Abstract
Inhibition of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) by channel blockade has been demonstrated with a variety of large organic cations, including several nicotinic agonists. We have studied the kinetics of channel blocking of a series of agonists which vary systematically in size and hydrophobicity due to a hydrocarbon chain from one to six carbons in length, as well as one agonist with a tertiary isomer of one hydrocarbon chain. Single-channel recording was used in combination with three different analysis techniques for determining the kinetic and equilibrium parameters of channel blockade. With an increasing number of methylenes, the blocking rates were essentially constant and the unblocking rates decreased exponentially. This is consistent with studies of the blocking properties of alcohols at the nAChR channel. Also, a linear decrease in the depth to which the larger agonists penetrate the membrane spanning region of the channel was observed. The three smaller agonists, however, all traverse approximately 75% of the membrane field, in agreement with previous measurements of the location of the narrowest region of the channel, the selectivity filter.
Full text
PDF



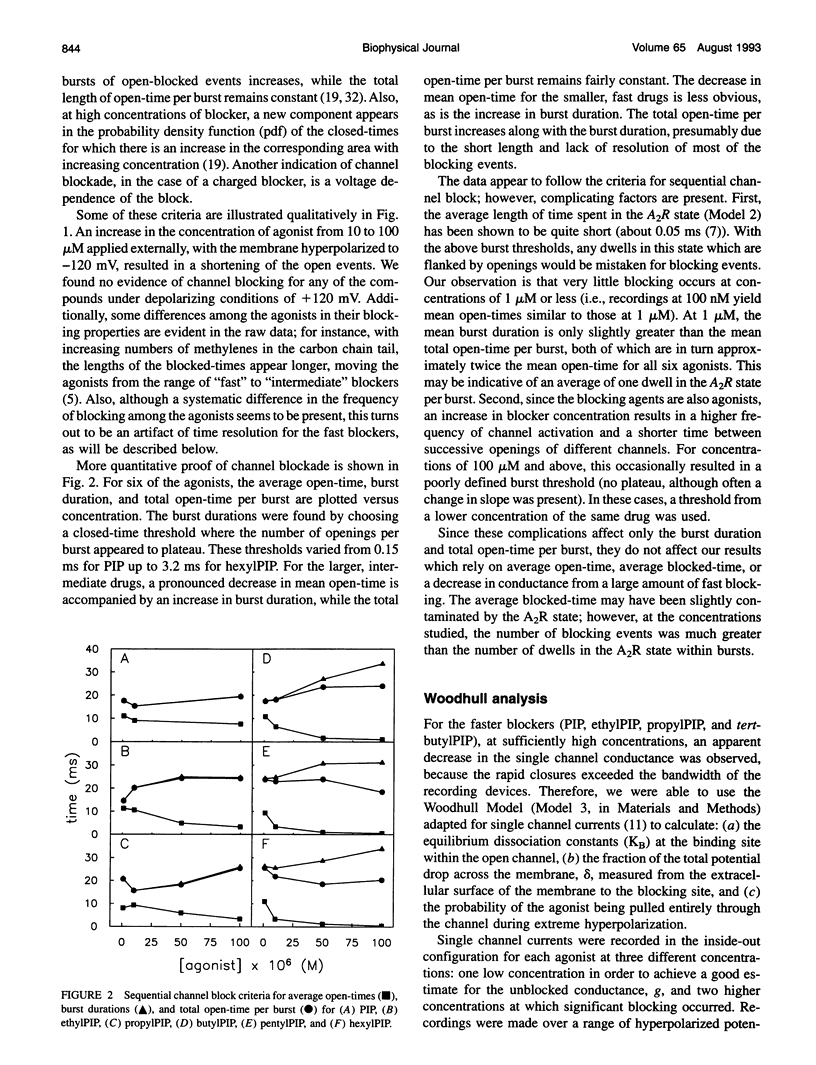
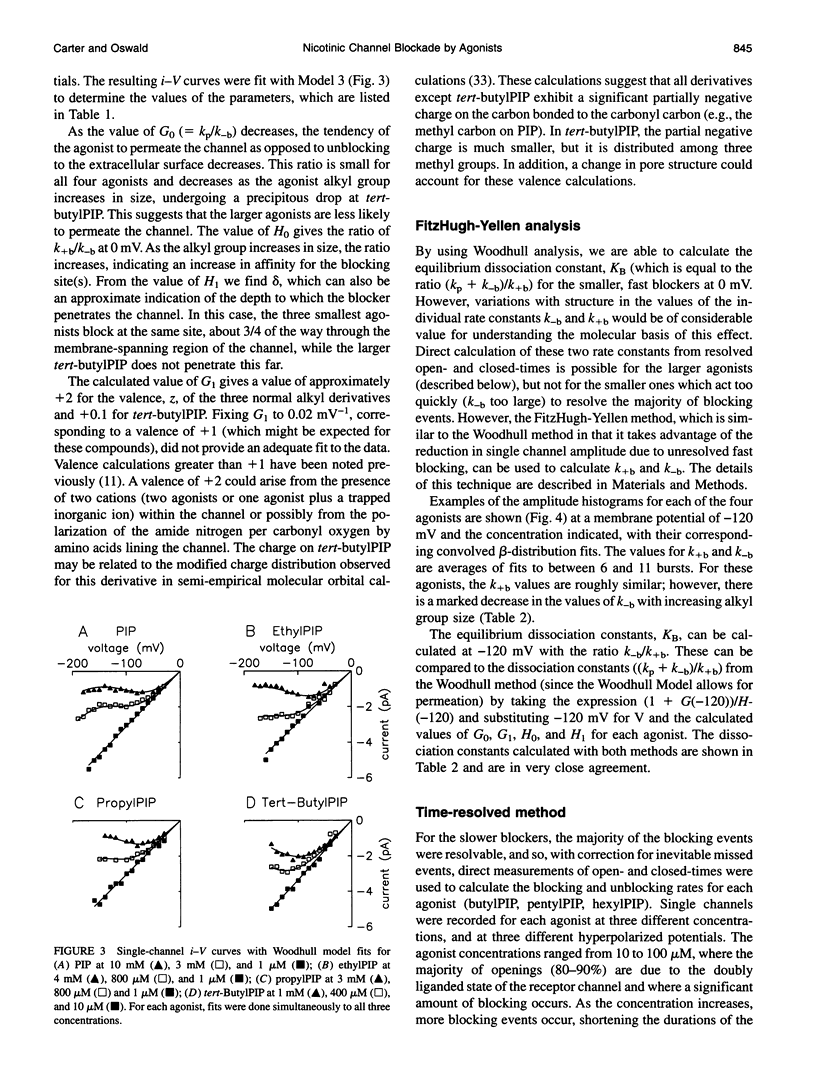
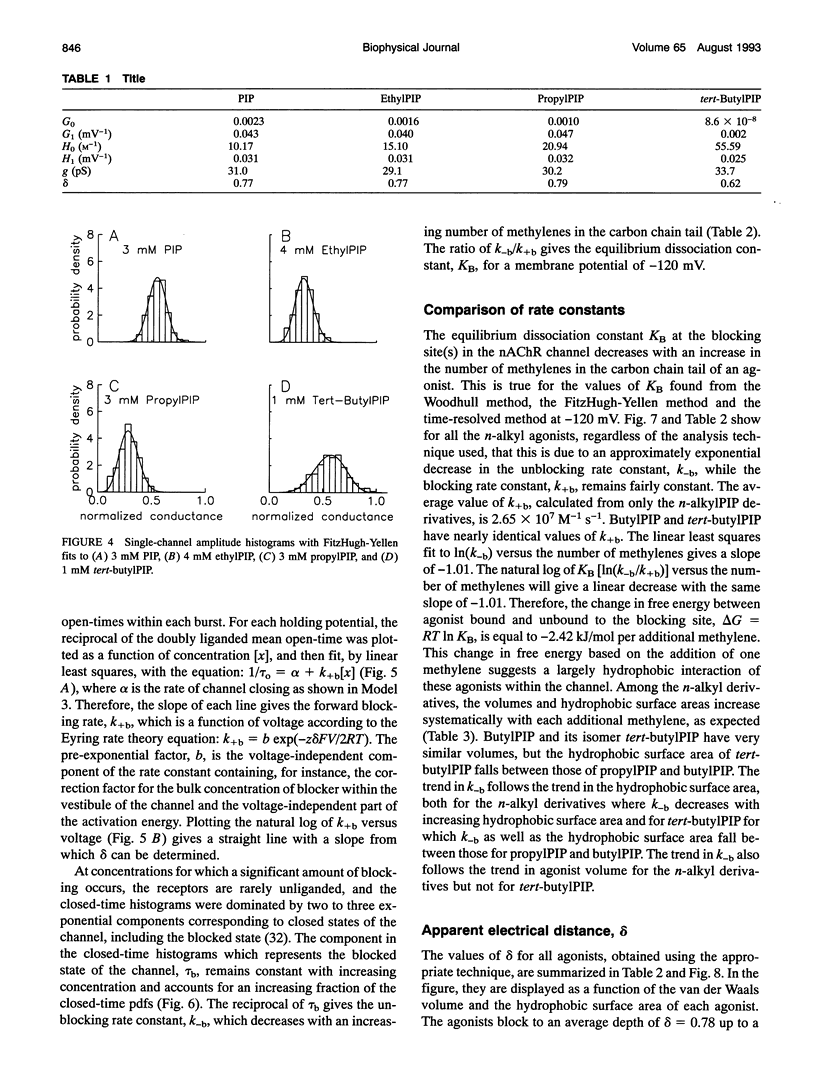


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R. Voltage jump analysis of procaine action at frog end-plate. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):291–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akabas M. H., Stauffer D. A., Xu M., Karlin A. Acetylcholine receptor channel structure probed in cysteine-substitution mutants. Science. 1992 Oct 9;258(5080):307–310. doi: 10.1126/science.1384130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):413–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beers W. H., Reich E. Structure and activity of acetylcholine. Nature. 1970 Dec 5;228(5275):917–922. doi: 10.1038/228917a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson A., Unwin P. N. Quaternary structure of the acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):474–477. doi: 10.1038/315474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnet P., Labarca C., Leonard R. J., Vogelaar N. J., Czyzyk L., Gouin A., Davidson N., Lester H. A. An open-channel blocker interacts with adjacent turns of alpha-helices in the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Neuron. 1990 Jan;4(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90445-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Ogden D. C. Activation of ion channels in the frog end-plate by high concentrations of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:131–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fast events in single-channel currents activated by acetylcholine and its analogues at the frog muscle end-plate. