Abstract
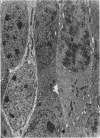
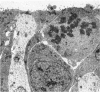
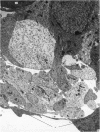
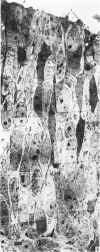
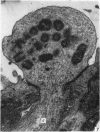
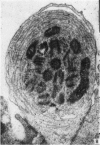
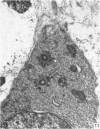
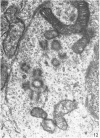
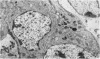
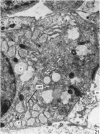
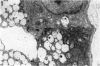
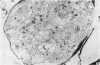
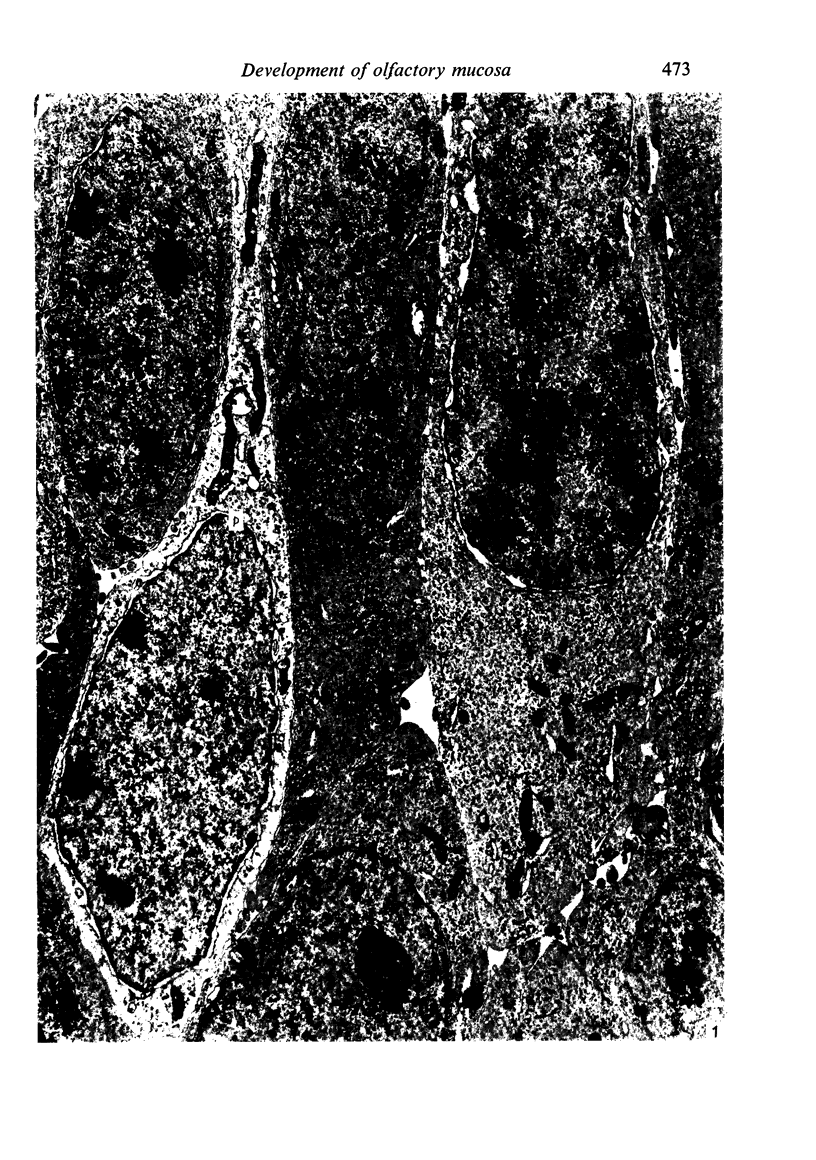
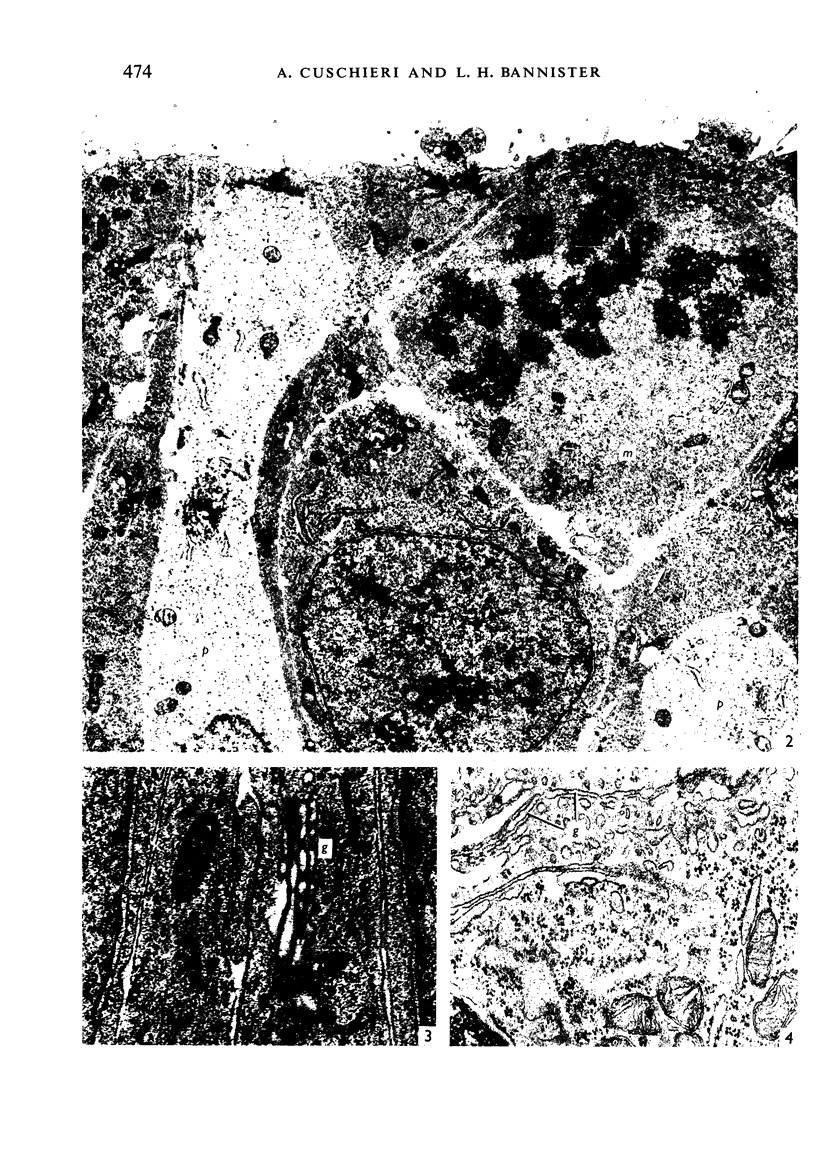
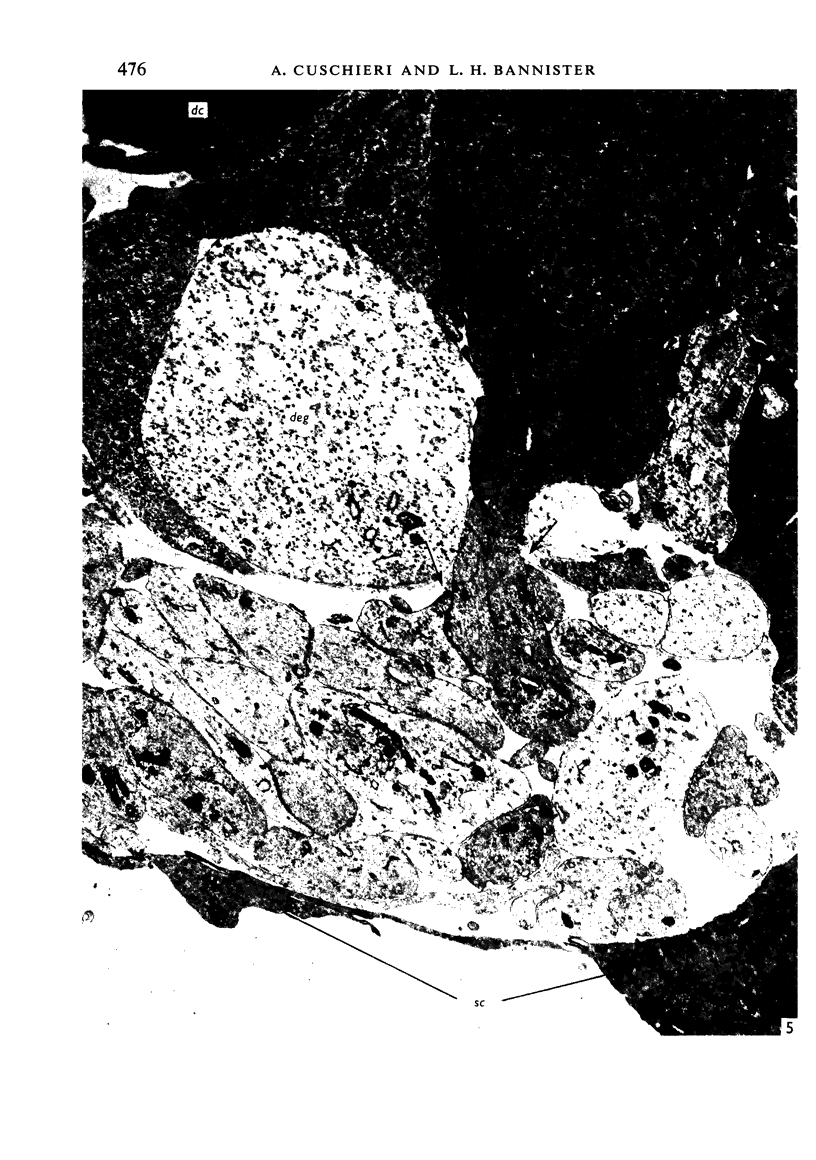
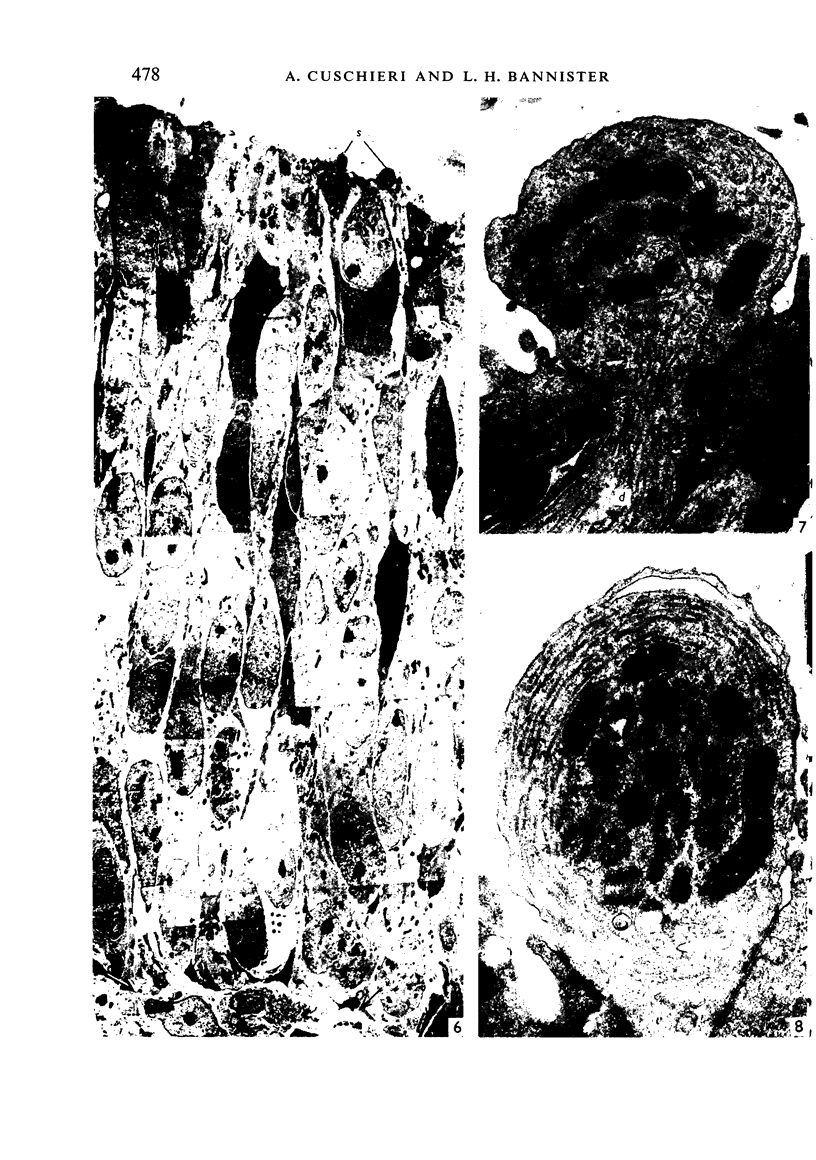
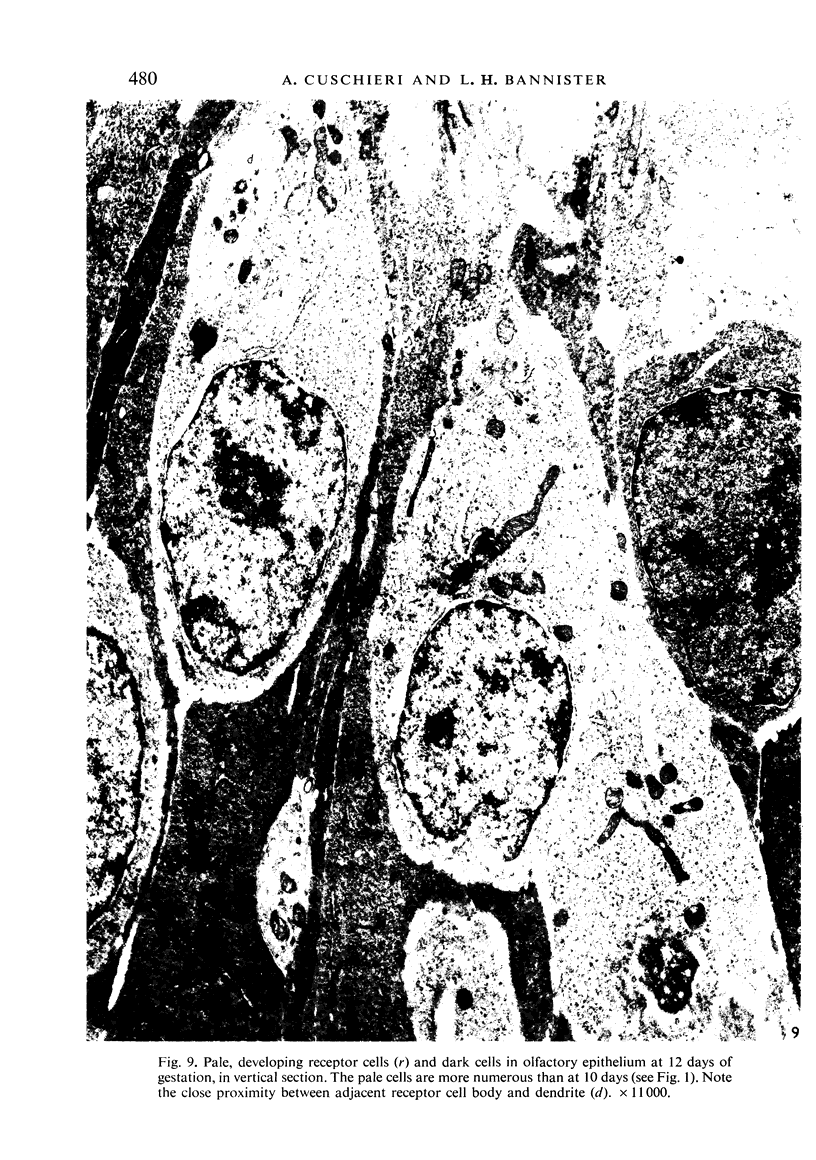
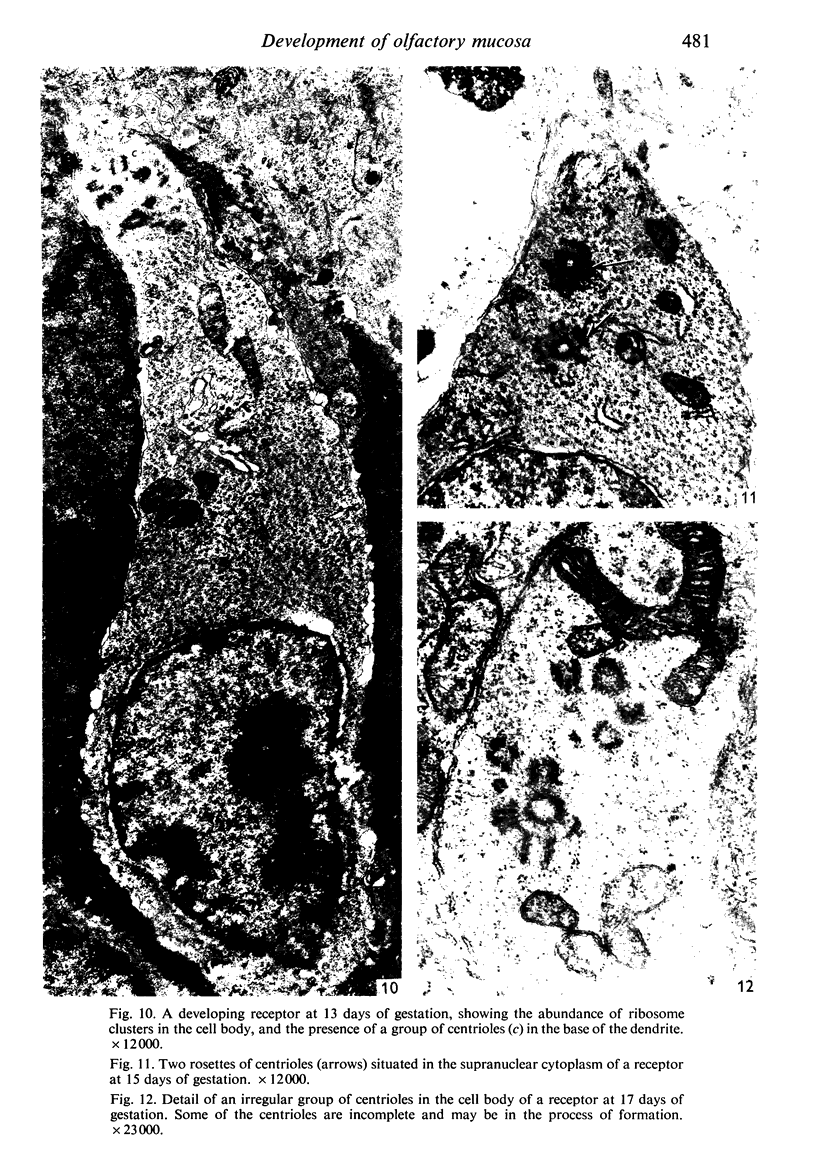
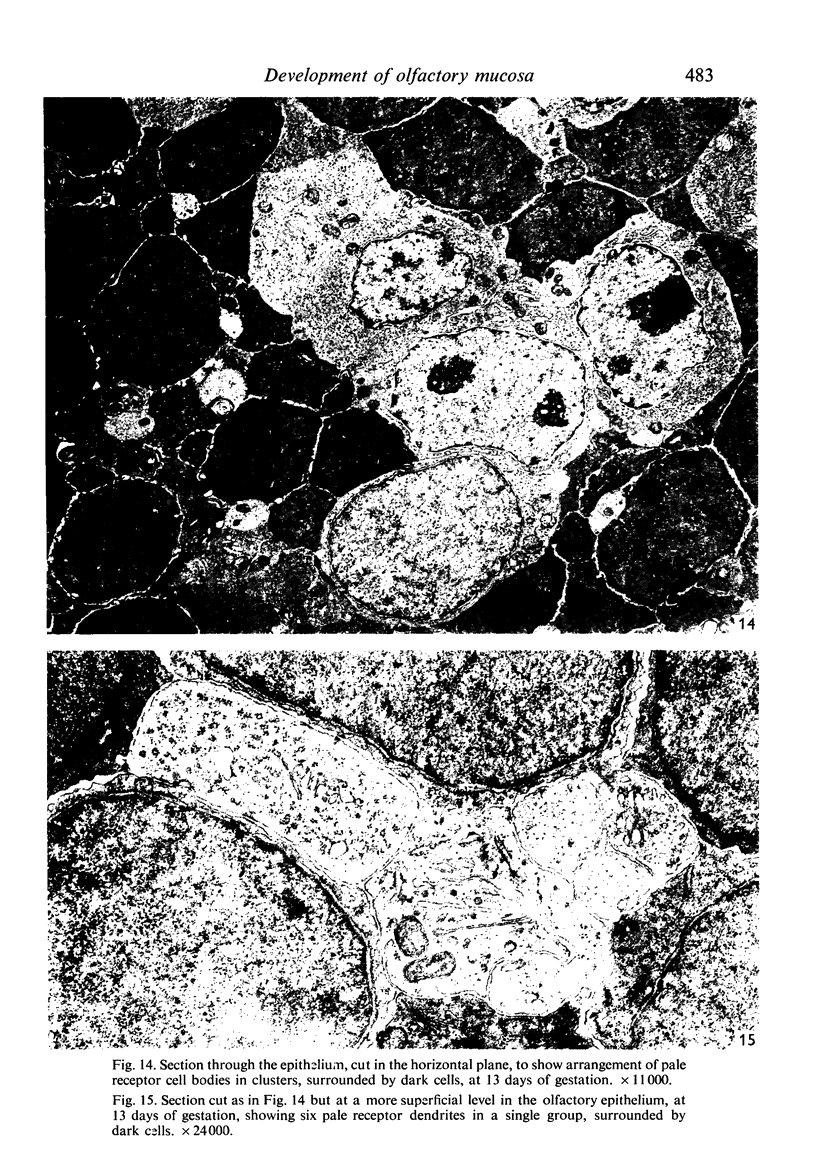
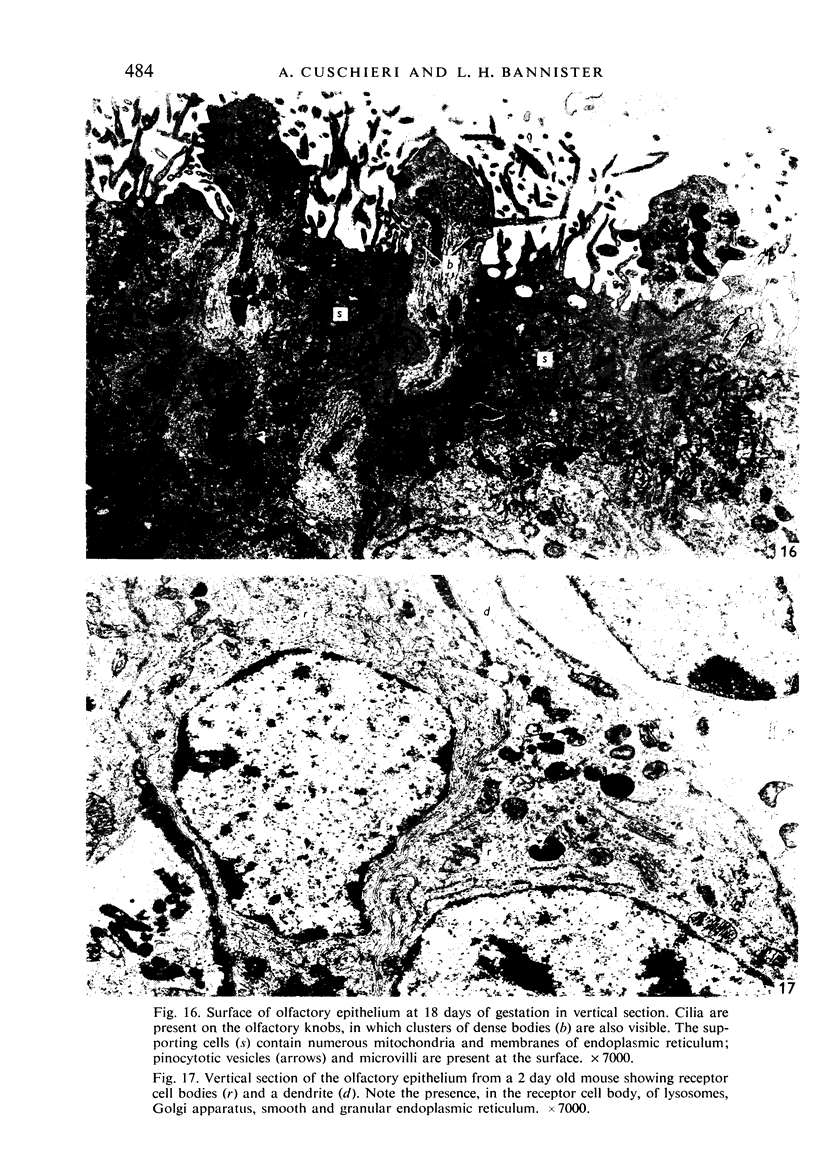
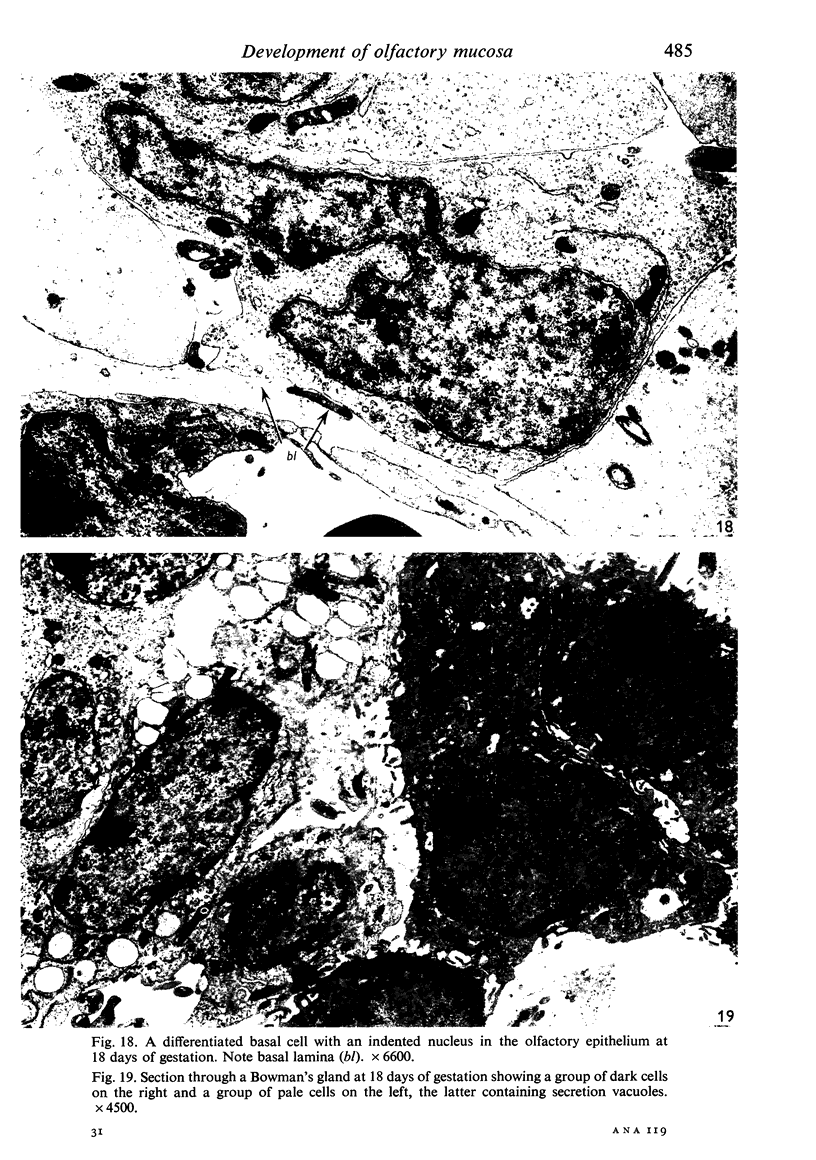
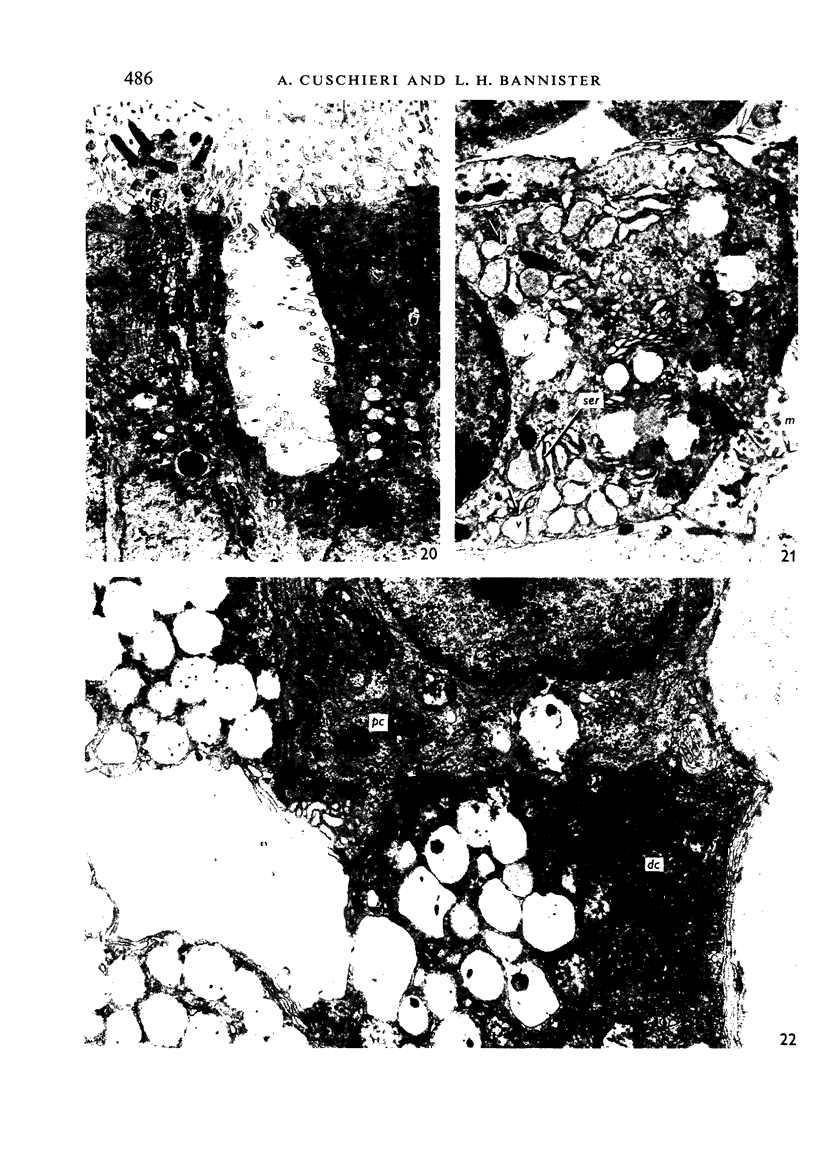
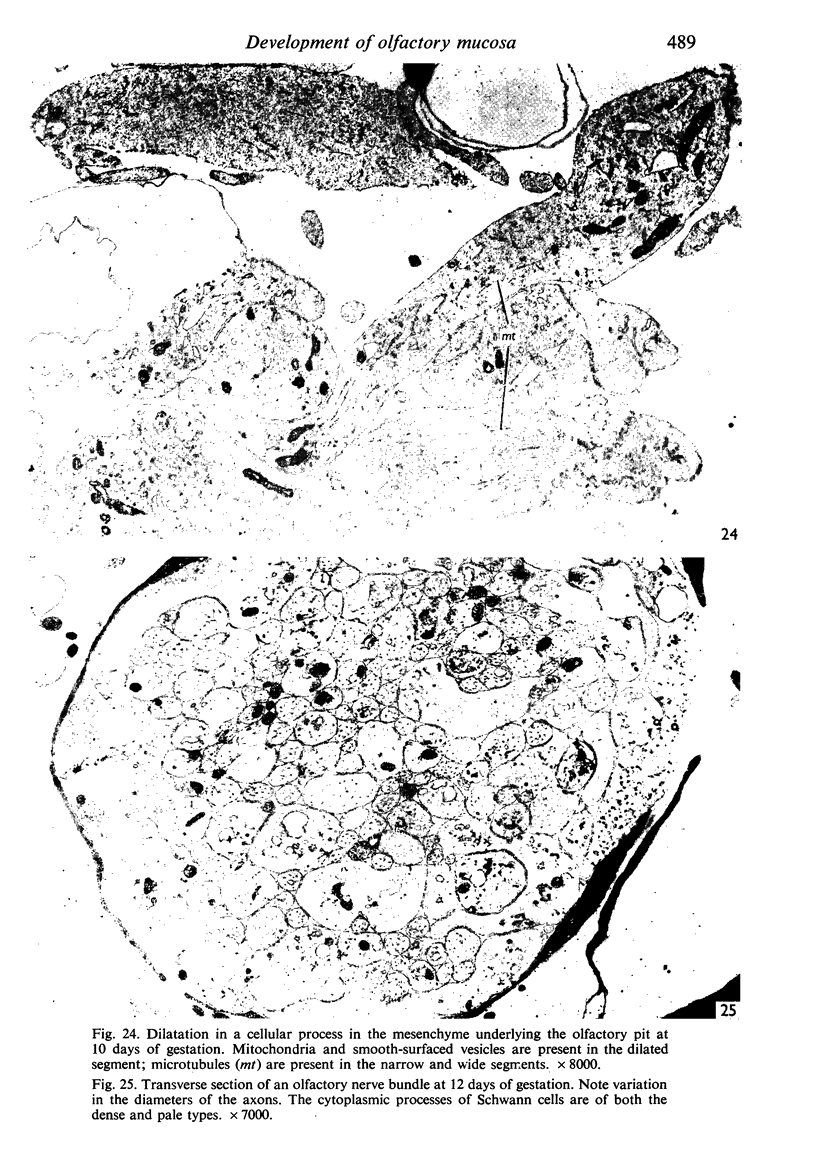
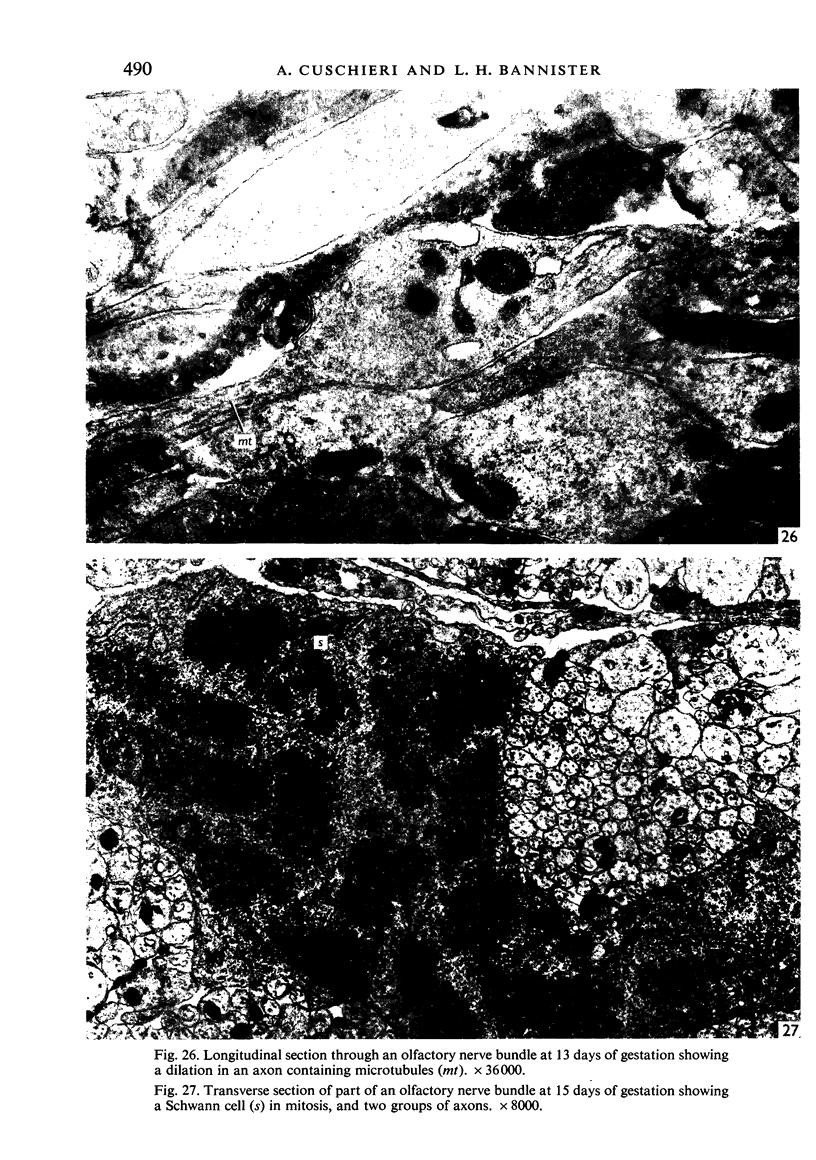
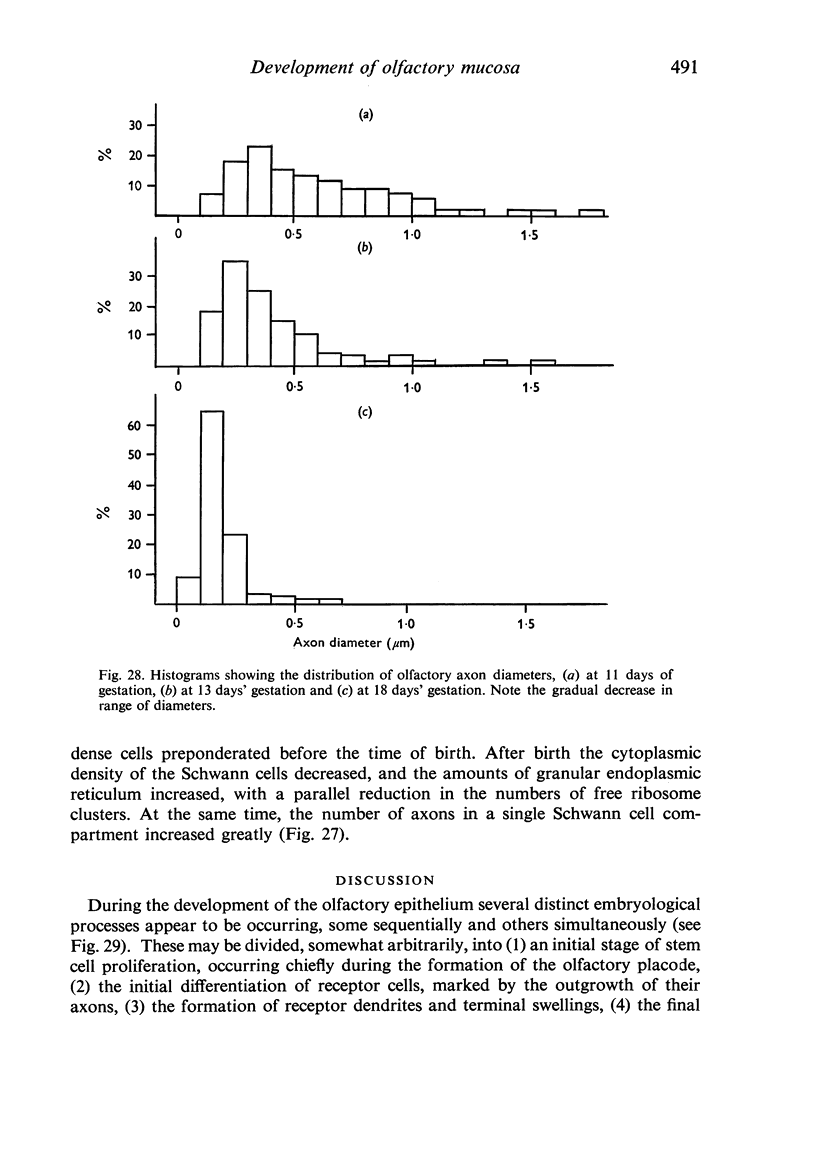
The development of the olfactory epithelium from the 10th day of gestation of postnatal life has been examined electron miscroscopically in the mouse. At 10 days' gestation the epithelium is already differentiated