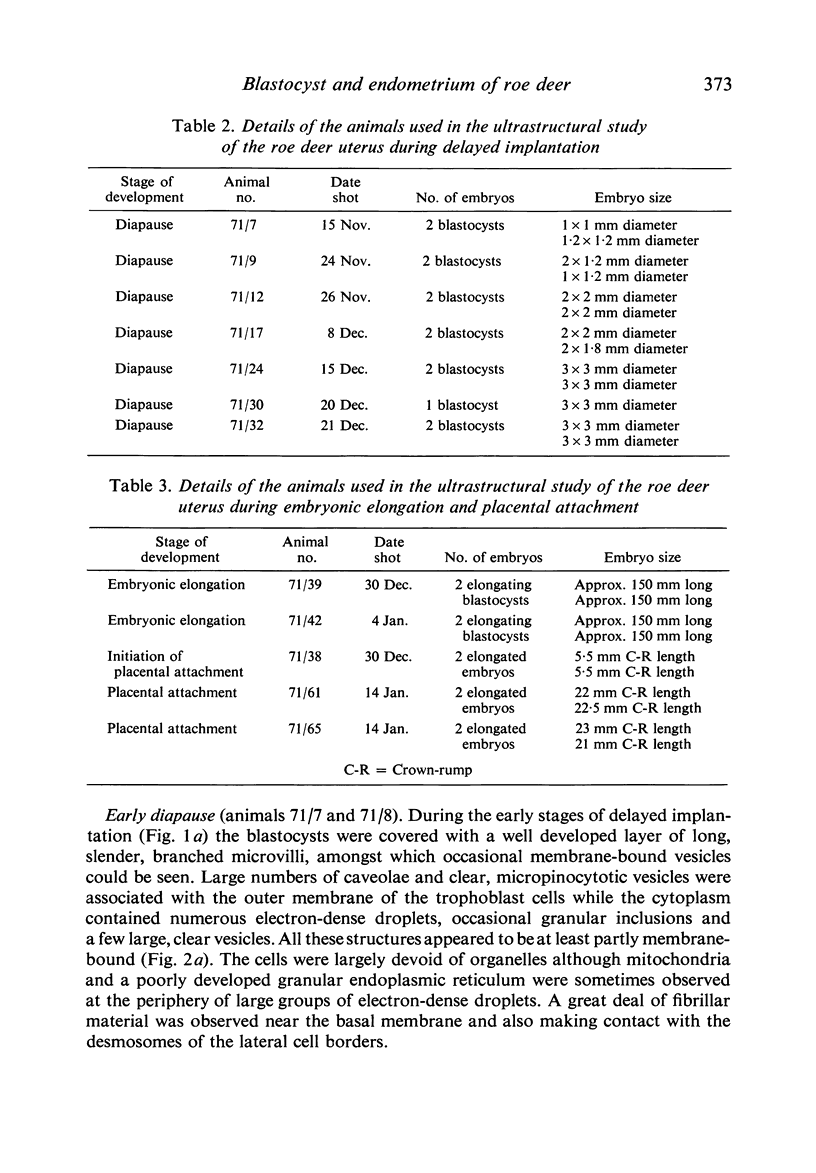
Abstract
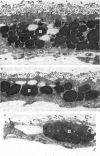
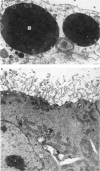
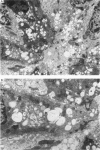
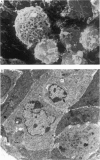
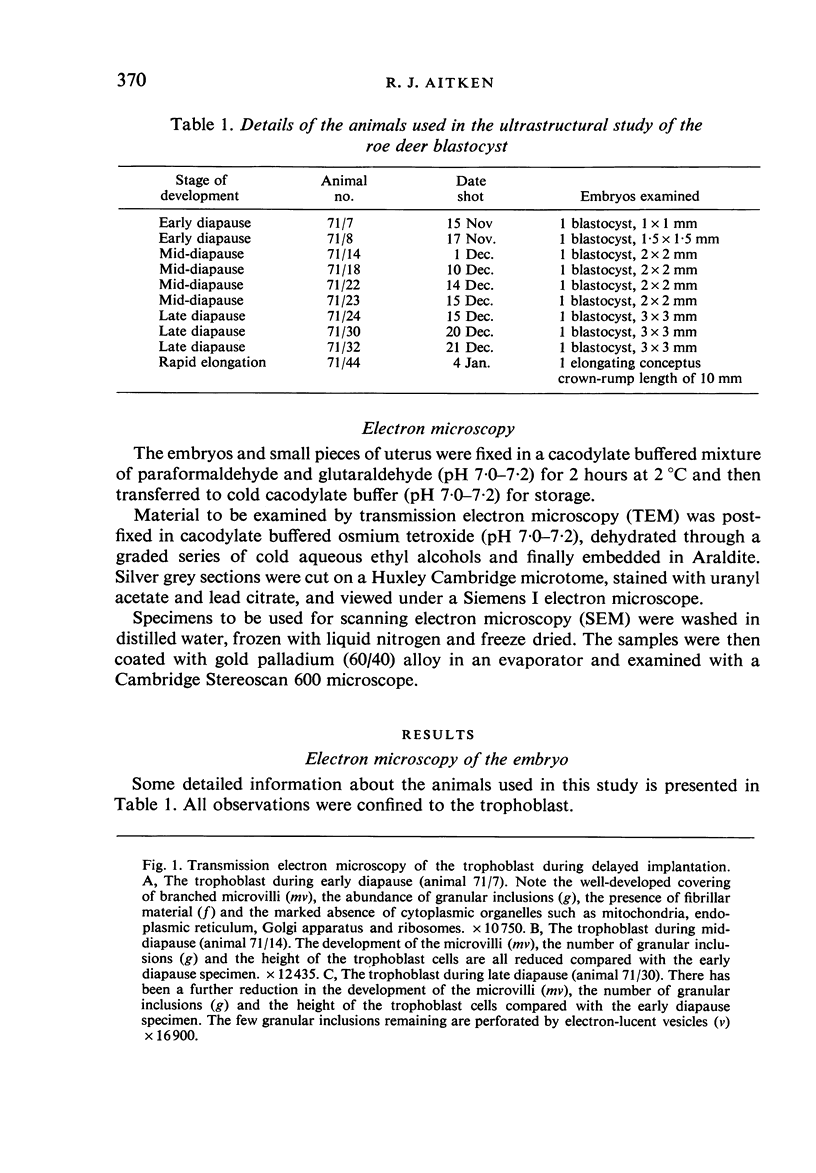
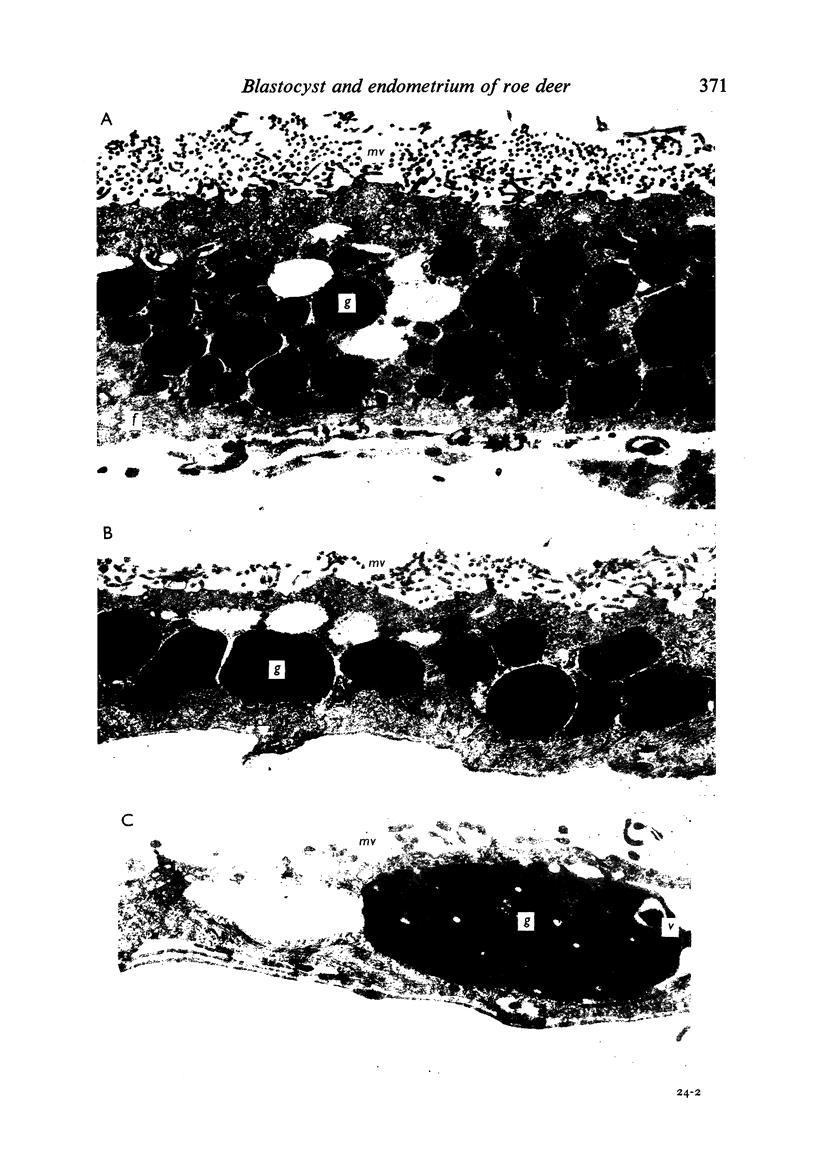
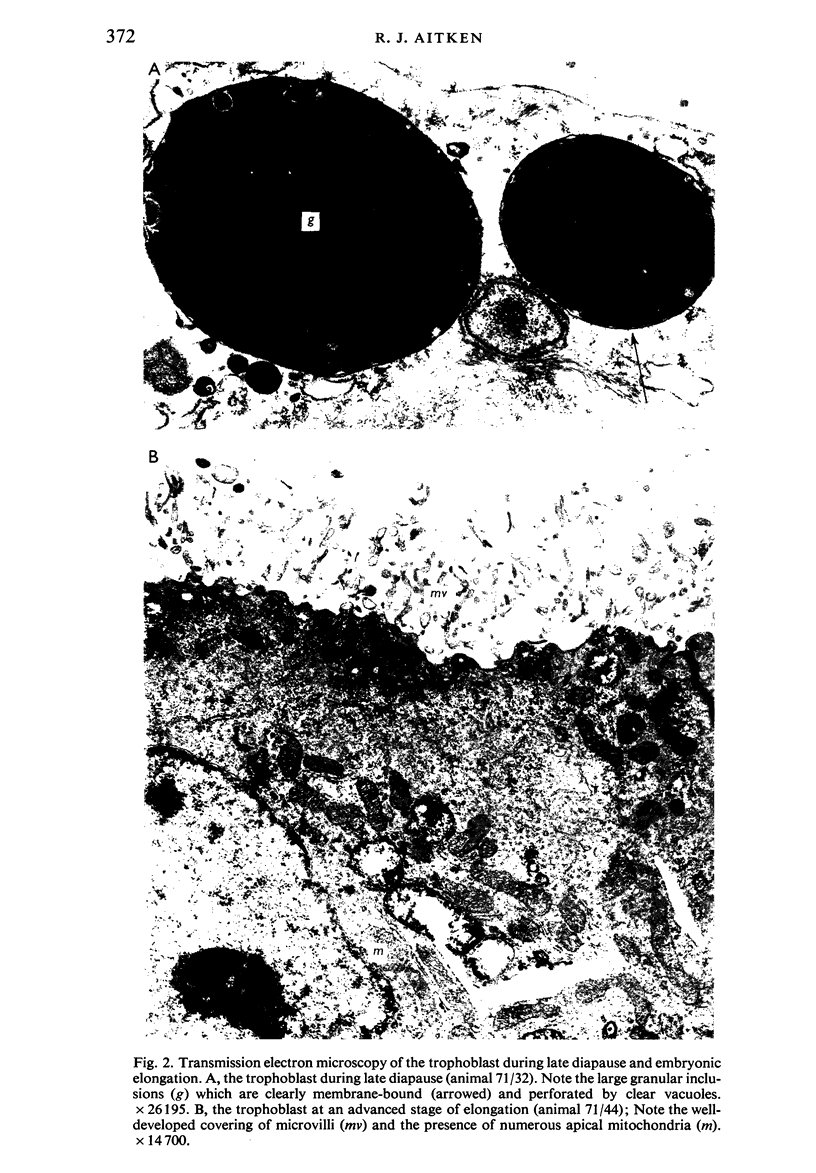
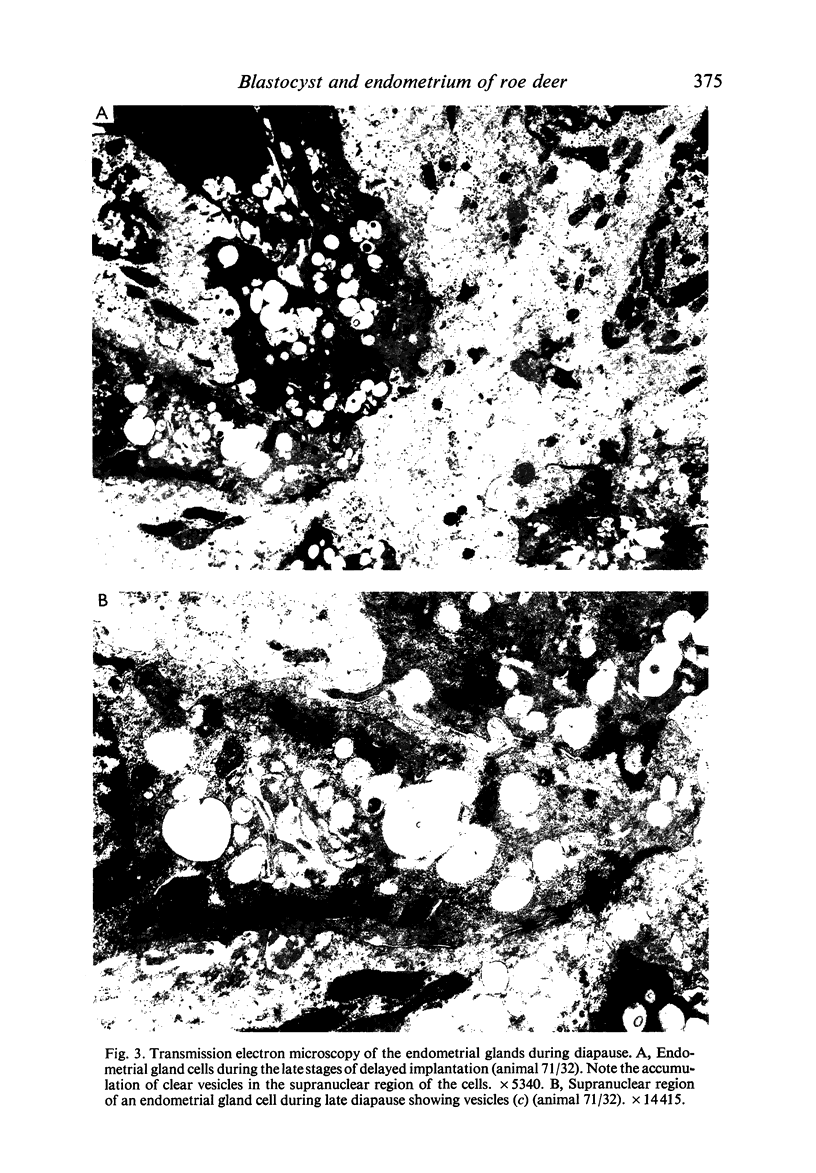
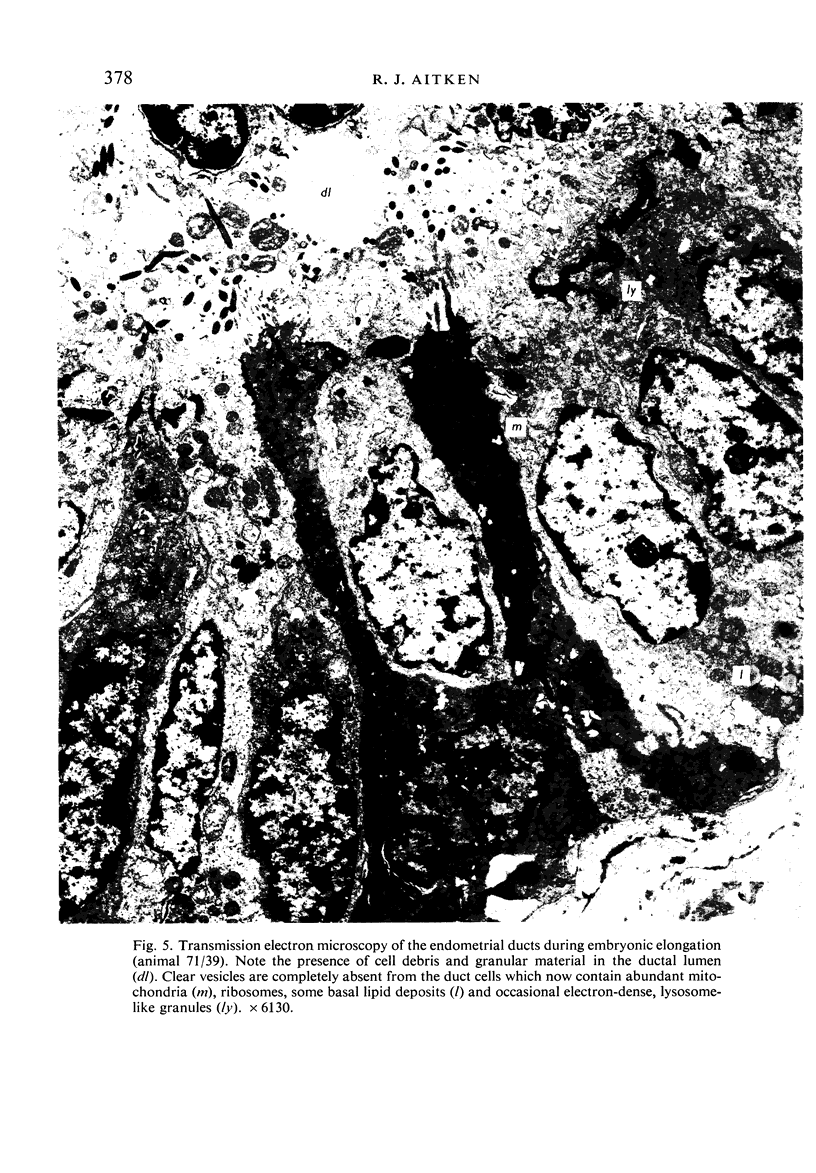
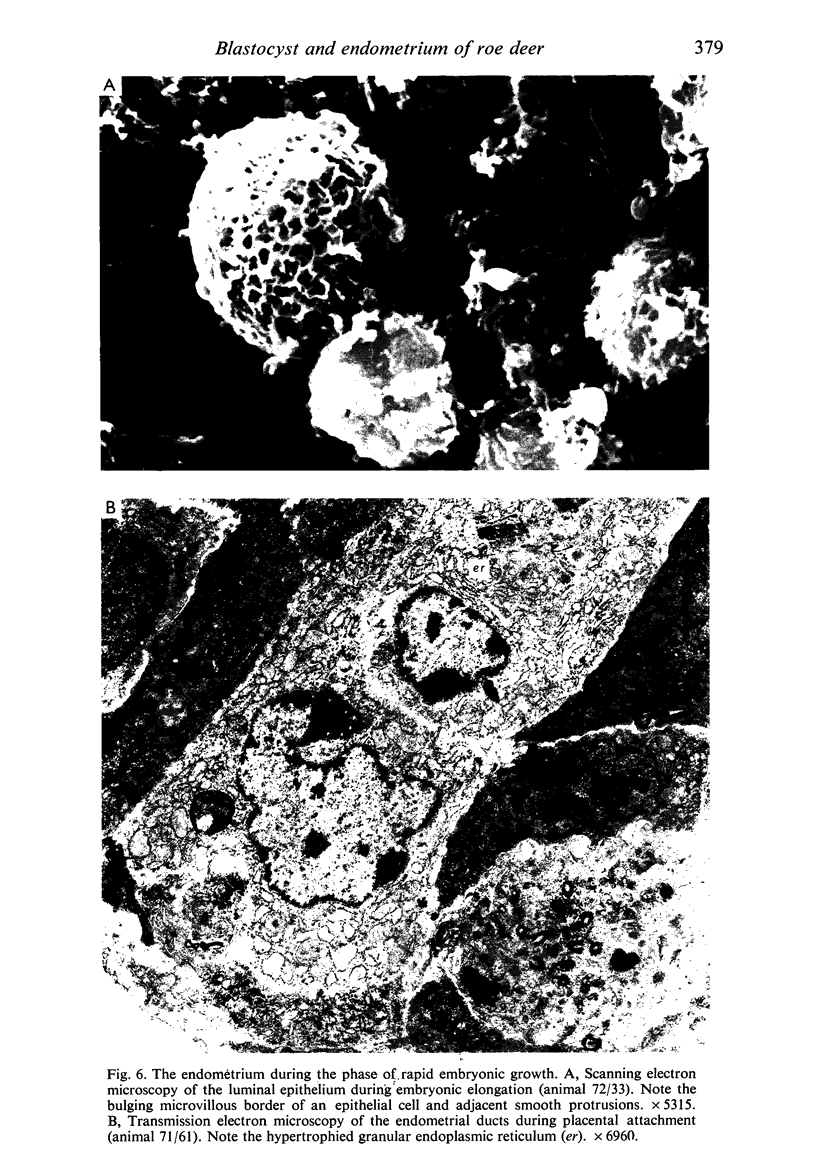
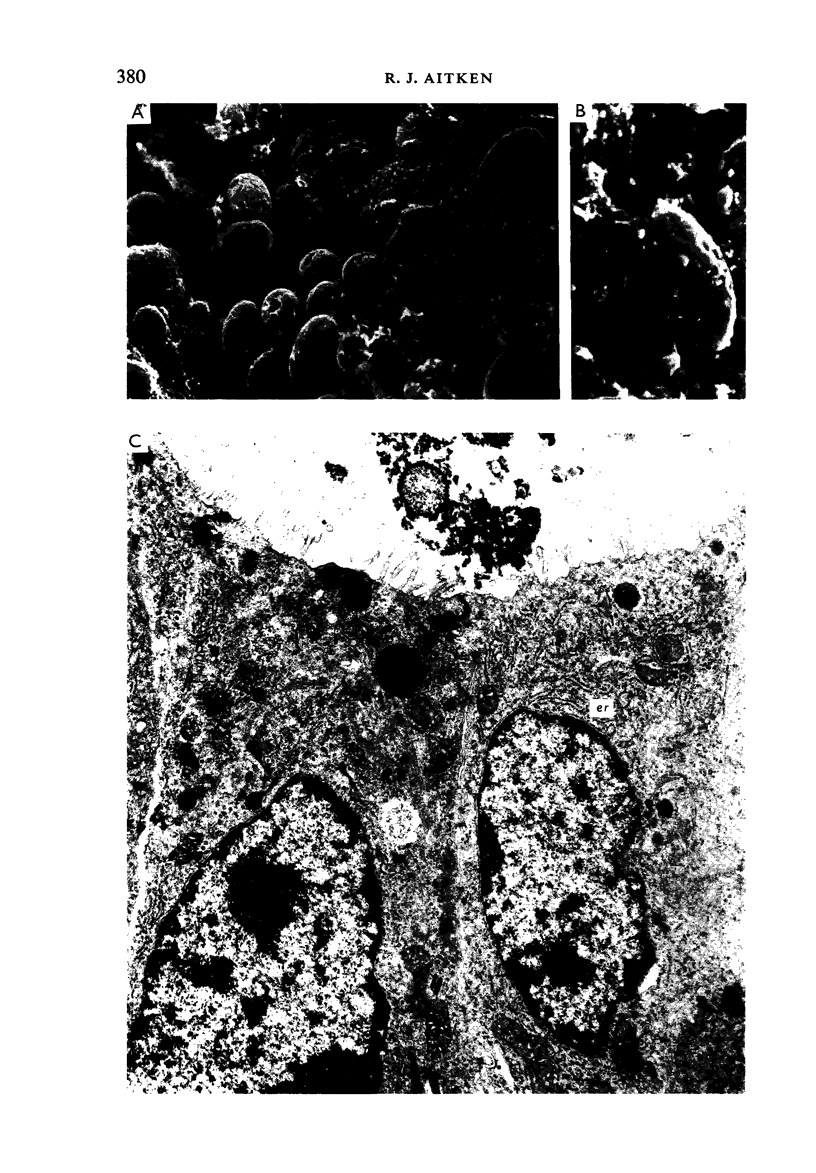