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:501–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani J. A., Eisenman G. Monovalent and divalent cation permeation in acetylcholine receptor channels. Ion transport related to structure. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jun;89(6):959–983. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.6.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani J. A. Ion-channel entrances influence permeation. Net charge, size, shape, and binding considerations. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):607–618. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83688-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani J. A. Open channel structure and ion binding sites of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channel. J Neurosci. 1989 Mar;9(3):884–892. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-03-00884.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani J. A. Site-directed mutagenesis and single-channel currents define the ionic channel of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Apr;12(4):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer T. M., Adams D. J., Hille B. The permeability of the endplate channel to organic cations in frog muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):469–492. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French R. J., Shoukimas J. J. An ion's view of the potassium channel. The structure of the permeation pathway as sensed by a variety of blocking ions. J Gen Physiol. 1985 May;85(5):669–698. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.5.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French R. J., Shoukimas J. J. Blockage of squid axon potassium conductance by internal tetra-N-alkylammonium ions of various sizes. Biophys J. 1981 May;34(2):271–291. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84849-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galzi J. L., Bertrand D., Devillers-Thiéry A., Revah F., Bertrand S., Changeux J. P. Functional significance of aromatic amino acids from three peptide loops of the alpha 7 neuronal nicotinic receptor site investigated by site-directed mutagenesis. FEBS Lett. 1991 Dec 9;294(3):198–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80668-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraudat J., Dennis M., Heidmann T., Chang J. Y., Changeux J. P. Structure of the high-affinity binding site for noncompetitive blockers of the acetylcholine receptor: serine-262 of the delta subunit is labeled by [3H]chlorpromazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2719–2723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Brodwick M. S., Dickey W. D. Asymmetry of the acetylcholine channel revealed by quaternary anesthetics. Science. 