into dark and pale cells, the former representing embryonic stem cells and the latter the developing receptors. Axons are also visible at this stage. At 11 days the first signs of dendrite formation appear, and at 12 days spheroidal terminal swellings containing numerous microtubules are present at the apices of receptor dendrites. Centriole clusters also appear in the receptor cell bodies and dendrites. From the 12th to the 16th day of gestation a few cilia are formed on the receptor endings. Final steps in the maturation of differentiating receptors begin on the 17th day of gestation, when membranous organelles and lysosomes increase greatly in numbers. However, immature receptors can still be found in the base of the epithelium in postnatal life. Supporting cells are first recognizable on the 17th day of gestation, derived apparently from the remaining stem cells. At the same time differentiated basal cells and glands of Bowman begin to appear. In the early develoment of the olfactory nerve bundles the axons have large and varying diameters, but later on axonal sizes are progressively reduced and the adult size range is achieved at about 18 days of gestation. The significance of these findings is discussed.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett M. V., Trinkaus J. P. Electrical coupling between embryonic cells by way of extracellular space and specialized junctions. J Cell Biol. 1970 Mar;44(3):592–610. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.3.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breipohl W., Laugwitz H. J., Bornfeld N. Topological relations between the dendrites of olfactory sensory cells and sustentacular cells in different vertebrates. An ultrastructural study. J Anat. 1974 Feb;117(Pt 1):89–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breipohl W., Mestres P., Meller K. Licht- und elektronenmikroskopische Befunde zur Differenzierung des Riechepithels der weissen Maus. Verh Anat Ges. 1972;67:443–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuschieri A., Bannister L. H. The development of the olfactory mucosa in the mouse: light microscopy. J Anat. 1975 Apr;119(Pt 2):277–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cerro M. P., Snider R. S. Studies on the developing cerebellum. Ultrastructure of the growth cones. J Comp Neurol. 1968 Jul;133(3):341–362. doi: 10.1002/cne.901330305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESTABLE C., ACOSTA-FERREIRA W., SOTELO J. R. An electron microscope study of the regenerating nerve fibers. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1957;46(4):387–399. doi: 10.1007/BF00345052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch D. Ultrastructure of mouse olfactory mucosa. Am J Anat. 1967 Jul;121(1):87–120. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001210107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita S. Quantitative analysis of cell proliferation and differentiation in the cortex of the postnatal mouse cerebellum. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):277–287. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASSER H. S. Olfactory nerve fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1956 Mar 20;39(4):473–496. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.4.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. C., Lettvin J. Y., Pitts W. H. Chemical transmission in the nose of the frog. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):525–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainger F., James D. W. Association of glial cells with the terminal parts of neurite bundles extending from chick spinal cord in vitro. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;108(1):93–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00335945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainger F., James D. W., Tresman R. L. An electron-microscopic study of the early outgrowth from chick spinal cord in vitro. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;90(1):53–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00496702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziadei P. P. Cell dynamics in the olfactory mucosa. Tissue Cell. 1973;5(1):113–131. doi: 10.1016/s0040-8166(73)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziadei P. P. Topological relations between olfactory neurons. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971 Jul;118(4):449–466. doi: 10.1007/BF00324613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heist H. E., Mulvaney B. D. Centriole migration. J Ultrastruct Res. 1968 Jul;24(1):86–101. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(68)80018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds J. W. Early neuron differentiation in the mouse of olfactory bulb. I. Light microscopy. J Comp Neurol. 1972 Oct;146(2):233–252. doi: 10.1002/cne.901460207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds J. W. Early neuron differentiation in the mouse olfactory bulb. II. Electron microscopy. J Comp Neurol. 