Abstract
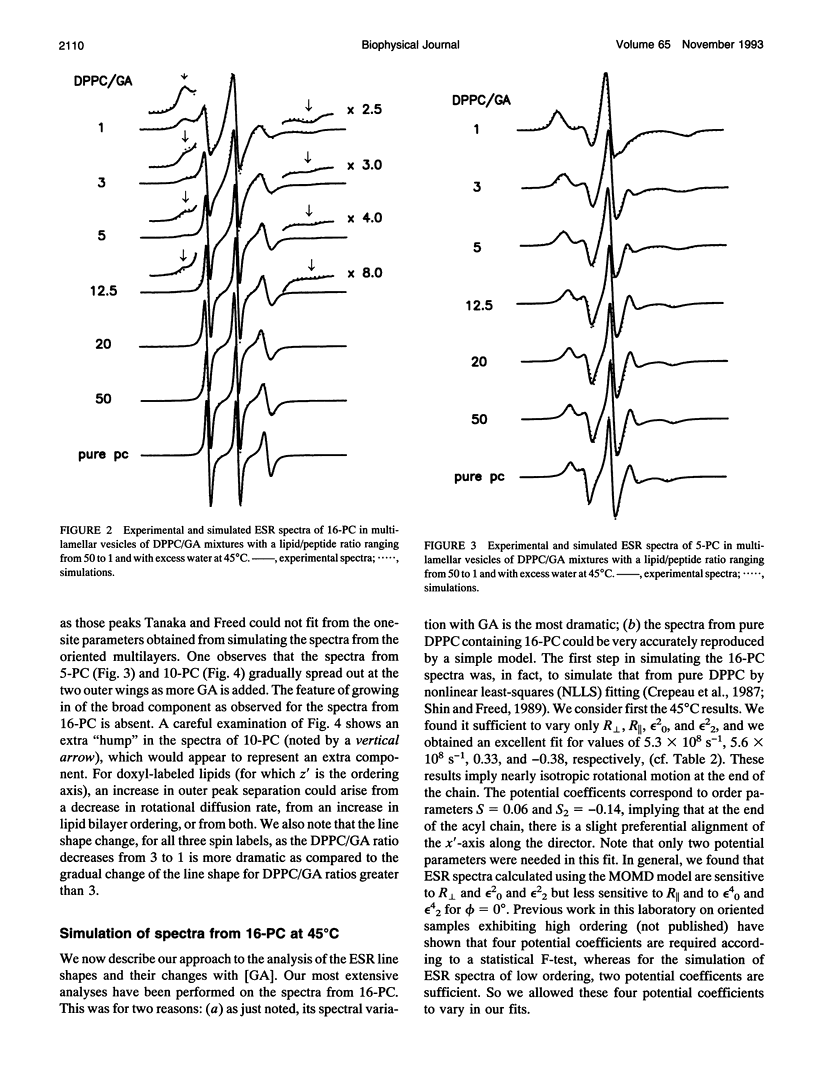
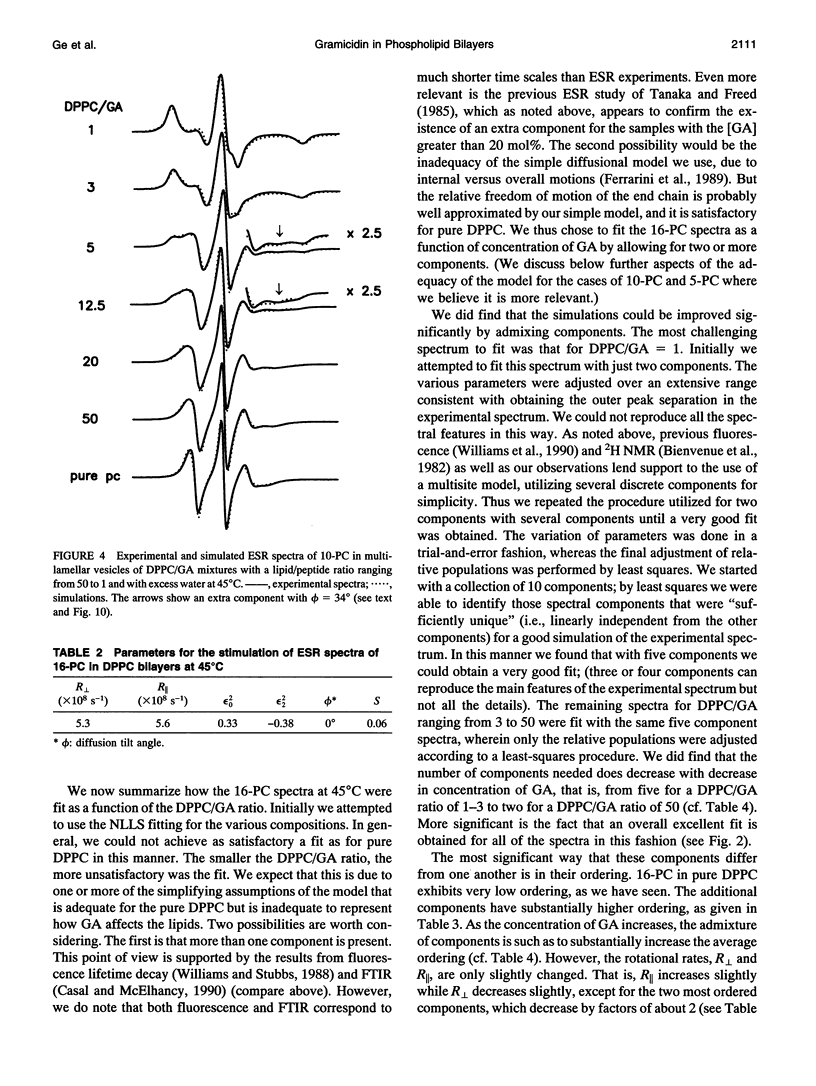
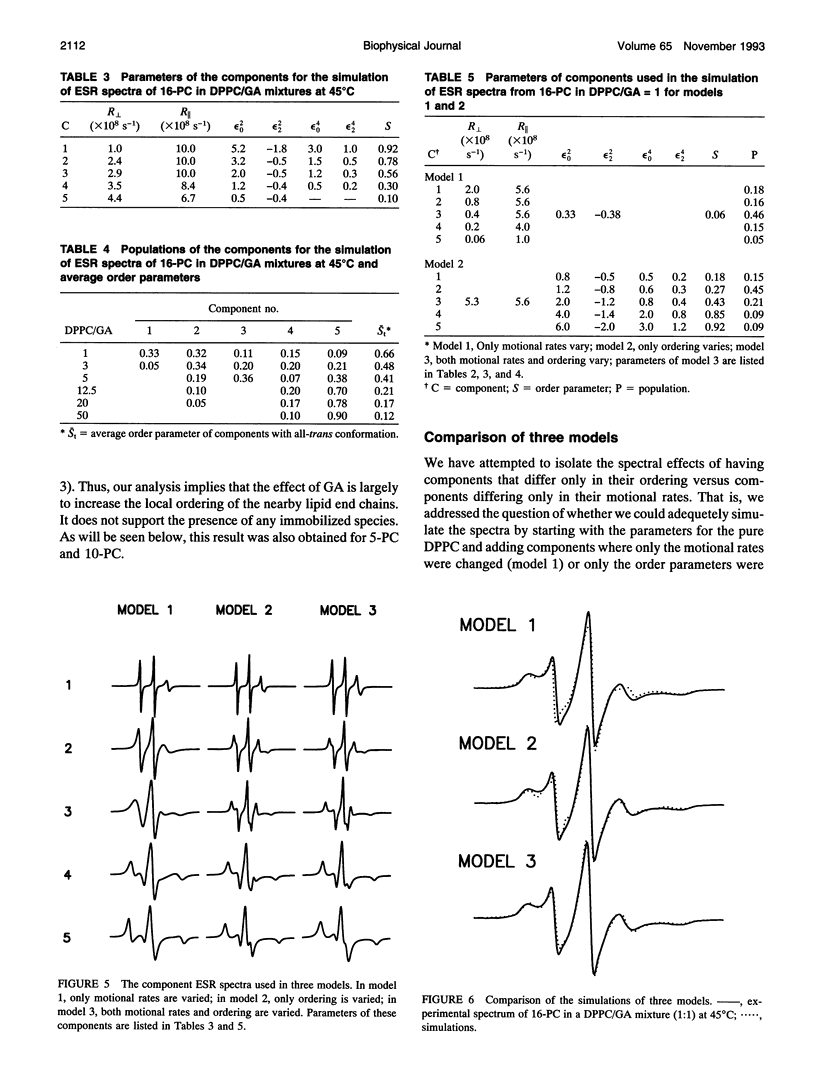
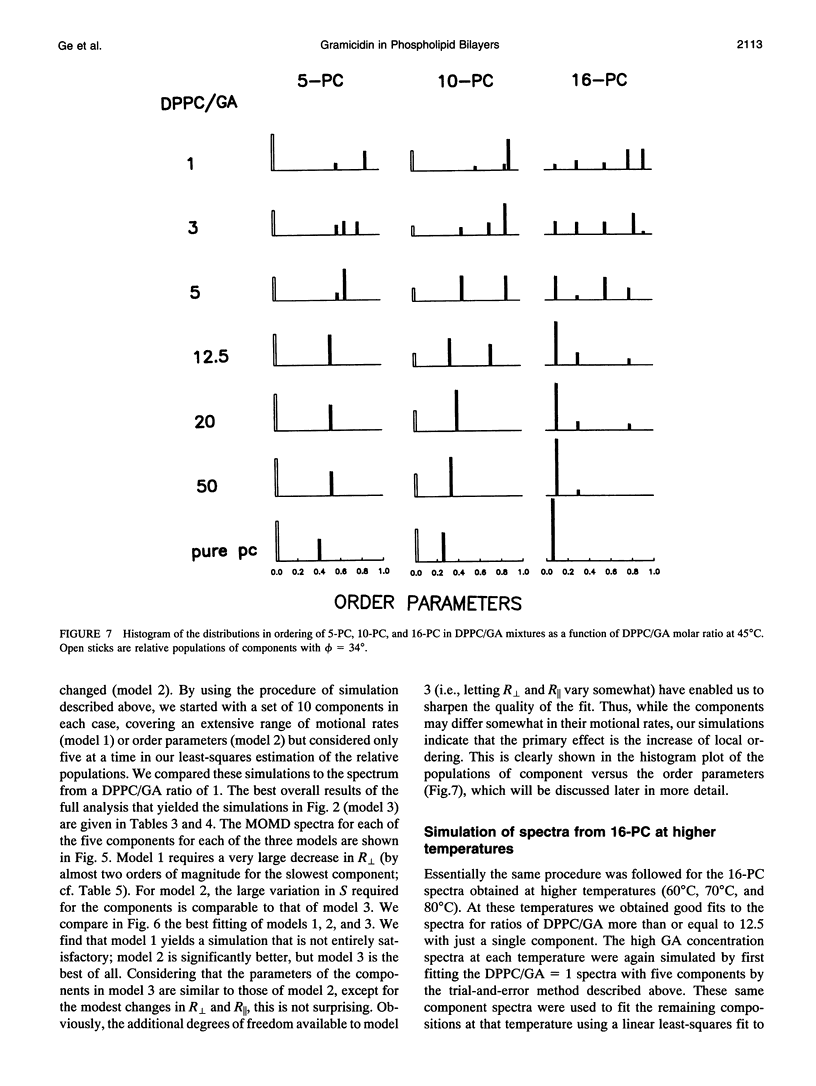
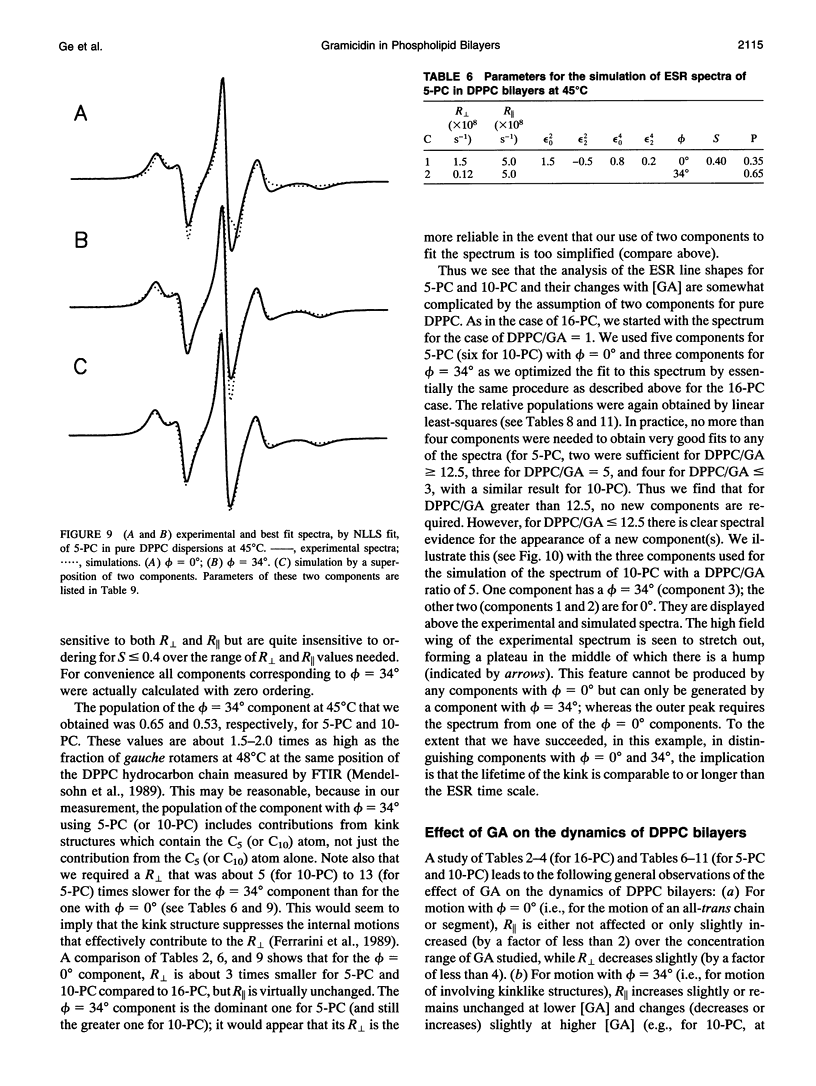
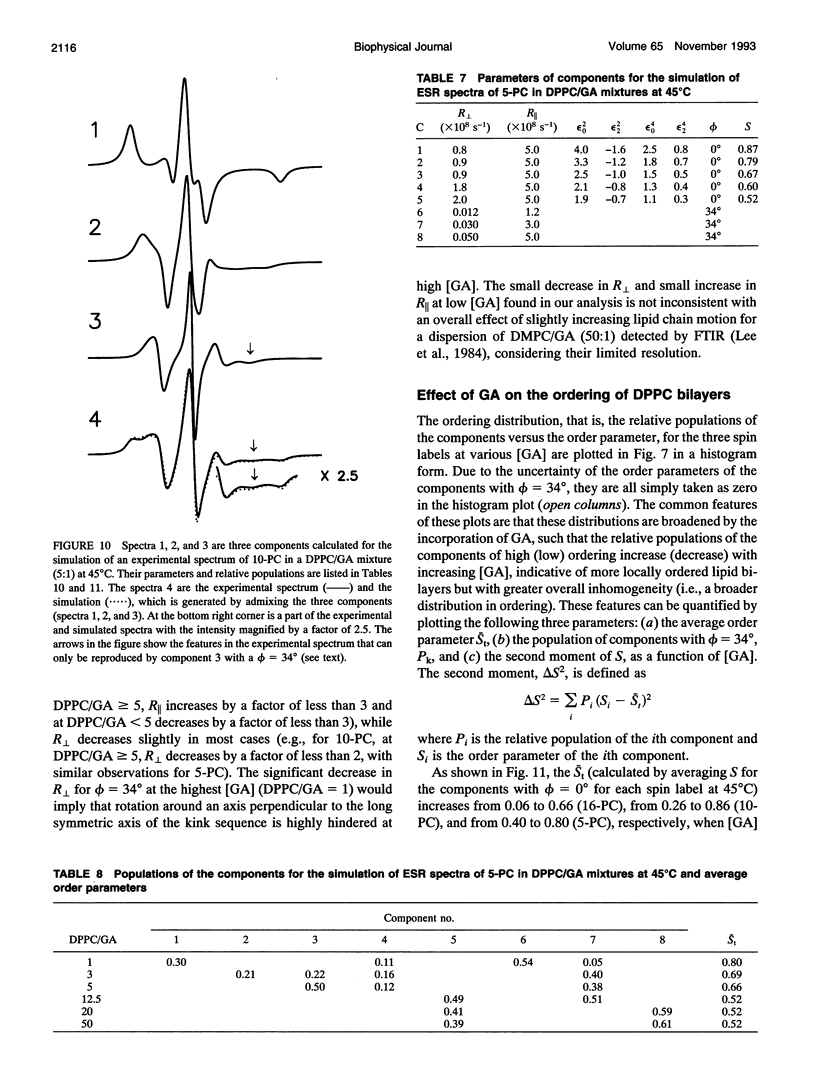
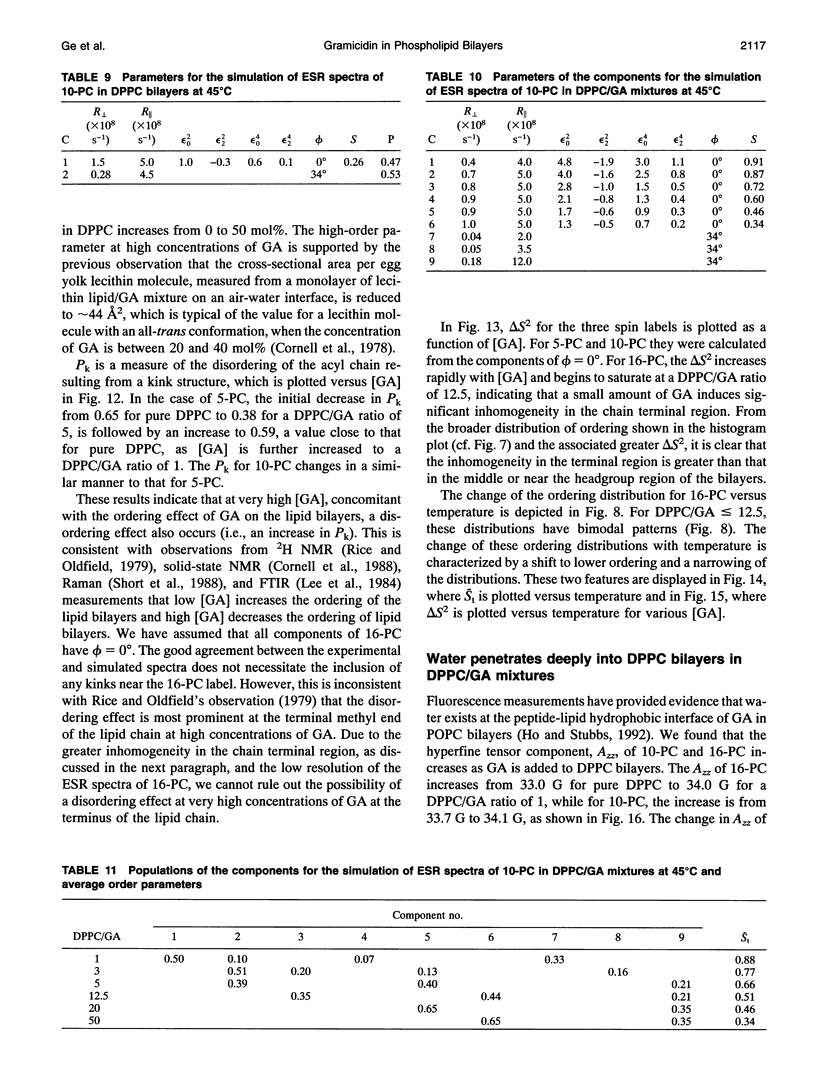
The model of microscopic order and macroscopic disorder was used to stimulate electron spin resonance spectra of spin-labeled lipids, 5-PC, 10-PC, and 16-PC in multilamellar vesicles of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) containing gramicidin A' (GA) at temperatures above the gel-to-liquid crystal transition of DPPC. The simulations show that at a lower concentration of GA (i.e., molar ratios of DPPC/GA greater than 3), GA has only a slight effect on the acyl chain dynamics. The rotational diffusion rate around the axis parallel to the long hydrocarbon chain remains unchanged or increases slightly, while the rate around the perpendicular axes decreases slightly. These spectra from DPPC/GA mixtures could only be fit successfully with two or more components consistent with the well-known concept of "boundary lipids," that is, the peptide induces structural inhomogeneity in lipid bilayers. However, the spectra were significantly better fit with additional components that exhibit increased local ordering, implying decreased amplitude of rotational motion, rather than immobilized components with sharply a reduced rotational rate. The largest relative effects occur at the end of the acyl chains, where the average local order parameter St of 16-PC increases from 0.06 for pure lipid to 0.66 for 1:1 DPPC/GA. The inhomogeneity in ordering in DPPC bilayers due to GA decreases with increasing temperature. The hyperfine tensor component Azz increases for 10-PC and 16-PC when GA is incorporated into DPPC