1980 Oct 10;210(4466):205–207. doi: 10.1126/science.6251552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucho F., Oberthür W., Lottspeich F. The ion channel of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is formed by the homologous helices M II of the receptor subunits. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 1;205(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80881-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto K., Busch C., Sakmann B., Mishina M., Konno T., Nakai J., Bujo H., Mori Y., Fukuda K., Numa S. Rings of negatively charged amino acids determine the acetylcholine receptor channel conductance. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):645–648. doi: 10.1038/335645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto K., Methfessel C., Sakmann B., Mishina M., Mori Y., Konno T., Fukuda K., Kurasaki M., Bujo H., Fujita Y. Location of a delta-subunit region determining ion transport through the acetylcholine receptor channel. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):670–674. doi: 10.1038/324670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca P., Montal M. S., Lindstrom J. M., Montal M. The occurrence of long openings in the purified cholinergic receptor channel increases with acetylcholine concentration. J Neurosci. 1985 Dec;5(12):3409–3413. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-12-03409.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. J., Charnet P., Labarca C., Vogelaar N. J., Czyzyk L., Gouin A., Davidson N., Lester H. A. Reverse pharmacology of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Mapping the local anesthetic binding site. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;625:588–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb33894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. J., Labarca C. G., Charnet P., Davidson N., Lester H. A. Evidence that the M2 membrane-spanning region lines the ion channel pore of the nicotinic receptor. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2462281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. G., Ogden D., Colquhoun D. Activation of ion channels in the frog endplate by several analogues of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:73–93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Bis-quaternary ammonium blockers as structural probes of the sarcoplasmic reticulum K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1982 May;79(5):869–891. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.5.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrell R. D., Braun M. S., Haydon D. A. Actions of n-alcohols on nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channels in cultured rat myotubes. J Physiol. 