Abstract
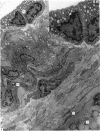
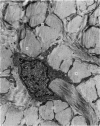
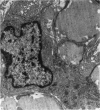
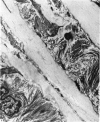
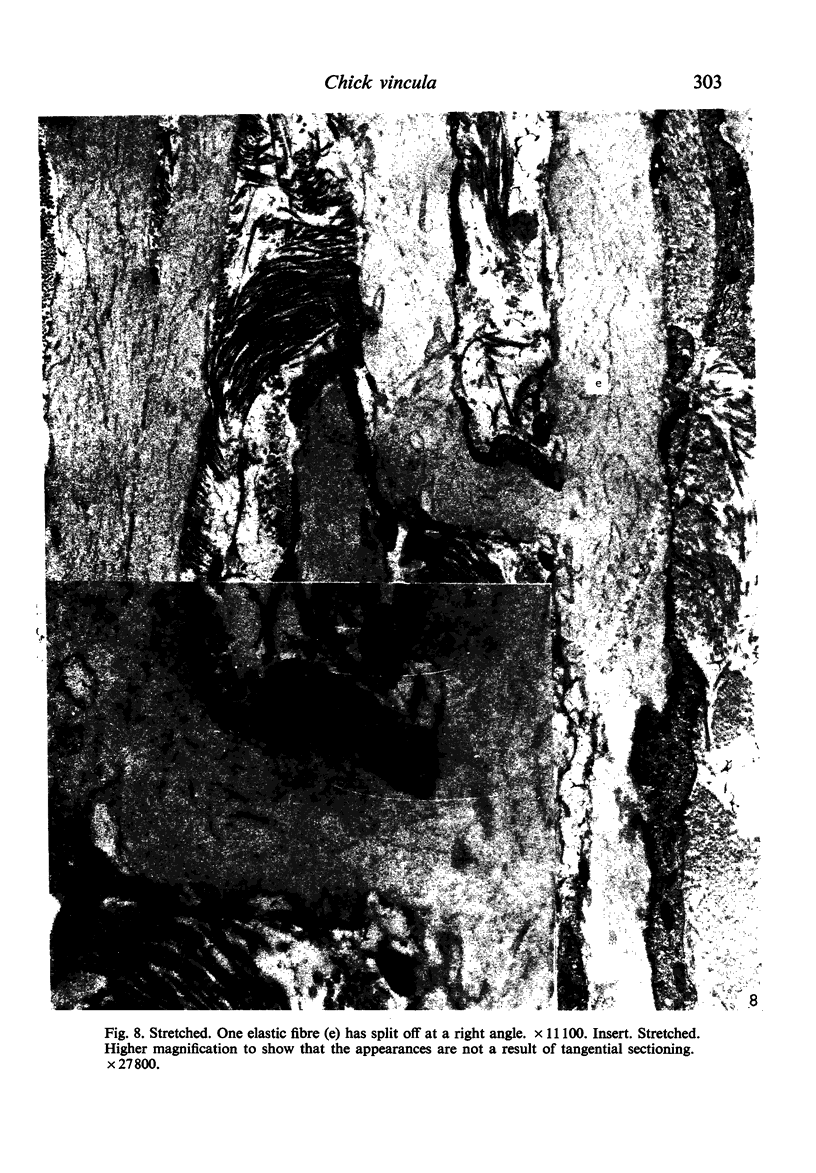
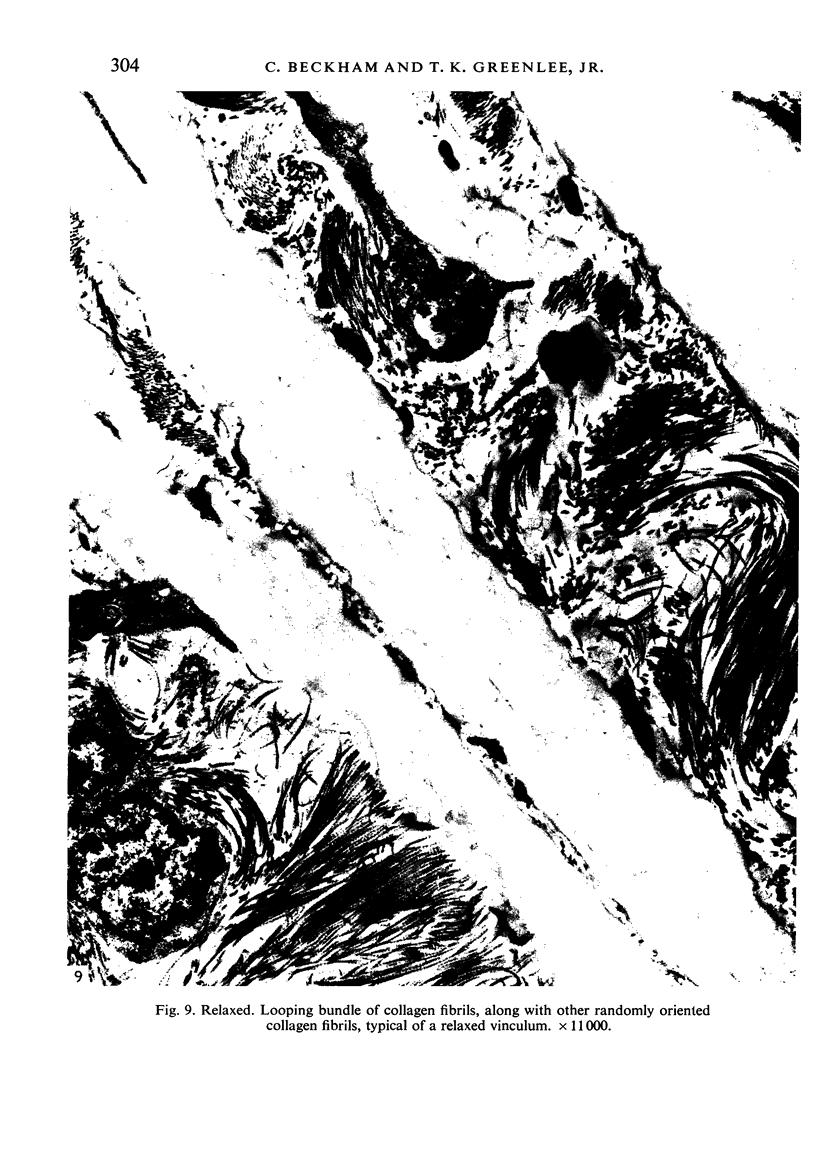
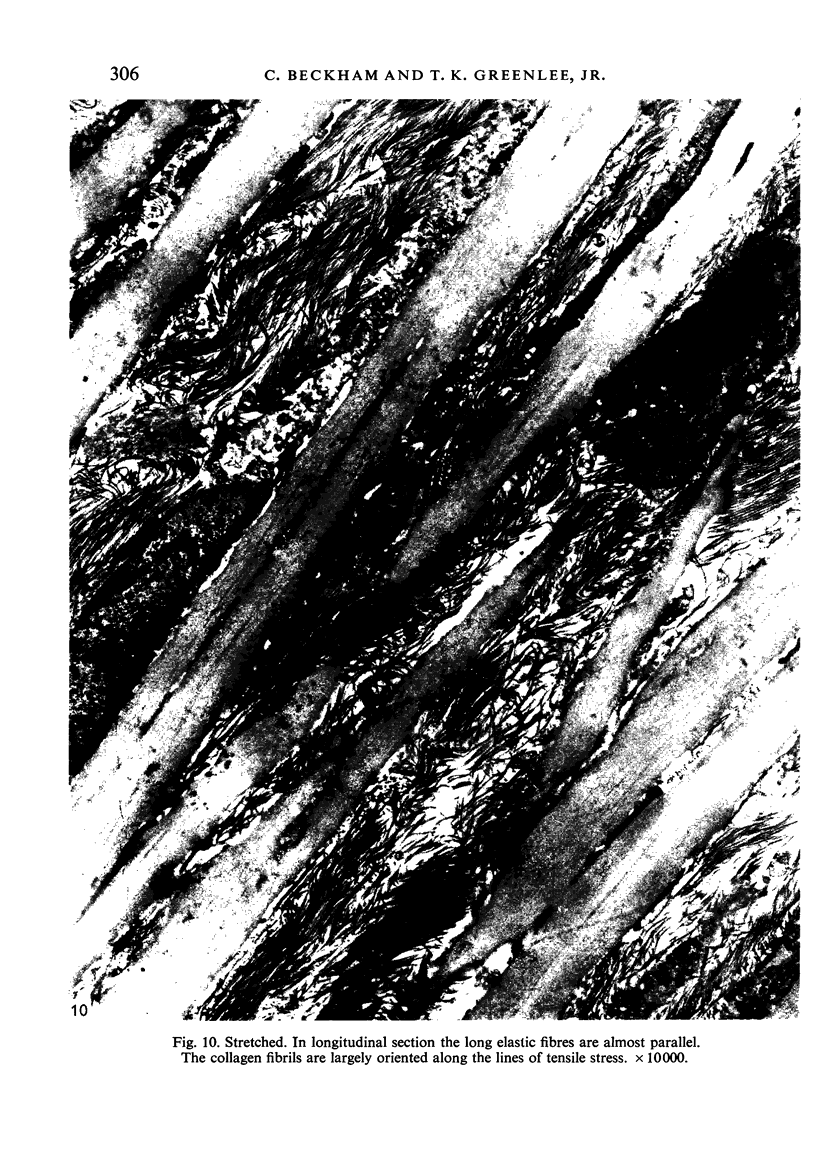
From their mode of attachment and their elastic composition, it is clear that the vincula of the chick serve other functions besides that of carrying blood vessels to the digital flexor tendons within their