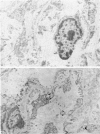
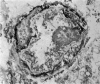
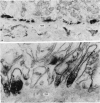
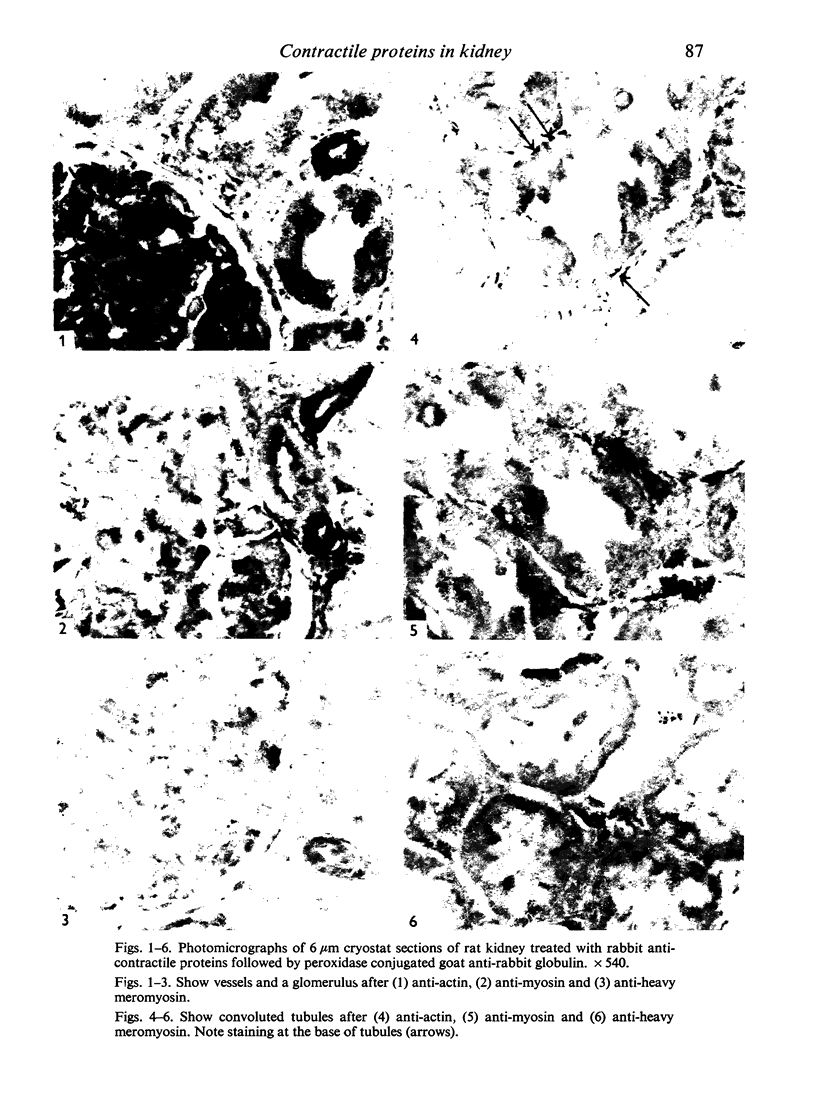
Abstract
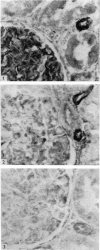
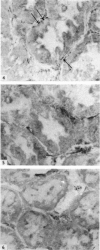
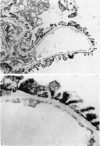
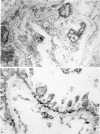
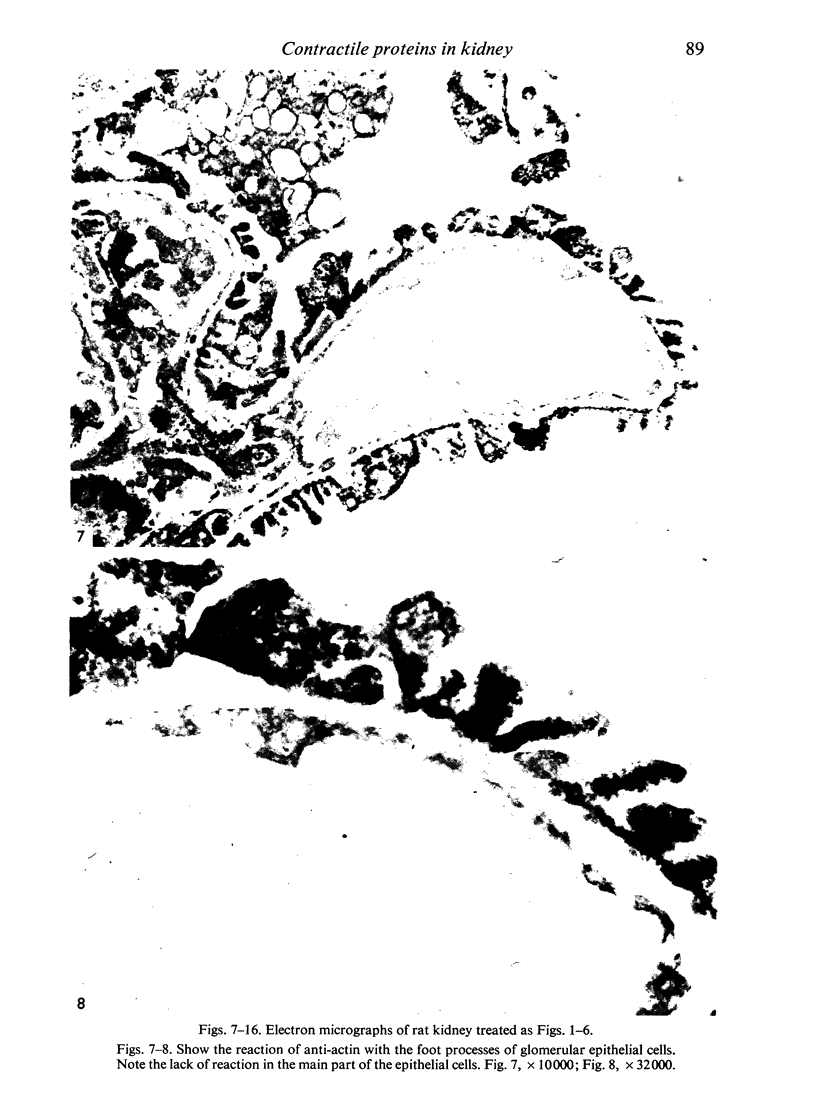
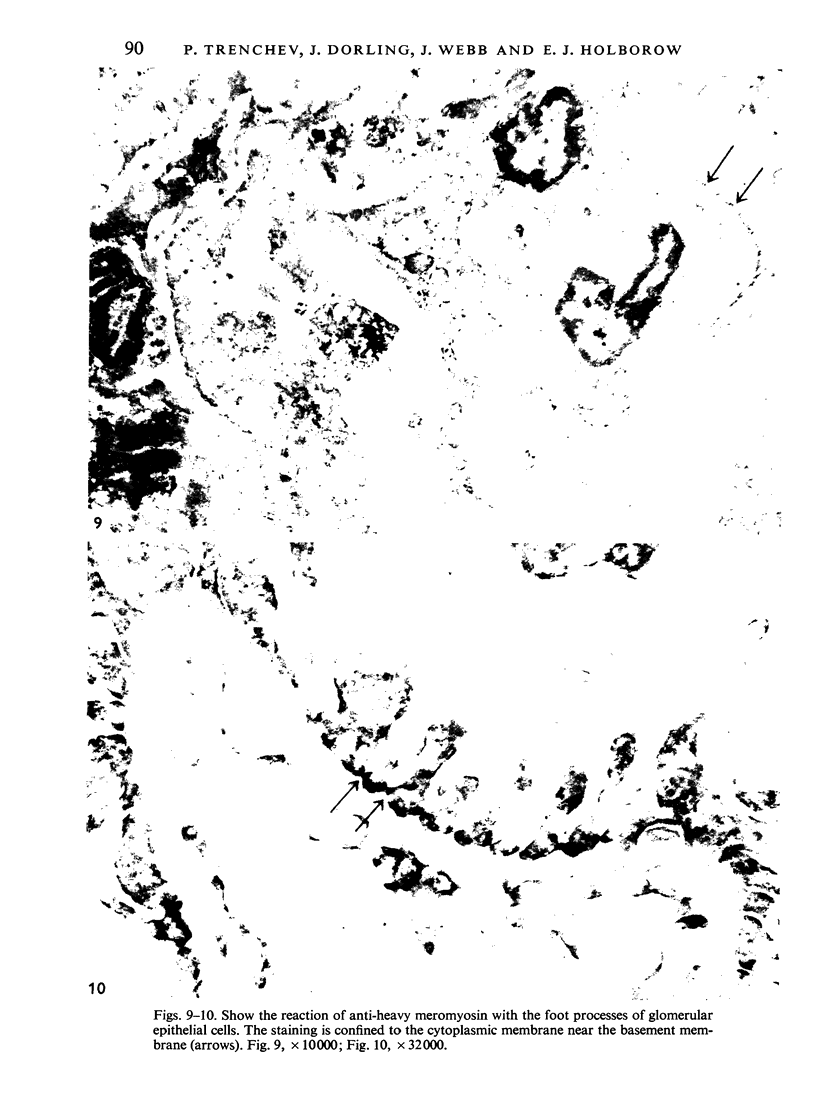
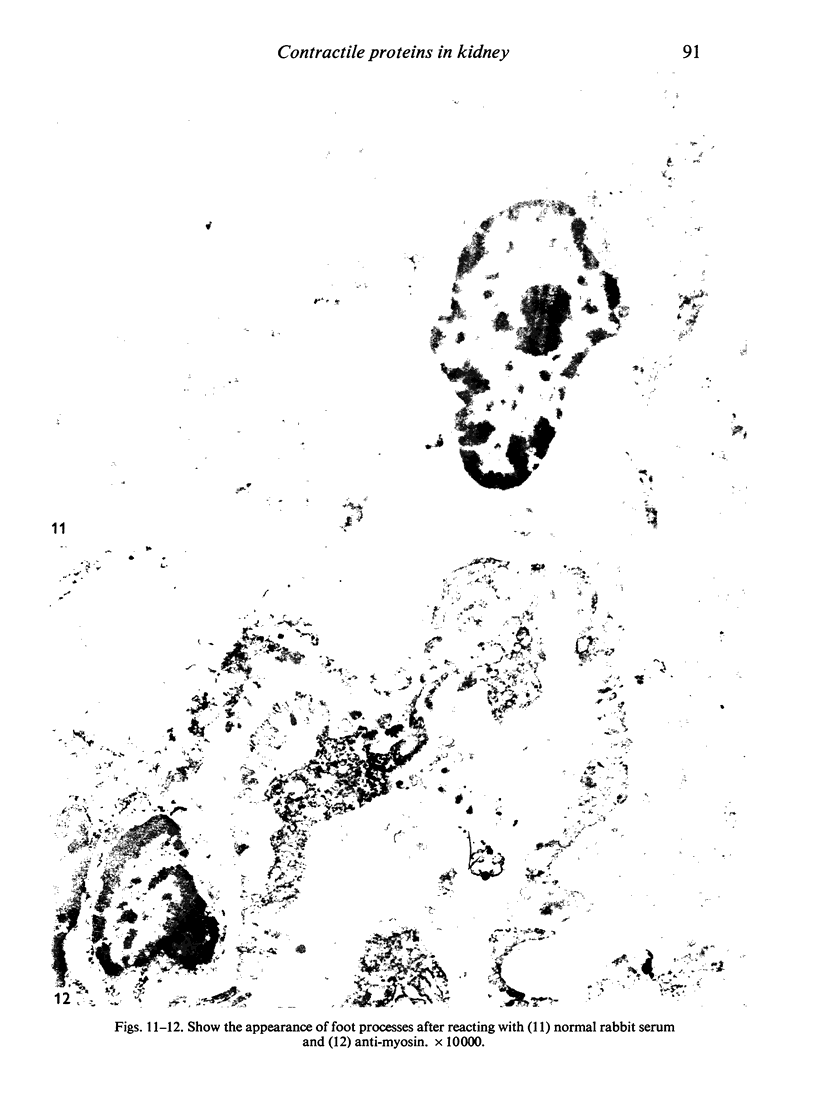
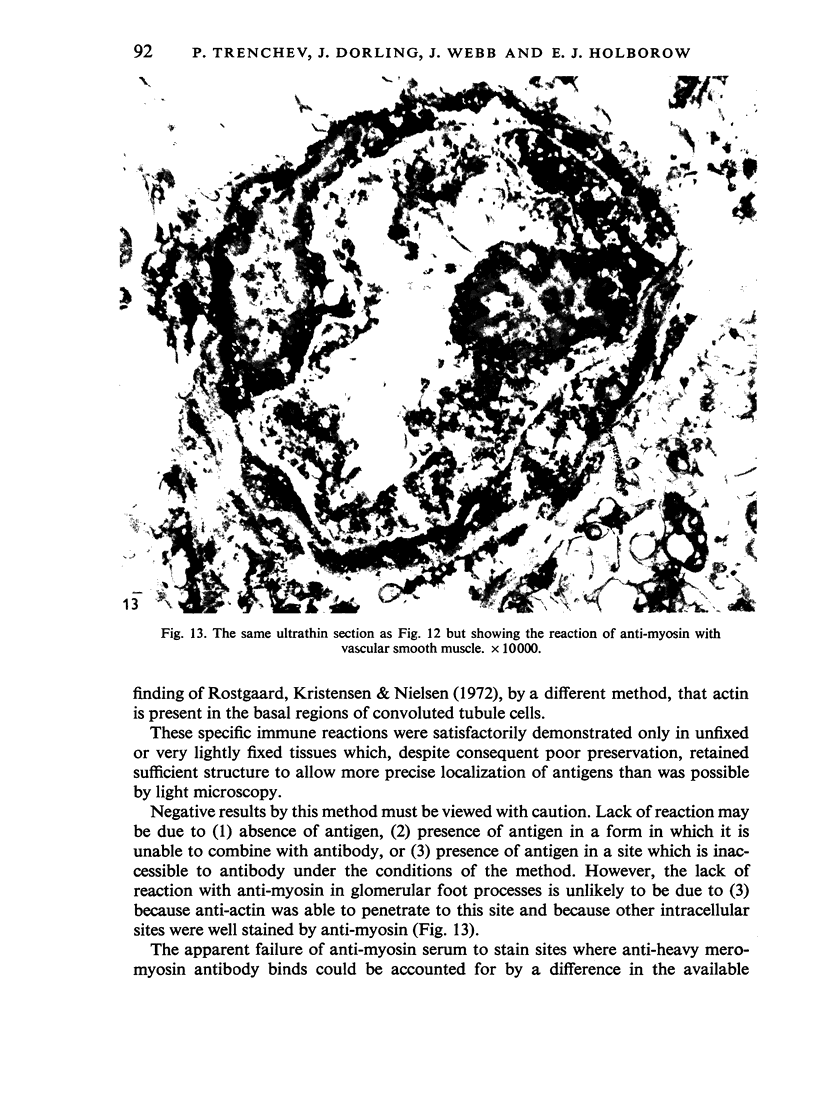
Contractile proteins of smooth muscle type were found in kidney cells by immunological methods. The reactions of rabbit anti-actin, anti-heavy meromyosin and anti-myosin antisera with rat kidney were investigated by immunoelectron microscopy. Anti-actin stained specifically the foot processes of epithelial cells in the glomerulus, the basal processes of tubular epithelial cells, and the cytoplasm of smooth muscle cells. Anti-heavy meromyosin stained the foot processes at