1991 Jun;437:431–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Steinbach J. H. Local anaesthetics transiently block currents through single acetylcholine-receptor channels. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:153–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden D. C., Colquhoun D. Ion channel block by acetylcholine, carbachol and suberyldicholine at the frog neuromuscular junction. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Sep 23;225(1240):329–355. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Glaser L., Merlie J. P., Sebanne R., Lindstrom J. Regulation of surface expression of acetylcholine receptors in response to serum and cell growth in the BC3H1 muscle cell line. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13946–13953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papke R. L., Millhauser G., Lieberman Z., Oswald R. E. Relationships of agonist properties to the single channel kinetics of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biophys J. 1988 Jan;53(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83059-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papke R. L., Oswald R. E. Mechanisms of noncompetitive inhibition of acetylcholine-induced single-channel currents. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):785–811. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Harris A. J., Devine C. E., Heinemann S. Characterization of a unique muscle cell line. J Cell Biol. 1974 May;61(2):398–413. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Agonists block currents through acetylcholine receptor channels. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):277–283. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84022-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak C. E., Gund T. M., Liang R. F., Waters J. A. Structural and electronic requirements for potent agonists at a nicotinic receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan 14;120(1):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90652-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak C. E., Waters J. A., Aronstam R. S. Binding of semirigid nicotinic agonists to nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):177–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. P., Jr Inactivation of potassium current in squid axon by a variety of quaternary ammonium ions. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Mar;77(3):255–271. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.3.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Ionic permeation and blockade in Ca2+-activated K+ channels of bovine chromaffin cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Aug;84(2):157–186. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]