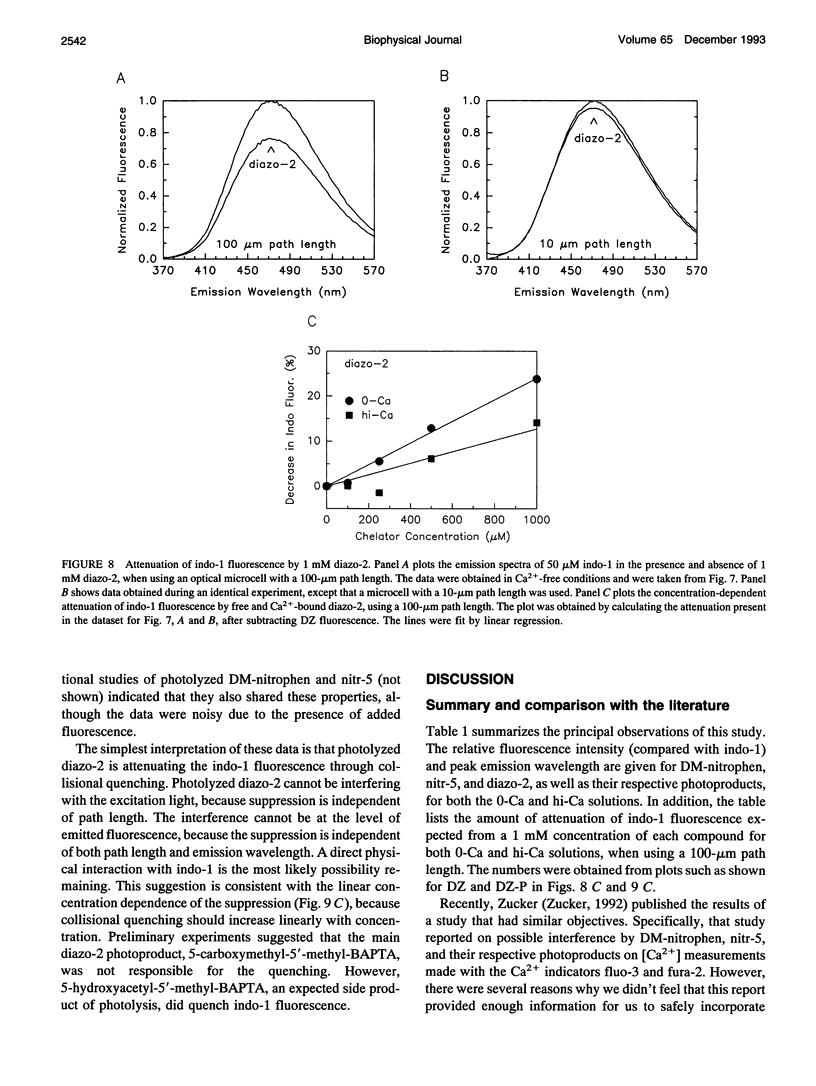
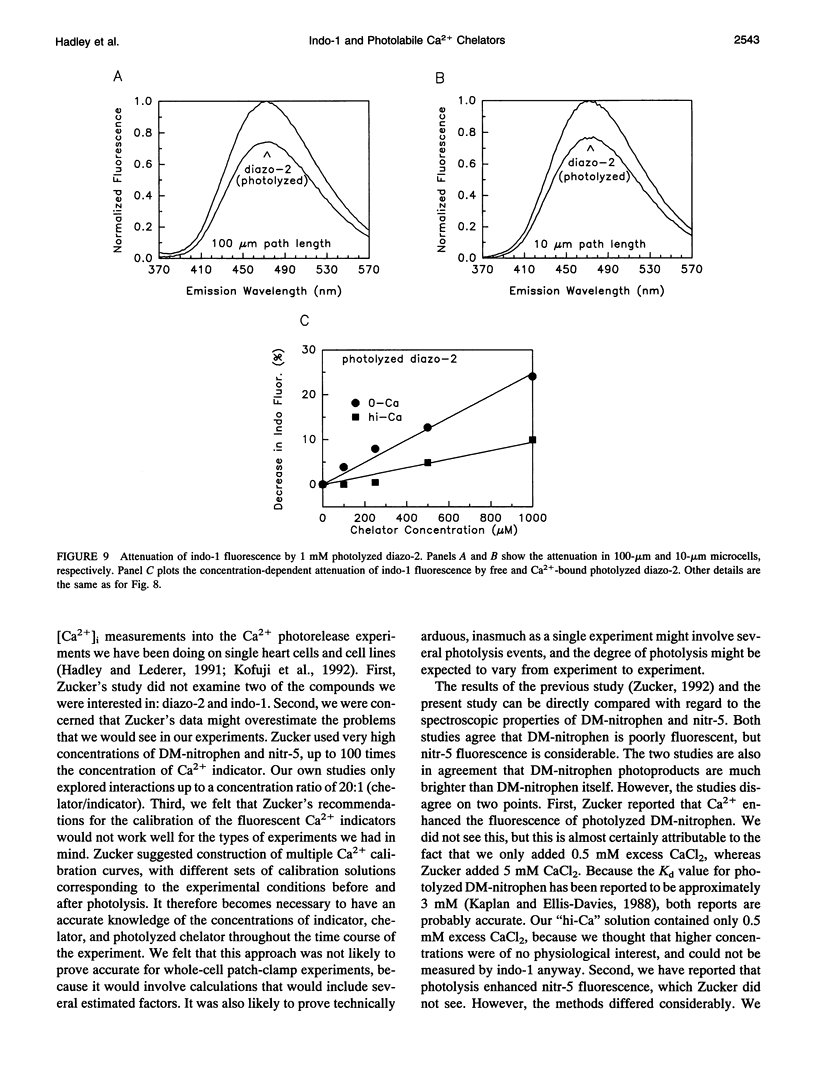
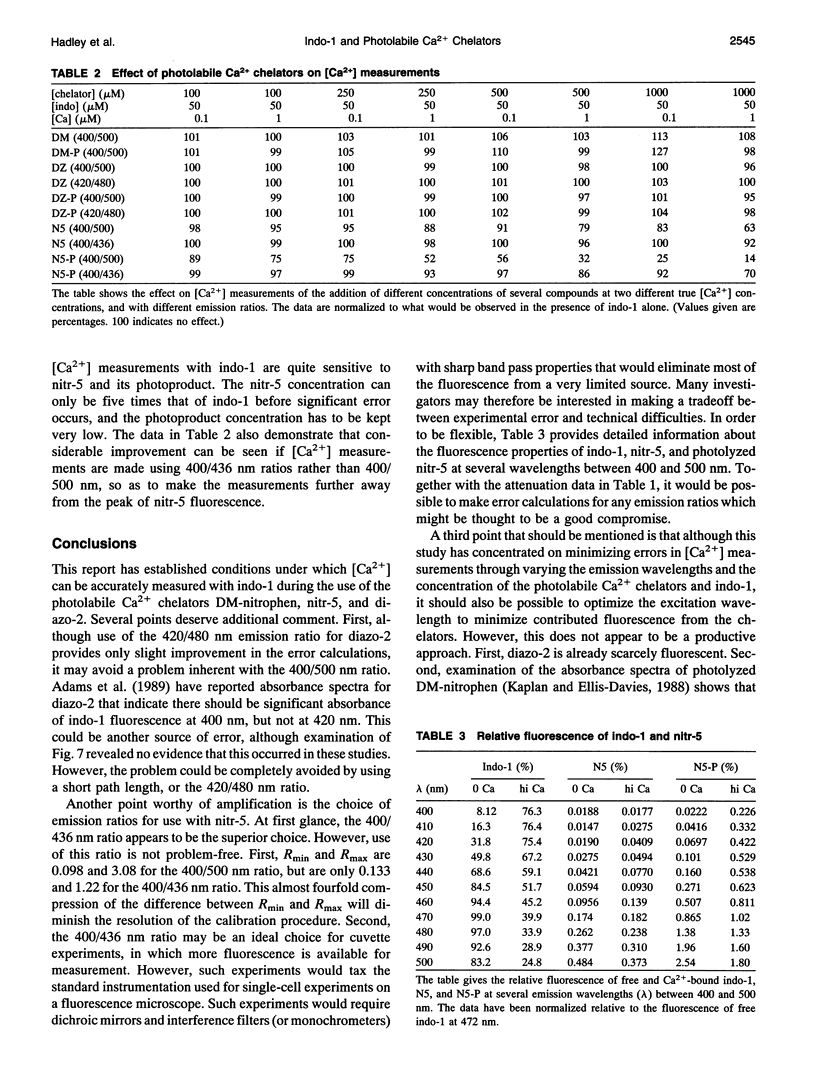
Abstract
Emission spectra of the photolabile Ca2+ chelators DM-nitrophen, nitr-5, and diazo-2 were studied alone, and in the presence of indo-1, to investigate potential interactions that would make the simultaneous manipulation and ratiometric measurement of the intracellular Ca2+ concentration difficult. Neither diazo-2 nor its photoproduct were found to be significantly fluorescent, and consequently concentrations of diazo-2 up to 20 times that of indo-1 did not distort the emission spectra of indo-1. DM-nitrophen was scarcely fluorescent, but its fluorescence did increase upon photolysis. In contrast to diazo-2 and DM-nitrophen, nitr-5 itself was found to be quite fluorescent, and this fluorescence was significantly increased upon photolysis. Thus, combined use of nitr-5 and indo-1 poses the most difficulty. The emission spectra of all the investigated compounds were used to define experimental conditions and calibration procedures that make possible simultaneous measurement and manipulation of the intracellular Ca2+ concentration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baylor S. M., Hollingworth S. Fura-2 calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:151–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaney K. R., Zucker R. S. Calcium released by photolysis of DM-nitrophen stimulates transmitter release at squid giant synapse. J Physiol. 1990 Jul;426:473–498. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney A. M., Charnet P., Pye J. M., Nargeot J. Augmentation of cardiac calcium current by flash photolysis of intracellular caged-Ca2+ molecules. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):65–68. doi: 10.1038/341065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadley R. W., Lederer W. J. Ca2+ and voltage inactivate Ca2+ channels in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes through independent mechanisms. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:257–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hove-Madsen L., Bers D. M. Indo-1 binding to protein in permeabilized ventricular myocytes alters its spectral and Ca binding properties. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81597-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. P., Harootunian A. T., Tsien R. Y. Photochemically generated cytosolic calcium pulses and their detection by fluo-3. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8179–8184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. H., Ellis-Davies G. C. Photolabile chelators for the rapid photorelease of divalent cations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6571–6575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofuji P., Hadley R. W., Kieval R. S., Lederer W. J., Schulze D. H. Expression of the Na-Ca exchanger in diverse tissues: a study using the cloned human cardiac Na-Ca exchanger. Am J Physiol. 1992 Dec;263(6 Pt 1):C1241–C1249. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.6.C1241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Lancaster B., Zucker R. S. Temporal limits on the rise in postsynaptic calcium required for the induction of long-term potentiation. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrion N. V., Zucker R. S., Marsh S. J., Adams P. R. Modulation of M-current by intracellular Ca2+. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):533–545. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morad M., Davies N. W., Kaplan J. H., Lux H. D. Inactivation and block of calcium channels by photo-released Ca2+ in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.2457253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli E., Lederer W. J. Molecular operations of the sodium-calcium exchanger revealed by conformation currents. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):621–624. doi: 10.1038/349621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli E., Lederer W. J. Voltage-independent calcium release in heart muscle. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):565–568. doi: 10.1126/science.2173135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdeolmillos M., O'Neill S. C., Smith G. L., Eisner D. A. Calcium-induced calcium release activates contraction in intact cardiac cells. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Apr;413(6):676–678. doi: 10.1007/BF00581820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Effects of photolabile calcium chelators on fluorescent calcium indicators. Cell Calcium. 1992 Jan;13(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(92)90027-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S., Haydon P. G. Membrane potential has no direct role in evoking neurotransmitter release. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):360–362. doi: 10.1038/335360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


