Abstract
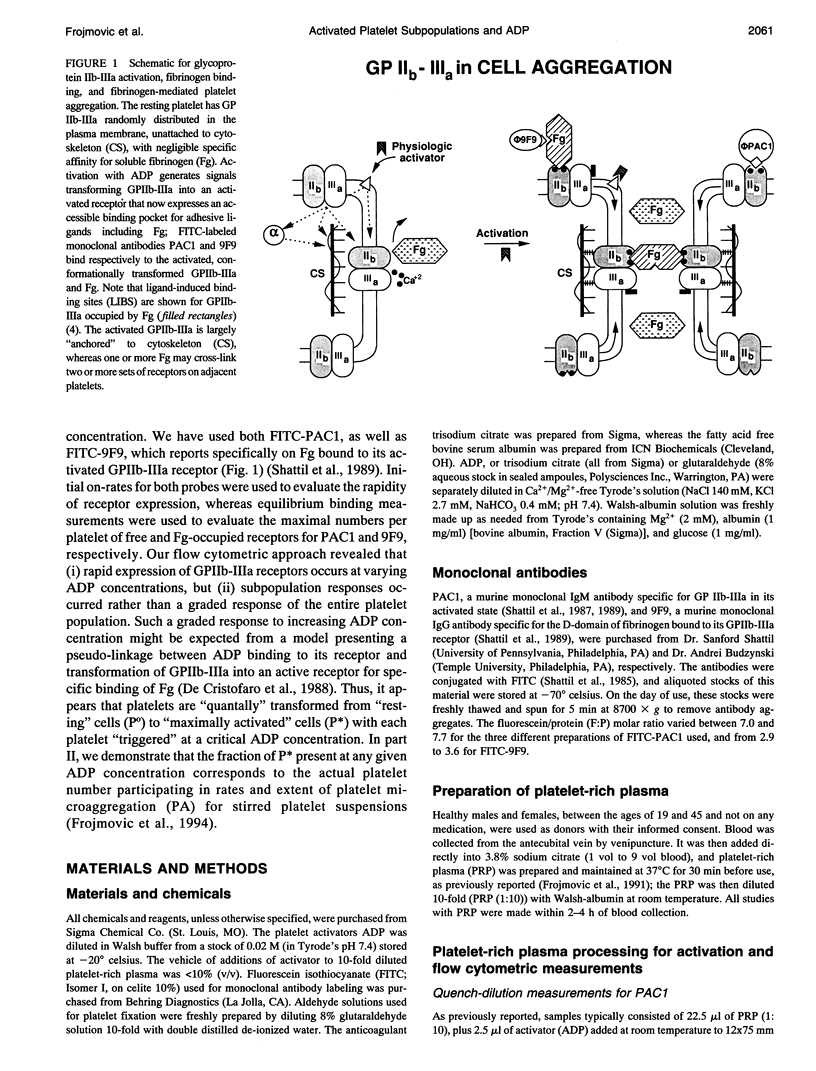
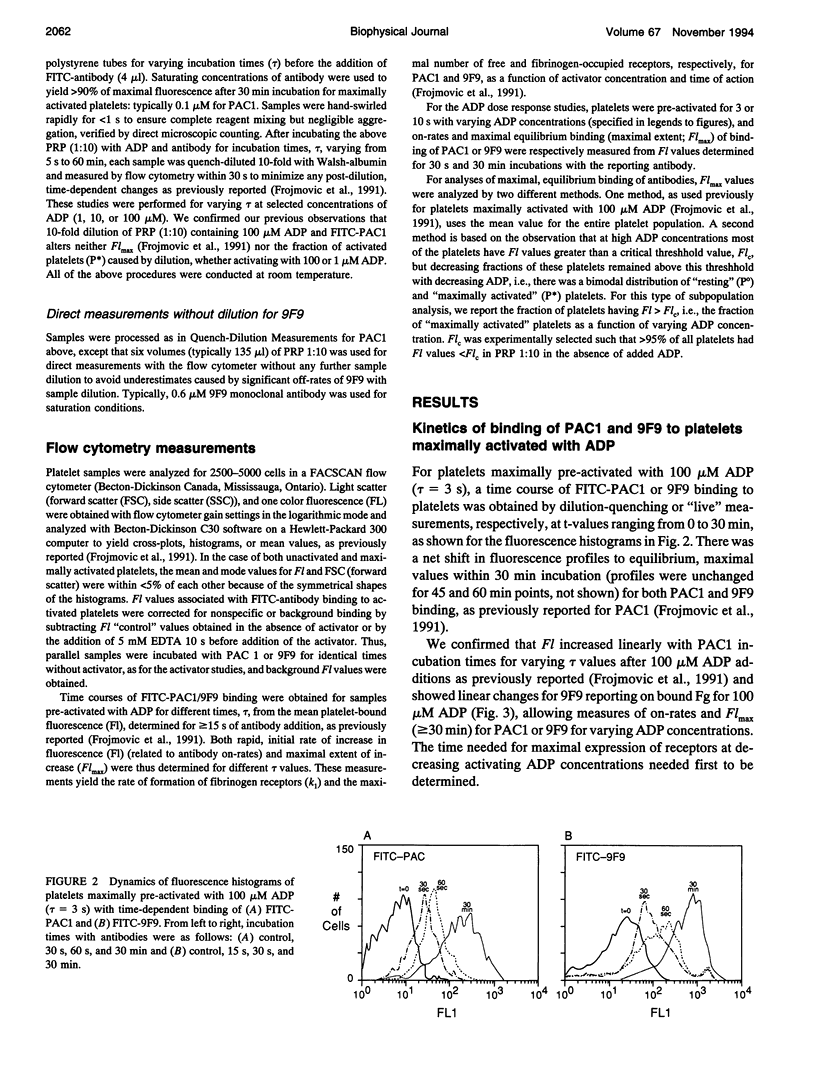
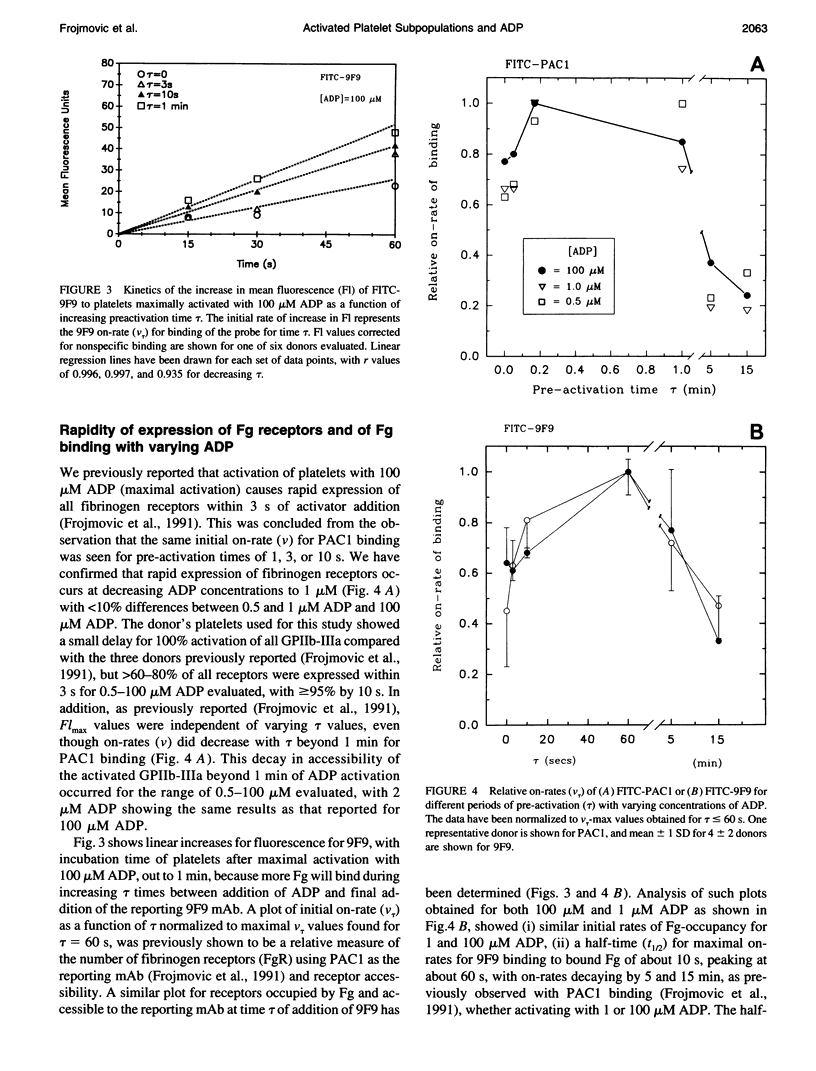
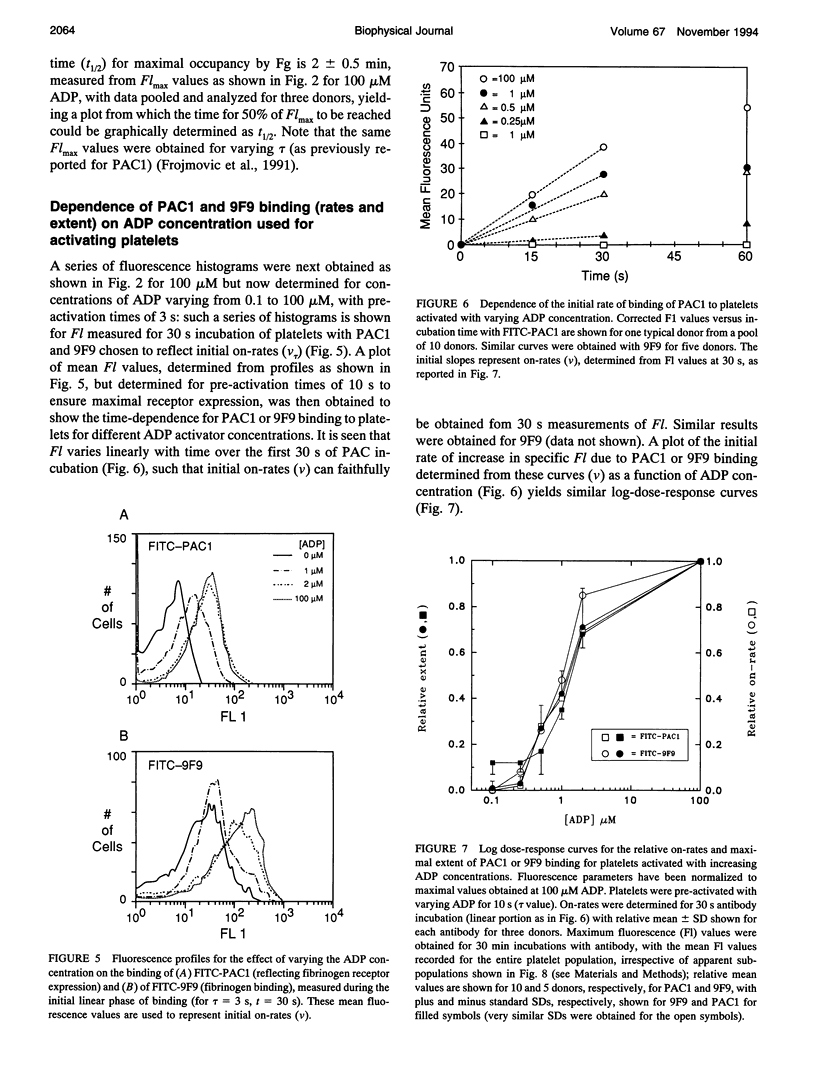
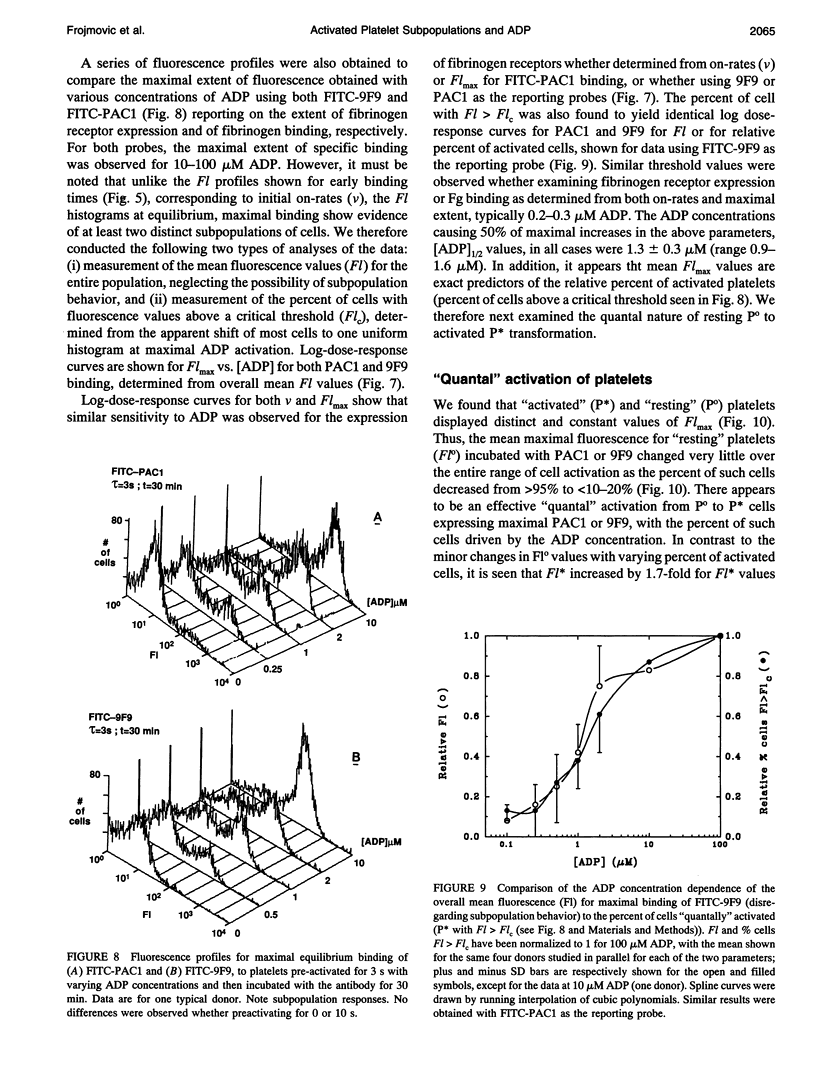
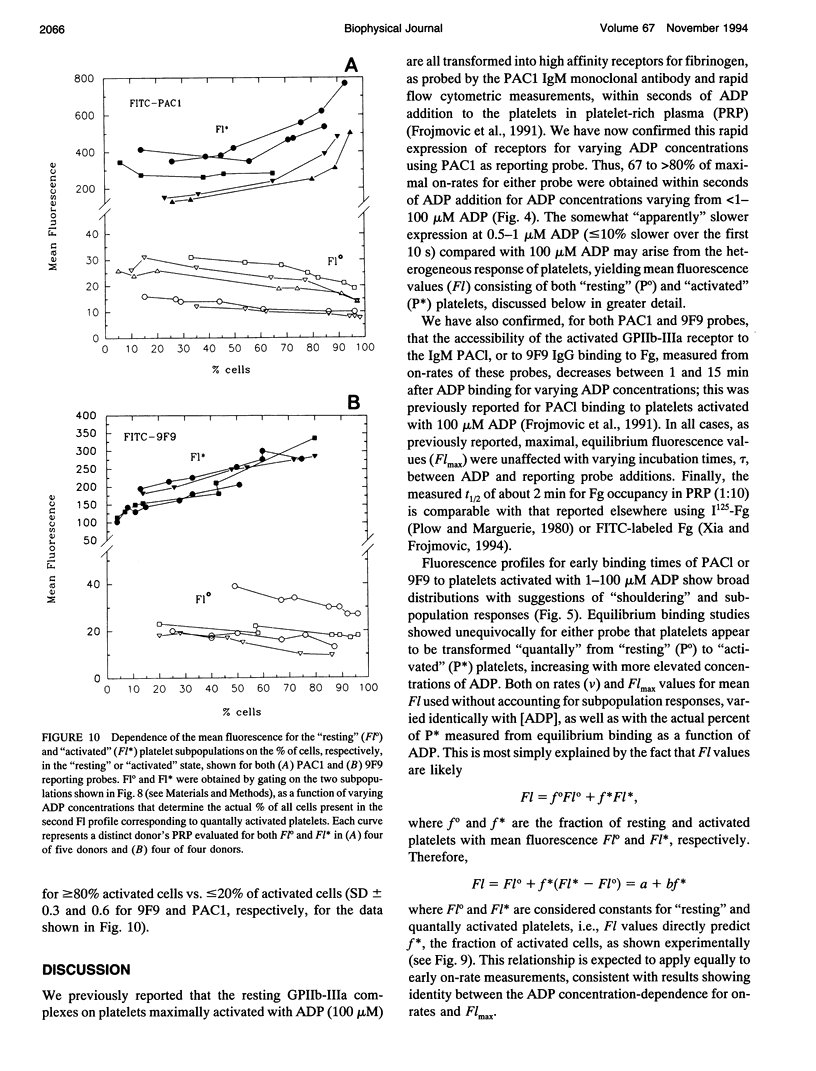
We have previously reported that maximal platelet activation with adenosine diphosphate (100 microM ADP) causes rapid expression of all GPIIb-IIIa receptors for fibrinogen (FgR) (< 1-3 s), measured with FITC-labeled PAC1 by flow cytometry. We have extended these studies to examine the effects of ADP concentration on the graded expression and Fg occupancy of GPIIb-IIIa receptors. Human citrated platelet-rich plasma, diluted 10-fold with Walsh-albumin-Mg+2 (2 mM), was treated with ADP (0.1-100 microM). The rates of GPIIb-IIIa receptor expression or Fg binding were measured in unstirred samples by flow cytometry, using FITC-labeled monoclonal antibodies (mAb) PAC1 and 9F9, respectively, from on-rates, using increasing times between mAb and ADP additions. Fibrinogen receptors were all expressed rapidly at low (1 microM) or high (100 microM) ADP (few seconds), whereas Fg occupancy was 50% of maximal by about 2 min. The maximal extent of GPIIb-IIIa receptor expression and Fg occupancy was determined from maximal binding (Flmax) at 30 min incubation with PAC1 or 9F9. On-rates and maximal extents of binding for either PAC1 or 9F9 probes showed identical [ADP]-response profiles ("KD" approximately 1.4 +/- 0.1 microM). However, Flmax studies showed bimodal histograms consisting of "resting" (Po) and