synovial sheaths. Evidence is presented in support of the argument that elastic fibres bear the brunt of rapidly applied tensile forces and that the interweaving collagen fibres only become taut when the vincula are stretched to the limit and about to tear. Our hypothesis is that the collagen serves as a check-rein mechanism in an otherwise elastic structure.
Full text
PDF
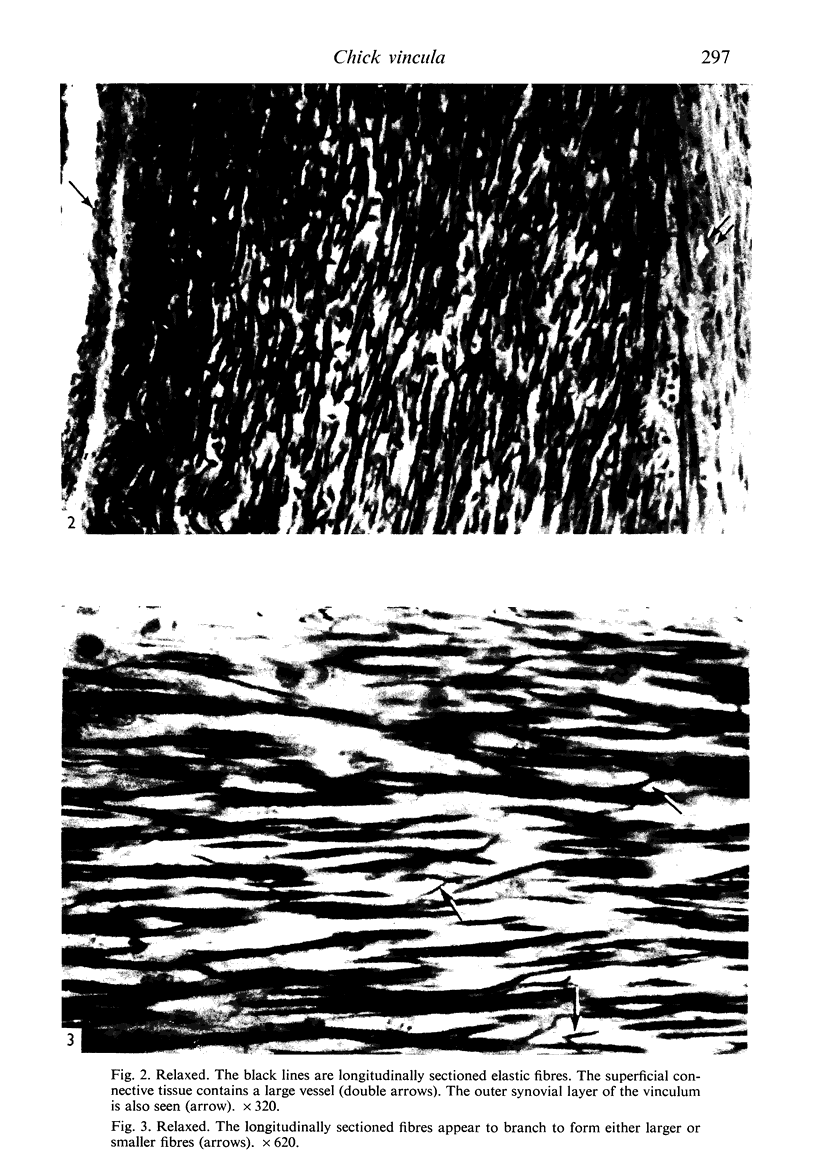
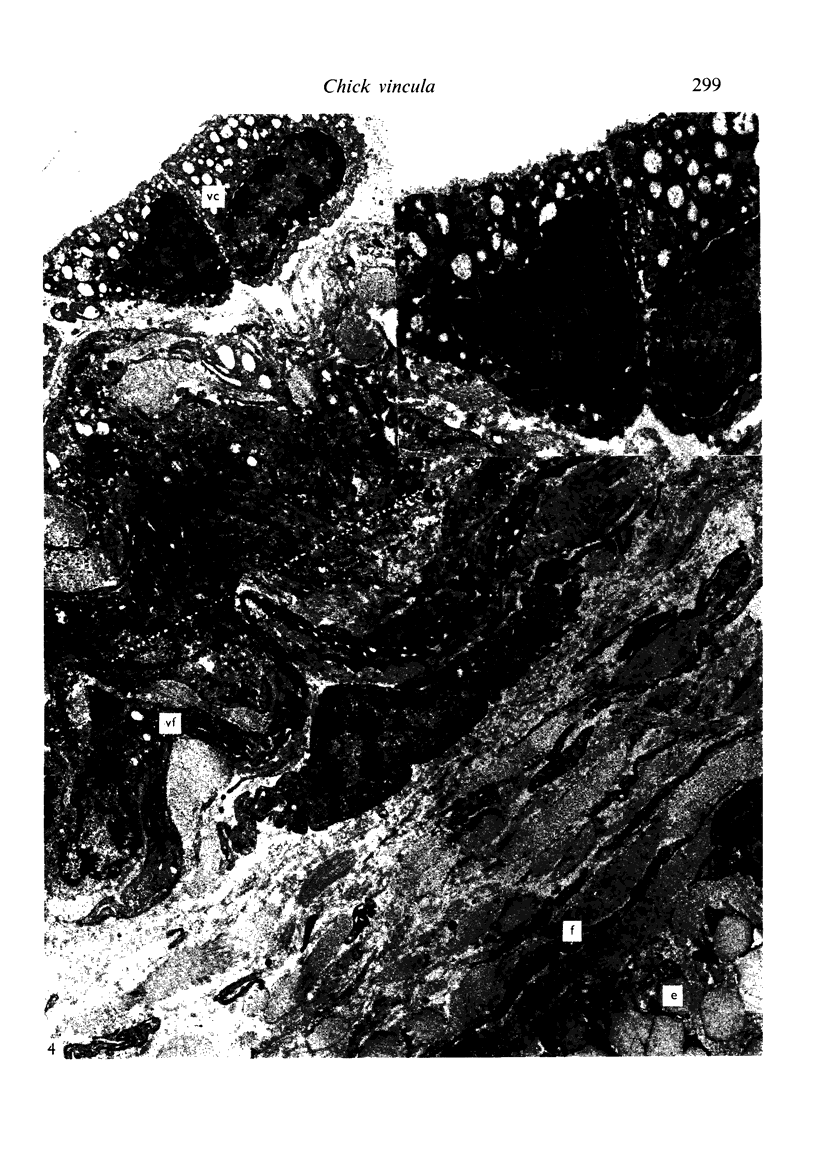
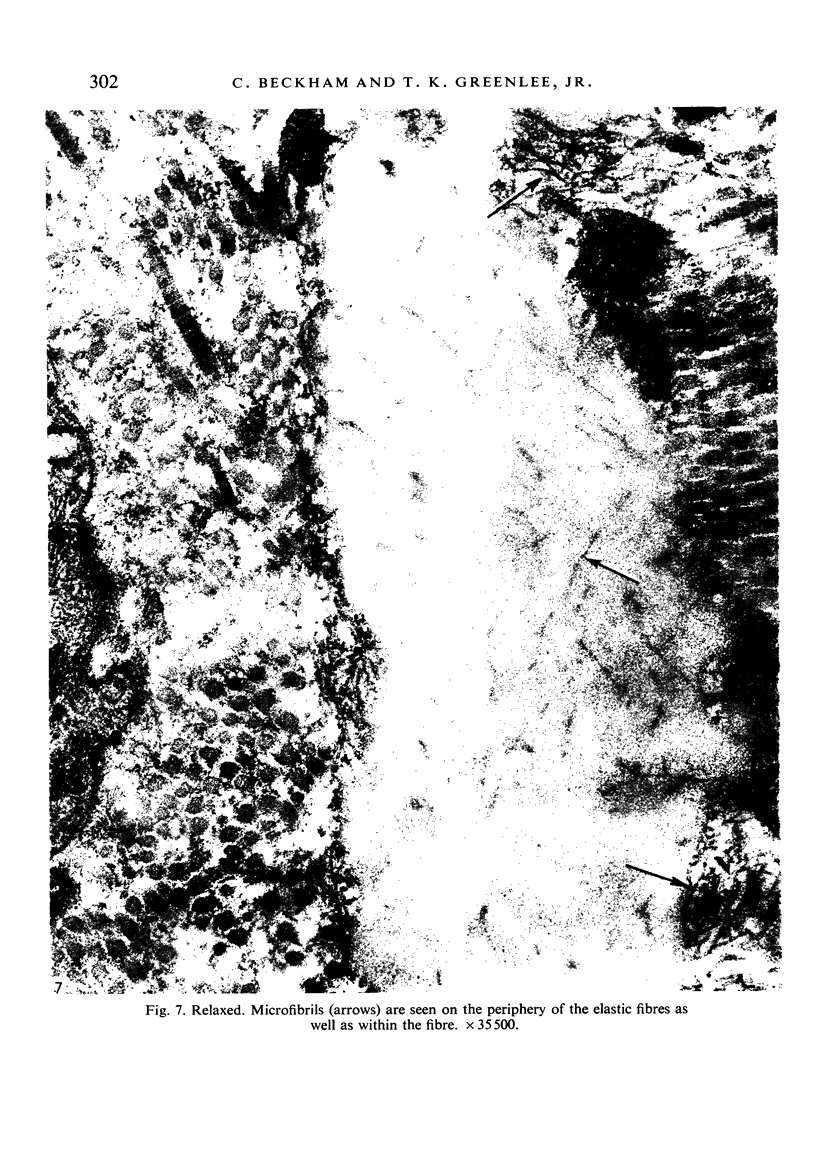
