Abstract
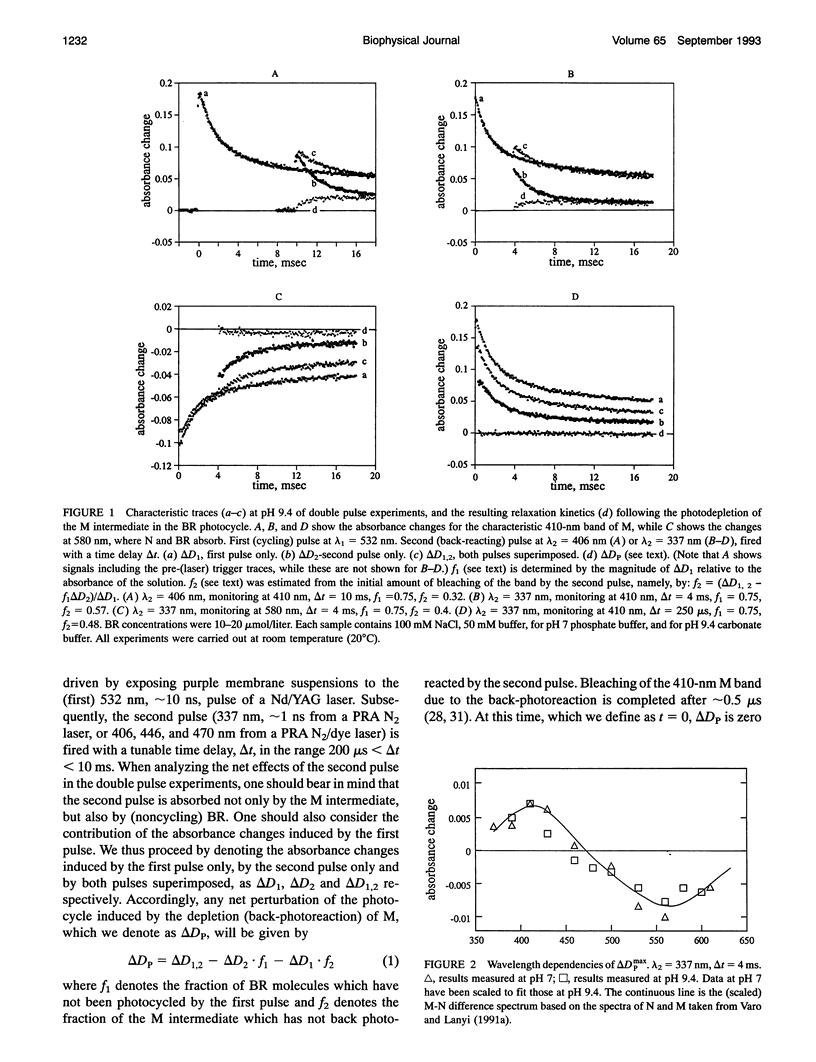
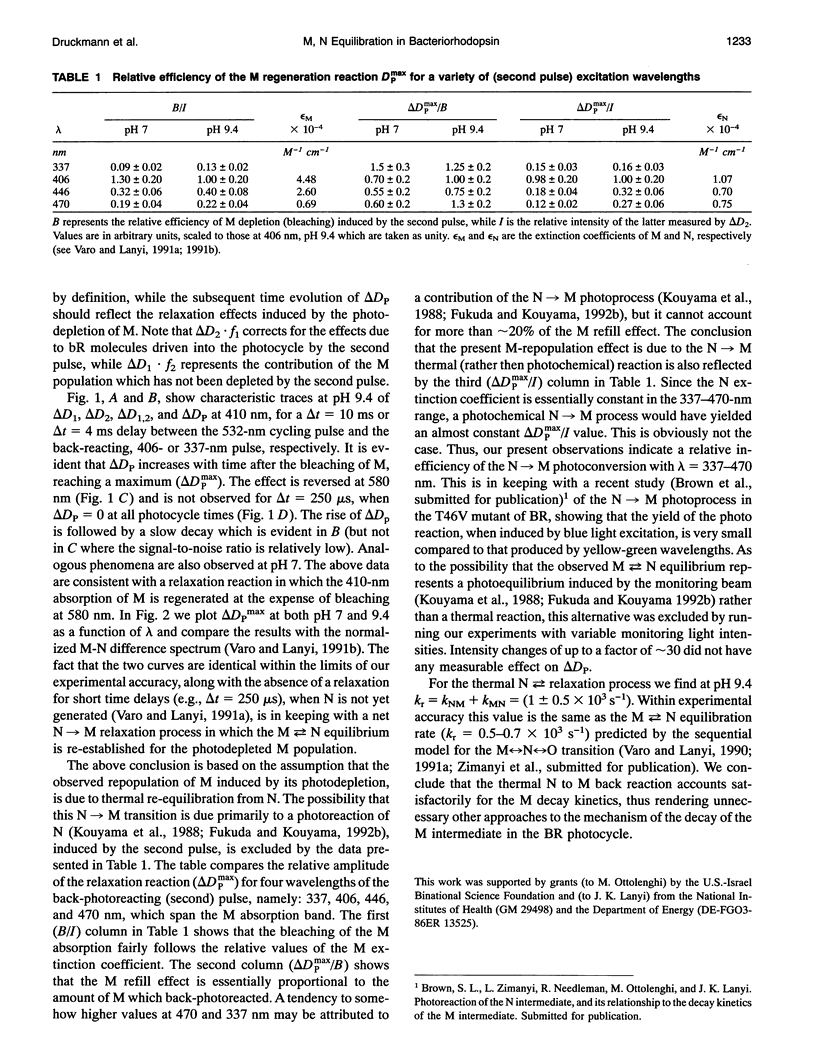
The stages in the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin (BR) involving the M and N intermediates are investigated using a double pulse excitation method. A first (cycling) pulse at 532 nm is followed, with an appropriate time delay, by a second pulse (337, 406, 446, or 470 nm) which induces the M-->BR back-photoreaction. After depletion by the second pulse a repopulation of M in the millisecond range is observed which is interpreted in terms of a thermal N-->M relaxation. It is thus concluded that a (thermal) M<-->N equilibrium accounts for the biphasic decay of M in the BR photocycle. Other models for this stage of the light-driven proton-pump are therefore unnecessary.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames J. B., Mathies R. A. The role of back-reactions and proton uptake during the N----O transition in bacteriorhodopsin's photocycle: a kinetic resonance Raman study. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 7;29(31):7181–7190. doi: 10.1021/bi00483a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Fendler K., Dér A., Bamberg E. Temperature jump study of charge translocation during the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biophys J. 1989 Nov;56(5):851–859. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82731-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancsházy Z., Govindjee R., Ebrey T. G. Independent photocycles of the spectrally distinct forms of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6358–6361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachev L. A., Kaulen A. D., Komrakov AYu Interrelations of M-intermediates in bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 30;313(3):248–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81202-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druckmann S., Friedman N., Lanyi J. K., Needleman R., Ottolenghi M., Sheves M. The back photoreaction of the M intermediate in the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin: mechanism and evidence for two M species. Photochem Photobiol. 1992;56(6):1041–1047. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1992.tb09727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda K., Kouyama T. Photoreaction of bacteriorhodopsin at high pH: origins of the slow decay component of M. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 1;31(47):11740–11747. doi: 10.1021/bi00162a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwert K., Souvignier G., Hess B. Simultaneous monitoring of light-induced changes in protein side-group protonation, chromophore isomerization, and backbone motion of bacteriorhodopsin by time-resolved Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec 15;87(24):9774–9778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanamoto J. H., Dupuis P., El-Sayed M. A. On the protein (tyrosine)-chromophore (protonated Schiff base) coupling in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7083–7087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalisky O., Ottolenghi M., Honig B., Korenstein R. Environmental effects on formation and photoreaction of the M412 photoproduct of bacteriorhodopsin: implications for the mechanism of proton pumping. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 3;20(3):649–655. doi: 10.1021/bi00506a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Nasuda-Kouyama A., Ikegami A., Mathew M. K., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin photoreaction: identification of a long-lived intermediate N (P,R350) at high pH and its M-like photoproduct. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):5855–5863. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Proton transfer and energy coupling in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Apr;24(2):169–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00762675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Xie A., Hofrichter J., Clore G. M. Reversible steps in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3610–3614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathies R. A., Lin S. W., Ames J. B., Pollard W. T. From femtoseconds to biology: mechanism of bacteriorhodopsin's light-driven proton pump. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:491–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Parodi L. A., Lozier R. H. Procedure for testing kinetic models of the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1982 May;38(2):161–174. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84543-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Tittor J., Bamberg E. A unifying concept for ion translocation by retinal proteins. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Apr;24(2):181–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00762676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto H., Marti T., Holz M., Mogi T., Lindau M., Khorana H. G., Heyn M. P. Aspartic acid-96 is the internal proton donor in the reprotonation of the Schiff base of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9228–9232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J. FTIR difference spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin: toward a molecular model. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Apr;24(2):147–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00762674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souvignier G., Gerwert K. Proton uptake mechanism of bacteriorhodopsin as determined by time-resolved stroboscopic-FTIR-spectroscopy. Biophys J. 1992 Nov;63(5):1393–1405. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81722-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokaji Z., Dancsházy Z. Kinetics of the N intermediate and the two pathways of recovery of the ground-state of bacteriorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1992 Oct 26;311(3):267–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokaji Z., Dancsházy Z. Light-induced, long-lived perturbation of the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):170–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80385-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Lanyi J. K. Kinetic and spectroscopic evidence for an irreversible step between deprotonation and reprotonation of the Schiff base in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biochemistry. 1991 May 21;30(20):5008–5015. doi: 10.1021/bi00234a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Lanyi J. K. Pathways of the rise and decay of the M photointermediate(s) of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 6;29(9):2241–2250. doi: 10.1021/bi00461a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Lanyi J. K. Thermodynamics and energy coupling in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biochemistry. 1991 May 21;30(20):5016–5022. doi: 10.1021/bi00234a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


