Abstract
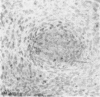
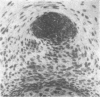
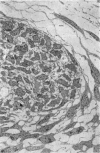
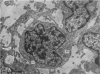
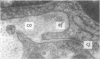
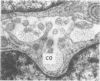
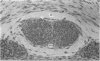
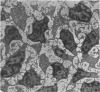
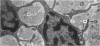
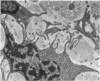
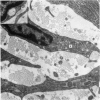
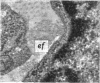
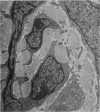
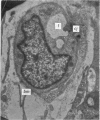
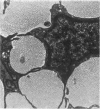
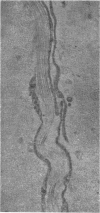
The development of human digital flexor and extensor tendons from 40 days to 112 days of gestation is described. The differentiation of the cell, the formation of collagen fibrils, and their organization into a relatively complex tendon organ are described. This word was supported by a grant from the Graduate Research Fund of the University of Washington. (Materials were obtained from the laboratory for human embryos which is supported by N.I.H. Grant no. HD00836.) We would like to thank Mrs Bea Watts for secretarial assistance.
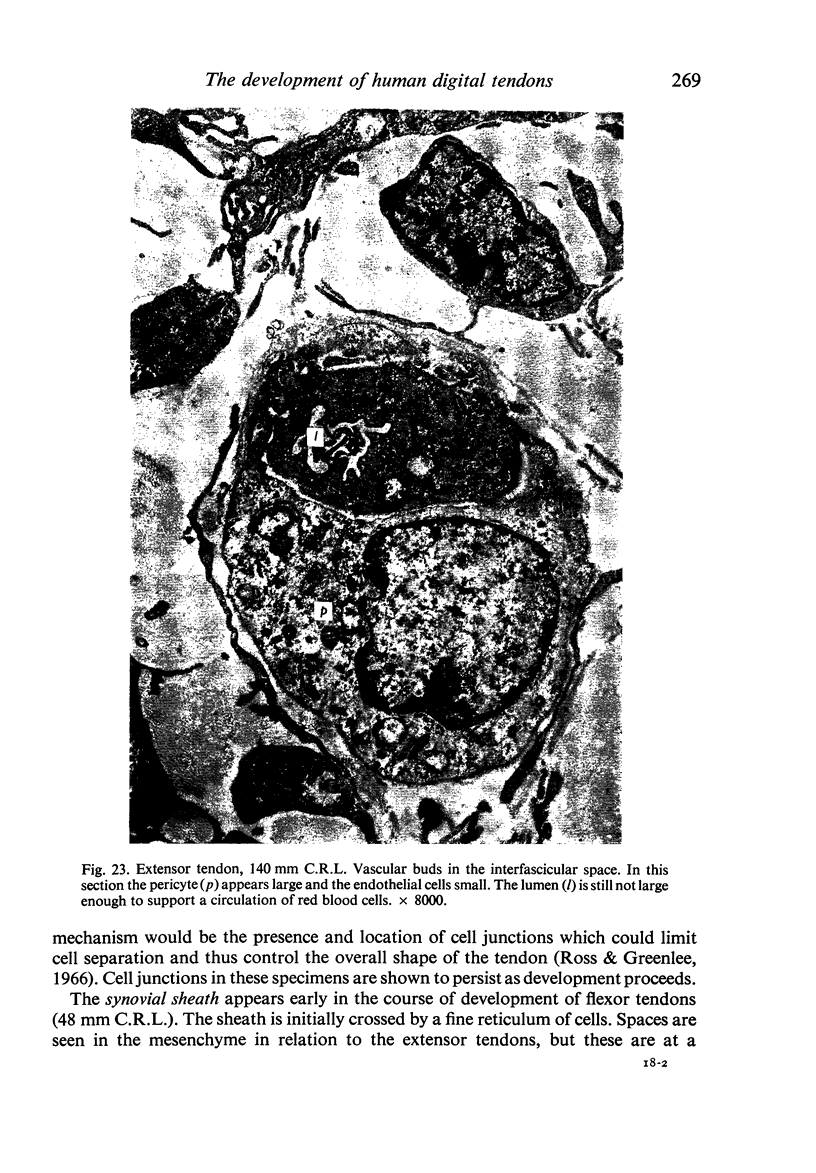
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROCKIS J. G. The blood supply of the flexor and extensor tendons of the fingers in man. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1953 Feb;35-B(1):131–138. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.35B1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckham C., Greenlee T. K., Jr Chick vincula: elastic structures with a check-rein mechanism. J Anat. 1975 Apr;119(Pt 2):295–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPMAN J. A. Fibroblasts and collagen. Br Med Bull. 1962 Sep;18:233–237. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. M. The vascular anatomy within normal tendons, divided tendons, free tendon grafts and pedicle tendon grafts in rabbits. A microradioangiographic study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1973 May;55(2):369–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee T. K., Jr, Ross R. The development of the rat flexor digital tendon, a fine structure study. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 May;18(3):354–376. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLONIG G. A modified procedure for lead staining of thin sections. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:736–739. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., JARETT L., FINKE E. H. Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1960 Nov;35:313–323. doi: 10.3109/10520296009114754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Greenlee T. K., Jr Electron microscopy: attachment sites between connective tissue cells. Science. 1966 Aug 26;153(3739):997–999. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3739.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The fibroblast and wound repair. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1968 Feb;43(1):51–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1968.tb01109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. W. BLOOD SUPPLY OF TENDONS. Am J Surg. 1965 Mar;109:272–276. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(65)80073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]