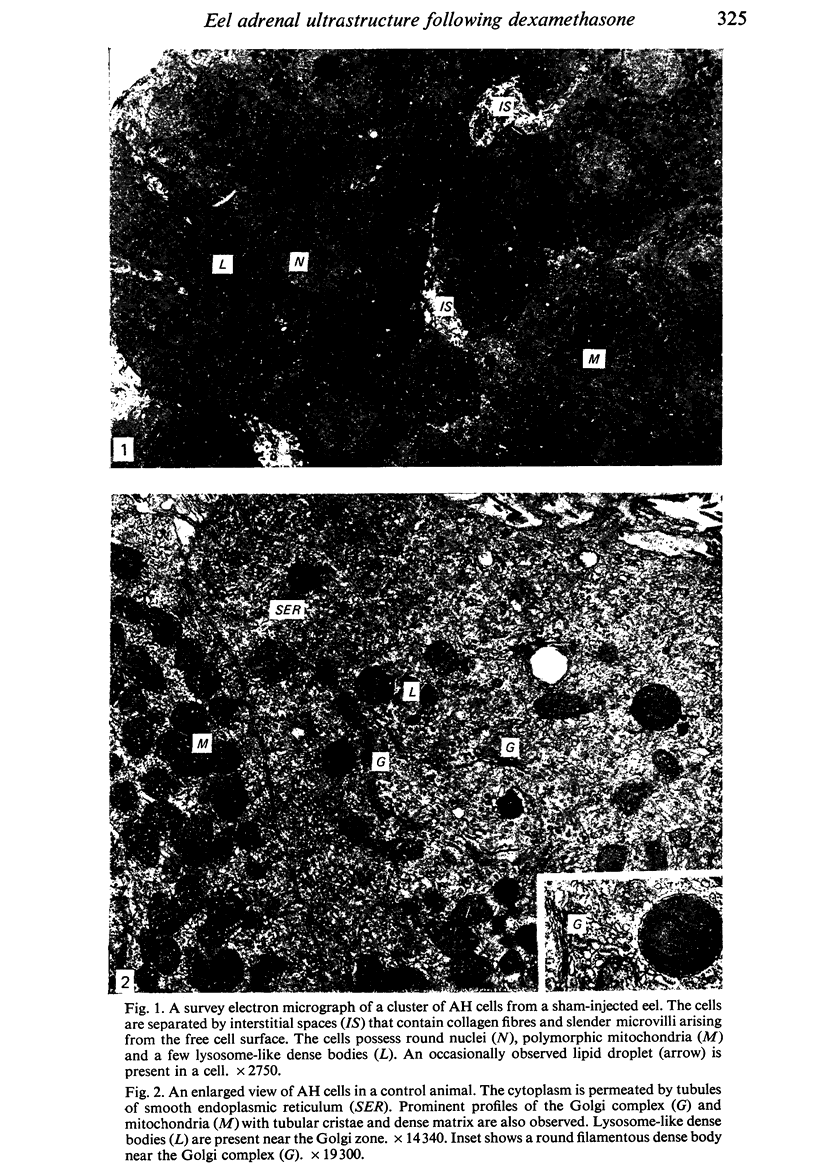
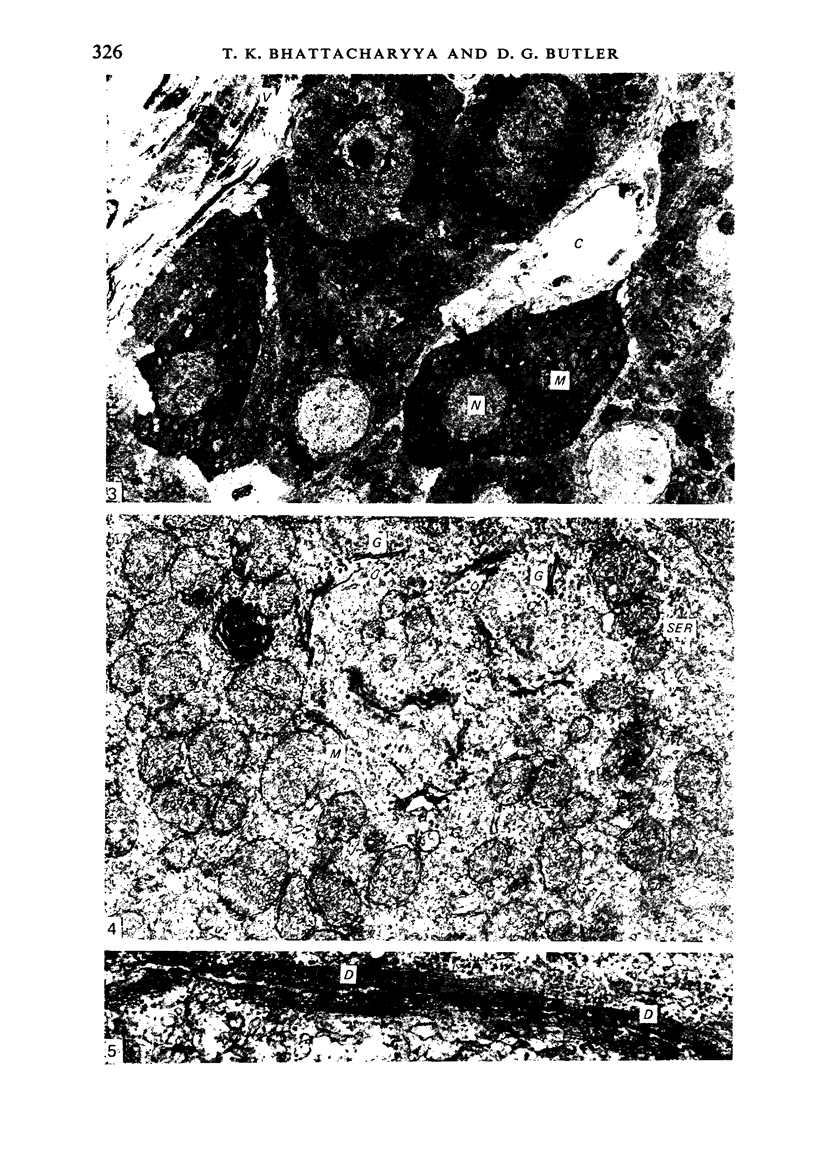
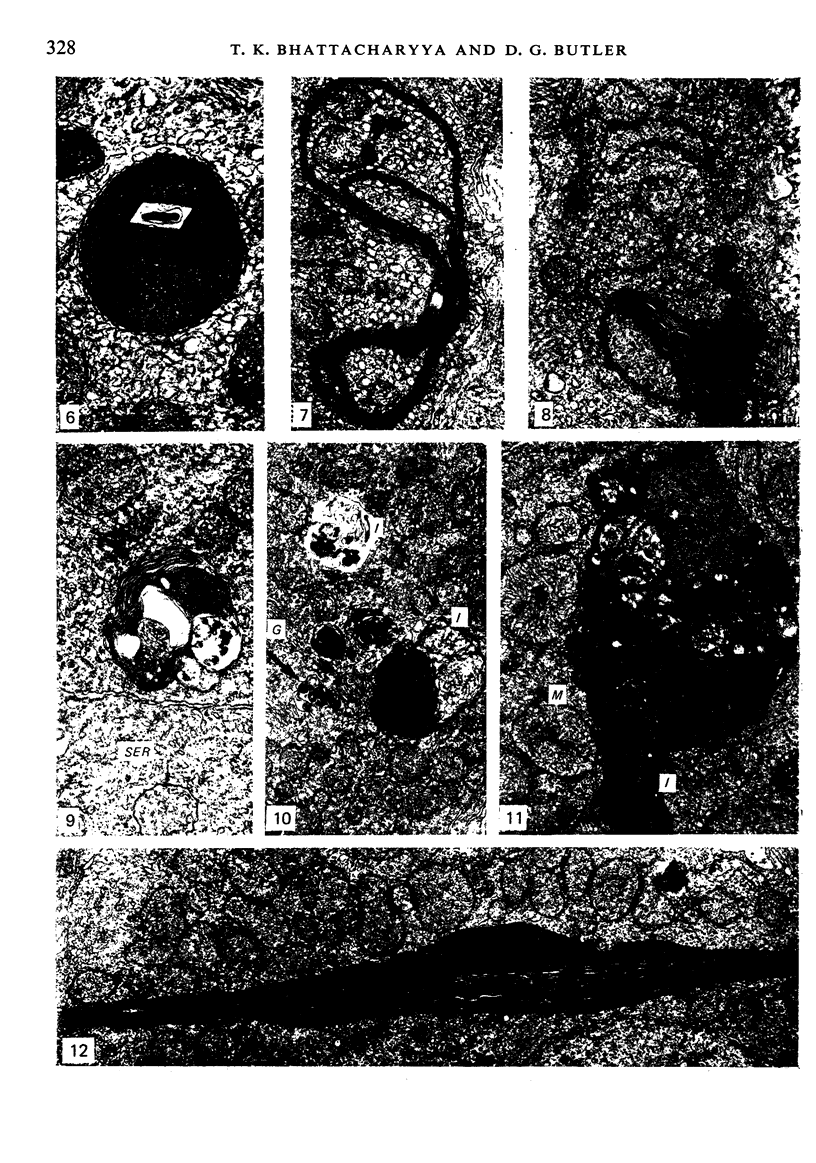
Abstract
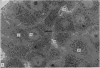
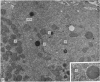
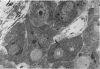
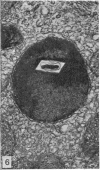
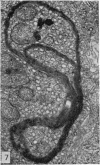
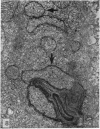
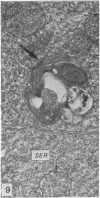
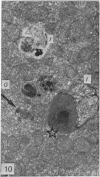
The ultrastructural modifications of the adrenocortical homologue (AH) in the North American eel (Anguilla rostrata) were studied following a 10 day treatment with dexamethasone (20 mg/day). The principal changes were: disorganization of smooth endoplasmic reticlum, regression and fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus, and a lowering of matrix density in the mitochondria. Steroid treatment also induced the appearance of numerous cytoplasmic inclusions: (a) lamellated bodies with electron-lucent cores; (b) membranous whorls isolating cytoplasmic regions containing smooth endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria and (c) complex aggregates showing whorls of membranes, residues of cytoplasmic organelles, and dense matrix. The non-accumulation of lipid droplets in repressed AH cells was noteworthy. These subcellular changes indicate endogenous cellular autophagy in the AH as a result of steroid-induced suppression of ACTH production by the pituitary.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharyya T. K., Butler D. G. Fine structure of the adrenocortical homologue in the North American eel and modifications following seawater adaptation. Anat Rec. 1979 Feb;193(2):213–231. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091930204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya T. K., Calas A., Assenmacher I. Effects of corticosteroid treatment and salt loading on the cytophysiology of the interrenal tissue in the pigeon and the quail. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1975 May;26(1):115–125. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(75)90222-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler D. G., Donaldson E. M., Clarke W. C. Physiological evidence for a pituitary-adrenocortical feedback mechanism in the eel (Anguilla rostrata). Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1969 Feb;12(1):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(69)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson E. M., McBride J. R. The effects of hypophysectomy in the rainbow trout Salmo gairdnerii (Rich.) with special reference to the pituitary-interrenal axis. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1967 Aug;9(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(67)90099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W., Long J. A., Jones A. L. The ultrastructure of endocrine glands. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:315–380. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571125-8.50010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryer J. N., Peter R. E. Hypothalamic control of ACTH secretion in goldfish. III. Hypothalamic cortisol implant studies. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1977 Oct;33(2):215–225. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(77)90246-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frühling J., Pecheux F. Subcellular steroid distribution in the rat adrenal cortex. Experientia. 1976;32(7):934–936. doi: 10.1007/BF02003777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita H. On the fine structure of alteration of the adrenal cortex in hypophysectomized rats. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;125(4):480–496. doi: 10.1007/BF00306655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell R. T., Stacy B. D., Thorburn G. D. Morphology of the regressing corpus luteum in the ewe. Biol Reprod. 1976 Apr;14(3):270–279. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod14.3.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke W., Bergerhoff K., Chan D. K. Histological observations on pituitary ACTH-cells, adrenal cortex, and the corpuscles of stannius of the european eel (Anguilla anguilla L.). Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1967 Aug;9(1):64–75. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(67)90097-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjaerheim A. Studies of adrenocortical ultrastructure. 3. Effects of dexamethasone and medroxyprogesterone on interrenal cells of the domestic fowl. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;91(3):456–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locke M., Sykes A. K. The role of the Golgi complex in the isolation and digestion of organelles. Tissue Cell. 1975;7(1):143–158. doi: 10.1016/s0040-8166(75)80012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H. L., Davis W. W., Rosenthal A. S., Garren L. D. Adrenal cholesterol: localization by electron-microscope autoradiography. Science. 1969 Mar 14;163(3872):1203–1205. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3872.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson P. A. Effect of testosterone, dexamethasone and hypophysectomy on membranous whorls in the adrenal gland of the Mongolian gerbil. Anat Rec. 1972 Oct;174(2):191–203. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091740205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novikoff A. B., Shin W. Y. Endoplasmic reticulum and autophagy in rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5039–5042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa M. Fine structure of the corpuscles of stannius and the interrenal tissue in goldfish, Carassius auratus. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;81(2):174–189. doi: 10.1007/BF02075969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivereau M. Effet d'un traitement par le cortisol sur la structure histologique de l'interrénal et de quelques tissus de l'anguille. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 1966 Sep-Oct;27(5):549–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paavola L. G. The corpus luteum of the guinea pig. Fine structure at the time of maximum progesterone secretion and during regression. Am J Anat. 1977 Dec;150(4):565–603. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001500406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pudney J., Fawcett D. W. Putative steroidogenic cells associated with the ductuli efferentes of the ground squirel (Citellus lateralis). Anat Rec. 1977 Aug;188(4):453–475. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091880406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quatacker J. R. Formation of autophagic vacuoles during human corpus luteum involution. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971;122(4):479–487. doi: 10.1007/BF00936082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodin J. A. The ultrastructure of the adrenal cortex of the rat under normal and experimental conditions. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Jan;34(1):23–71. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. C., Conklin P. M. TSH and ACTH secretion and cyclic adenosine 3'5' monophosphate content following stimulation with TRH or lysine vasopressin in vitro: suppression by thyroxine and dexamethasone. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Sep;158(4):524–529. doi: 10.3181/00379727-158-40239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasano N., Miyazawa H., Shimizu K., Koizumi K. Stimulation of rat adrenocortical cells by glycyrrhizin with special reference to its inhibitory effect on dexamethasone-induced atrophy of the adrenal cortex. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1966 Dec;90(4):391–403. doi: 10.1620/tjem.90.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton J. H., Jones A. L. The fine structure of the mouse adrenal cortex and the ultrastructural changes in the zona glomerulosa with low and high sodium diets. Anat Rec. 1971 Jun;170(2):147–181. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091700204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subhedar N., Rao P. D. Effects of some corticosteroids and metopirone on the corpuscles of Stannius and interrenal gland of the catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch). Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1974 Aug;23(4):403–414. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(74)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suyama A. T., Long J. A., Ramachandran J. Ultrastructural changes induced by ACTH in normal adrenocortical cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1977 Mar;72(3):757–763. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanek R. Pouvoir freineteur de divers cortico-stéroïdes de synthèse sur la sécrétion d'ACTH. Etude comparative. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 1965 Nov-Dec;26(6):799–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]