bilayers, indicating that water has deeply penetrated into the DPPC bilayers. Simulations of published electron spin resonance spectra of 14-PC in dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine/cytochrome oxidase complexes were also better fit by additional components that were more ordered, rather than immobilized. The average local order parameter in this case is found to increase from 0.11 for pure dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine to 0.61 for a lipid/protein ratio of 50. These spectra and their simulations are similar to the results obtained with 16-PC in the DPPC/GA mixtures. The relevance to studies of lipid-protein interactions for other proteins is briefly discussed.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bienvenue A., Bloom M., Davis J. H., Devaux P. F. Evidence for protein-associated lipids from deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance studies of rhodopsin-dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine recombinants. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3032–3038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casal H. L., McElhaney R. N. Quantitative determination of hydrocarbon chain conformational order in bilayers of saturated phosphatidylcholines of various chain lengths by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5423–5427. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Cornell B. A., Ellasz A. W., Perry A. Interactions of helical polypepetide segments which span the hydrocarbon region of lipid bilayers. Studies of the gramicidin A lipid-water system. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul 5;113(3):517–538. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell B. A., Sacré M. M., Chapman D. The modulation of lipid bilayer fludity by intrinsic polypeptides and proteins. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 1;90(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell B. A., Weir L. E., Separovic F. The effect of gramicidin A on phospholipid bilayers. Eur Biophys J. 1988;16(2):113–119. doi: 10.1007/BF00255521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortijo M., Alonso A., Gomez-Fernandez J. C., Chapman D. Intrinsic protein-lipid interactions. Infrared spectroscopic studies of gramicidin A, bacteriorhodopsin and Ca2+-ATPase in biomembranes and reconstituted systems. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 5;157(4):597–618. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90501-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlquist F. W., Muchmore D. C., Davis J. H., Bloom M. Deuterium magnetic resonance studies of the interaction of lipids with membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5435–5439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaux P. F., Seigneuret M. Specificity of lipid-protein interactions as determined by spectroscopic techniques. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 12;822(1):63–125. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser A. F., Lanyi J. K. Structure of the lipid phase in cell envelope vesicles from Halobacterium cutirubrum. Biochemistry. 1973 May 8;12(10):1933–1939. doi: 10.1021/bi00734a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. H., Dehlinger P. J., Van S. P. Shape of the hydrophobic barrier of phospholipid bilayers (evidence for water penetration in biological membranes). J Membr Biol. 1974;15(2):159–192. doi: 10.1007/BF01870086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Houslay M. D., McGill K. A., Birdsall N. J., Metcalfe J. C., Warren G. B. Annular lipids determine the ATPase activity of a calcium transport protein complexed with dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 21;15(19):4145–4151. doi: 10.1021/bi00664a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho C., Stubbs C. D. Hydration at the membrane protein-lipid interface. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):897–902. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81671-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P. C., Griffith O. H., Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. Evidence for boundary lipid in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):480–484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang S. Y., Gutowsky H. S., Hsung J. C., Jacobs R., King T. E., Rice D., Oldfield E. Nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of the cytochrome oxidase--phospholipid interaction: a new model for boundary lipid. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3257–3267. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kar L., Ney-Igner E., Freed J. H. Electron spin resonance and electron-spin-echo study of oriented multilayers of L alpha-dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine water systems. Biophys J. 1985 Oct;48(4):569–595. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83814-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killian J. A. Gramicidin and gramicidin-lipid interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 11;1113(3-4):391–425. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(92)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Kawato S., Ikegami A., Yoshida S., Orii Y. The effect of cytochrome oxidase on lipid chain dynamics. A nanosecond fluorescence depolarization study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 21;647(1):7–17. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles P. F., Watts A., Marsh D. Spin-label studies of lipid immobilization in dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine-substituted cytochrome oxidase. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4480–4487. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Durrani A. A., Chapman D. A difference infrared spectroscopic study of gramicidin A, alamethicin and bacteriorhodopsin in perdeuterated dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 11;769(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longmuir K. J., Capaldi R. A., Dahlquist F. W. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of lipid-protein interactions. A model of the dynamics and energetics of phosphatidylcholine bilayers that contain cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5746–5755. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn R., Davies M. A., Brauner J. W., Schuster H. F., Dluhy R. A. Quantitative determination of conformational disorder in the acyl chains of phospholipid bilayers by infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 31;28(22):8934–8939. doi: 10.1021/bi00448a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn R., Dluhy R., Taraschi T., Cameron D. G., Mantsch H. H. Raman and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic studies of the interaction between glycophorin and dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 10;20(23):6699–6706. doi: 10.1021/bi00526a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owicki J. C., McConnell H. M. Theory of protein-lipid and protein-protein interactions in bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4750–4754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owicki J. C., Springgate M. W., McConnell H. M. Theoretical study of protein--lipid interactions in bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1616–1619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddy M. R., Dahlquist F. W., Davis J. H., Bloom M. Dynamical and temperature-dependent effects of lipid-protein interactions. Application of deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy to the same reconstitutions of cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3152–3162. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen N. O., Chan S. I. More on the motional state of lipid bilayer membranes: interpretation of order parameters obtained from nuclear magnetic resonance experiments. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2657–2667. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajan S., Kang S. Y., Gutowsky H. S., Oldfield E. Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance study of membrane structure. Interactions of lipids with protein, polypeptide, and cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1160–1166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice D., Oldfield E. Deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the interaction between dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine and gramicidin A'. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3272–3279. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. The dynamic structure of fatty acyl chains in a phospholipid bilayer measured by deuterium magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4839–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Seelig A. Lipid conformation in model membranes and biological membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 Feb;13(1):19–61. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin Y. K., Freed J. H. Thermodynamics of phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol mixed model membranes in the liquid crystalline state studied by the orientational order parameter. Biophys J. 1989 Dec;56(6):1093–1100. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82757-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short K. W., Wallace B. A., Myers R. A., Fodor S. P., Dunker A. K. Comparison of lipid/gramicidin dispersions and cocrystals by Raman scattering. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 27;26(2):557–562. doi: 10.1021/bi00376a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. A molecular theory of ion-conductng channels: a field-dependent transition between conducting and nonconducting conformations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1610–1614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed pi(L,D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts A., Volotovski I. D., Marsh D. Rhodopsin-lipid associations in bovine rod outer segment membranes. Identification of immobilized lipid by spin-labels. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):5006–5013. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. W., Scotto A. W., Stubbs C. D. Effect of proteins on fluorophore lifetime heterogeneity in lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3248–3255. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. W., Stubbs C. D. Properties influencing fluorophore lifetime distributions in lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):7994–7999. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfs J. A., Horváth L. I., Marsh D., Watts A., Hemminga M. A. Spin-label ESR of bacteriophage M13 coat protein in mixed lipid bilayers. Characterization of molecular selectivity of charged phospholipids for the bacteriophage M13 coat protein in lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 26;28(26):9995–10001. doi: 10.1021/bi00452a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