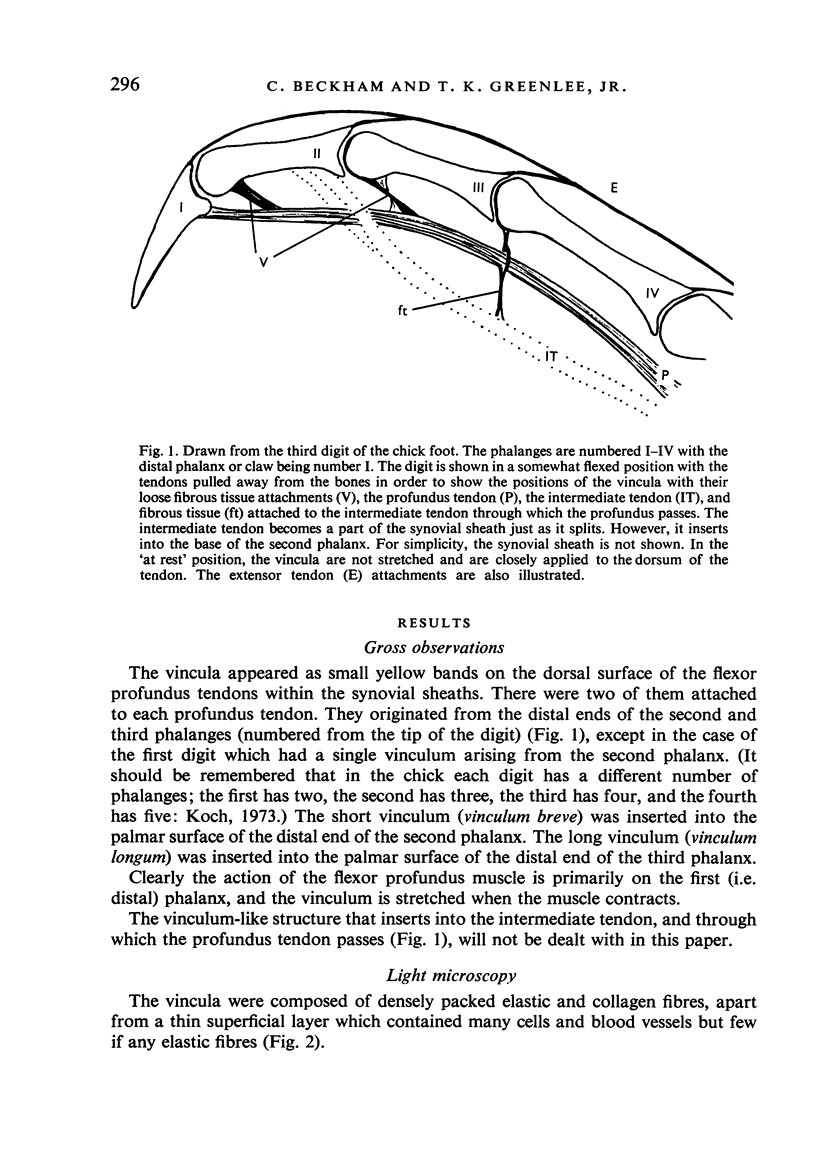



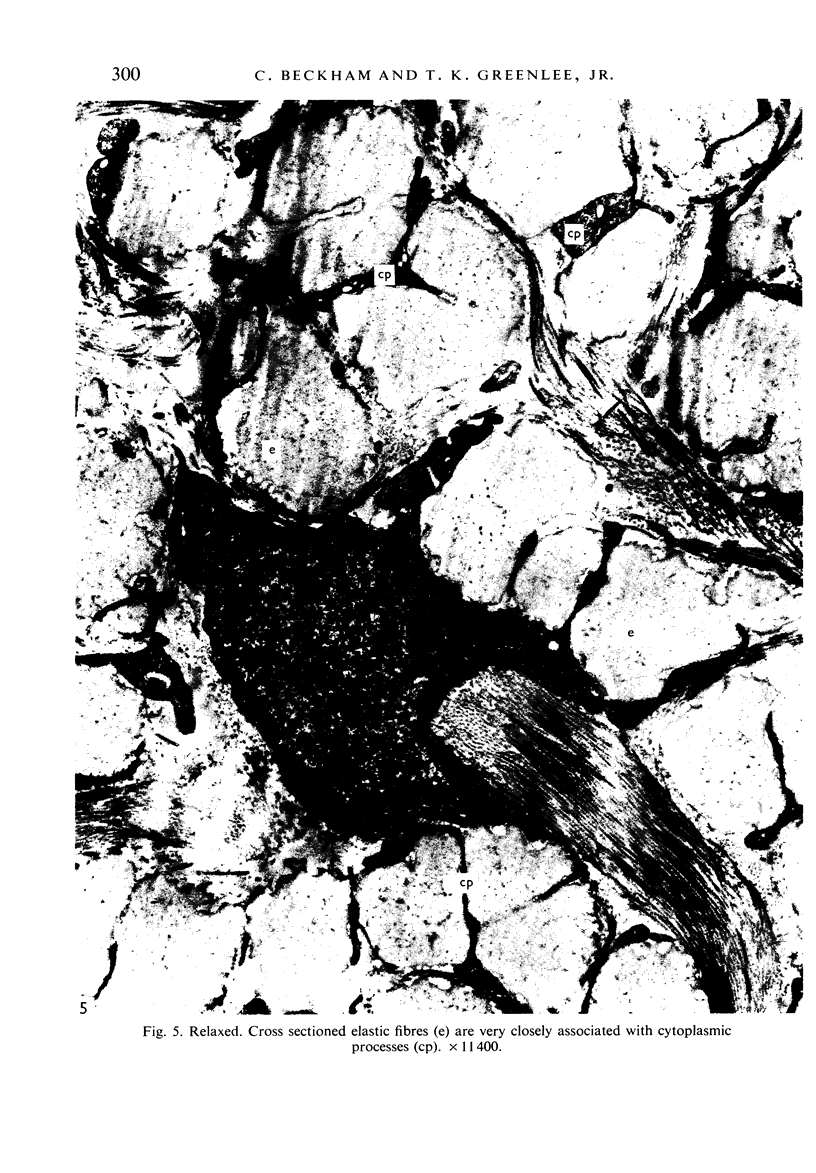








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert E. N. Developing elastic tissue. An electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1972 Oct;69(1):89–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT H. S., LUFT J. H. zeta-Collidine as a basis for buffering fixatives. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Aug;6(1):113–114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.6.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKIS J. G. The blood supply of the flexor and extensor tendons of the fingers in man. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1953 Feb;35-B(1):131–138. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.35B1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. M. The vascular anatomy within normal tendons, divided tendons, free tendon grafts and pedicle tendon grafts in rabbits. A microradioangiographic study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1973 May;55(2):369–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. A. The blood supply and lymphatic drainage of tendons. J Anat. 1946 Jul;80(Pt 3):147–152.2. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee T. K., Jr, Ross R., Hartman J. L. The fine structure of elastic fibers. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jul;30(1):59–71. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haust M. D., More R. H., Bencosme S. A., Balis J. U. Elastogenesis in human aorta: an electron microscopic study. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Oct;4(5):508–524. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman A. S., Park J. B., Abrahamson J. Sequential enzymolysis of ligament and resultant stress-strain behavior. Biomater Med Devices Artif Organs. 1973;1(3):453–467. doi: 10.3109/10731197309118556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLONIG G. A modified procedure for lead staining of thin sections. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:736–739. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., JARETT L., FINKE E. H. Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1960 Nov;35:313–323. doi: 10.3109/10520296009114754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdan C. E. Half a century of flexor-tendon surgery. Current status and changing philosophies. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972 Apr;54(3):472–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]