1972 Oct;146(2):253–276. doi: 10.1002/cne.901460208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds J. W., Hinds P. L. Reconstruction of dendritic growth cones in neonatal mouse olfactory bulb. J Neurocytol. 1972 Sep;1(2):169–187. doi: 10.1007/BF01099183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolnberger I. Vergleichende Untersuchungen am Riechepithel, insbesondere des Jacobsonschen Organs von Amphibien, Reptilien und Säugetieren. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971;122(1):53–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYSER K. M. EARLY DIFFERENTIATION OF MOTOR NEUROBLASTS IN THE CHICK EMBRYO AS STUDIED BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. I. GENERAL ASPECTS. Dev Biol. 1964 Dec;10:433–466. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(64)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W. A comparative electron microscopic study of reactive, degenerating, regenerating, and dystrophic axons. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1967 Jul;26(3):345–368. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196707000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyser K. M. Early differentiation of motor neuroblasts in the chick embryo as studied by electron microscopy. II. Microtubules and neurofilaments. Dev Biol. 1968 Feb;17(2):117–142. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meller K., Eschner J., Glees P. The differentiation of endoplasmatic reticulum in developing neurons of the chick spinal cord. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1966;69:189–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00406274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvaney B. D. Chemography of lysosome-like structures in olfactory epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1971 Nov;51(21):568–575. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.2.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce E. T. Histogenesis of the nuclei griseum pontis, corporis pontobulbaris and reticularis tegmenti pontis (Bechterew) in the mouse. An autoradiographic study. J Comp Neurol. 1966 Feb;126(2):219–254. doi: 10.1002/cne.901260205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANBORN E., KOEN P. F., MACNABB J. D., MOORE G. CYTOPLASMIC MICROTUBULES IN MAMMALIAN CELLS. J Ultrastruct Res. 1964 Aug;11:123–138. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(64)80097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart I. H. Location and orientation of mitotic figures in the developing mouse olfactory epithelium. J Anat. 1971 Jul;109(Pt 2):243–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennyson V. M. Electron microscopic study of the developing neuroblast of the dorsal root ganglion of the rabbit embryo. J Comp Neurol. 1965 Jun;124(3):267–317. doi: 10.1002/cne.901240302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. E., Peters A. Electron microscopy of the early postnatal development of fibrous astrocytes. Am J Anat. 1967 Jul;121(1):131–152. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001210109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WETTSTEIN R., SOTELO J. R. Electron microscope study on the regenerative process of peripheral nerves of mice. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1963;59:708–730. doi: 10.1007/BF00319067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Spooner B. S., Wessells N. K. Ultrastructure and function of growth cones and axons of cultured nerve cells. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):614–635. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]