their bases near the cell membrane and close to the basement membrane. Anti-myosin stained the cytoplasm of vascular smooth muscle cells. It is suggested that actin and heavy meromyosin-like proteins may act together to cause movement of foot process cytoplasm.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADELSTEIN R. S., GODFREY J. E., KIELLEY W. W. G-actin:preparation by gel filtration and evidence for a double stranded structure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jul 10;12:34–38. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S. Coupling of enzymes to proteins with glutaraldehyde. Use of the conjugates for the detection of antigens and antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K. A comparison of fibroblast and smooth muscle myosins. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 1;45(1):14–17. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80799-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goli D. E., Suzuki A., Temple J., Holmes G. R. Studies on purified -actinin. I. Effect of temperature and tropomyosin on the -actinin-F-actin interaction. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):469–488. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90464-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock S. E. Detection of actin filaments in homogenates of developing muscle using heavy meromyosin. Dev Biol. 1971 Aug;25(4):492–501. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. Muscular contraction and cell motility. Nature. 1973 Jun 22;243(5408):445–449. doi: 10.1038/243445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Bischoff R., Holtzer H. Formation of arrowhead complexes with heavy meromyosin in a variety of cell types. J Cell Biol. 1969 Nov;43(2):312–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik M. N., Martonosi A. The regulation of the rate of ATP hydrolysis by H-meromyosin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Sep;152(1):243–257. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90212-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oplatka A., Werber M. M., Danchin A. Specific interaction of cobaltic complexes with myosin. FEBS Lett. 1974 Oct 1;47(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80413-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostgaard J. Electron microscopy of filaments in the basal part of rat kidney tubule cells, and their in situ interaction with heavy meromyosin. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;132(4):497–521. doi: 10.1007/BF00306638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb J. A., Dorling J. The use of peroxidase-labelled antiglobulin for ultrastructural localization of tissue antigens reacting with serum antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1973 Jan;2(2):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(73)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]