Transmission electron microscopy of the trophoblast cells during diapause revealed an abundance of electron-dense, membrane-bound granular inclusions and a marked lack of cytoplasmic organelles. The cells also possessed a well-developed covering of branched microvilli, numerous caveolae, micropinocytotic vesicles and a lamina of fine fibrillae. The progressive enlargement of the blastocyst during diapause was correlated with a decline in the height of the trophoblast cells and a reduction in the density of microvilli and caveolae associated with the outer membrane. The granular inclusions also declined in number and electron density during the delay phase, suggesting the progressive utilisation of energy reserves. Embryonic elongation was associated with the disappearance of the granular inclusions, a reduction in the amount of fibrillar material and a dramatic increase in the development of cytoplasmic organelles. During diapause, clear vesicles, apparently derived from the Golgi apparatus, gradually accumulated in the supranuclear region of each gland and non-ciliated duct cell. Embryonic elongation was associated with the sudden release of these vesicles into the glandular lumen and thence into the uterine lumen. Numerous apical protrusions were also observed projecting from the luminal and ductal epithelia at this time, suggesting the formation of an apocrine secretion. Another type of secretion was produced during the early stages of placental attachment by the hypertrophied granular endoplasmic reticulum of the ductal epithelium.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken R. J., Burton J., Hawkins J., Kerr-Wilson R., Short R. V., Steven D. H. Histological and ultrastructural changes in the blastocyst and reproductive tract of the roe deer, Capreolus capreolus, during delayed implantation. J Reprod Fertil. 1973 Sep;34(3):481–493. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0340481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken R. J. Calcium and zinc in the endometrium and uterine flushings of the roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) during delayed implantation. J Reprod Fertil. 1974 Oct;40(2):333–340. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0400333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken R. J. Delayed implantation in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus). J Reprod Fertil. 1974 Jul;39(1):225–233. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0390225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Nilsson O. Various types of embryo-endometrial contacts during delay of implantation in the mouse. J Reprod Fertil. 1973 Mar;32(3):531–533. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0320531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMPSEY E. W., WISLOCKI G. B., AMOROSO E. C. Electron microscopy of the pig's placenta, with especial reference to the cell membranes of the endometrium and chorion. Am J Anat. 1955 Jan;96(1):65–101. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000960104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENDERS A. C., ENDERS R. K., SCHLAFKE S. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE GLAND CELLS OF THE MINK ENDOMETRIUM. J Cell Biol. 1963 Aug;18:405–418. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyes A. D. The endometrial glands of the pregnant sheep: an ultrastructural study. J Anat. 1972 Jan;111(Pt 1):55–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]