- 15 mumol/l cell H2O. Correction for buffering attributable to cytosolic indo-1 gives intrinsic cytosolic Ca2+ buffering parameters of KD = 0.96 +/- 0.18 microM and Bmax = 123 +/- 18 mumol/l cell H2O. The fast Ca2+ buffering measured in this manner agrees reasonably with the characteristics of known rapid Ca buffers (e.g., troponin C, calmodulin, and SR Ca-ATPase), but is only about half of the total Ca2+ buffering measured at equilibrium. Inclusion of slow Ca buffers such as the Ca/Mg sites on troponin C and myosin can account for the differences between fast Ca2+ buffering in phase with the Ca current measured in the present experiments and equilibrium Ca2+ buffering. The present data indicate that a rapid rise of [Ca2+]i from 0.1 to 1 microM during a contraction requires approximately 50 microM Ca2+ to be added to the cytosol.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backx P. H., Ter Keurs H. E. Fluorescent properties of rat cardiac trabeculae microinjected with fura-2 salt. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 2):H1098–H1110. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.264.4.H1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balke C. W., Egan T. M., Wier W. G. Processes that remove calcium from the cytoplasm during excitation-contraction coupling in intact rat heart cells. J Physiol. 1994 Feb 1;474(3):447–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassani J. W., Bassani R. A., Bers D. M. Relaxation in rabbit and rat cardiac cells: species-dependent differences in cellular mechanisms. J Physiol. 1994 Apr 15;476(2):279–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassani J. W., Bassani R. A., Bers D. M. Twitch-dependent SR Ca accumulation and release in rabbit ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 1):C533–C540. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.2.C533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassani R. A., Bassani J. W., Bers D. M. Mitochondrial and sarcolemmal Ca2+ transport reduce [Ca2+]i during caffeine contractures in rabbit cardiac myocytes. J Physiol. 1992;453:591–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release in frog skeletal muscle fibres estimated from Arsenazo III calcium transients. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:625–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin J. R., Konishi M. Ca2+ transients in cardiac myocytes measured with high and low affinity Ca2+ indicators. Biophys J. 1993 Oct;65(4):1632–1647. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81211-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Allen L. A., Kim Y. Calcium binding to cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles: potential role as a modifier of contraction. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 1):C861–C871. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.6.C861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Bridge J. H. Relaxation of rabbit ventricular muscle by Na-Ca exchange and sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. Ryanodine and voltage sensitivity. Circ Res. 1989 Aug;65(2):334–342. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.2.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Lederer W. J., Berlin J. R. Intracellular Ca transients in rat cardiac myocytes: role of Na-Ca exchange in excitation-contraction coupling. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):C944–C954. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.5.C944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter L. A., Wier W. G. Intracellular diffusion, binding, and compartmentalization of the fluorescent calcium indicators indo-1 and fura-2. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1491–1499. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82494-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borzak S., Kelly R. A., Krämer B. K., Matoba Y., Marsh J. D., Reers M. In situ calibration of fura-2 and BCECF fluorescence in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):H973–H981. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.3.H973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Berlin J. R., Lederer W. J. Effect of membrane potential changes on the calcium transient in single rat cardiac muscle cells. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1419–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.2446391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Lederer W. J. A novel experimental chamber for single-cell voltage-clamp and patch-clamp applications with low electrical noise and excellent temperature and flow control. Pflugers Arch. 1986 May;406(5):536–539. doi: 10.1007/BF00583378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Calcium-induced release of calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C1–14. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankis M. B., Lindenmayer G. E. Sodium-sensitive calcium binding to sarcolemma-enriched preparations from canine ventricle. Circ Res. 1984 Nov;55(5):676–688. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.5.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. M., Bers D. M. The effect of temperature and ionic strength on the apparent Ca-affinity of EGTA and the analogous Ca-chelators BAPTA and dibromo-BAPTA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 13;925(2):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Calcium channel selectivity for divalent and monovalent cations. Voltage and concentration dependence of single channel current in ventricular heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):293–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hove-Madsen L., Bers D. M. Indo-1 binding to protein in permeabilized ventricular myocytes alters its spectral and Ca binding properties. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81597-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hove-Madsen L., Bers D. M. Passive Ca buffering and SR Ca uptake in permeabilized rabbit ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 1):C677–C686. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.3.C677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnke U., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Comparison of the Mg2+ and Ca2+ binding properties of troponin complexes P1-TI2C and TI2C. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(2):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janczewski A. M., Lakatta E. G. Buffering of calcium influx by sarcoplasmic reticulum during the action potential in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1993 Nov;471:343–363. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby M. S., Sagara Y., Gaa S., Inesi G., Lederer W. J., Rogers T. B. Thapsigargin inhibits contraction and Ca2+ transient in cardiac cells by specific inhibition of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12545–12551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Berlin J. R. Ca transients in cardiac myocytes measured with a low affinity fluorescent indicator, furaptra. Biophys J. 1993 Apr;64(4):1331–1343. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81494-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Olson A., Hollingworth S., Baylor S. M. Myoplasmic binding of fura-2 investigated by steady-state fluorescence and absorbance measurements. Biophys J. 1988 Dec;54(6):1089–1104. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83045-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBelle E. F., Racker E. Cholesterol Stimulation of Penetration of Unilamellar Liposomes by Hydrophobic Compounds. J Membr Biol. 1977 Mar 8;31(3):301–315. doi: 10.1007/BF01869410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Rios E., Schneider M. F. A general procedure for determining the rate of calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1987 Jun;51(6):849–863. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83413-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra R., Morad M. A uniform enzymatic method for dissociation of myocytes from hearts and stomachs of vertebrates. Am J Physiol. 1985 Nov;249(5 Pt 2):H1056–H1060. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.249.5.H1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata H., Silverman H. S., Sollott S. J., Lakatta E. G., Stern M. D., Hansford R. G. Measurement of mitochondrial free Ca2+ concentration in living single rat cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 2):H1123–H1134. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.4.H1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moravec C. S., Bond M. Calcium is released from the junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum during cardiac muscle contraction. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 2):H989–H997. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.260.3.H989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y. Calcium binding to troponin C and troponin: effects of Mg2+, ionic strength and pH. J Biochem. 1985 Apr;97(4):1011–1023. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
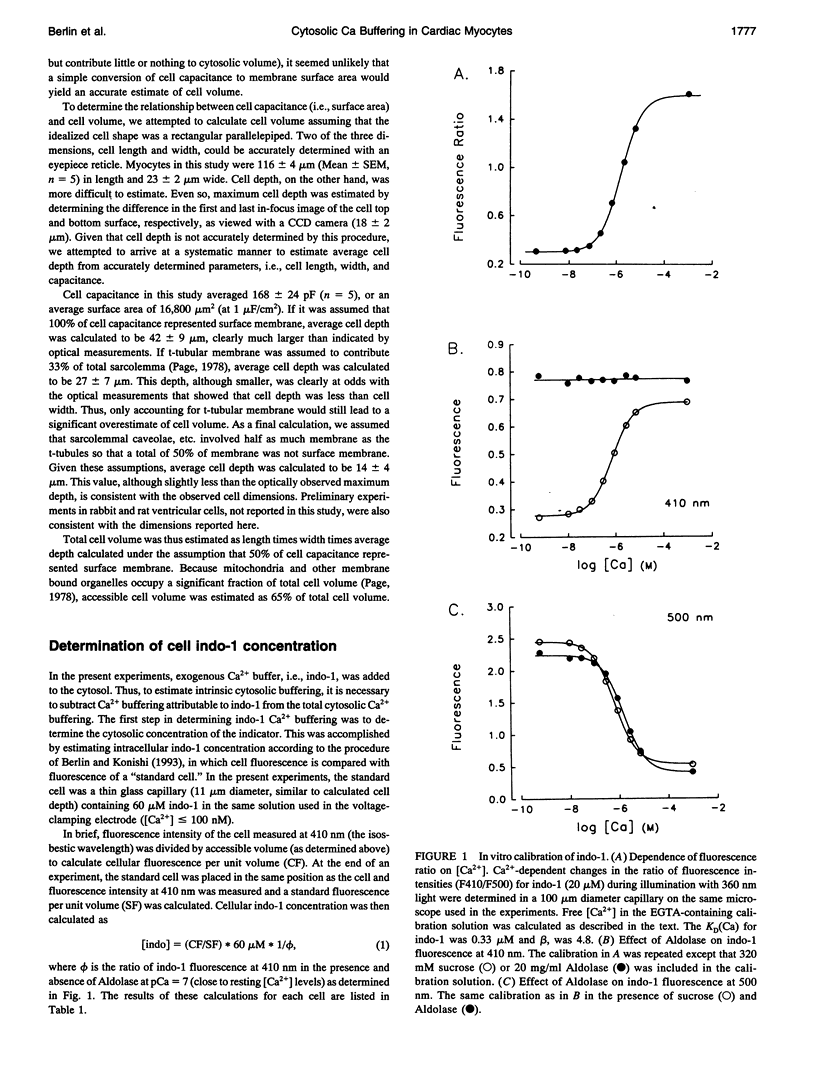
- Page E. Quantitative ultrastructural analysis in cardiac membrane physiology. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):C147–C158. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1978.235.5.C147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan B. S., Solaro R. J. Calcium-binding properties of troponin C in detergent-skinned heart muscle fibers. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7839–7849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce G. N., Philipson K. D., Langer G. A. Passive calcium-buffering capacity of a rabbit ventricular homogenate preparation. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):C248–C255. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.3.C248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post J. A., Langer G. A., Op den Kamp J. A., Verkleij A. J. Phospholipid asymmetry in cardiac sarcolemma. Analysis of intact cells and 'gas-dissected' membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Aug 18;943(2):256–266. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90557-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. P., Johnson J. D., Potter J. D. The time-course of Ca2+ exchange with calmodulin, troponin, parvalbumin, and myosin in response to transient increases in Ca2+. Biophys J. 1981 Jun;34(3):559–569. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84868-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagara Y., Inesi G. Inhibition of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transport ATPase by thapsigargin at subnanomolar concentrations. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13503–13506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solaro R. J., Wise R. M., Shiner J. S., Briggs F. N. Calcium requirements for cardiac myofibrillar activation. Circ Res. 1974 Apr;34(4):525–530. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.4.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer J. R., Waugh R. A. The ultrastructure of the mammalian cardiac muscle cell--with special emphasis on the tubular membrane systems. A review. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jan;82(1):192–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendt-Gallitelli M. F., Isenberg G. Total and free myoplasmic calcium during a contraction cycle: x-ray microanalysis in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:349–372. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wier W. G., Egan T. M., López-López J. R., Balke C. W. Local control of excitation-contraction coupling in rat heart cells. J Physiol. 1994 Feb 1;474(3):463–471. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Neher E. Mobile and immobile calcium buffers in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1993 Sep;469:245–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zot H. G., Potter J. D. Calcium binding and fluorescence measurements of dansylaziridine-labelled troponin C in reconstituted thin filaments. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1987 Oct;8(5):428–436. doi: 10.1007/BF01578432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