maximally "activated" (P*) platelets for both PAC1 and 9F9 binding, with the fraction of "activated" platelets increasing with ADP concentration. The data best fit a model where platelet subpopulations are "quantally" transformed from Po to P*, expressing all GPIIb-IIIa receptors, rapidly filled by Fg, but "triggered" at critical ADP concentrations. Larger, but not the largest, platelets appear to be the most sensitive subpopulation. The implications for clinical studies are discussed, and the relationship to dynamics of aggregation are described in a companion paper.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams C., Shattil S. J. Immunological detection of activated platelets in clinical disorders. Thromb Haemost. 1991 May 6;65(5):467–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault K. A., Rinder H. M., Mitchell J. G., Rinder C. S., Lambrew C. T., Hillman R. S. Correlated measurement of platelet release and aggregation in whole blood. Cytometry. 1989 Jul;10(4):448–455. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990100413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carty D. J., Gear A. R. Fractionation of platelets according to size: functional and biochemical characteristics. Am J Hematol. 1986 Jan;21(1):1–14. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830210102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corash L., Tan H., Gralnick H. R. Heterogeneity of human whole blood platelet subpopulations. I. Relationship between buoyant density, cell volume, and ultrastructure. Blood. 1977 Jan;49(1):71–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies T. A., Weil G. J., Simons E. R. Simultaneous flow cytometric measurements of thrombin-induced cytosolic pH and Ca2+ fluxes in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11522–11526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cristofaro R., Landolfi R., De Candia E., Castagnola M., Di Cera E., Wyman J. Allosteric equilibria in the binding of fibrinogen to platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8473–8476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frojmovic M. M., Milton J. G. Human platelet size, shape, and related functions in health and disease. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jan;62(1):185–261. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.1.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frojmovic M. M., Mooney R. F., Wong T. Dynamics of platelet glycoprotein IIb-IIIa receptor expression and fibrinogen binding. II. Quantal activation parallels platelet capture in stir-associated microaggregation. Biophys J. 1994 Nov;67(5):2069–2075. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80690-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frojmovic M., Wong T. Dynamic measurements of the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa receptor for fibrinogen by flow cytometry. II. Platelet size-dependent subpopulations. Biophys J. 1991 Apr;59(4):828–837. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82295-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frojmovic M., Wong T., van de Ven T. Dynamic measurements of the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa receptor for fibrinogen by flow cytometry. I. Methodology, theory and results for two distinct activators. Biophys J. 1991 Apr;59(4):815–827. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82294-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gear A. R. Rapid platelet morphological changes visualized by scanning-electron microscopy: kinetics derived from a quenched-flow approach. Br J Haematol. 1984 Mar;56(3):387–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb03969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Frelinger A. L., Lam S. C., Forsyth J., McMillan R., Plow E. F., Shattil S. J. Analysis of platelet aggregation disorders based on flow cytometric analysis of membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa with conformation-specific monoclonal antibodies. Blood. 1990 Nov 15;76(10):2017–2023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. W., Jennings L. K. Heterogeneity of fibrinogen receptor expression on platelets activated in normal plasma with ADP: analysis by flow cytometry. Br J Haematol. 1989 Jul;72(3):407–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb07724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll M. H., Schafer A. I. Biochemical mechanisms of platelet activation. Blood. 1989 Sep;74(4):1181–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marguerie G. A., Edgington T. S., Plow E. F. Interaction of fibrinogen with its platelet receptor as part of a multistep reaction in ADP-induced platelet aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):154–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Kornecki E., Budzynski A. Z., Morinelli T. A., Tuszynski G. P. Fibrinogen interaction with platelet receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:536–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedvis L. G., Wong T., Frojmovic M. M. Differential inhibition of the platelet activation sequence: shape change, micro- and macro-aggregation, by a stable prostacyclin analogue (Iloprost). Thromb Haemost. 1988 Apr 8;59(2):323–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I. The platelet fibrinogen receptor. Semin Hematol. 1985 Oct;22(4):241–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penington D. G., Streatfield K., Roxburgh A. E. Megakaryocytes and the heterogeneity of circulating platelets. Br J Haematol. 1976 Dec;34(4):639–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb03611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Cellular adhesion: GPIIb-IIIa as a prototypic adhesion receptor. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1989;9:117–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Marguerie G. A. Participation of ADP in the binding of fibrinogen to thrombin-stimulated platelets. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):553–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Budzynski A., Scrutton M. C. Epinephrine induces platelet fibrinogen receptor expression, fibrinogen binding, and aggregation in whole blood in the absence of other excitatory agonists. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):150–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Cunningham M., Hoxie J. A. Detection of activated platelets in whole blood using activation-dependent monoclonal antibodies and flow cytometry. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):307–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Hoxie J. A., Cunningham M., Brass L. F. Changes in the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb.IIIa complex during platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11107–11114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warkentin T. E., Powling M. J., Hardisty R. M. Measurement of fibrinogen binding to platelets in whole blood by flow cytometry: a micromethod for the detection of platelet activation. Br J Haematol. 1990 Nov;76(3):387–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb06373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T., Pedvis L., Frojmovic M. Platelet size affects both micro- and macro-aggregation: contributions of platelet number, volume fraction and cell surface. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Sep 29;62(2):733–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Z., Frojmovic M. M. Aggregation efficiency of activated normal or fixed platelets in a simple shear field: effect of shear and fibrinogen occupancy. Biophys J. 1994 Jun;66(6):2190–2201. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)81015-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


